선천성 횡격막 헤르니아(선천성 횡격막 탈장) Congenital diaphragmatic hernia of newborn infants
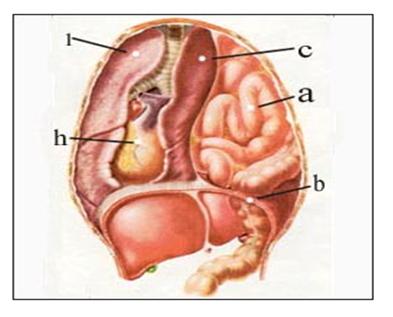
그림 36. 선천적으로 왼쪽 횡격막이 없이 태어 났기 때문에 복강 내 위와 장관의 일부가 왼쪽 흉곽 강 속으로 탈장되어 있다. 그와 동시 왼쪽 폐가 쪼그라들고 무기폐가 되고 심장이 왼쪽 흉강 속에서 오른쪽 흉강 속으로 밀려갔다.
a-소관장,
b-결손된 횡격막.
c-쪼그라든 좌 무기폐, h-심장,
i-우 폐. 출처- Ross Lab, Columbus. Ohio. USA와 소아가정간호 백과
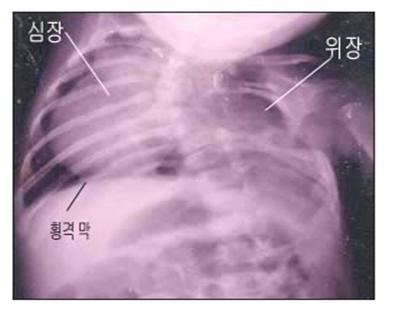
사진 37. 선천적 왼쪽 횡격막 헤르니아를 진단하기 위해 촬영한 가슴과 복부 X선 사진. 선천적으로 왼쪽 횡격막이 없기 때문에 복강 내 위와 소장의 일부가 왼쪽 흉강 속으로 탈장되어 있다. 그와 동시 왼쪽 폐가 쪼그라들고 무기폐가 되고 심장이 오른쪽 흉강 속으로 밀려갔다.
출처- Used with permission from Ross Lab, Columbus. Ohio. USA 와 소아가정간호백과
| 선천성 횡격막 헤르니아(선천성 횡격막 탈장)의 원인 |
- 원인은 확실히 모른다.
- 늑막과 복막의 형성 이상으로 횡격막이 선천적으로 없어 복강 내 장기의 일부가 흉강 내로 이탈되는 일종의 탈장을 선천성 횡격막 헤르니아 또는 선천성 횡격막 탈장이라고 한다.
- 선천성 횡격막 헤르니아는 좌측 횡격막이나 우측 횡격막, 또는 양쪽 횡격막에 생길 수 있다. 왼쪽에 더 자주 생긴다.
- 오른쪽 횡격막에 헤르니아가 생기면 간의 일부가 오른쪽 흉강 내로 이탈될 수 있다.
- 왼쪽 횡격막에 헤르니아가 생기면 위, 비장, 소장의 일부, 또는 왼쪽 간엽 등이 왼쪽 흉강 내로 이탈 될 수 있다.
- 선천성 횡격막 헤르니아로 인해 흉강 내 심장의 위치에 변화가 생기고 횡격막 일부의 결손 부위를 통해 흉강 내로 이탈되고 전위된 소장 등으로 폐가 눌릴 수 있다.
- 선천성 횡격막 헤르니아는 다른 종류의 선천성 기형과 함께 생겨 있는 경우가 많다.
- 약 3000~4000명의 신생들 중 1명이 이 병을 가지고 태어난다.
- 사망률이 30~50%정도 된다(출처; Consultant for pediatricians, October 2008 p.77).
- 선천성 횡격막 헤르니아만 있는 경우도 있지만(60%), 동맥관 개존, 선천성 소장 기형, 선천성 심장 기형, 부속 비장 등 선천성 기형을 함께 가지고 태어 날 수 있다.
| 선천성 횡격막 헤르니아(선천성 횡격막 탈장)의 증상 징후 |
- 선천성 횡격막 헤르니아만 생겼느냐, 왼쪽에만 생겼느냐, 오른쪽에만 생겼느냐 또는 좌우 양쪽 횡격막에 다 생겼느냐에 따라 증상 징후가 다르다.
- 갓 태어난 신생아가 제대로 숨을 쉴 수 없고
- 호흡곤란이 심하게 생기고
- 복벽이 움푹 쑥 들어가 함몰되고
- 신생아의 피부가 창백하고 전신 청색증이 생기고
- 숨이 넘어갈 듯이 숨을 쉬는 것이 보통이다.
| 선천성 횡격막 헤르니아(선천성 횡격막 탈장)의 진단 |
- 증상 징후 진찰소견 등을 종합하고 이 병이 의심되면 가슴과 복부 X선 사진 검사로 진단한다.
| 선천성 횡격막 헤르니아(선천성 횡격막 탈장)의 치료 |
- 선천성 횡격막 헤르니아를 외과적 수술로 응급치료 한다.
- 수술치료를 받은 후 신생아는 대개 신생아 집중 치료실에서 장기간 입원 치료를 계속 받는 것이 보통이다.
- 선천성 횡격막 헤르니아를 수술로 치료받은 이후 호흡부전증, 위식도 역류, 성장 지연, 신경 발육지연, 행동장애, 청력 상실, 허니아 재현, 정형외과 질환 등이 생길 수 있다(Pediatrics March 2008).
- 그런 공존이환을 필요에 따라 여러 종류의 전문과의 전문의들에 의해서 치료 한다.
Congenital diaphragmatic hernia of newborn infants 선천성 횡격막 헤르니아(선천성 횡격막 탈장)

