세균뇨 Bacteriuria

사진 1-22. 소변에 세균이 나오는지 멀티스틱스 소변 화학검사로 알아볼 수 있다. 그리고 소변 침전물을 현미경으로 검사하여, 세균이 소변에 있는지, 세균의 종류가 무엇인지 알아볼 수 있다. 소변 침전물은 그람 염색 현미경 검사를 해서 그 세균이 그람 음성균인지 그람 양성균인지 더 자세한 세균검사를 할 수 있다.
Copyrightⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee,MD., FAAP
세균뇨의 정의
-
남녀노소 누구든지 자연적으로 본 소변 속에 박테리아가 조금 들어 있는 것이 보통이다.
-
그러나 소변에 세균(박테리아)이 다음과 같이 정상 이상으로 많이 있는 소변을 세균뇨라고 한다.
-
외생식기를 청결하게 처치한 후 받은 소변 1ml(1cc)로 혈액 우무 세균 배양지에 세균배양을 했을 때 거기에 자란 세균 집락(Bacterial colony) 수가 100,000(십만)개 이상 일 때
-
치골 결합 상부 방광 소변 흡인술(치골 상부 방광 주사 천자)로 얻은 소변(Suprapubic aspiration urine) 1ml(1cc)로 혈액 우무 세균 배양지에 세균 배양 검사를 했을 때 세균 집락 수가 100,000개 이상 배양될 때
-
반복 채취 소변으로 혈액 우무 세균 배양지에 세균배양을 같은 방법으로 검사할 때 같은 종류의 세균 집락 수가 100,000개 이상 배양될 때 소변에 세균이 정상 이상으로 많이 나올 수 있다.
-
요로 감염이 있을 때 소변에 세균이 정상 이상으로 많아 나올 수 있다.
-
소변 세균 검사용 피검물을 받기 위해 소아청소년의 소변을 받는 데 상당한 시간과 기술이 필요하다. 특히 영유아의 소변 세균 검사용 피검물 소변을 받는 데는 더 그렇다.
다음과 같은 경우, 소변에 세균이 정상 이상 더 발견될 수 있다.
- 영유아의 소변을 받을 때 소변 속에 대변이 눈곱만큼 소량 들어갈 때 대변에 있던 세균이 소변으로 들어 갈 수 있다.
- 소변을 받는 중 남·여아의 외생식기, 특히 여아의 외생식기와 그 주위의 피부의 상존 세균이 소변으로 오염되어 요로에서는 나오지 않은 세균이 소변에 들어 있을 수 있다.
- 소변을 받을 수 있는 영아 소변 주머니나 용기가 불결할 때
- 외생식기를 적절히 씻지 않고 처치하지 않고 소변을 받을 때
- 받은 소변을 한두 시간 이상 실내 온도에 방치할 때
- 받은 소변을 불결한 손으로 만질 때
- 요로 감염병이 있을 때
- 그 외
-
이런저런 이유로 영유아들이나 학령기 아이들, 사춘기 아이들의 소변에서 세균이 정상 이상으로 더 많이 발견될 수 있다.
-
이런 이유로 소변 세균 배양 검사를 할 때 검사용 소변을 받는 데 상당히 주의해야 한다.
-
때로는 살균 요도 세관을 요도관 속을 통해 방광 속에 넣고 방광 속 소변을 직접 채취해 소변 세균 배양 검사를 하며,
-
때로는 주사바늘로 하 복벽을 통해 방광 속 소변을 뽑아, 즉 치골 결합 상부 방광 소변 흡인술로 채취한 소변으로 소변 세균 배양 검사를 하기도 한다.
-
요로 감염이 있을 때에는, 소변 세균 배양 검사 결과가 비정상으로 나타나는 것이 보통이고 멀티스틱스 소변 화학 검사에서 백혈구·적혈구·세균 등이 비정상적으로 많이 나오는 검사 결과가 나타나는 것이 보통이다.
-
요로 감염이 있을 때, 멀티스틱스 소변 화학 검사, 소변 세균 배양 검사 결과의 대부분은 비정상으로 나타난다.
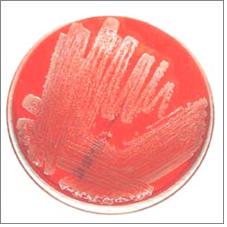
사진 1-23.혈액 우무 세균 배양 배지에 자란 소변 세균 집락.
어떤 종류의 세균이 소변에 있는지 알아보기 위해 적절하게 받은 피검물을 소변으로 그람 염색 현미경 검사를 한다.
Copyrightⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee,MD., FAAP
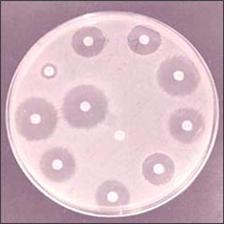
사진 1-24. 항생제 세균 감수성 검사를 한다.
