식품 알레르기(음식물 알레르기/음식물 알러지) Food allergy, 카페인 Caffeine
식품 알레르기와 식품첨가물로 생기는 식품 알레르기
① 식품 유해 작용(Food adverse reaction)
② 식품 과민작용(식품 알레르기 반응/Food hypersensitivity)
③ 식품 아나필락시스 (Food anaphylaxis)
④ 식품 불내증 (Food intolerance) 등이 생길 수 있다.
- 식품(음식물)으로 유발된 알레르기를 식품 알레르기(Food allergy), 식품 알레르기 질환, 음식물 알레르기, 식물성 알러지, 식품 알러지 또는 소화관 알러지라고 한다.
- IgE 중개 식품 알레르기는 미국과 영국의 소아청소년들의 6~8%,
- 성인들의 2%에게 생긴다(출처; The New England Journal of Medicine, Sep.18, 2008).
- IgE 중개 식품 알레르기가 성인들에게 25%정도 생길 수 있다는 연구도 있지만 실제로는 3%이하로 생기는 것이 정론이다.
- 미국에서는 식품 알레르기로 연간 30,000여명이 응급 치료를 받고 거의 2,000명이 사망한다.
- 신생아들과 영유아들에게 생긴 식품 알레르기의 대부분은 점차로 성장하면서 자연히 없어지기도 하지만
- 땅콩이나 호두, 피칸, 피스타치오, 브라질 호두 등 나무 견과류, 또는 어패류, 해산물 식품 알레르기는 계속 성장하는 소아청소년들로부터 완전히 없어지지 않고 일생동안 지속 될 수 있다.
- 동물성 음식물이나 식물성 음식물에 있는 글라이코프로테인(단백질) 성분으로 식품 알레르기가 생길 수 있다.
- 달걀, 우유, 땅콩, 나무 견과류 등 음식물이 영유아들에게 식품 알레르기를 가장 흔히 일으킬 수 있다.
- 최근에는 키위(Kiwi) 알레르기가 증가 추세이다.
- 밀가루 음식물이나 메주콩 음식물로 식품 알레르기가 생길 수 있지만 임상적으로 확실히 진단하기가 어려운 실정이다.
- 소아청소년 식품 알레르기의 95%는 달걀, 우유, 땅콩과 메주콩 이 4가지 음식물로 인해 주로 생긴다고 한다③.
- 성인들에서는 조개류 해산물, 생선, 땅콩, 나무 견과류의 음식물로 식품 알레르기가 가장 흔히 생길 수 있다.
- 식품 알레르기의 발생률은 사는 나라와 지역에 따라 다르다.
- 예를 들면 불란서에서는 머스타드 식품 알레르기가 더 많이 발생되고,
- 이스라엘에서 참깨 알레르기가 더 많이 발생되고,
- 달걀 음식물 알레르기와 우유 음식물 알레르기는 전 세계적으로, 지역이나 지방의 차이가 없이 가장 흔한 생기는 소아청소년 음식물 알레르기이다(출처; Food allergy, The New England Journal of Medicine, Sept. 18, 2008).
- 달걀 음식물로 생긴 알레르기는 소아들의 1.5~3.2%에서 생긴다.
- 달걀 음식물로 생긴 알레르기의 66%는 5세 될 때까지 없어질 수 있고,
- 7세가 될 때 75%는 없어진다고 한다.
- 달걀 음식물 알레르기가 생후 16세까지 없어지지 않으면 일생동안 계속된다고 한다.
- 아토피 체질이 있는 소아청소년들에게 아토피 체질이 없는 소아청소년들 보다 식품 알레르기가 더 잘 발생되는 것이 보통이다.
- 또 아토피성 체질이 있는 소아청소년들에 식품 알레르기가 더 잘 생길 수 있고 음식물을 먹을 때 그 음식물로 인해 알레르기 질환이 생길 가능성이 더 많다.
- 어떤 종류의 음식물이든 식품 알레르기를 일으킬 수 있다고 가정하고, 음식물을 접하는 것이 상식일 것 같다.
- 식품 알레르기가 아닌 다른 어떤 병으로 생긴 증상 징후가 식품 알레르기로 생긴 증상 징후와 비슷할 수 있다.
- 그래서 다른 어떤 병으로 생긴 증상 징후를 식품 알레르기로 생긴 증상 징후로 잘못 판단하는 경우도 많다.
- 예를 들면, 유당 불내증, 식중독, 감염병, 또는 정신 신경질환 등으로 생긴 증상 징후가 식품 알레르기로 생긴 증상 징후와 거의 비슷할 수 있다.
- 그 때문에 유당 불내증이나 식중독, 또는 감염병 등을 음식 알레르기로 오진할 수 있다.
- 때로는 식품 알레르기로 생긴 증상 징후와 거의 똑같은 증상 징후가 식품 알레르기가 아닌 다른 병으로도 생길 수 있다.
- 예를 들면, 유당 불내증으로 생긴 복통과 우유 단백 알레르기로 생긴 복통과 거의 비슷할 수 있다.
- 이런 이유로, 식품 알레르기로 생긴 증상 징후와 다른 병으로 생긴 증상 징후를 감별 진단해야 한다. [부모도 반의사가 되어야한다-소아가정간호백과]-제5권 인공영양, 이유식, 비타민, 미네랄, 지방, 단백질-아기가 우유로 만든 인공영양을 먹을 수 없는 경우, 제12권 소아 신경계 정신, 정서, 행동, 심리, 수면문제- 단순 틱증 참조.

사진 132. 소아청소년(0~18세)들에게 식품 알레르기(음식물 알러지)를 가장 흔히 일으킬 수 있는 식품.
달걀, 우유, 땅콩, 메주콩, 밀 음식물, 나무 견과(호두, 피칸, 피스타치오, 브라질 호두 등), 패류, 생선 등으로 식품 알레르기가 가장 잘 생길 수 있다. 소아청소년들에게 생기는 식품 알레르기의 95%는 달걀, 우유, 땅콩, 또는 메주콩 등으로 유발된다고 한다.
Copyright ⓒ 2013 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

사진 133. 우유, 달걀, 땅콩, 견과류, 생선, 밀가루 식품 등은 식품 알레르기를 더 잘 일으킬 수 있는 음식물이다.
