선천성 식도폐쇄와 기관식도 누관(선천성 식도 폐쇄증/기관식도 루) Congenital esophageal atresia and tracheoesophageal fistula
| 선천성 식도폐쇄와 기관식도 누관(선천성 식도 폐쇄증/기관식도 루)의 개요 및 원인 |
- 식도는 인두의 맨 밑 부분에서 시작해 식도의 맨 하단 부분이 위(胃)에 연결되는 소화관의 일부분이다.
- 선천적으로 식도의 일부나, 또는 전부가 막힐 수 있다. 이런 선천성 기형을 선천성 식도 폐쇄라 한다.
- 식도의 일부가 완전히 막힌 선천성 식도 폐쇄를 가지고 갓 태어난 신생아가 모유나 인공영양을 처음 한 목음을 먹을 때 먹은 모유 등이 식도관 속을 통과해서 위 속으로 전혀 내려갈 수 없다.
- 맨 처음 먹은 모유나 인공영양을 자연적으로 구토하게 된다.
- 식도 폐쇄의 형은 여러 종류가 있다(그림 38 참조).
- 식도의 일부분이 완전히 또는 불완전하게 막힌 선천성 식도 폐쇄도 있고 막힌 식도의 부분의 바로 위에 있는 식도 부분과 기관 사이를 연결하는 통로(누관/루/Fistula)가 있는 식도 폐쇄 기형도 있다.
- 폐쇄된 식도 부분의 바로 위에 있는 식도 부분과 기관 사이를 연결하는 통로를 기관 식도 누관(루), 또는 기관 식도 루 또는 기관 식도 샛길이라고 한다. 기관 식도 샛길이란 말은 최신 의학용어집에서 얻은 정보이다.
선천성 식도폐쇄와 기관식도 누관(선천성 식도 폐쇄증/기관식도 루)의 증상 징후
- 선천성 식도 폐쇄의 형과 정도에 따라 증상 징후가 많이 다르다.
- 갓 태어난 신생아의 식도의 일부분이 선천성 식도 폐쇄로 완전히 막히면 갓 태어난 신생아가 삼킨 침, 양수, 모유, 인공영양 등이 막힌 식도 부분까지만 내려갔다가 위(胃)가 있는 쪽으로 더 이상 내려가지 못하므로 역류해서 바로 토하는 것이 보통이다.
- 침이나 점액이 정상 이상으로 많이 입 안과 인두 강 속에 괼 수 있다.
- 맨 처음 먹인 젖이나 인공영양, 또는 물 등이 막힌 식도 부분을 통과해서 위 속으로 전혀 들어갈 수 없기 때문에 모유나 인공영양 등을 한두 번 빨아먹은 후에 바로 금방 토한다. [부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다-소아가정간호백과]-제4권 모유, 모유수유, 이유-모유수유 시작, 제5권 인공영양, 이유식, 비타민, 미네랄, 지방, 단백질 참조.
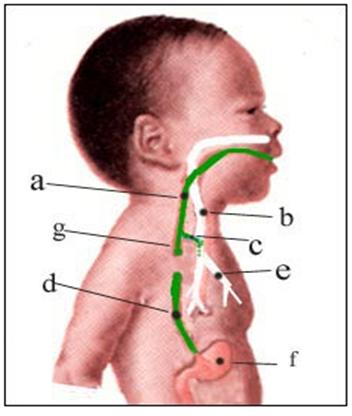
그림 38. 선천성 식도 폐쇄와 식도와 기관 사이에 생긴 누관(루) 식도의 중간 부분이 폐쇄되고 폐쇄된 식도의 상단 부분은 기관 속에, 하단 부분은 위 속에 연결됐다.
a-식도, b-기관, c-식도와 기관 사이에 생긴 누관(루), d-폐쇄 된 식도의 하부는 위에 연결됐다. e-기관지, f- 위, g-폐쇄된 식도의 상단 부분. 출처; Ross Lab columbus Ohio와 소아가정간호백과
- 식도와 기관 사이에 생긴 기관 식도 누관(루)이 있는 식도 폐쇄를 가지고 있는 신생아가 먹은 젖이나 인공영양 등이 식도→누관(루)→기관 속→기관지 속을 통과해서→ 폐 속으로 흡인해서 들어갈 수 있다. 이 때 흡인성 폐렴이 생길 수 있다.
- 이런 기형을 가진 신생아가 젖이나 인공영양을 먹은 바로 후 재채기, 기침, 호흡곤란, 질식 등의 증상 징후가 생길 수 있다.
- 식도관 속과 기관 속 사이에 누관(루)도 생길 수 있고, 식도관 속의 일부분이 불완전하게 조금 막히고 위 속으로 연결된 식도관 폐쇄가 있을 때는 먹은 젖이나 인공영양 등이 불완전하게 막힌 식도 폐쇄 부분을 통과해서 위 속으로 내려갈 수 있고, 또 다른 일부의 음식물이 식도관 속과 기관 속 사이에 있는 누관(루)을 통과해서 폐 속으로 들어갈 수 있다.
