소아 학대와 소아 무관심(아동 학대와 아동 무관심/어린이 학대와 어린이 무시 방치/아동 학대와 아동 무시), Child abuse and child neglect
소아 학대와 소아 무관심(아동 학대와 아동 무관심/어린이 학대와 어린이 무시 방치/아동 학대와 아동 무시)의 개요
-
오늘 날 전 세계 각처에서 소아청소년들(0~18세)이 그들의 부모, 보호자, 또는 그 외 위정자들로부터 신체 학대, 성 학대, 정서 학대, 약물 학대, 방임 학대, 무관심 학대(무시 학대/방치 학대), 또는 부적절한 체벌 학대를 받는다.
-
소아청소년들(0~18세)이 이런 종류의 학대를 받는 것을 통틀어 소아 학대 또는 아동 학대라고 한다.
| “ 아동은 심신이 완전히 청년기에 달하지 않은 사람, 대개 3~12세의 어린 아이“를 말한다
(출처-국어 대사전 이희승 박사 저). 여기서 다루는 소아학대는 소아청소년들, 즉 0~18세 연령층 소아들에게 생기는 학대에 관해 설명한다. 아동의 연령층은 3~12세이기 때문에 아동 학대란 말 대신 0~18세에 속하는 소아청소년 학대 또는 소아(1~18세) 학대란 말을 쓰는 것이 더 적합하다. |
-
소아 학대를 받은 일부 소아들은 신체적, 정서적, 사회적 성장발육 면에 위중한 손상을 받을 수 있다. 심지어 소아 학대로 생명도 잃는다.
-
부모가 자녀의 잘못된 행동을 바로 잡기위해 자녀 양육 방법으로 주는 체벌로 소아 신체 학대 죄로 취급받는 실예도 있다.
-
어떤 성인은 이웃집 아이가 귀여워서 안아준 후 소아 성 학대를 했다고 법정에 섰던 실예도 있다.
-
부모들이 “소아학대”가 무엇이지 확실히 몰라 소아청소년 자녀를 사랑으로 양육하다가 신체 학대, 성 학대, 또는 무관심적 학대를 하지 않도록 예방하는 것은 부모들의 중요한 책임이고 의무이다.
-
여기서 다룬 소아 학대의 내용의 거의가 미국 소아 학대 연구 자료와 저자가 40여년 동안 소아진료 임상경험을 통해서 얻은 정보이다.
-
미국 사회에서 일어나는 소아 학대와 소아 무관심은 미국 이외 다른 나라에서 일어나는 소아 학대와 소아 무관심의 실제가 다를 수 있다.
-
세계 어디서 살든, 소아청소년 자녀를 둔 부모건 아니건 소아 학대에 관한 정보를 많이 알아둘 필요가 있다.
-
여기서 다룬 소아 신체 학대, 소아 성 학대, 소아 무관심적 학대로 생기는 비기질적 성장 발육 지연 등을 잘 이해하고 소아 학대를 예방하고 적절히 처리하는데 도움이 되기 바란다.
|
한국 중앙아동 보호 전문기관의 2015년 상반기 아동학대 현황에 따르면, 2015년 1~6월까지 아동학대로 판정된 사건은 5,432건으로 이중 12명의 아동이 사망했다. 한 달에 2명이 사망했다. 소스: 미주 한국일보 2015년 9월 30일. .
|
소아 학대(아동 학대/어린이 학대)의 정의
-
이미 위에서 설명했지만 여기서 다시 설명하면.
-
소아 학대를 어린이 학대, 소아청소년 학대, 또는 아동 학대라고도 한다.
-
나라, 종교, 인종, 또는 각 개인에 따라 소아 학대를 다르게 정의한다.
-
미 소아청소년과는 소아 학대를 다음과 같이 정의한다.
-
소아(0~18세 연령층에 속해 있는 아이들) 또는 소아청소년 (0~18세)이 그들의 부모, 보호자, 돌보는 사람, 그 외 사람에 의해 신체적으로나 감정적으로 손상을 받거나, 성장 발육이 지연되거나, 성희롱을 당하거나, 성교를 하거나 강간을 당하는 것을 통털어 소아 학대 또는 아동학대라 한다.
-
소아의 신체에 부상을 입혀 소아의 건강과 안녕에 위험성을 조성하는 행위를 소아 신체학대라고 한다.
-
인간 기본 생명 유지에 필요로 하는 것–옷, 집, 음식물, 사랑, 수면, 보살핌 등을 적절히 제공하지 않거나, 교육을 적절히 시키지 않거나, 건강관리 및 건강 증진을 적절히 해 주지 않거나 방치해서 소아의 건강과 안녕에 위험을 주는 행위를 소아 무관심 학대(소아 무시 학대 또는 어린이 방치 학대)라고 한다.
-
미 오하이오주 주법에 의하면,
-
보살핌, 부양과 보호할 의무를 다하지 않아 소아의 신체적, 정신적, 정서적 건강과 안녕에 위험성을 충분히 조장하는 행위를 소아 학대라고 정의했다.
-
소아를 잔인하게 취급하거나
-
과도하게 벌주거나
-
소아의 행동을 보통 이상으로 제한하기 위해 육체적으로 감금하거나,
-
정신적 육체적 성장 발육에 손상을 끼치거나,
-
교육을 적절히 시키지 않거나,
-
불공평하게 대하거나,
-
부적절하게 훈련시키거나
-
질병을 적절히 치료해 주지 않거나,
-
질병의 예방을 소홀히 하는 것도 소아 학대에 속한다.
소아 학대(아동 학대/어린이 학대)의 분류
소아 학대(아동학대)를
-
소아 신체 학대,
-
소아 성 학대,
-
소아 무관심적 학대로 생긴 “비기질적인 성장발육 지연“등으로 분류하기도 한다.
-
영유아의 신체를 고의적으로 심하게 흔들어 신체 손상을 입히는 셰이큰 영아 증후군(흔들린 아이 증후군),
-
소아청소년들에게 불필요한 약물을 먹이는 소아 약물 학대,
-
소아가 사회적으로 정서적으로 정상 발육되지 않게 소아의 정신, 감정, 정서를 손상시키는 소아 감정적 학대,
-
대리인에 의한 뮌하우젠 증후군 등의 소아 학대로 분류할 수 있다.
소아 신체 학대
소아 성 학대
-
- ① 소아 성희롱 성 학대
- ② 소아 성교 성 학대
소아 강간 성 학대
소아 감정적 학대
- 무관심으로 생긴 비기질적 성장 발육지연 학대(소아 무관심적 학대/소아 방치 학대/ 소아 무시학대)
- 몸을 심하게 흔들어 신체에 손상을 입히는 흔들린 아이 증후군 학대(셰이큰 영아 증후군)
- 소아 약물 학대
- 대리인에 의한 뮌하우젠 증후군
- 그외
-
출처 및 참조문헌
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처-14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 그 외
표 22. 엄마가 폭력적 파트너나 비폭력적 파트너와 살 때 그 엄마의 소아청소년 자녀가 소아 학대를 당한 %
| 심리적 학대 받는 % | 무관심적 학대 받는 % | 신체적 학대 받는 % | 성적 학대 받는 % | |
| 폭력적 파트너 | 44.0 % | 20.5 | 19.0 | 0.3 |
| 비폭력적 파트너 | 8.0 % | 8.0% | 8.0 | – |
1,232명의 엄마와 엄마 같이 사는 엄마의 파트너들을 대상으로 조사한 결과
출처 및 참조문헌
- Elsevier Global Medical News and Dr. Zolotor
- 그 외
다음 처지에 있는 엄마 아빠는 소아 신체적 학대를 할 가능성이 더 높다.
|
다음 처지에 있는 소아들은 소아 신체 학대를 받을 가능성이 더 높다
|
소아 신체 학대로 부상이 가장 많이 발견된 신체 부위
|
소아 신체 학대의 역학
-
소아 신체학대를 아동 신체학대, 어린이 학대, 또는 소아청소년 학대라고 한다.