Copyright ⓒ 2013 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

사진 134. 우유나 우유로 만든 식품으로 우유 알레르기가 생길 수 있다.
Copyright Ⓒ 2013 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
식품 알레르기의 원인
- 식품 알레르기의 원인을 다음과 같이 분류해서 생각해 볼 수 있다.
면역글로불린 E(IgE) 매개로 생긴 식품 알레르기(즉, 식품 알레르기)
다음 1~4종류 형으로 나누어 생각 할 수 있다.
1. 1차적 표적 기관들은 구강과 인두 등 소화관이다.
- 다음 1~2의 증상 징후와 식품 알레르기가 생길 수 있다.
- 구강 알레르기 증후군(Oral allergy syndrome)-입술, 구강, 인두가 붓고 가려운 증상이 생길 수 있다.
- 위장 아나필락시스(Gastrointestinal anaphylaxis)-구기, 구토, 상복부 복통, 복부팽만, 방구, 설사 등의 증상 징후가 생길 수 있다.
2. 2차적 표적 계통의 기관들은 피부, 폐, 혈관 등이다. 다음에 있는 증상 징후와 식품알레르기가 생길 수 있다.
- 급성 두드러기, 혈관 부종(Acute urticaria and Angioedema), 아토피성 피부염이 피부에 생길 수 있다. 기관지 천식 및, 또는 알레르기 비염 이 생길 수 있고,
- 아나필락시스(Anaphylaxis) – 숨이 가쁘고, 전신 청색증이 생기고, 저혈압, 쇼크 등 증상 징후가 생길 수 있다.
면역글로불린 E(IgE)와 비 면역글로불린 E(IgE)의 혼합형 식품 알레르기가 다음과 같이 생길 수 있다.
- 아토피성 피부염(Atopic dermatitis)
- (부모도 반의사가 되어야한다-소아가정간호백과-제17권 소아청소년 피부질환-아토피성 피부염 참조)
- 알레르기성 호산성(호산구성) 식도염(Allergic eosinophilic esophagitis) 호산성 식도염 참조)
- 알레르기성 호산성 위장염(Allergic eosinophilic gastroenteritis)-구기, 구토, 설사, 심한 상복부 복통 등의 증상이 생길 수 있다. 호산구가 증가되고 위장관 장벽에 호산구가 증가된다. 알레르기를 일으킨 식품에 대한 피부검사가 양성으로 나타난다. 그 식품을 먹으면 증상이 더 해진다.
비 면역글로불린 E(IgE) 매개로 생기는 식품 알레르기
- 음식단백 유발성 항문대장염(Food protein-induced proctocolitis)
- 음식단백 유발성 소장결장염(Food protein-induced enterocolitis)
출처; Pediatric annals, vol 37, November 8, 2008
- 화분으로 생기는 알레르기 비염은 IgE 매개로 생기고, 구강 내 소양증이나, 구강 내에 얼얼한 증상이 생기는 구강 내 식품 알레르기의 대개가 IgE 매개에 의해서 생긴다.
- IgE 매개에 의해서 생기는 식품 알레르기는 식품을 먹은 후 불과 몇 초 내지 몇 분에 생기는 것이 보통이다.
- 늦게는 먹은 후 한두 시간 내 생길 수 있다.
- 우유 단백 알레르기나 콩 단백 알레르기로 생기는 소장 결장염은 T-세포 매개로 생긴다.
- T-세포 매개로 생긴 식품 알레르기는 먹은 후 3~4시간 후 생기는 것이 보통이다.
- 식품 알레르기는 소아청소년들의 5~8%에게 생길 수 있지만 식품 알레르기가 아닌 식품 유해 반응(Food adverse reaction)은 25%정도 생길 수 있다.
- 우유, 달걀, 땅콩, 메주콩, 밀가루, 조개, 물고기, 호두류 견과, 초콜릿 등의 식품은 다른 종류의 식품보다 식품 알레르기를 더 잘 유발시킬 수 있다.
- 일반적으로 쌀 식품은 저 알레르기성 식품이라고 알려졌다. 쌀 단백질 알레르기로 인해 소장결장염이 유발됐다는 연구 결과도 있다.출처; Journal watch pediatrics and adolescent medicine vol #1
- 경미한 우유 알레르기나 달걀 알레르기는 점점 더 성장하면서 더 이상 생기지 않을 수 있으나 땅콩이나 나무 견과류 알레르기는 점점 더 성장하는 것과는 관계없이 일생동안 계속 생길 수 있다.
식품 알레르기 감별진단
① 식품을 요리할 때 첨가한 각종의 인공색소, 조미료나 방부제로 생긴 식품 부작용의 증상 징후
-
- 식용색소 황색 제4호(food yellow no4 tartrazineTartrazine 등 인공색소,
- 단일 나트륨 글루탐 산염(Monosodium glutamate),
- 아질산염(Nitrites)이나,
- 식품 향미 강화제(Nitrates sulfiting agents) 등 음식물 방부제를 넣고 만든 음식물을 먹고 생긴 유해성 반응으로 생긴 증상 징후는 식품 알레르기로 생긴 증상 징후와 비슷한 증상 징후가 생길 수 있다.
② 페니실린이나 다른 여러 종류 항생제로 치료 받았던 젖소에서 짠 우유를 먹을 때 우유 속에 든 항생제로 아나필락시스이 생길 수 있다. 아나필락시스은 식품 알레르기의 일종이고 생명에도 위험한 심한 즉시 알레르기이다.
③ 박테리아, 몰드, 약물, 곤충이 든 음식물로 생기는 증상 징후이나 병
④ 버섯 중독, 조개 중독
⑤ 소화성 궤양, 횡격막 탈장, 장관폐쇄 등 위장 질환
⑥ 1차 이(2)당류 효소 결핍증 또는 2차 이당류 효소 결핍증, 갈락토스증 등
약물 성분이 든 음식물로 생긴 증상 징후-알코올, 히스타민, 카페인 등이 든 음식물로 생긴 증상
⑦ 내분비 병
⑧ 박테리아 감염, 바이러스 감염, 또는 기생충 감염
⑨ 심리적 문제로 생긴 증상 징후
⑩ 그 외
출처 및 참조문헌,Clinical Semina, Richard Evans, III, M.D., M.P.H and Richard J. Summers, M.D
식품 알레르기 증상 징후
- IgE 매개에 의해서 생기는 식품 알레르기는 식품 알레르기 반응이 신체의 한 계통의 한 기관에만 나타날 수도 있고 여러 계통의 여러 기관에 동시 나타날 수 있고, 전신에 나타날 수 있고 신체의 한 국소에만 나타날 수 있다.