Fig. 36. Because the birth was born without a left diaphragm, the stomach and intestines in the abdominal cavity are partially hernias into the left thoracic cavity. At the same time, the left lung collapsed and became atelectasis, and the heart was pushed from the left chest cavity into the right chest cavity. a-director, b-defective diaphragm. c-shrink left atelectasis, h-heart, i-right lung. Source- Ross Lab, Columbus. Ohio. USA and the Encyclopedia of Child and Family Nursing

Picture 37. X-ray of the chest and abdomen taken to diagnose congenital left diaphragmatic hernia. Because there is no left diaphragm by nature, the stomach and small intestine in the abdominal cavity are hernias into the left chest cavity. At the same time, the left lung contracted and became atelectasis, and the heart was pushed into the right chest cavity. Source-Used with permission from Ross Lab, Columbus. Ohio. USA and Child and Family Nursing Encyclopedia
Causes of congenital diaphragmatic hernia (congenital diaphragmatic hernia)
• The cause is not clear.
• A type of hernia in which the diaphragm is congenital due to abnormal formation of the pleura and peritoneum, and part of the organs in the abdominal cavity deviates into the chest cavity. This is called congenital diaphragmatic hernia or congenital diaphragmatic hernia.
• Congenital diaphragmatic hernia can develop in the left or right diaphragm, or both. It occurs more often on the left side. • When hernia develops in the right diaphragm, a portion of the liver can dislodge into the right chest cavity. • When a hernia develops in the left diaphragm, the stomach, spleen, part of the small intestine, or the left mesenchymal can be dislodged into the left chest cavity. • Congenital diaphragmatic hernia causes a change in the position of the heart in the chest cavity, and the lungs may be pressed by the displaced small intestine and dislocated into the chest cavity through a defect in part of the diaphragm.
• Congenital diaphragmatic hernia is often associated with other types of congenital anomalies.
About 1 in 3000 to 4000 newborns are born with this disease.
• The mortality rate is around 30-50% (source; Consultant for pediatricians, October 2008 p.77).
• Although there are only congenital diaphragmatic hernias (60%), they can be born with congenital anomalies such as open arterial ducts, congenital small bowel anomalies, congenital heart anomalies, and an appendage spleen.
Symptoms signs of congenital diaphragmatic hernia (congenital diaphragmatic hernia)
• Symptoms differ depending on whether only congenital diaphragmatic hernia occurs, only on the left side, only on the right side, or both sides of the diaphragm. • Newborn babies cannot breathe properly • Severe breathing difficulties occur
• The abdominal wall is pitted and depressed • The newborn’s skin is pale, systemic cyanosis develops,
• It is common to breathe out of breath.

Picture 159: Sternal retraction With severe pneumonia, the sternum can be depressed each time you breathe. The gastrointestinal tract in the abdominal cavity is hernias into the chest cavity and the abdomen is depressed. Source: Used with permission from Ross Laboratories, Columbus, Ohio 43216, Division of Laboratories, USA and Pediatric Family Nursing Encyclopedia. Diagnosis of congenital diaphragmatic hernia (congenital diaphragmatic hernia)
• Comprehensive symptoms, signs, examination findings, etc. If this disease is suspected, it is diagnosed with chest and abdominal X-rays. Treatment of congenital diaphragmatic hernia (congenital diaphragmatic hernia)
• Congenital diaphragmatic hernia is treated as an emergency surgical procedure. • After receiving surgical treatment, newborns usually continue to receive long-term hospitalization in the neonatal intensive care unit.
• After receiving congenital diaphragmatic hernia surgery, respiratory failure, gastroesophageal reflux, growth retardation, neurodevelopment, behavioral disorders, hearing loss, honeycomb regeneration, orthopedic diseases may occur (Pediatrics March 2008).
• Such coexistence is treated by specialists in different types of specialists as needed.
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제9권 소아청소년 소화기 질환
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th — 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
-
Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, Harvey grant, and Robert Murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
-
The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
-
Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care
-
응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
-
Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
-
Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
-
Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
-
소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”