-
여기서 소아란 말은 0~18세 연령층 속하는 아이들 또는 소아청소년들을 의미한다.
-
연구에 의하면, 미국 소아청소년(0~18세)들(소아들)의 2~3%(1.4백만 명)가 연간 소아 신체 학대와 소아 무관심 학대를 받고,
-
연간 16만 명의 소아들의 생명이 위협받을 수 있을 정도로 소아 신체 학대로 부상 입고,
-
1000~2000 명의 소아청소년들이 소아 신체 학대로 사망하고,
-
그 중 80%는 5세 이하 영유아들이고, 40%는 1세 이전 영아들이었다.
-
1994년에 미 48주에서 약 1백만 명의 소아들이 소아 신체 학대와 소아 무관심 학대를 받았고,
-
그 중 52%는 소아 무관심 학대,
-
26%는 소아 신체 학대,
-
14%는 소아 성 학대,
-
5%는 소아 감정적 학대,
-
3%는 건강관리를 적절히 받지 않은 소아 무시 학대이였고,
-
같은 해에 미 43주에서 소아 학대로 1111명의 소아들이 사망했다고 한다.
-
소아 신체 학대는 미국 인구 백만 명 중 1,200명의 소아들에게 발생됐다.
-
연간 3백만 명의 미국 소아들에게 신체, 감정, 성, 무관심 학대가 있었다.
-
그 중 25%는 소아 신체 학대였다 출처– 미 소아 보호국이 보고.
-
소아 신체 학대로 응급 치료를 받았던 미국 소아들의 10%가 5세 이하 영유아들이었고,
-
소아 신체 학대를 받은 소아들의 ⅓은 1세 미만, ⅓은 1~6세, ⅓은 6세 이상이었다.
-
소아 신체 학대를 받은 소아들 중 95%는 소아의 친엄마 아빠, 소아들을 돌보는 친척, 홀 엄마의 친구로부터 받았고, 4%는 그 외 사람에 의해 받았고, 1%는 형제자매들에 의해 받았다고 한다.
-
알코올 중독 부모, 약물 중독 부모, 우울증 등 정신병을 앓는 부모는 소아 신체 학대를 받는 율이 그렇지 않은 부모들 보다 2~3배 더 높다.
-
부모들의 인종, 나라, 종교, 민족, 직업, 교육, 문화, 경제, 사회의 각계층에 관계없이 소아 신체 학대 발생률은 거의 같다.
-
소아 신체 학대를 한 부모들의 90%는 범법행위의 경험도 없었고 정신병도 앓지 않았다고 한다.
소아 학대(아동 학대)를 받았다고 의심하거나 받은 것이 확실할 때 소아 보호 관계당국에 보고해야 할 법적 의무를 가지고 있는 사람들은 다음과 같다( 미국의 경우).
|
안전사고로 인한 정신적 신체적 손상과 소아 학대
-
“예방을 잘 하면 모든 사고는 생기지 않을 수 있다“고 생각하는 사람들은 안전사고 예방을 소홀히 해서 신체적 손상이 소아에게 생기거나 감정적 손상이 소아에게 생겨도 소아 학대를 한 것으로 따진다.
-
안전사고로 생긴 정신적 신체적 손상은 부모의 무관심으로 생긴 것이라고 인정되기 때문이다. 그러나 안전사고로 입은 정신적 신체적 손상은 소아 학대가 아니라고 주장하는 사람들도 있다.
스팽킹 체벌과 소아 학대
-
연구에 의하면, 75%의 소아청소년과 전문의들은 외상을 입힐 정도로 가한 스팽킹 체벌은 부적절한 스팽킹 체벌로 인정하지만 소아 신체 학대로 간주하지 않는다고 주장한다.
-
나머지 25%의 소아청소년과 전문의들은 부모가 자녀 양육상 스팽킹 체벌을 했지만 타박상을 입힐 정도로 스팽킹 체벌을 가했으면 그런 유형의 스팽킹 체벌도 소아 신체 학대에 해당되고 아동 보호관계당국에 보고해야 한다고 주장했다.
체벌과 소아 학대
-
미 초중교와 가정에서 소아들에게 교육, 지도, 훈련, 양육을 목적으로 소아들에게 체벌을 주기도 한다.
-
체벌은 동서고금 자녀훈련을 시키는 통상적인 방법의 하나로 알려졌다. 연구에 의하면, 미국 초중교사들의 60%가 연간 적어도 한번 정도 학생에게 체벌을 주고,
-
미국 1,146쌍의 부모들의
-
73%가 3~17세 연령층에 있는 유아들, 학령기 아이들과 사춘기 아이들을 양육, 훈련 목적으로 육체적 정신적 폭력을 가했고,
-
58%는 스팽킹 체벌을 주고,
-
13%는 물건으로 때렸고,
-
5%는 물건을 던졌고,
-
3%는 발로 차고 물고 주먹으로 때렸고,
-
1%는 과거 1년 동안 자녀를 적어도 한번 정도 매로 때린 적이 있다고 설문조사에
-
응답했다.
-
많은 미국 사람들은 자녀 양육, 훈련을 할 때 적절한 체벌을 가해도 괜찮다고 믿고 있다.
-
미 소아청소년과 학회는 자녀 양육, 훈련을 하기 위해 1세 이후 유아나 학령기 아이의 손이나 엉덩이를 부모가 활짝 핀 손바닥으로 한두 번 정도 찰싹 치는 체벌은 자녀 양육 훈련에 필요한 스팽킹 체벌이고 소아 신체 학대에 속하지 않는다고 믿고 있다.
-
소아 자녀의 비행을 바로 잡기 위해 엄마 아빠가 활짝 핀 손바닥 이외 어떤 종류의 기구를 이용해 소아 자녀의 신체의 어느 부위를 때리는 것은 소아 신체 학대에 속한다고 정의한다.
-
소아 자녀에게 체벌을 줄 때 자녀의 얼굴이나 머리를 때리는 것은 자녀 양육, 훈련을 위한 체벌로 간주하지 않고 소아 신체 학대에 해당된다고 정의한다.
-
소아 자녀를 돌보는 베이비시터나 보호자가 어떤 이유로든 소아의 잘못한 행동을 바로 잡기 위해 소아에게 체벌을 주어
-
신체적 손상을 입혔을 때,
-
소아의 손이나 엉덩이 이외 신체 다른 부위를 손바닥이나 다른 것으로 때렸을 때,
-
활짝 핀 손바닥으로 체벌을 받은 엉덩이나 손에 홍색 피부 반점이나 적색 피부 반점이 나 타나는 이외 어떤 신체적 손상이 생기면 소아 신체 학대로 취급된다.