- IgE 매개에 의해서 생기는 식품 알레르기로 두드러기가 국소적으로 날 수 있고,
- 전신적으로 나타 날 수 있고, 생명도 잃을 수 있는 아나필락시스과 동시 생길 수 있다.
- 신체 각 계통의 기관에 생기는 식품 알레르기의 증상 징후는 다음 각항을 참조.
① 호흡기에 생길 때-콧물, 비염, 천식, 천명 등
② 피부와 점막층에 생길 때-두드러기, 피부 홍조, 혈관 부종, 접촉성 두드러기, 아토피성 피부염의 증상과 징후가 더 심해지는 등
③ 소화기에 생길 때-구토, 복통, 설사 등
④ 중추신경계에 생길 때 음식물 기피증, 감정의 변화, 우울증 등
⑤ 근육 골격계에 생길 때-근육 골격통, 성장통 등
⑥ 혈관과 심장계에 생길 때-가성 빈혈, 편두통 등
⑦ 그 외 계통의 기관에 생길 때
달걀-달걀 증후군 Egg-egg syndrome(Occupational egg allergy)
- 달걀 단백 성분이 든 약품이나 음식물을 만드는 과정에서 미세 용량의 달걀 단백 성분만 들어 있어도 그 달걀 단백 성분으로 인해 달걀 알레르기가 생길 수 있다.
- 이렇게 생기는 증상을 달걀-달걀 증후군이라고 한다(참조; Food allergy, The New England Journal of Medicine, Sep.18, 2008).
식품 알레르기가 시작하는 최초연령
① 달걀 식품 알레르기- 생후 6~24개월
② 우유 식품 알레르기- 생후 6~12개월
③ 땅콩 식품 알레르기- 생후 6~24개월
④ 나무 견과류 식품 알레르기- 1~17세
⑤ 참깨 식품 알레르기- 생후 6~36개월
⑥ 생선 식품 알레르기- 후기 사춘기나 성인기
⑦ 조개류 식품 알레르기- 성인기
⑧ 밀가루 식품 알레르기- 생후 6~24개월
⑨ 메주콩 식품 알레르기- 생후 6~24개월
⑩ 키위 식품 알레르기- 어느 연령
⑪ 사과 식품 알레르기- 후기 사춘기와 성인기
⑫ 당근 식품 알레르기- 후기 사춘기와 성인기
⑬ 복숭아 식품 알레르기- 후기 사춘기와 성인기
출처-Food allergy, The New England Journal of Medicine, Sep.18, 2008
식품 알레르기의 진단
- 병력, 증상 징후, 진찰소견 등을 종합해 식품 알레르기를 진단하는 것이 보통이다.
- 필요에 따라 혈중 IgE 항체(면역 글로불린 E 항체)의 혈중 농도를 알아보는 혈액검사
- 알레르기 피부 가시 검사
- 유발 검사
- IgE를 검사하기 위해 방사선 알러젠 흡수검사(RAST)
- 필요에 따라 피부 생체 조직 검사나 소대장관 벽 생체조직검사
- 위장관 내시경검사 등으로 식품 알레르기를 진단하기도 한다.
- 그 중에서 환아에 생겼던 과거·현재의 병력, 그리고 가족 병력이 식품 알레르기를 진단하는데 가장 가치가 있다.
- 식품 알레르기를 진단할 때 식품 알레르기를 일으키는 음식물을 더 이상 섭취하지 않으면서 식품 알레르기의 증상 징후가 없어지나 덜 한가 또는 조금도 차도가 없는지 있는지, 보고 진단할 수도 있다.
- 다시 말하면, 식품 알레르기를 진단하는 동시에 식품 알레르기도 치료할 수 있다.
- 일반적으로 IgE 항체에 관련된 식품 알레르기를 일으킨다고 생각되는 음식물을 1~2주 동안 섭취하지 않으면 식품 알레르기의 증상 징후가 없어지는 것이 보통이다.
- 또 식품 알레르기로 생긴 소대장염의 대부분은 알레르기를 일으켰던 음식물을 더 이상 섭취하지 않기 시작한 날로부터 3~6주 이후에야 증상 징후가 없어지는 것이 보통이다.
- 우유, 달걀, 땅콩 등에 알레르기가 있는 소아청소년들의 우유, 달걀, 땅콩 등의 식품 단백 IgE 항체의 혈중 농도가 증가되어 있는 것이 보통이다.
- 어떤 특정 식품 알레르기 피부검사의 결과가 양성으로 나타나면 그 음식물(항원)에 대한 항체가 피검자의 체내에 있다는 것을 의미한다. 그러나 피부검사의 결과가 양성이라고 해서 그 음식물로 인해 식품 알레르기가 꼭 나타날 수 있다고 장담할 수 없다.
다음과 같이 유발 검사
우유 단백 알레르기 질환으로 생기는 설사,
유발 검사,
우유 단백질 알레르기 질환의 진단 참조를 해서 식품 알레르기를 진단할 수 있다.
식품 알레르기 유발 검사
- 유발 검사는 식품 알레르기의 증상 징후가 경미하고 유발 검사로 인해 위험성이 생기지 않을 경우에만 의사의 지시에 따라 집에서도 할 수 있다.
- 그렇지만 식품 알레르기의 증상 징후가 경미하든 심하든, 알레르기 전문의에 의해서 유발 검사를 실행해야 한다.
- 식품 알레르기를 일으킨다고 의심되는 음식물을 2∼4주 동안 일절 섭취하지 말고, 그 음식물로 인해서 생겼던 식품 알레르기의 증상 징후가 계속 생기는지, 생기지 않는지, 또는 생기지만 증상의 정도가 덜 하는지 주의 관찰한다.