어떤 종류의 세균이 소변에 있는지 알아본다. 그리고 그 세균이 어떤 종류의 항생제 치료에 가장 잘 죽을 수 있는지 알아보는 항생제 세균 감수성 검사를 할 수 있다.
Copyrightⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee,MD., FAAP
-
소아청소년의 경우, 세균 배양 검사를 통해서 요로 감염이 어떤 세균 감염에 의해 생겼는지 진단하는 때가 많다.
-
연구에 의하면, 항생제로 치료받기 전, 맨 처음 실시한 소변 세균 배양 검사의 결과가 비정상일 때 요로 감염에 걸려 있는 확률은 60%이고,
-
첫 번째와 두 번째 둘 다 소변 세균 배양 검사의 결과가 비정상일 때 요로 감염에 걸려 있는 확률은 90%이며,
-
첫 번째, 두 번째, 세 번째 소변 세균 배양 검사의 결과가 모두 비정상일 때 요로 감염에 걸려 있는 확률은 98%이다.
-
이 연구의 결과에서, 한번 실시한 소변 세균 배양 검사의 결과로 요로 감염이 있다고 확실히 진단할 수 없다는 결론이 나온다.
-
소변 세균 배양 검사에서 한 종류의 세균 집락이 100,000(십만)개 이상 나오면, 요로 감염이 있을 확률이 아주 높다.
-
여러 종류의 세균 집락이 소변 세균 배양 검사에서 배양될 때도 있다. 세균 배양 검사용 피검물, 즉 소변을 받을 때 외생식기나 항문 주위에 있는 여러 종류의 세균이 피검물용 소변 속으로 오염되어 소변 세균 배양 검사에서 여러 종류의 세균이 배양됐다고 평가하는 경우가 많다.
-
대부분의 경우, 여러 종류의 세균 집락이 소변 세균 배양 검사에서 배양될 때에는 요로 감염을 일으킨 세균 집락이 자란 것이 아니라고 판단할 때가 많다.
-
이 경우, 때로는 잡균이 자랐다는 말도 쓴다.
-
이런저런 이유로, 영유아들의 소변 세균 배양 검사의 결과로만 요로 감염을 확진할 수 없는 때도 있다.
요로 감염을 진단할 때 다음과 같은 세균 검사 결과 나오면
-
요로 감염의 증상 징후가 있고
-
멀티스틱스 소변 화학 검사 결과가 비정상으로 나타나고,
-
소변 세균 배양 검사에서 100,000개 이상의 같은 세균 집락이 배양되고,
-
세균 집락이 같은 종류이면,
-
요로 감염이 있다고 거의 확실히 진단할 수 있다.
요로 감염을 진단할 때 쓰는 영상 검사
-
정맥 내 신우 촬영술(IVP),
-
배뇨성 방광 요도 조영술(Voiding cystourethrogram/VCUG) 검사,
-
신장 요관 방광 초음파 검사,
-
DMSA(Dimercaptosuccinic acid) 신장 스캔 검사 등으로 신장·요관·방광·요도 등에 선천성 기형이나 후천성 이상이 있는지, 요로 감염 등으로 인해 신장·요관 등에 어떤 종류의 손상이 있는지, 손상이 있다면 어느 정도인지 알아보는 것이 보통이다.요로 감염 참조.
Bacteriuria 세균뇨

Photo 1-22. You can check for bacteria in your urine with a multistick urine chemistry test. And by examining the urine sediment under a microscope, you can see if the bacteria are in the urine and what kind of bacteria are. Urine sediment can be examined under a Gram staining microscope to determine if the bacteria are Gram-negative or Gram-positive. Copyrightⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
Definition of bacteriuria
• It is common for people of all ages to have some bacteria in their natural urine. • However, urine with more than normal bacteria (bacteria) in the urine is called bacteriuria. • When bacteria are cultured in a blood mud bacterial culture medium with 1 ml (1 cc) of urine received after cleanly treating the exogenous organ, when the number of bacterial colonies grown there is more than 100,000 (100,000).
• When a bacterial culture test is performed on a blood-dried bacterium culture medium with 1 ml (1 cc) of suprapubic aspiration urine obtained by aspiration of the suprapubic aspiration urine (superpubic bladder injection puncture), when the number of bacterial colonies is cultured over 100,000
• Repeated collection of blood with urine When bacterial cultures are tested in the same way on a bacterial culture medium, when the number of colonies of the same type is more than 100,000, more than normal bacteria may appear in the urine.
• When you have a urinary tract infection, there may be more bacteria in your urine than normal.