-
생후 12개월 이전 영아들에게 어떤 방법으로든 체벌을 가하면 소아 신체 학대에 해당된다.
-
손바닥이 아닌 어떤 종류의 기구로 신체의 어느 부위든지 체벌을 주는 것도 소아 신체 학대에 해당된다.
-
밀거나, 접촉시키거나, 충돌시키거나,
-
자상을 입히거나,
-
열이나 부식성 화학물질에 접촉시키거나,
-
불필요한 약물을 먹이는 행동도 소아 신체 학대에 해당된다.
소아 신체 학대의 증상 징후
-
소아 신체 학대를 한 부모나 보호자가 자발적으로 소아 신체 학대를 했던 사실을 인정하면서 병원 응급실이나 소아청소년과로 소아 자녀를 데리고 오는 경우도 가끔 있다.
-
대부분의 경우, 소아 신체 학대로 생긴 부상 때문에 소아들을 병원에 데리고 왔을 때, 그 부상의 원인, 정도, 입은 때, 상처 받은 경로, 방법과 장소 등에 관한 병력에 모순성이 많이 있고 사실성과 거리가 멀고 병력에 일률성이 없는 때가 많다.
-
소아들에게 상처가 있을 때, 상처가 생기게 된 이유를 확실히 설명할 수 없는 때는 그 상처가 소아 신체 학대로 인해 생겼나 의심해 보는 것이 보통이다.
-
소아 신체 학대로 생긴 상처의 대부분은 소아청소년의 나이와 성장 발육에 일치되지 않을 때가 많다.
-
소아 신체 학대로 상처가 생겼을 때는 상처를 입은 후 치료를 곧 받지 않고 늦게 치료받는 경향이 있다.
-
소아 신체 학대를 받고 자란 소아들에게 공격적 성격, 대인관계 문제, 우울증, 애정문제, 약물남용, 알코올 중독 등 행동 정서 감정 대인 관계에 문제가 잘 생긴다.
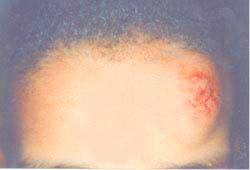
▴ 사진 433. 소아 신체 학대로 생긴 두피좌상.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
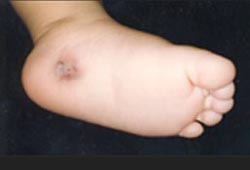
▴ 사진 434. 담뱃불로 지져 생긴 열화상도 소아 신체 학대에 속한다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
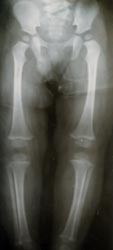
▴ 사진 437. 소아 신체 학대를 진단하기 위해 하지와 상지 이외 전신의 뼈(골) X선 사진 검사를 할 때도 있다. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
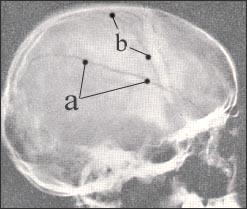
▴ 사진 438. 소아 신체 학대로 생긴 심한 두개골 골절
a-두개골 골절, b-두개골 봉합
참조문헌:Textbook of surgery, Christopher, 3rd ed.
- 체중 및, 또는 신장이 5 퍼센타일이거나 그 이하일 때가 더 많다.
다음과 같은 증상 징후가 있을 때 소아 신체 학대나 소아 무관심 학대를 의심할 수 있다.
-
위아래 입술의 소대의 외상,
-
확실히 이유를 밝힐 수 없는 치아 외상이나 입안의 외상,
-
양쪽 눈언저리에 생긴 멍, 눈의 망막 출혈 등
-
피부 멍, 특히 멍든 피부색이 여러 종류일 때, 대퇴부나 복부,
-
위팔의 연조직에 생긴 부상이나 화상,
-
사람에게 물린 이빨자국,
-
타박상, 매질 자국, 열상, 상흔, 혈종, 출혈 반점, 외상성 두피 탈모증, 손톱자국이나 손자국, 질식 시도로 목에 생긴 자국 등
-
담즙이 섞인 구토 물, 재발성 구토, 재발성 설사, 만성 복통, 복강 내 장기파열, 구토나 설사 등을 한다고 엄마가 호소하지만 엄마 이외 사람은 그 아이가 구토나 설사를 하는 것을 목격할 수 없을 때
-
두개골 골절, 경막하 출혈, 두개 강 내 뇌압 상승, 혼수, 경련, 무호흡 등
-
골막 하 출혈, 각종 골절 등
-
만성 회음부 통증, 외음부 통증, 항문 통증, 외음부 부상, 항문 부상 등
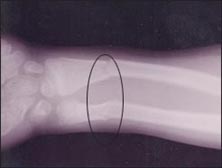
▴ 사진 435. 소아 신체 학대로 생긴 척골 골절과 요골의 골절.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
▴ 사진 436. 소아 신체 학대로 생긴 절상.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
소아 신체 학대로 생긴 부상이 신체의 어느 부위에 있는지 부상의 종류에 따라 설명하면
소아 신체 학대로 생긴 화상
-
소아 신체 학대로 생긴 부상의 10%는 담뱃불, 전기 곤로, 끓는 물, 뜨건 목욕탕 물 등으로 손발, 얼굴, 발목, 손목, 엉덩이 등에 입은 열화상이나 열탕화상.
-
소아 신체 학대로 입은 화상의 신체 부위나 모양, 정도, 깊이 등이 안전사고로 입은 화상의 것에 비해 차이가 많이 나고 이상하다.
소아 신체 체벌의 예후
- 소아기 중 체벌(스팽킹 체벌도 포함)을 받고 성장한 성인들에게 불안, 습관성 약물 남용, 정신 장애와 성격 이상 등 문제발생률이 높다. 소스; Contemporary pediatrics :소스; July 12, 201
출처 및 참조문헌
- Moritz AR. Henriques FC: Studies of thermal injury: Pathology and pathogenesis of cutaneous burns experimental study. Am I Pathol 23:915-941, 1947
- 그외
표 53. 1도 화상이나 2도 화상을 입을 수 있는 물의 온도와 화상을 입을 때까지의 노출 시간
| 물의 온도 |
1~2도 화상을 입을 때까지의 노출시간 | |
| 섭씨 | 화씨 | |
| 52도 | 125.6도 | 70초 |
| 54도 | 129.2도 | 30초 |
| 56도 | 132.8도 | 14초 |
| 58도 | 136.4도 | 6초 |
| 60도 | 140도 | 3초 |
| 62도 | 143.6 도 |
1.6초 |
| 64도 | 147.2도 | 1초 |
소아 신체 학대로 두개골과 뇌에 생긴 상처소아의 두개골과 뇌에 생긴 외상의 70~75%는 소아 신체 학대로 생기고
-
2세 이전 영유아에게 생긴 두개골과 뇌의 외상의 95%는 소아 신체 학대로 생긴다고 한다.
-
소아 신체 학대로 생긴 두개골 골절은 소아 신체 학대로 생긴 영유아들의 모든 골절 중 두 번째로 흔한 것이다.
-
3세 이전 영유아들에게 생긴 두개 강 내 부상의 95%는 소아 신체 학대로 인한 것이다.
-
경막하 출혈, 무호흡증, 두개 강 내 뇌압 상승, 혼수, 경련 등이 소아 신체 학대로 인해 생긴 두부 외상으로 생길 수 있고 그로 인해 사망 할 수 있다.