- 관찰하는 중 식품 알레르기로 생겼던 증상 징후가 현저히 생기지 않거나, 덜 생기면, 그 음식물로 식품 알레르기가 생긴다고 추정할 수 있다. 그러나 아직도 유발 검사 단계에서, 그 음식물로 식품 알레르기가 생겼다고는 확실히 진단할 수는 없다.
- 그 후 그 음식물을 조심히 또다시 섭취하면서 식품 알레르기의 증상 징후가 또 생기나 관찰한다.
- 그 음식물을 먹을 때 전과 같이 거의 같은 증상 징후가 또 생기면 그 음식물에 식품 알레르기가 ‘있는 것 같다’고 추정 진단할 수 있다. 이렇게 식품 알레르기 질환을 추정 진단할 수 있다.
|
새우 한 마리를 먹은 후 아나필락시스이 생겨 죽은 실례도 있었다.
|
식품 알레르기 치료
- 거의 모든 음식물로 식품 알레르기가 생길 가능성이 있고, 또 많은 종류의 음식물 중 우유, 달걀, 땅콩, 어패류, 또는 나무 견과류 등의 음식물로 식품 알레르기가 더 잘 생길 수 있다.
- 어떤 아이에게 식품 알레르기를 특히 더 잘 일으킬 수 있는 음식물이 따로 있다.
- 그런 음식물을 먹지 않는 것이 식품 알레르기의 예방이고 또한 치료이다.
- 최근에, 땅콩 알레르기가 있는 남자 친구가 피넛버터를 먹은 여자 친구와 키스를 한 후 땅콩 알레르기가 생겨 그로 인해 아나필락시스이 생겨 죽은 예도 있다.
- 다시 말하면, 알레르기를 일으킬 수 있는 음식물을 먹지도 말고 접촉하지도 말고 피해서 식품 알레르기를 예방하고 치료한다. (사실 실천하기가 참 어려운 권장이지만 실천해야 한다.)
- 미국 소아청소년과 학회에서는 아토피성 체질이 있는 부모에서 태어난 영아들에게 우유와 우유 음식물은 적어도 생후 6~12개월 이전에는 전혀 먹이지 말라고 권장한다.
- 달걀은 적어도 생후 12~24개월까지 먹이지 말아야 한다.
- 땅콩이나 나무 견과류나 생선은 생후 2~4세까지 먹이지 않는 것이 식품 알레르기를 예방하는 좋은 방법이라고 강조했다.
- 친 부모 형제자매들에게 여러 종류의 알레르기 질환이 있거나 아토피성 체질이 있거나, 우유, 달걀, 초콜릿, 콩, 나무 견과류 등 음식물로 식품 알레르기가 있을 때는 그 부모 형제자매들 중 다른 누구에게도 식품 알레르기 질환이 더 잘 생길 수 있다.
- 따라서 그 형제자매들은 될 수 있는 한 식품 알레르기를 잘 일으킬 수 있는 음식물을 의사의 지시에 따라 먹지 말아야 한다.
- 분만하기 훨씬 이전부터 장차 태어날 신생아를 모유수유로 키울 것인지, 또는 인공영양을 먹여 키울 것인지 의사와 상의해서 결정해야 한다. 모유를 수유해서 식품 알레르기가 아기에게 덜 생기게 하고 또 수유모 자신도 식품 알레르기를 잘 일으킬 수 있는 음식물을 될 수 있는 한 피한다.
- 식품 알레르기를 예방하기 위해 장차 태어날 신생아에게는 될 수 있는 한 인공영양을 먹이는 대신 모유를 먹일 준비를 임신 중 해야 한다.
- 친 부모 형제자매들 중 누군가가 아토피성 체질이면 아기에게 인공영양을 먹이는 대신 모유를수유하는 것을 권장한다.
- 아토피 체질이 있는 자녀들에게는 달걀, 우유, 초콜릿, 나무 견과류, 콩류, 생선 등 식품 알레르기가 더 잘 생길 수 있는 음식물을 될 수 있는 한 먹이지 않는다.[부모도 반의사가 되어야한다-소아가정간호백과]-제4권 모유, 모유수유, 이유-모유와 알레르기 참조.
- 과거에 확실히 식품 알레르기를 일으켰던 음식물이나 식품 알레르기를 일으켰다고 의심되는 음식물은 확실히 규명될 때까지 또다시 먹지 말아야 한다.
- 식품 알레르기가 있는 자녀들에게는 집 먼지, 집 먼지 진드기, 짐승의 털이나 비듬, 또는 침, 꽃가루, 곰팡이 등으로 알레르기 질환이 생길 가능성이 상당히 더 높다. 알레르기 질환을 잘 일으킬 수 있는 것(항원)들을 될 수 있는 한 피하든지 제거해 더 이상 접촉하지 말아야 한다.
- 어떤 음식물을 먹은 후, 벌에 쏘인 후, 또는 어떤 약물로 치료받은 후 아나필락시스가 생길 때 응급으로 치료 할 수 있는 에피네프린 주사약이나 에피펜 주사를 소아 자녀 본인이 평소 지참하고 다니든지, 필요할 때 즉시 에피펜 주사를 놓아 줄 수 있도록 집, 승용차 또는 적절한 장소에 보관한다. 식품 아나필락시스가 생기면 본인이나 주위에 있는 사람이 아나필락시스를 응급으로 치료해야 한다.
- 그와 동시에, 의료구급대나, 병원 응급실, 또는 단골 의사의 지시에 따라 추적 응급처치를 계속 해야 한다.
- 과거에 식품 아나필락시스이 생겼던 아이들에게 식품 아나필락시스이 또 다시 생기면 자신이나 부모가 즉시 응급 치료를 할 수 있게 에피네프린 주사나 아나키트, 또는 에피펜(EpiPen)주사약 한두 개를 집, 학교, 승용차 등에 항상 보관한다.
- 아나필락시스을 유발시킨 원인에 관계없이 아나필락시스이 생길 때는 에피네프린이나 에피펜, 또는 아나키트 자가 주사기 주사약으로 즉시 응급치료를 해야 한다.
- 가능하면 의료구급대, 단골 의사, 병원 응급실의 지시에 따라 가장 가깝고 적절한 치료를 받을 수 있는 병원이나 종합병원 응급실로 데리고 가서 따라잡기 치료를 해야 한다.