• A considerable amount of time and skill is required to receive urine from children and adolescents in order to receive a specimen for urine bacterial testing. This is especially true for receiving urine from a specimen for testing urine bacteria of infants and young children.
In the following cases, more bacteria than normal may be found in the urine.
1. When receiving urine from infants and young children, bacteria in the stool can enter the urine when feces enter the urine as small as the eye drop.
2. While receiving urine, the ectogenital organs of boys and girls, especially the exogenital organs of girls, and bacteria of the skin around them, are contaminated with urine, and bacteria that did not come out of the urinary tract may be contained in the urine.
3. When an infant urine bag or container that can receive urine is dirty
4. When urinating without proper washing or treatment of exogenous organs
5. When the received urine is left at room temperature for more than one or two hours
6. When you touch the urine received with dirty hands
7. When you have a urinary tract infection
8. Others
• For one reason or another, more bacteria than normal can be found in the urine of infants, school-age children, and adolescent children.
• For this reason, you should be very careful in receiving your urine for testing when doing a urine bacterial culture test.
• Sometimes, sterile urethral tubules are put into the bladder through the urethral tube, and urine from the bladder is directly collected and tested for culture of urine bacteria.
• Sometimes, urine is drawn from the bladder through the lower abdominal wall with a needle, ie, urine obtained by aspiration of the upper bladder in the pubic joint is used for a urine bacterial culture test.
• When there is a urinary tract infection, the urine bacterial culture test results are usually abnormal, and the multistick urine chemistry test usually shows abnormally large amounts of white blood cells, red blood cells, and bacteria.
• When you have a urinary tract infection, most of the results of the Multistick urine chemistry test and urine bacterial culture are abnormal.

Picture 1-23: A colony of urine bacteria grown on a culture medium of blood mucus bacteria. In order to find out what kind of bacteria are in the urine, an appropriately received specimen is subjected to a Gram stain microscopic examination with urine. Copyrightⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Photo 1-24. Antibiotic bacterial susceptibility tests are performed. Find out what kinds of bacteria are in your urine. You can also do an antibiotic bacteriological susceptibility test to see which type of antibiotic treatment is most likely to kill the bacterium. Copyrightⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
• In children and adolescents, bacterial culture tests are often used to diagnose which bacterial infection is caused by a urinary tract infection.
• Studies have shown that there is a 60% chance of getting a urinary tract infection when the first urine bacterial culture test done before receiving antibiotics is abnormal.
• There is a 90% chance of having a urinary tract infection when the results of the urine bacterial culture test are abnormal in both the first and the second,
• If the results of the first, second, and third urine bacterial culture tests are all abnormal, the probability of having a urinary tract infection is 98%.
• From the results of this study, it is concluded that the result of a single urine bacterial culture test cannot be reliably diagnosed with a urinary tract infection.
• If your urine bacterial culture test shows more than 100,000 (100,000) colonies of one type of bacteria, you are very likely to have a urinary tract infection.
• Several bacterial colonies are sometimes cultured in a urine bacterial culture test. When receiving urine for a bacterial culture test, that is, when receiving urine, various types of bacteria around the exogenital organ or anus are contaminated into the urine for the test object, and the urine bacterial culture test often evaluates that various types of bacteria have been cultured.
• In most cases, when several bacterial colonies are cultured in a urine bacterial culture test, it is often judged that the bacterial colony that caused the urinary tract infection did not grow.
• In this case, sometimes it is said that various germs have grown.
• For one reason or another, sometimes a urinary tract infection cannot be confirmed only as a result of a urine bacterial culture test in infants and young children.
When diagnosing a urinary tract infection, if the following bacterial test results come out:
• There are signs of symptoms of a urinary tract infection
• Multistick urine chemistry test results are abnormal,
• In the urine bacterial culture test, more than 100,000 colonies of the same bacteria are cultured,
• If the bacterial colonies are of the same type,
• You can almost certainly diagnose a urinary tract infection.
Imaging tests used to diagnose urinary tract infections
• intravenous pyelography (IVP),
• Voiding cystourethrogram (VCUG) examination,
• kidney ureter bladder ultrasound,
• Find out if there are congenital malformations or acquired abnormalities in the kidneys, ureters, bladder, urethra, etc. through a DMSA (Dimercaptosuccinic acid) kidney scan, and what kind of damage to the kidneys, ureters, etc. is caused by a urinary tract infection, and how much if there is damage. It is common to see, see Urinary Tract Infection.
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제10권. 소아청소년 신장 비뇨 생식기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제7권 소아청소년 감염병
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th — 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
-
Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, Harvey grant, and Robert Murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
-
The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
-
Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care
-
응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
-
Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
-
Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
-
Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
-
소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”