-
소아 신체 학대로 두개 강 내 심한 뇌 손상이 생길 수 있고 두피 좌상, 두개골 골절 등이 동시 생길 수 있다.
-
소아를 심하게 흔들어서 생기는 흔들린 아이 증후군이 있을 수 있고, 소아의 머리를 매트리스 등에 강제로 부딪칠 때, 또는 소아를 던질 때 두개 강 내 뇌 손상이 심하게 생길 수 있으나 두피 좌상, 두개골 골절 등은 생기지 않을 수 있다.
-
두개 강 내 뇌 손상이 있을 때 눈 망막 출혈이 동시 생길 수 있다.
-
소아의 허리 부위를 손으로 잡고 소아의 몸 전체를 심하게 흔들거나 소아를 던져 소아 학대를 할 때 학대하기 위해 손으로 잡았던 흔적이 몸통에 생길 수 있다.
소아 신체 학대로 가슴에 생긴 부상
소아 신체 학대를 받은 소아들의 5~27%에게 늑골 골절이 발견되었고 소아 신체 학대로 늑골 골절을 입었던 소아들의 90%는 2세 이하의 영유아들이었다.
소아 신체 학대로 척추에 생긴 부상
소아 신체 학대로 척추 골절은 잘 생기지 않지만 일단 생기면 흉부 척추 골절과 요부 척추 골절이 더 잘 생긴다.
소아 신체 학대로 복강에 생긴 부상
혈종이 십이지장관 벽이나 그 외 소장관 벽, 또는 대장관 벽에 생길 수 있고 췌장 외상으로 췌장염이 생길 수 있고 간장 파열 비장 파열, 신장 파열 등 여러 종류의 복강 내 장기에 부상이 생길 수 있고, 위 천공도 생길 수 있다.
소아 신체 학대로 피부나 연조직에 생긴 부상
피부 층, 피하 조직, 근육 등 연조직에 좌상, 혈종, 열창, 자상이 신체의 학대로 생길 수 있고 최근에 생긴 신체 손상도 있고 오래 전에 생겼던 손상도 있고, 특히 각종의 좌상이 피부에 생길 수 있다.
표 54. 피부 좌상이 생긴 날부터 다 나아갈 때까지 좌상 피부색
| 좌상 입은 후 일 수 | 좌상을 입은 피부색 |
| 1~2일 | 적색이나 청색 |
| 3~5일 | 청자색 |
| 6~7일 | 록색 |
| 8~10 | 황갈색 |
| 13~21일 원래 | 원래 피부색으로 회복되는 기간 |
출처; Wilson EF: Estimation of the age of cutaneous contusions in child abuse. Pediatrics 60:750-752, 1977
그외
소아 신체 학대로 골격에 생긴 부상
-
소아 신체 학대를 받은 소아들의 36%에게 골절이 발견되고 골절의 83%는 뼈 X선 검사에 나타난다.
-
금방 생긴 골절, 오래 전에 생겼던 골절, 한 개의 뼈 골절, 여러 종류의 뼈 골절, 나아가는 골절, 골막 하에 새 뼈가 형성되고 있는 골절, 골간 골절, 골단 골절, 손발 뼈의 골절, 사지 뼈
표 55. 소아 뼈 X선 검사에 나타난 골절이 나아가는 상태와 기간
|
뼈 X-선 검사에 나타난 |
뼈 X-선 검사에 나타난 |
|
골절 부위 연조직의 부종이 없어지는 기간 |
4~10일 |
|
골막하에 새 뼈가 형성되는 기간 |
10~14일 |
|
골절선이 없어지는 기간 |
14~20일 |
|
연가골 형성이 시작하는 기간 |
14~20일 |
|
경가골 형성이 시작하는 기간 |
20~40일 |
|
골절 흔적이 완전히 없어지고 새뼈가 형성되는 기간 |
평균 1년 |
출처;Alter O’Connor. JF and Cohen, J.: Dating Fractures in Kleinman. P K. Ed D. Agnostic Imaging of Child Abuse. Baltimore, Williams & Wilkens, 1987
그외
소아 신체 학대의 진단
-
병력, 증상 징후, 진찰소견 등을 종합하고 소아 신체 학대가 의심되면 두개골, 등뼈, 사지 뼈, 가슴 늑골 외 신체의 거의 모든 뼈 X선 검사를 하고 필요에 따라 1차 뼈 X선 검사를 한 후 2주에 2차 뼈 X선 검사를 해야 한다.
-
필요에 따라 뼈 스캔 검사, 뼈 MRI 검사, 초음파 검사와 임상검사 등으로 진단한다.
-
사회 복지사, 간호사, 소아 신체 학대 관계당국으로 받은 보고를 종합해 진단할 때도 많다.
소아 신체 학대의 감별진단
-
비타민 C 결핍증,
-
매독,
-
안전사고로 인한 부상,
-
출혈성 질환 등으로 인한 상처 등과 감별 진단하기 위해 적절한 임상검사를 필요에 따라 한다.
소아 신체 학대의 치료와 대처
-
미국에서는, 소아청소년(0~18세)이 소아 신체 학대를 받았다고 의심되거나 확실한 진단이 나오면 법에 따라 소아 학대 관계당국에 바로 전화로 구두 보고하고 난 후 따라잡기 서류 보고를 해야 한다.
-
소아 학대 관계 당국에 밤낮 24시간 어느 때든지 보고할 수 있다.
-
응급실이나 클리닉 또는 그 외 진료소에서 소아 환아를 보는 의사, 간호사, 또는 사회복지사 등은 소아가 신체 학대를 받은 것 같으면 소아 학대 관계당국에 즉시 보고해야 하고 소아 학대 관계당국의 허락 없이 소아 학대를 받은 소아를 그의 가정으로 보낼 수 없는 때가 많다.
-
소아 신체 학대를 받은 소아들의 20% 정도는 살고 있던 자기 가정으로 되돌려 보내지 않고 양부모의 집이나 다른 적절한 가정에서 임시 안전하게 보호받으면서 살도록 조치할 때도 있고 필요에 따라 병원에 입원 치료하면서 퇴원 후 장기간 추적 치료를 하는 경우도 있다
-
소아 신체 학대를 하게 된 동기가 무엇이었든 부모는 죄책감에 사로잡히는 것이 보통이다.
-
부모를 동정적으로 대해주고 그들이 필요로 하는 감정 정서적 지지, 경제 원조, 직업 소게 등 삶의 모든 국면과 의식주를 국가적인 차원에서 보살피고 도와주어야 한다.
-
간호사, 임상 심리사, 정신과 전문의, 소아청소년과 전문의, 사회 복지사, 소아 학대 관계당국 요원으로 구성된 소아학대 해결 팀이 소아 신체 학대 응급 문제를 우선 해결해 주면서 아이의 안녕 문제를 장기적으로 해결해 주고 부모와 소아 학대를 받은 소아 자녀가 가능한 빠른 시일 내에 재결합 하도록 도와준다.
-
소아청소년들은 나라의 희망이요 국가의 자산이라는 것을 명심하고 소아(0~18세) 학대를 해결해주고 예방하기 위한 소아 청소년 보호기관을 두면 좋을 것이다.