- 아나필락시스를 일으킨 음식물을 또다시 먹어서는 절대로 안 된다. 약물로 인한 아나필락시스 참조
- 식품 알레르기가 있는 소아청소년들이나 아토피성 체질이 있는 소아청소년들은 포장해서 파는 음식물이나 사서 먹는 음식물을 먹기 전 그 음식물에 어떤 성분의 음식물이 들어있는지 알아봐야 한다.
- 과거 식품 알레르기를 일으켰던 음식물의 성분이 그 음식물에 들어있나 확인한 후 식품 알레르기를 일으켰던 음식물 성분이 들어 있지 않을 때만 그 음식물을 먹는다.
- 식품 알레르기로 생긴 여러 가지 증상 징후에 따라 식품 알레르기를 대증 치료 한다.
- 아토피 체질이 있는 신생아들이나 영아들에게 될 수 있는 한 모유를 먹인다.
- 아토피 체질과 다른 어떤 알레르기 질환이 있는 영아들에게 모유를 수유하는 동안 수유모는 우유, 달걀, 초콜릿 등 알레르기 질환을 잘 유발시킬 수 있는 음식물은 될 수 있는 한 먹지 않는다.
- [부모도 반의사가 되어야한다-소아가정간호백과]-제4권 모유, 모유수유, 이유-모유와 알레르기 참조.
- 식품 알레르기에 대한 더 자세한 정보는 www.foodallergy.org 참조.
- 우유, 달걀, 생선이나 새우 조개, 나무 견과류, 밀가루 음식, 땅콩, 메주콩 등에서 나온 단백질이 든 음식물은 식품 알레르기(음식물 알레르기)를 더 잘 일으킬 수 있다.
- 그런 음식물을 조리해서 파는 음식물 제조 회사는 음식물 성분 속에 이상 설명한 식품의 단백질이 들어 있다는 사실을 소비자가 알고 먹을 수 있도록 음식물 포장지에 명시하도록 Food allergen labeling and consumer protection act of 2004에 의해서 법적으로 정해졌다(Pediatrics News October 2008).
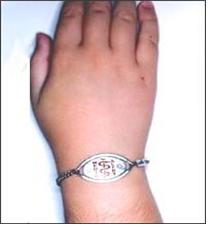
사진 135. 과거에 어떤 식품 아나필락시스가 있던 소아청소년들은 아나필락시스를 일으켰던 음식물의 이름이 적혀있는 팔찌나 목걸이를 평소에 하고 다녀야 한다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
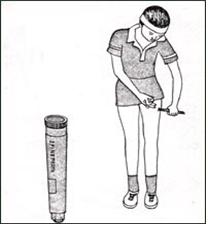
사진 136. 과거에 어떤 식품 아나필락시스이 있던 소아청소년은 같은 종류의 음식물 성분으로 아나필락시스이 또 생길 수 있다. 아나필락시스이 생길 때 응급 치료를 할 수 있는 에피네프린 주사약을 집, 학교, 승용차, 또는 그 외 적절한 다른 장소에 항상 보관하고, 또 가지고 다니다가 아나필락시스이 생기면 본인이나 부모나 주위 사람이 바로 주사를 놓아 응급 치료를 해야 한다.
Copyright Ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
|
알레르기 행진을 중지시키려면 1. 적어도 생후 4~12개월까지 모유를 먹인다. 2. 보충 음식물이 필요하면 가수화단백 포물라를 먹인다. 3. 이유식을 생후 4개월 이전에는 먹이지 않는다. 4. 흡연하는 사람 주위에 있지 않는다. |
Update: Spoonfulone을 생후 4-6월부터 먹여 음식물 알레르기를 예방 할 수 있다.
Update: Caffeinez카페인은 카페인 열매니 티잎 등에서 얻을 수 있고 음료나 그외 다른 형의 음식 물을 통해 섭취 할 수 있다. 미국 인들의 85%가 카페인을 1일 135mg 을 섭취 한다.
카페인을 적절히 섭취 하면 피로 회복, 민첩성증가, 우울증 감소, 자살율 감소 된다. 또 밥맛을 떨어트리고 체중을 감소시킨다. 과량 섭취는 불안하고 수면 장애도 일으킬 수 있다.갑자기 커피를 더 이상 섭취하지 안 하면 피로, 두통, 우울감이 생길 수 있다. JAMA, 2/15/2022
Update: Spoonfulone can be fed from 4-6 month old infant to prevent food allergy. Update: Caffeine can be obtained from the caffeine beans, tea leaves, etc., and can be consumed through beverages or other types of food. 85% of Americans consume 135 mg of caffeine per day. Adequate intake of caffeine reduces fatigue, increases agility, reduces depression, and reduces suicide rates.
It also reduces the appetite and reduces weight. Excessive consumption can cause anxiety and sleep disturbance. Sudden stop drinking coffee can lead to fatigue, headaches and depression. JAMA, 2/15/2022
Food allergy (food allergy/food allergy)식품 알레르기(음식물 알레르기/음식물 알러지), 카페인 Caffeine
Food allergy and food allergy caused by food additives
① Food adverse reaction
② Food hypersensitivity (food allergic reaction/Food hypersensitivity)
③ Food anaphylaxis
④ Food intolerance can occur.
• Allergies caused by food (food) are called food allergy, food allergies, food allergies, plant allergies, food allergies, or digestive tract allergies.
• IgE-mediated food allergy is 6-8% of children and adolescents in the US and UK,
• It occurs in 2% of adults (source; The New England Journal of Medicine, Sep. 18, 2008).
• There are studies showing that IgE-mediated food allergies can occur in adults by 25%, but in reality, it is the theory that it occurs in less than 3%.
• In the United States, food allergies result in 30,000 people receiving emergency treatment and nearly 2,000 deaths per year.
• Most of the food allergies in newborns and infants disappear spontaneously as they grow. • Allergies to tree nuts such as peanuts, walnuts, pecans, pistachios and Brazilian walnuts, or fish and shellfish, and seafood food allergies can persist throughout life, without being completely eliminated from growing children and young adults.
• Food allergies can occur due to the glycoprotein (protein) component in animal or vegetable foods.
• Foods such as eggs, milk, peanuts, and tree nuts are the most common causes of food allergies in infants and young children.
