소화계 식품 알레르기 food allergy of digestive system
사진 151. 식품 알레르기로 설사를 할 수 있다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
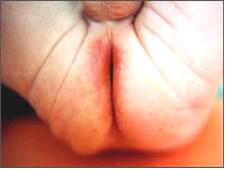
사진 152. 식품 알레르기로 설사도 할 수 있고 항문 주위 피부염도 생길 수 있다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
- 음식물로 유발된 식품 알레르기를 위장관 식품 알레르기라고 한다.
- 식품 알레르기를 유발시킬 수 있는 음식물을 먹는 신생아들, 영유아들이나 학령기 아이들, 사춘기 아이들에게 알레르기 질환이 소화기계, 특히 위장관에 비교적 잘 유발될 수 있다.
- 어디가 아픈 것을 말로 잘 표현할 수 없는 영유아들의 위장관에 식품 알레르기가 생기면 자주 울고 짜증내고 보채고 잠을 푹신 자지 않을 수 있다. 그 외 구토, 설사, 복통, 위장관 경련, 혈변, 점액변, 영아산통 등의 증상 징후가 생길 수 있다.
- 어떤 식품을 섭취한 후 위장관에 식품 알레르기가 유발됐던 아이들에게 전에 먹었던 어떤 음식물을 또다시 먹으라고 주면 그 음식물을 먹기 싫다고 말로 거절하기도 한다. 말로 먹기 싫다고 표현을 할 수 없는 영유아들은 위장관 알레르기를 전에 일으켰던 음식물을 손으로 밀거나 또 입을 다물고 받아먹지 않을 수 있다. 이런 현상을 “음식물 기피 현상(Food evasion)”이라고 한다.
- 식품 알레르기를 유발시키는 음식물을 장기간 계속 먹이면 영양실조에 걸리고 성장 발육 지연도 생긴다.
- 우유 단백질이나 콩 단백질이 든 인공영양을 먹는 신생아들이나 영유아들에게 우유 단백 또는 콩 단백 음식물로 식품 알레르기가 유발될 수 있다. 우유 단백질이 든 인공영양이나 콩 단백질이 든 인공영양으로 식품 알레르기가 유발되면 그로 인해 배가 아프고, 설사하고, 구토할 수 있고 영아산통이 생길 수 있다.
- 신생아들이나 영아들에게 생기는 영아산통도 식품 알레르기의 일종이라고 한다. 영아들이 영아산통에 걸리면 신생아나 영아가 심하게 울고 보채고 잠도 잘 못 잔다.
- 우유 단백질에 알레르기가 심하게 생기는 영아들은 우유 단백질의 성분이 소량 든 식품이나 우유 단백질이 든 인공영양 등을 조금만 먹을 때도 위장관에 우유 알레르기가 생길 수 있다.
- 확실한 이유 없이 구토, 설사, 복통 등의 증상 징후가 식품 알레르기로 생길 수 있다. [부모도 반의사가 되어야한다-소아가정간호백과]-제6권 신생아 질환-영아산통 참조.
- 위장관에 생긴 식품 알레르기로 위장관의 점막층이 붓고 손상될 수 있고 그로 인해 손상된 위장관 벽 점막층에서 피가 나서 대변에 나온 피를 육안으로 볼 수 있다. 때로는 육안으로 볼 수 없을 정도로 피가 대변으로 소량 나올 수 있다. 이런 위장관 출혈을 위장관 잠복성 출혈(위장관 잠혈)이라고도 한다. 드물게는 점액 변도 눈다.
- 위장관 식품 알레르기를 유발시키는 음식물을 장기간 계속 많이 먹으면 증상 징후가 더 심해질 수 있다. 드물게는 식품 알레르기로 아나필락시스이 유발될 수 있고 그로 인해 사망할 수 있다.
- 가성빈혈, 주의력 결핍장애, 편두통, 행동과다증(과도 활동장애), 현기증 등이 생길 수 있다.
- 글루텐 유발 장증(셀이악 병), 호산성 식도염, 호산성 위장염 등도 위장관 식품 알레르기 질환에 속한다([부모도 반의사가 되어야한다-소아가정간호백과]-제9권 소아청소년 소화기 질환 참조),
Food allergy of digestive system 소화계 식품 알레르기

Picture 151. Food allergy can cause diarrhea. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Photo 152. Food allergy can cause diarrhea and perianal dermatitis. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
• Food allergies caused by food are called gastrointestinal food allergies.
• In newborns, infants, school-age children, and adolescents who eat foods that can cause food allergies, allergic diseases can be relatively prevalent in the digestive system, especially the gastrointestinal tract.
• When food allergies develop in the gastrointestinal tract of infants and toddlers who can’t verbally describe the pain somewhere, they can often cry, become irritable, flirt, and not sleep well. Other symptoms may include vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, gastrointestinal cramps, bloody stools, mucous stools, and infant colic.
• When children who have had food allergies in the gastrointestinal tract after eating certain foods are told to eat a food they had previously eaten again, they refused by saying that they do not want to eat the food. Infants and toddlers who are unable to express their dislike with words may not eat foods that previously caused gastrointestinal allergies with their hands or with their mouths closed. This phenomenon is called “food evasion.”
• Long-term feeding of foods that cause food allergies leads to malnutrition and delays growth and development.
• Food allergies can be triggered by milk protein or soy protein foods in newborns and infants who eat artificial nutrition with milk protein or soy protein. Artificial nutrition with milk protein or artificial nutrition with soy protein can cause food allergies, which can lead to stomach pain, diarrhea, vomiting, and infant colic.
• Infant colic in newborns and infants is also said to be a type of food allergy. When infants suffer from infant colic, newborns or infants cry badly, cry, and sleep poorly.
• Infants who are severely allergic to milk protein can develop a milk allergy in the gastrointestinal tract even if they eat a small amount of foods containing a small amount of milk protein or artificial nutrients containing milk protein.
• Symptoms such as vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain can result from food allergies for no apparent reason.
www.drleepediatrics.com-Volume 6 Newborn Diseases-Refer to Infant Colic.
• Food allergies to the gastrointestinal tract can cause swelling and damage to the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract, resulting in bleeding from the mucous membrane layer of the damaged gastrointestinal tract, so that the blood in the stool can be seen with the naked eye. Sometimes a small amount of blood can come out of your stool that you can’t see with the naked eye. This gastrointestinal bleeding is also called latent gastrointestinal bleeding (occult blood in the gastrointestinal tract). Rarely, mucous stools are also open.
• If you eat a lot of foods that cause gastrointestinal food allergies over a long period of time, your symptoms may be worse. Rarely, food allergies can cause anaphylaxis and death.
• Pseudo anemia, attention deficit disorder, migraines, hyperactivity (hyperactivity disorder), and dizziness may occur.
• Gluten-induced bowel disease (celiac disease), eosinophilic esophagitis, and eosinophilic gastroenteritis are also included in gastrointestinal food allergies-www.drleepediatrics.com-see Volume 9, Children’s and Adolescent Digestive Diseases),
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com제8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제9권 소아청소년 소화기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제10권. 소아청소년 신장 비뇨 생식기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제11권. 소아청소년 심장 혈관계 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제12권. 소아청소년 신경 정신 질환, 행동 수면 문제
- www.drleepediatrics.com제13권. 소아청소년 혈액, 림프, 종양 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제14권. 소아청소년 내분비, 유전, 염색체, 대사, 희귀병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제15권. 소아청소년 알레르기, 자가 면역질환
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th — 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
-
Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, Harvey grant, and Robert Murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
-
The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
-
Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care
-
응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
-
Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
-
Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
-
Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
-
소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”