소아 신체 학대의 예방
-
소아청소년(0~18세) 자녀를 조건 없이 진심으로 사랑하고 보살필 줄을 모르는 부모,
-
특히 미혼모,
-
초보 부모,
-
사춘기 부모,
-
원하지 않은 임신으로 태어난 자녀를 가진 부모,
-
자녀를 학대한 적이 있었던 부모,
-
자녀의 안녕과 행복에 관심이 없는 부모,
-
알코올에 중독된 부모,
-
약물 남용을 하는 부모,
-
정신병이 있는 부모,
-
신생아나 영유아를 부정적으로 대하는 부모,
-
눈길 접촉 사랑이나 신체적 접촉 사랑을 하지 않는 부모,
-
미숙 신생아나
-
지체 장애아의 부모,
-
영아를 과도 스팽킹하는 부모,
-
아기의 청결과 건강관리에 무관심한 부모들은
-
소아청소년 자녀를 학대할 가능성이 더 많다.
-
의사, 간호사, 사회 복지사, 소아 학대 관계당국 요원으로 구성된 소아 학대 해결 팀은 소아 신체 학대를 할 가능성이 더 있는 처지에 있는 부모가 소아 학대를 하지 않게 예방하는데 힘쓴다. 소아 학대 예방은 범국가적 차원에서 이루어 져야한다.
소아 신체 학대의 예후
-
소아 신체 학대를 받은 소아이나 소아 무관심 학대를 받은 소아들의 80~90%는 이상 열거한 의사, 간호사, 사회 복지사 등 전문가의 도움을 적절히 받으면 정상적으로 성장 발육할 수 있는 것이 보통이다.
-
도움을 적절히 받지 않고 학대를 했던 부모나 보호자과 함께 같은 가정에서 계속 살면 그들의 25%는 소아 신체 학대를 계속 받게 되고 5%는 소아 신체 학대로 살해되기도 한다.
-
[부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다–소아가정간호백과]-제22권 아들 딸 이렇게 키우세요–조건 없는 자녀 사랑, 눈길 접촉 사랑, 신체적 접촉 사랑, 집중적 관심적 사랑, 나를 사랑하시나요,
-
그릇된 사랑 – 소유적 사랑, 대리적 사랑, 유혹적 사랑, 역할 전도적 사랑 참조
Child abuse and child neglect
소아 학대와 소아 무관심(아동 학대와 아동 무관심/어린이 학대와 어린이 무시 방치/아동 학대와 아동 무시)
- Child abuse and child neglect (child abuse and child neglect/child abuse and child neglect/child abuse and child neglect)
Overview of Child Abuse (Child Neglect)
- Today, children and adolescents (ages 0-18) in various parts of the world are physically abused, sexually abused, emotionally abused, drug abused, neglect abuse (ignored abuse) from their parents, guardians, or other authorities or being abused by inappropriate corporal punishment.
- Collectively, this type of abuse by children and adolescents (ages 0-18) is called pediatric abuse or child abuse.
- “A child refers to a person whose mind and body are not fully adolescent, usually young children aged 3 to 12” (Source-Korean Ambassadorial Exhibition by Dr. Hee-Seung Lee).
- The pediatric abuse covered here describes the abuse that occurs in children and adolescents, ie, children aged 0-18.
Children’s age group is 3-12 years old, so it is more appropriate to use
the term pediatric abuse or pediatric abuse (1-18 years old), which falls
within the ages of 0-18, instead of child abuse.
- Some children who have been abused in children may suffer serious damage to their physical, emotional, and social growth and development.
- Even pediatric abuse kills lives.
- There is also an example of being treated as a child’s physical abuse as a corporal punishment given by parents as a way of raising their children to correct their children’s wrongdoing.
- There is an example in which an adult stood in court saying that a neighbor’s child was cute and hugged him and then abused the child.
- Parents are not sure what “child abuse” is, and it is an important responsibility and duty of parents to protect children and adolescents from loving physical abuse, sexual abuse, or indifferent abuse.
- Most of the contents of pediatric abuse covered here are data obtained from US pediatric abuse research data and the author’s 40 years of clinical experience in pediatric treatment.
- Pediatric abuse and pediatric apathy in American society may differ from the reality of pediatric abuse and pediatric neglect outside the United States.
- No matter where you live in the world, whether you are a parent or not with a child or adolescent, you need to know a lot of information about child abuse.
- We hope that this will help us to better understand the pediatric physical abuse, pediatric sexual abuse, and delayed growth and development caused by pediatric neglect abuse, and help prevent and appropriately deal with pediatric abuse.
According to the status of child abuse in the first half of 2015 by the Korean central child protection agency, between January and June 2015, 5,432 cases were determined as child abuse, of which 12 children died. Two people died a month. Source: Hankook Ilbo in the Americas, September 30, 2015.
. Definition of Child Abuse (Child neglect)
- I have already explained the above, but if I explain it again here. Child abuse is also referred to as pediatric abuse or child abuse.
- Child abuse is defined differently depending on the country, religion, race, or individual.
- The Department of Pediatrics and Adolescents defines pediatric abuse as follows. Children (children in the 0-18 years old) or juveniles (0-18 years old) are physically or emotionally damaged by their parents, guardians, caregivers, or other persons, delayed growth, or sexual harassment
- To be treated, sexual intercourse or rape are collectively referred to as child abuse or child abuse.
- Pediatric physical abuse is the act of injuring a child’s body and creating a risk to the child’s health and well-being.
- Things necessary for maintaining basic human life-clothes, houses, food, love, sleep, care, etc. are not properly provided, education is not properly provided, or health management and health promotion are not adequately provided or neglected to prevent children’s health and health.
- Behaviors that endanger well-being are called pediatric neglected abuse (child neglect abuse or child neglect abuse).
- According to US state law, Child abuse was defined as the act of not fulfilling its obligations to care, support and protect, thereby creating a sufficient risk to the physical, mental, and emotional health and well-being of children.
- Treat children cruelly
- Excessive punishment
- Physically confined to limit the child’s behavior beyond normal, or Impair mental and physical growth or development, or Are not properly educated, or Treat them unfairly,
- Improperly trained or Does not properly treat the disease, or Neglect of disease prevention also belongs to child abuse.
Classification of pediatric abuse (child abuse)
- Child physical abuse,
- Pediatric sex abuse,
- It is also classified as “non-substrate delay in growth and development” caused by child indifference abuse.
- Shaken Infant Syndrome (Shaken Child Syndrome), which causes physical damage by deliberately violently shaking the infant’s body,
- Child drug abuse, which feeds children and adolescents with unnecessary drugs,
- Child emotional abuse that damages the child’s mind, emotions, and emotions so that the child does not develop socially and emotionally,
- It can be classified as pediatric abuse such as Münhausen syndrome by an agent.