• Recently, kiwi allergy is on the rise.
• Food allergies may occur from wheat flour or soybean meal, but it is difficult to diagnose clinically with certainty.
• It is said that 95% of food allergies in children and adolescents are mainly caused by the four foods: eggs, milk, peanuts, and soybeans
③ In adults, food allergies are most common with foods such as shellfish, seafood, fish, peanuts, and tree nuts.
• The incidence of food allergies varies depending on the country and region in which you live.
• For example, in France, mustard food allergies are more common,
• Sesame allergy is more prevalent in Israel,
• Egg food allergies and milk food allergies are the most common childhood and adolescent food allergies worldwide, with no regional or regional differences (source; Food allergy, The New England Journal of Medicine, Sept. 18, 2008).
• Allergies caused by egg food occur in 1.5-3.2% of children.
• 66% of allergies from egg food can go away by the age of five,
• At the age of 7, 75% are said to disappear.
• If the egg food allergy does not go away by the age of 16, it is said to persist throughout life.
• It is common for children with an atopic constitution to develop food allergies more often than children without an atopic constitution.
• In addition, children and adolescents with an atopic constitution are more likely to develop food allergies and are more likely to develop allergic diseases from the food when they eat it.
• Assuming that any kind of food can cause food allergies, it seems common sense to have access to food.
• Symptoms resulting from a disease other than a food allergy may be similar to those resulting from a food allergy.
• Therefore, it is often wrongly judged that the symptom of any other disease is a symptom of a food allergy.
• For example, symptoms of lactose intolerance, food poisoning, infectious diseases, or mental neurological disorders may be similar to those of food allergies.
• Because of this, lactose intolerance, food poisoning, or infectious diseases can be misdiagnosed as food allergies.
• Sometimes, symptoms that are almost identical to those of a food allergy can result from a disease other than a food allergy.
• For example, it may be similar to abdominal pain resulting from lactose intolerance and abdominal pain resulting from a milk protein allergy.
• For this reason, it is necessary to differentiate between the symptoms of food allergies and those of other diseases. www.drleepediatrics.com-Vol. 5 Artificial nutrition, baby food, vitamins, minerals, fats, proteins-If the baby cannot eat artificial nutrition made from milk, Vol. 12 Pediatric Nervous System Mind, Emotional, behavioral, psychological, and sleep problems-see simple tics.

Photo 132. Foods that can most commonly cause food allergies (food allergies) in children and adolescents (0-18 years old). Eggs, milk, peanuts, soybeans, wheat foods, tree nuts (walnuts, pecans, pistachios, Brazilian walnuts, etc.), shellfish, and fish are the most common food allergies. It is said that 95% of food allergies in children and adolescents are caused by eggs, milk, peanuts, or soybeans. Copyright ⓒ 2013 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Picture 133. Milk, eggs, peanuts, nuts, fish, and flour foods are foods that can cause food allergies better. Copyright ⓒ 2013 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Picture 134. Milk or milk-based foods can cause a milk allergy. Copyright Ⓒ 2013 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
Causes of food allergies
• The causes of food allergies can be classified as follows.
Food allergy (i.e. food allergy) mediated by immunoglobulin E (IgE)
You can think of it by dividing it into the following 1 to 4 types.
1. The primary target organs are the oral cavity and the digestive tract such as the pharynx.
• The following 1 or 2 symptoms and signs and food allergies may occur.
• Oral allergy syndrome-swelling and itching of the lips, mouth and pharynx can occur.
• Gastrointestinal anaphylaxis-Symptoms may include nausea, vomiting, epigastric abdominal pain, bloating, farting, and diarrhea.
2. Organs of the secondary target system are skin, lungs, and blood vessels. The following signs of symptoms and food allergies can occur.
• Acute urticaria, angioedema (Acute urticaria and Angioedema), and atopic dermatitis can develop on the skin. Bronchial asthma and, or allergic rhinitis, may develop,
• Anaphylaxis-Shortness of breath, systemic cyanosis, hypotension, shock, and other symptoms may occur.
A mixed food allergy of immunoglobulin E (IgE) and non-immunoglobulin E (IgE) can occur as follows:
- Atopic dermatitis
2. (Parents should also be anti-doctors-Refer to Encyclopedia of Child and Family Nursing-Volume 17, Pediatric Skin Diseases-Atopic Dermatitis)
3. Allergic eosinophilic esophagitis (see eosinophilic esophagitis)
4. Allergic eosinophilic gastroenteritis-Symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and severe epigastric abdominal pain may occur. Eosinophils are increased and eosinophils in the gastrointestinal tract are increased. The skin test for the food that caused the allergy is positive. Eating those foods makes your symptoms worse.
Food allergy mediated by non-immunoglobulin E (IgE)
1. Food protein-induced proctocolitis
2. Food protein-induced enterocolitis source; Pediatric annals, vol 37, November 8, 2008
• Allergic rhinitis caused by pollen is caused by IgE-mediated, and most of the oral food allergies, which cause itching in the mouth or tingling symptoms in the mouth, are caused by IgE-mediated.
• Food allergies caused by IgE mediation usually occur only seconds to minutes after eating the food.
• It can occur late within an hour or two after eating.
• Small intestinal colitis caused by milk protein allergy or soy protein allergy is T-cell mediated.
• Food allergies caused by T-cell mediation usually occur 3 to 4 hours after eating. • Food allergies can occur in 5-8% of children and adolescents, but food adverse reactions that are not food allergies can occur in as much as 25%.
• Foods such as milk, eggs, peanuts, soybeans, flour, shellfish, fish, walnut nuts, and chocolate may cause food allergies more than other types of foods.
• In general, rice foods are known to be hypoallergenic. Research has also shown that rice protein allergy caused small bowel colitis. Journal watch pediatrics and adolescent medicine vol #1
• Mild milk allergies or egg allergies may no longer occur as they grow older, but peanut or tree nut allergies can continue throughout life regardless of growing growth.
Differential diagnosis of food allergy
① Symptoms of food side effects caused by various artificial colors, seasonings or preservatives added when cooking food
o Food yellow No. 4 (artificial pigments such as food yellow no4 tartrazineTartrazine,
o Monosodium glutamate,
o Nitrites,
o Symptoms resulting from adverse reactions resulting from eating foods made with food preservatives such as food flavor enhancers (Nitrates sulfiting agents) may cause symptoms similar to those resulting from food allergies.