- Child physical abuse
- Pediatric sex abuse- Child sexual harassment Sexual abuse, Pediatric sexual abuse
- Child Rape Sexual Abuse
- Childhood emotional abuse
- Non-tempered growth and developmental delay abuse caused by
- Indifference (children’s indifference abuse/children neglect abuse/children neglect abuse)
- Shaky Child Syndrome Abuse (Shaken Infant Syndrome), which causes damage to the body by violently shaking the body
- Child drug abuse Münhausen syndrome caused by an agent etc Sources and references Vol. 1 Child and Adolescent Emergency Medical References and Sources-14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, others
Table 22. Percentage of child abuse by mother’s juvenile child when mother lives with a violent or non-violent partner Psychological Abuse% Indifferent Abuse% Physical Abuse% Sexual Abuse%
표 22. 엄마가 폭력적 파트너나 비폭력적 파트너와 살 때 그 엄마의 소아청소년 자녀가 소아 학대를 당한 %
| 심리적 학대 받는 % Psychological abuse% | 무관심적 학대 받는 %
Indifferent abuse% |
신체적 학대 받는 %
Physical abuse% |
성적 학대 받는 %
Sexual abuse% |
|
| 폭력적 파트너 Violent Partner | 44.0 % | 20.5% | 19.0% | 0.3% |
| 비폭력적 파트너
Nonviolent Partner |
8.0 % | 8.0% | 8.0% | – |
Results of a survey of 1,232 mothers and mothers’ partners who live with their mothers
Sources and references- Elsevier Global Medical News and Dr. Zolotor and etc
- The next mothers and fathers are more likely to be physically abused in children. Lonely Parents Parents who get angry easily even under a little stress
- Parents who are easily angry with their children’s minor misconduct Unemployed parents
- Parents who live with many family members
- Parents with economic and social problems
- Poor parents
- Profession soldier parents abusing their spouse
- Parents addicted to alcohol or drugs
- Parents who were raised after being physically abused as children
- Parents in a broken marriage
- Extremely tired parents
- Parents under extreme stress Parents with mental illness
- Parents who display anger inappropriately
- Parents who truly love and care for their children unconditionally, especially single mothers, novice parents, teenage parents,
- Parents who abused their children
- Parents who are not interested in the well-being and happiness of their children Parents treating newborns negatively
- Parents who don’t love eye contact or physical contact
- Parents of premature infants or children with physical disabilities
- Parents spanking infants
- Parents who are indifferent to their child’s hygiene concept
- Parents of families who are abusing domestic violence, sibling violence, or marital abuse
- etc
Children with the following conditions are more likely to be physically abused
- Children premie
- A child with a physical disability
- Children who are difficult to raise according to their natural temperament A crying child A child who pee
- Negative children
- Poor children
Part of the body where injuries are most often found in children’s physical abuse
- Group 1-hips, face, arms, lower legs, back,
- Group 2- Head, eyes, and chest.
- Abdomen, hands and wrists, neck,
- Group 3-shoulders, ears, feet, vulva, nose, mouth, skull,
- Group 4-skull, brain, anus, teeth, bladder, and so on.
- Group 1 is the most common area Group 4 is the least common area
The epidemiology of physical abuse in children
- Physical abuse of children is called physical abuse of children, abuse of children, or abuse of children and adolescents.
- Here, the term “children” refers to children or children within the age range of 0-18. According to a study, 2-3% (1.4 million) of pediatric and adolescents (ages 0-18) (children) in the U.S. receive annual pediatric physical abuse and pediatric indifference abuse,
- Annually, 160,000 children are injured due to physical abuse of children, which could endanger the lives of children.
- 1,000 to 2,000 children and adolescents died from physical abuse of children, Among them,
- 80% were infants under the age of 5, and 40% were infants before the age of 1.
- In 1994, about 1 million children in the US 48 weeks were abused in pediatric physical abuse and pediatric indifference,
- 52% of them are child indifference abuse,
- 26% are physically abused in childhood,
- 14% are pediatric abuse,
- 5% were pediatric emotional abuse,
- 3% were pediatric negligence with poor health care,
- In the same year, 1111 children died from child abuse in the US 43 weeks.
- Physical abuse in children has occurred in 1,200 children in a million people in the United States.
- Physical, emotional, sexual, and indifference abuse occurred to 3 million American children a year. Among them, 25% were children’s physical abuse. Source-Reported by the US Child Protection Agency. 10% of American children who received emergency treatment for physical abuse in children were infants under the age of 5,
- Children who were physically abused were under the age of 1, ⅓1 to 6 years old, and ⅓6 years or older.
- Among the children who received physical abuse in children, 95% received it from the child’s birth mother, father, relatives caring for the children, and friends of the lone mother, 4% received it by others, and 1% received it by siblings.
- Parents with mental illness, such as alcoholic parents, drug-addicted parents, and depression, have a two to three times higher rate of physical abuse in children than those who do not.
- The incidence of physical abuse in children is almost the same regardless of the parents’ race, country, religion, ethnicity, occupation, education, culture, economy, and society.
- It is said that 90% of parents who abused children had no experience of criminal activity and had no mental illness.
People who have a legal obligation to report to pediatric protection authorities when they suspect or are certain that they have suffered pediatric abuse (child abuse) include (in the United States):
- Clinical Psychologist,
- Social Worker,
- Doctor,
- Doctor Assistant,
- Nurse,
- Dentist,
- Lawyer,
- Podiatry,
- Language correction expert,
- Employees and caretakers working in children’s homes or day care centers,
- Coroner,
- Osteopath,
- Optometrist,
- Chiropractor,
- Pastor,
- Priest,
- Dental hygienist,
- Chemist,
- Police officer,
- Principal,
- School teachers where possible,
- Such as school counselors.
Mental and physical damage due to safety accidents and child abuse
- People who think that “if prevention is done well, all accidents may not occur” neglect to prevent safety accidents, so that even if physical damage occurs to children or emotional damage occurs to children, they are said to have abused children.
- This is because it is recognized that the mental and physical damage caused by safety accidents is caused by parental indifference. However, some argue that the mental and physical damage inflicted by safety accidents is not child abuse.
Spanking corporal punishment and pediatric abuse
- Studies have shown that 75% of pediatric and adolescent physicians claim that inflicting traumatic spanking corporal punishment is considered inappropriate spanking corporal punishment, but is not considered child physical abuse.
- The remaining 25% of pediatric and adolescent doctors argued that if parents used spanking corporal punishment for raising their children, but if they inflicted spanking corporal punishment enough to inflict bruises, that type of spanking corporal punishment is also a child’s physical abuse and should be reported to the child protection authorities.
Corporal punishment and child abuse
In elementary and junior high schools and at home, children are subjected to
corporal punishment for the purpose of education, guidance, training, and parenting.
- Corporal punishment has been known as one of the common methods of training children from east to west.
- According to research, 60% of elementary and middle school teachers in the United States inflict corporal punishment to students at least once a year, US 1,146 pairs of parents
- 73% of them inflicted physical and mental violence for the purpose of raising and training infants, school-age children and adolescent children in the 3-17-year-old,
- 58% gave spanking corporal punishment,
- 13% hit with objects,
- 5% threw things,
- 3% kicked, bitten, and punched,
- 1% reported that they had beaten their children at least once in the past year. Replied.
- Many Americans believe that it is okay to inflict appropriate corporal punishment when raising and training children.
- The American Academy of Pediatrics and Adolescents said that physical punishment in which the hands or hips of infants or school-age children after the age of 1 are swiped once or twice with the open palm of an infant or school-age child after the age of 1 for child-rearing and training is a spanking corporal punishment necessary for child rearing training and against physical abuse in children.
- Iit is defined as pediatric bodily abuse if a mother and father strikes any part of the child’s body with some kind of device other than the open palm.
- It is defined that hitting the child’s face or head when giving corporal punishment to a child is not regarded as corporal punishment for child-rearing or training, but as a child’s physical abuse.