② When eating milk from cows that have been treated with penicillin or other antibiotics, anaphylaxis can occur due to antibiotics in the milk. Anaphylaxis is a type of food allergy and is a severe immediate allergy that is dangerous to life.
③ Symptoms or diseases caused by food containing bacteria, molds, drugs, or insects
④ Mushroom poisoning, shellfish poisoning
⑤ Gastrointestinal diseases such as peptic ulcer, diaphragmatic hernia, and intestinal obstruction
⑥ Deficiency of primary di(2) saccharide enzyme or deficiency of secondary disaccharide enzyme, galactose, etc. Symptoms caused by foods containing drug ingredients-Symptoms caused by foods containing alcohol, histamine, caffeine, etc.
⑦ endocrine disease ⑧ bacterial infection, viral infection, or parasitic infection ⑨ Symptoms caused by psychological problems
⑩ Other Sources and References, Clinical Semina, Richard Evans, III, M.D., M.P.H and Richard J. Summers, M.D.
Signs of food allergy symptoms
• Food allergies caused by IgE mediation may cause a food allergic reaction to appear only in one organ of the body, may appear simultaneously in several organs of several strains, may appear throughout the body, and may occur only in one area of the body.
• IgE-mediated food allergy can cause local hives,
• It can be systemic and co-occur with anaphylaxis, which can lead to loss of life.
• Refer to the following sections for the symptoms and signs of food allergy in organs of the body.
① When it occurs in the respiratory system-runny nose, rhinitis, asthma, wheezing, etc.
② When it occurs on the skin and mucous membranes-Urticaria, skin redness, angioedema, contact urticaria, symptoms and signs of atopic dermatitis worsen, etc.
③ When it occurs in the digestive system-vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea, etc. ④ When it occurs in the central nervous system, avoidance of food, changes in emotions, depression, etc.
⑤ When it occurs in the musculoskeletal system-musculoskeletal pain, growth pain, etc.
⑥ When it occurs in blood vessels and heart system-pseudo anemia, migraine, etc.
⑦ When it occurs in other systems
Egg-egg syndrome (Occupational egg allergy)
• In the process of making drugs or foods containing egg protein, even if only a small amount of egg protein is contained, the egg protein component can cause egg allergy.
• This symptom is called egg-egg syndrome (see Food allergy, The New England Journal of Medicine, Sep. 18, 2008).
First age at which food allergies begin
① Egg food allergy-6~24 months old
② Milk food allergy-6-12 months old
③ Peanut food allergy-6~24 months old ④ Tree nut food allergy-1-17 years old ⑤ Sesame food allergy-6 to 36 months old ⑥ Fish food allergy-late puberty or adulthood
⑦ Shellfish food allergy- adulthood
⑧ Flour food allergy-6~24 months old
⑨ Meju bean food allergy-6 to 24 months old
⑩ Kiwi food allergy-any age
⑪ Apple food allergy-late puberty and adulthood
⑫ Carrot food allergy-late puberty and adulthood
⑬ Peach food allergy-late puberty and adulthood Source-Food allergy, The New England Journal of Medicine, Sep. 18, 2008
Diagnosis of food allergy
• It is common to diagnose food allergies based on medical history, symptoms, and medical examination findings.
• If necessary, a blood test to determine the blood level of the IgE antibody (immunoglobulin E antibody) in the blood.
• Allergic skin thorn test
• Provocation test
• Radiation allergen absorption test (RAST) to test for IgE • Skin biopsy or platoon wall biopsy, if necessary
• Food allergies may be diagnosed through gastrointestinal endoscopy.
• Among them, the past and present medical history and family medical history of the patient are the most valuable in diagnosing food allergies.
• When diagnosing a food allergy, you may be able to diagnose by looking at whether the symptoms of a food allergy disappear, but are less free or have no remission, without further consuming the food causing the food allergy.
• In other words, it can diagnose food allergies while also treating food allergies.
• Symptoms of a food allergy usually disappear if foods that are thought to cause food allergies related to IgE antibodies are not consumed for 1 to 2 weeks.
• In addition, most of the symptoms of small colitis caused by food allergies usually disappear after 3 to 6 weeks from the day when you no longer consume the food that caused the allergy.
• It is common for children and adolescents who are allergic to milk, eggs, and peanuts to have elevated blood levels of food protein IgE antibodies such as milk, eggs, and peanuts.
• If the result of a specific food allergy skin test is positive, it means that antibodies to that food (antigen) are present in the subject’s body. However, just because a skin test result is positive, we cannot guarantee that a food allergy may be caused by the food. Provoking test as follows Diarrhea caused by milk protein allergy disease, Provoking test, You can diagnose a food allergy by referring to the Diagnosis of Milk Protein Allergy Disease.
Food allergy provoking test
• Trigger tests can be done at home, as directed by a doctor, only if the symptoms of a food allergy are mild and the trigger test does not pose a risk.
• However, whether the symptoms of a food allergy are mild or severe, trigger tests should be performed by an allergist.
• Do not consume any foods suspected of causing food allergies for 2 to 4 weeks, and observe carefully whether symptoms of food allergy caused by the food persist, do not occur, or are less severe.
• If the symptoms of a food allergy do not develop significantly or less during observation, it can be assumed that the food allergies are caused by the food. However, still at the provoking test stage, it is not possible to definitively diagnose that a food allergy has occurred with the food.
• After that, take the food again carefully and observe if any other symptoms of food allergy develop.
• If the same symptoms occur again as before when eating the food, it can be presumed to be diagnosed with a food allergy to the food. In this way, food allergy diseases can be presumed and diagnosed.
There was also an example of death due to anaphylaxis after eating a shrimp.
• Even if a food allergy has been mildly caused by any food in the past, the patient, the child’s parent, or the caregiver should never perform a trigger test without the instructions of a doctor to diagnose a food allergy caused by food.
• It is the principle of the provocation test that the allergist, just in case, prepares to perform progressive CPR on the spot and conducts this provocative test. In some cases, a trigger test is performed in the hospital emergency room.
• Parents should never do a trigger test at home to diagnose a particularly severe food allergy.