- A child’s babysitter or caregiver for a child imposes corporal punishment on the child to correct the child’s wrongdoing for any reason.
- In case of physical damage,
- When a child’s hand or hip is hit with a palm or other part of the body, Any physical damage other than red skin spots on the hip or hand that was punished with the open palm is treated as a child’s physical abuse.
- Infants before 12 months of age are subjected to physical punishment by any means, which constitutes physical abuse of children.
- Inflicting corporal punishment on any part of the body with any kind of device other than the palm of the hand is also a child’s physical abuse.
- Pushing, contacting, colliding, wounded, contact with heat or corrosive chemicals, or Unnecessary drug feeding is also a child’s physical abuse.
Symptoms, signs of physical abuse in children
- Sometimes parents or guardians who have abused children bring their children to hospital emergency rooms or pediatrics departments, acknowledging that they have voluntarily abused children.
- In most cases, when children are brought to the hospital due to injuries caused by physical abuse of children, there is a lot of contradiction in the medical history of the cause of the injury, the degree of the injury, the time of wearing it, the path of the injury, the method and location, etc.
- There are many times when there is no uniformity in military history.
- When children have injuries, when it is not possible to clearly explain the reason for the injuries, it is common to suspect that the injuries are caused by physical abuse of children.
- Most of the injuries caused by physical abuse in children are often inconsistent with the age and development of adolescents.
- When injuries are caused by physical abuse in children, there is a tendency to receive treatment late without receiving treatment soon after the injury.
- Children’s behavioral, emotional interpersonal problems, such as aggressive personality, interpersonal problems, depression, affection problems, drug abuse, alcohol addiction, etc., are common in children who have been raised after being physically abused.

▴ Photo 433. Scalp strain caused by physical abuse of a child. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

▴ Photo 434. A thermal burn caused by a cigarette light also belongs to child physical abuse. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

▴ Picture 437. In some cases, an X-ray examination of bones of the whole body other than the lower extremities and upper extremities is sometimes performed to diagnose pediatric physical abuse. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

▴ Photo 438. Severe skull fracture caused by physical abuse in children a-cranial fracture, b-cranial suture. Reference: Textbook of surgery, Christopher, 3rd ed. More often, the weight and height are 5 percent or less.
Child physical abuse or pediatric neglect abuse can be suspected when the following symptomatic signs and symptoms are present:
- The trauma of the upper and lower lips,
- Tooth trauma or mouth trauma that cannot be clearly stated,
- Bruises on the edges of both eyes, retinal bleeding in the eyes, etc.
- Skin bruises, especially when there are multiple types of bruised skin, such as in the thigh or abdomen,
- Injuries or burns to the soft tissues of the upper arm,
- Human bite marks, bruises, streaks, lacerations, scars, hematomas, bleeding spots, traumatic scalp alopecia, nail marks or hand marks, marks on the neck due to choking attempts, etc.
- Vomiting water mixed with bile, recurrent vomiting, recurrent diarrhea, chronic abdominal pain, organ rupture in the abdominal cavity, vomiting or diarrhea, etc.
- Skull fracture, subdural hemorrhage, increased brain pressure in the cranial cavity, coma, convulsions, apnea, etc.
- Subperiosteal bleeding, various fractures, etc. Chronic perineal pain, vulva pain, anal pain, vulva injury, anal injury, etc.

▴ Picture 435. A fracture of the ulna and a fracture of the radius caused by physical abuse in children. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

▴ Photo 436. The laceration is caused by physical abuse of children. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
If you describe where in the body the injury caused by the child’s physical abuse is located, depending on the type of injury,
- Burns from physical abuse in children10% of injuries caused by physical abuse in children are thermal burns or hot bath burns in the hands and feet, face, ankles, wrists, buttocks, etc., caused by cigarette fire, electric stove, boiling water, hot bath water, etc.
- The body part, shape, degree, and depth of burns caused by child physical abuse are significantly different and strange than those of burns caused by safety accidents.
The prognosis of corporal punishment in children
- Adults who have grown up after receiving corporal punishment (including spanking corporal punishment) during childhood have a high incidence of problems such as anxiety, habitual substance abuse, mental disorders and personality abnormalities. Sauce; Contemporary pediatrics: source; July 12, 201
- Sources and references Moritz AR. Henriques FC: Studies of thermal injury: Pathology and pathogenesis of cutaneous burns experimental study. Am I Pathol 23:915-941, 1947, etc
Table 53. The temperature of the water can cause 1 degree or 2-degree burns and exposure time until burns
표 53. 1도 화상이나 2도 화상을 입을 수 있는 물의 온도와 화상을 입을 때까지의 노출 시간
| 물의 온도 Water temperature |
1~2도 화상을 입을 때까지의 노출시간
1-2 degrees Exposure time until burns |
|
| 섭씨 Celsius | 화씨Fahrenheit | |
| 52 degrees | 125.6 degrees | 70 seconds |
| 54 degrees | 129.2 degrees | 30 seconds |
| 56 degrees | 132.8 degrees | 14 seconds |
| 58 degrees | 136.4 degrees | 6sseconds |
| 60 degrees | 140 degrees | 3 seconds |
| 62 degrees | 143.6 degrees | 1.6 seconds |
| 64degrees | 147.2degrees | 1 second |
Injuries to the skull and brain due to physical abuse
- In children, 70-75% of trauma to the skull and brain in children is caused by physical abuse in children.
- It is said that 95% of trauma to the skull and brain inflicted on infants before 2 years of age is caused by physical abuse in children.
- Skull fractures resulting from pediatric physical abuse are the second most common of all fractures in infants and young children resulting from pediatric physical abuse.
- 95% of intracranial injuries to infants and toddlers before the age of 3 are due to the physical abuse of children.
- Subdural hemorrhage, apnea, increased brain pressure in the cranial cavity, coma, and convulsions can be caused by head trauma caused by physical abuse of children and may result in death.
- Children’s physical abuse can lead to severe brain damage in the cranial cavity, scalp contusion, and skull fractures at the same time.
- There may be a shaking child syndrome caused by violently shaking a child, and when forcibly bumping the child’s head into a mattress, etc., or when throwing a child, the brain damage in the cranial cavity may be severe, but a scalp contusion or a skull fracture may not occur. have.
- Ocular retinal bleeding can occur simultaneously when there is an intracranial brain injury.
- When pediatric abuse is carried out by holding the child’s waist with his hand and shaking the child’s entire body violently or by throwing the child, traces that were held by the hand for abuse may appear on the torso.
Injuries to the chest due to physical abuse in children
- Rib fractures were found in 5 to 27% of children who suffered physical abuse in children, and 90% of children who suffered a rib fracture as a result of physical abuse in children were infants under the age of 2 years.
Injuries to the spine from physical abuse in children
- Fractures of the vertebrae are less common due to physical abuse in children, but once they do, fractures of the thoracic and lumbar vertebrae are more common.
Injury to the abdominal cavity due to physical abuse in children
- Hematoma may form on the wall of the duodenal duct or another intestinal tract, or on the wall of the colon, pancreatic trauma may lead to pancreatitis, liver rupture, spleen rupture, kidney rupture, and other injuries to various types of abdominal organs.
- Perforation can also occur.