Food allergy treatment
• Almost all foods are likely to cause food allergies, and many types of foods, such as milk, eggs, peanuts, fish and shellfish, or tree nuts, are more likely to develop food allergies.
• There are other foods that can cause food allergies especially in some children.
• Not eating such foods is a prevention and treatment of food allergies.
• Recently, a peanut allergy boyfriend died after kissing his girlfriend who ate peanut butter, resulting in a peanut allergy, resulting in anaphylaxis.
• In other words, avoid eating or contacting foods that may cause allergies to prevent and treat food allergies. (In fact, it’s a very difficult recommendation to put into practice, but it should be done.)
• The American Academy of Pediatrics and Adolescents recommends that infants born to parents with atopic constitutions do not feed milk and milk foods at least before 6-12 months of age.
• Eggs should not be fed until at least 12 to 24 months of age.
• He stressed that not feeding peanuts, tree nuts or fish until the age of 2-4 is a good way to prevent food allergies.
• When siblings of biological parents have various types of allergic diseases, atopic constitution, food allergies such as milk, eggs, chocolate, beans, tree nuts, etc., food allergic disease to any other of the parents’ siblings. This can happen better.
• Therefore, the siblings should, as far as practicable, avoid eating foods that may cause food allergies as directed by their doctor.
• Long before delivery, you should discuss with your doctor whether you will breastfeed or feed your newborn baby with artificial nutrition. Breastfeeding makes food allergies less likely in the baby, and the nursing mother herself should avoid food allergies as much as possible.
• In order to prevent food allergies, the newborn baby should be prepared to breastfeed during pregnancy instead of artificial nutrition as much as possible.
• If any of your parents’ siblings have an atopic constitution, it is recommended that you breastfeed your baby instead of artificial nutrition.
• Children with atopic constitution should not be fed food allergies such as eggs, milk, chocolate, tree nuts, legumes, and fish as much as possible. -See Volume 4 Breast Milk, Breastfeeding, Reasons-Breast Milk and Allergies.
• Any food that you suspect has caused a food allergy in the past should not be eaten again until it is clearly identified.
• Children with food allergies are significantly more likely to develop allergic conditions from house dust, house dust mites, animal hair or dandruff, or saliva, pollen, and mold. Anything that can cause allergic diseases (antigens) should be avoided or removed as much as possible so that no further contact should be made.
• When anaphylaxis develops after eating any food, after being stung by a bee, or after being treated with a drug, epinephrine injections or epipen injections, which can be treated as an emergency, are taken by children, whether they normally carry with them, or as soon as they are needed. Keep it at home, in a car, or in an appropriate place to give you the injection. When food anaphylaxis occurs, you or someone around you should treat anaphylaxis as an emergency.
• At the same time, follow-up first aid should continue as directed by a medical paramedic, hospital emergency room, or regular doctor.
• Always keep one or two epinephrine injections, anakits, or EpiPen injections in your home, school, or car so that you or your parents can provide immediate emergency treatment if food anaphylaxis occurs again in children who have had food anaphylaxis in the past.
• Regardless of the cause of anaphylaxis, when anaphylaxis develops, immediate emergency treatment with epinephrine, epiphene, or anakit auto-injection drug is required.
• If possible, follow the instructions of a medical paramedic, regular doctor, or hospital emergency room to take them to the nearest and most appropriate hospital or hospital emergency room for catch-up treatment.
• Never eat food that caused anaphylaxis again. See drug-induced anaphylaxis • Children and adolescents with food allergies or children with atopic constitutions should find out what ingredients they contain before eating packaged or purchased foods.
• After checking whether the food that caused the food allergy in the past is contained in the food, eat the food only when it does not contain the food that caused the food allergy.
• Treat food allergies symptomatically according to the symptoms and signs of food allergies.
• Feed as much breast milk as possible to newborns or infants with atopic constitution.
• While breastfeeding infants with atopic constitution and any other allergic disease, breastfeeding mothers avoid eating as much food as possible, such as milk, eggs, and chocolate, which can cause allergic diseases.
•www.drleepediatrics.com-Volume 4 Breast Milk, Breastfeeding, Reasons-See Breast Milk and Allergies.
• For more information on food allergies, visit www.foodallergy.org.
• Foods containing protein from milk, eggs, fish or shrimp clams, tree nuts, flour foods, peanuts, and soybeans are more likely to cause food allergies (food allergies).
• Food allergen labeling and consumer protection act of 2004 has legally mandated that food manufacturing companies that prepare and sell such foods must specify on their food packaging that consumers know and eat that the food ingredients contain the protein of the food described above. (Pediatrics News October 2008).

Photo 135. Children and adolescents who had some food anaphylaxis in the past should wear bracelets or necklaces with the names of the foods that caused anaphylaxis on a regular basis. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Picture 136. Children and adolescents who have had some food anaphylaxis in the past may develop anaphylaxis again due to the same type of food ingredients. When anaphylaxis develops, the epinephrine injection drug, which can provide emergency treatment, is always kept at home, school, car, or another appropriate place. If anaphylaxis develops, you, your parents, or someone around you should immediately give an injection for emergency treatment. do. Copyright Ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
To stop the allergy march
1. Breastfeed at least 4-12 months old.
2. If supplementary food is needed, feed the hydrolyzed protein formula.
3. Do not feed baby food before 4 months of age.
4. You are not around the person who smokes.
Note-Recently, allergy foods can be introduced in more early life according to study.
Update: Spoonfulone can be fed from 4-6 month old infant to prevent food allergy. Update: Caffeine can be obtained from the caffeine beans, tea leaves, etc., and can be consumed through beverages or other types of food. 85% of Americans consume 135 mg of caffeine per day. Adequate intake of caffeine reduces fatigue, increases agility, reduces depression, and reduces suicide rates.
It also reduces the appetite and reduces weight. Excessive consumption can cause anxiety and sleep disturbance. Sudden stop drinking coffee can lead to fatigue, headaches and depression. JAMA, 2/15/2022
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- Caffeibne and Health.JAMA, 2/15/2022
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제9권 소아청소년 소화기 질환
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th — 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
-
Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, Harvey grant, and Robert Murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
-
The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
-
Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care
-
응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
-
Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
-
Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
-
Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
-
소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”