Injuries to the skin or soft tissues resulting from physical abuse in children
- Strain, hematoma, fissure, and cuts in soft tissues such as the skin layer, subcutaneous tissue, and muscles can be caused by abuse of the body, there are recent physical damage, and some damage that occurred long ago, especially various strains can occur on the skin.
Table 54. The color of the upper left skin from the day of the occurrence of the skin seat until it is all gone
표 54. 피부 좌상이 생긴 날부터 다 나아갈 때까지 좌상 피부색
| 좌상 입은 후 일 수
The number of days after the wound was worn. |
좌상을 입은 피부색
Skin color after the wound was worn |
| 1~2 days | 적색이나 청색
Red or blue |
| 3~5 days | 청자색
Blue purple |
| 6~7 days | 록색
Green |
| 8~10 days | 황갈색 Yellow-brown |
| 13~21 days | 원래 피부색으로 회복되는 기간
Period to recover to original skin color |
출처; Wilson EF: Estimation of the age of cutaneous contusions in child abuse. Pediatrics 60:750-752, 1977
Injuries to the skeleton due to physical abuse in children
- Fractures are found in 36% of children who have undergone physical abuse in children, and 83% of fractures appear on bone X-ray examination.
- Fractures that occurred immediately, fractures that occurred a long time ago, fractures of one bone, fractures of various types of bones, advanced fractures, fractures with new bones forming under the periosteum, interosseous fractures, epiphyseal fractures, fractures of the bones of the hands and feet, limb bones
Table 55. The condition and duration of the fracture indicated in the pediatric bone x-ray examination 표 55. 소아 뼈 X선 검사에 나타난 골절이 나아가는 상태와 기간
|
뼈 X-선 검사에 나타난 Bone x-ray The duration of the pediatric fracture |
뼈 X-선 검사에 나타난 The period in which the swelling of the soft tissue at the fracture site disappears |
|
골절 부위 연조직의 부종이 없어지는 기간 The period in which the swelling of the soft tissue at the fracture site disappears |
4~10 days |
|
골막하에 새 뼈가 형성되는 기간 The period during which new bones form under the periosteum |
10~14days |
|
골절선이 없어지는 기간 The period during which the fracture line disappears |
14~20 days |
|
연가골 형성이 시작하는 기간 The period when cartilage formation begins |
14~20 days |
|
경가골 형성이 시작하는 기간 The period when tibial bone formation begins |
20~40 days |
|
골절 흔적이 완전히 없어지고 새뼈가 형성되는 기간 The period during which the fracture marks disappear completely and new bones are formed. |
평균 1년
Average 1 year |
Source; Alter O’Connor. JF and Cohen, J.: Dating Fractures in Kleinman. P K. Ed D. Agnostic Imaging of Child Abuse. Baltimore, Williams & Wilkens, 1987 etc
Diagnosis of physical abuse in children
- Comprehensive medical history, symptoms, medical findings, etc., and if a child’s physical abuse is suspected, almost all bones of the body other than the skull, spine, limb bones, and chest ribs are x-rayed and, if necessary, after a primary bone x-ray examination.
- A second bone x-ray examination should be performed weekly. If necessary, the diagnosis is made through a bone scan test, a bone MRI test, an ultrasonic test and a clinical test. In many cases, reports received from social workers, nurses, and authorities related to the physical abuse of children are synthesized and diagnosed.
Differential diagnosis of physical abuse in children
- Vitamin C deficiency syndrome,
- Syphilis,
- Injuries due to safety accidents,
- Appropriate clinical tests are performed as needed to differentially diagnose wounds caused by bleeding diseases, etc.
Treatment and coping of physical abuse in children
- In the United States, if a child or adolescent (ages 0-18) is suspected of being physically abused or a positive diagnosis is made, according to the law, the law requires an oral report to the child abuse authorities directly, followed by a catch-up document report.
- Reports may be made to the child abuse authorities at any time, 24 hours a day, 7 days a week.
- Doctors, nurses, or social workers who see children in emergency rooms, clinics, or other clinics must immediately report to the child abuse authorities if the child appears to have been physically abused, and children who have been abused without permission from the child abuse authorities.
- There are many times when it is not possible to send them to his home. About 20% of children who have been physically abused in children do not return to their own home where they lived, but take measures to live in a temporary and safe place in a foster parent’s home or another appropriate home. If necessary, hospitalization and long-term follow-up treatment are provided after discharge.
- In some cases regardless of what motivated them to commit physical abuse in children, it is common for parents to feel guilty.
- It is important to treat parents compassionately and take care of and help all aspects of life and food, clothing, and shelters, such as emotional and emotional support, economic aid, and job hunting that they need at a national level.
- A pediatric abuse resolution team composed of nurses, clinical psychologists, psychiatrists, pediatricians and adolescents specialists, social workers, and pediatric abuse-related authorities first solves the child’s physical abuse emergency problem and solves the child’s well-being problem in the long term,
Helps a child abused child reunite as soon as possible. - Keeping in mind that children and adolescents are the country’s hopes and assets of the country, it would be good to have a child and adolescent protection institution to resolve and prevent child abuse (ages 0-18).
Prevention of physical abuse in children
- Children and adolescents (0-18 years old):
- Parents who sincerely love and care for their children without conditions,
- Especially single mothers,
- Novice parents,
- Adolescent parents,
- Parents with children born of unwanted pregnancy,
- Parents who have ever abused their children,
- Parents who are not interested in the well-being and happiness of their children, parents who are addicted to alcohol,
- Parents of substance abuse,
- Mentally ill parents, Parents who treat newborns or infants negatively, Parents who do not love eye contact or physical contact, Immature newborn baby Parents of children with physical disabilities, Parents who overspan their infants,
- Parents who are indifferent to baby’s cleanliness and health care They are more likely to abuse children and adolescents.
- The pediatric abuse resolution team, composed of doctors, nurses, social workers, and pediatric abuse officials, strives to prevent pediatric abuse from parents who are more likely to engage in physical abuse of children. Prevention of child abuse should be carried out at the national level.
The prognosis of physical abuse in children
- It is common for 80-90% of children who have undergone physical abuse in children or children who have been abused by child indifference to normal growth and development with appropriate help from experts such as doctors, nurses and social workers listed above.
- If they continue to live in the same family with the abused parent or guardian without adequate assistance, 25% of them will continue to receive physical abuse in children, and 5% will be killed for physical abuse in children.
- [Parents should also be at least the half-doctors-Children and Family Nursing Encyclopedia]-Vol. 22 Raise your sons and daughters like this-Unconditional love for children, love for eye contact, love for physical contact, intensive love, love with interest, do you love me, Wrong Love-Refer to Possession Love, Proxy Love, Temptation Love, Role Evangelistic Love
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
소아 학대(아동 학대 ) 출처 및 참조문헌
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처-9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 그외
-
Pediatric News, July 2007
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, Harvey grant and Robert Murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care 응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과-부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원 저
-
The pregnancy Bible. By Joan stone, MD. Keith Eddleman, MD
-
Preparation for Birth. Berverly Savage and Dianna Smith
-
임신에서 신생아 돌보기까지. 이상원
-
Breastfeeding. by Ruth Lawrence and Robert Lawrence
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 18th edition
-
Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
-
Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th-21st Edition
-
Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
-
Growth and Development of Children, George H. Lowrey 8th edition
-
소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”