선천성 식도폐쇄와 기관식도 누관(선천성 식도 폐쇄증/기관식도 루)의 진단
- 병력 증상 징후 진찰소견 등을 종합해서 이 병이 의심되면 흉부와 복부의 X선 사진검사, 흉부와 복부의 초음파 검사, 바륨 식도 X선 사진 검사, 기관 내시경, 식도와 위 내시경검사 등으로 진단할 수 있다.
선천성 식도폐쇄와 기관식도 누관(선천성 식도 폐쇄증/기관식도 루)의 치료
- 식도 폐쇄의 정도와 형에 따라 치료가 다르다.
- 이 병이 의심되면 확실한 진단을 할 때까지 경구로 아무 음식물도 먹이지 말아야 한다.
- 확실히 진단 치료를 하기 위해 신생아 집중 치료실에 곧 입원해야 한다.
- 진단을 한 후 적절한 시기에 선별적 수술 치료를 한다.
- 기형의 형에 따라 예후가 다르다.
- 심한 식도 폐쇄를 가지고 있는 아이들도 수술 치료를 받고 정상적으로 잘 성장 발육하는 예도 봤다.
Congenital esophageal atresia and tracheoesophageal fistula 선천성 식도폐쇄와 기관식도 누관(선천성 식도 폐쇄증/기관식도 루)
Overview and causes of congenital esophageal obstruction and tracheoesophageal fistula (congenital esophageal atresia/tracheoesophageal fistula)
• The esophagus is the part of the digestive tract that starts at the bottom of the pharynx and connects the bottom of the esophagus to the stomach.
• Some or all of the esophagus may be blocked by birth. This congenital malformation is called congenital esophageal obstruction.
• A newborn baby with congenital esophageal obstruction in which a part of the esophagus is completely blocked. When a newborn baby eats breast milk or artificial nutrients for the first time, the breast milk that has been eaten cannot pass through the esophagus and go down into the stomach at all.
• You will naturally vomit from the first breast milk or artificial nutrients you eat.
• There are several types of esophageal obstruction (see Figure 38).
• Some congenital esophageal obstruction, in which a portion of the esophagus is completely or incompletely blocked, and some esophageal obstruction anomalies with a passage (fistula/fistula/fistula) that connects the trachea and the part of the esophagus just above the obstructed portion of the esophagus.
• The passage that connects the trachea and the part of the esophagus that is directly above the obstructed part of the esophagus is called the tracheal esophageal fistula (fistula), or the tracheal esophageal fistula, or tracheo-esophageal by way.
The term tracheal esophageal path is information obtained from the latest medical glossary.
Symptoms, Signes of congenital esophageal obstruction and tracheoesophageal fistula (congenital esophageal atresia/tracheoesophageal fistula)
• Symptoms vary greatly depending on the type and severity of congenital esophageal obstruction.
• When a part of the esophagus of a newborn baby is completely blocked by congenital esophageal obstruction, reflux because saliva, amniotic fluid, breast milk, artificial nutrition, etc. swallowed by the newborn baby only go down to the blocked esophagus and can no longer descend to the stomach. It is common to vomit right away.
• More than normal saliva or mucus may get in the mouth and in the pharyngeal cavity.
• The first milk or artificial nutrition, or water, etc. can pass through the blocked esophagus and enter the stomach at all, so immediately after sucking on breast milk or artificial nutrition once or twice, vomit immediately. [Parents should also be anti-doctors-Encyclopedia of Pediatric Family Nursing]-Volume 4 Breast Milk, Breastfeeding, Reasons-Start Breastfeeding, Volume 5 Artificial Nutrition, Baby Food, Vitamins, Minerals, Fat, Protein.

Figure 38. Congenital esophageal obstruction and fistula (ru) between the esophagus and trachea
The middle part of the esophagus was closed and the upper part of the closed esophagus was connected to the trachea, and the lower part was connected to the stomach. a-esophageal, b-trachea, c-fistula (fistula) between the esophagus and trachea, d-closed lower part of the esophagus connected to the stomach. e-bronchi, f-gastric, g-closed upper part of the esophagus. source; Ross Lab columbus Ohio and Pediatric Home Nursing Encyclopedia
• A newborn baby with an esophageal fistula (fistula) formed between the esophagus and trachea (fistula) is fed milk or artificial nutrition from the esophagus → fistula (loo) → trachea → trachea → through the bronchi → aspirated into the lungs I can enter. This can lead to aspiration pneumonia.
• Newborns with these malformations may develop symptoms such as sneezing, coughing, shortness of breath, and suffocation immediately after feeding breast milk or artificial nutrition.
• A fistula (fistula) may also form between the inside of the esophagus and trachea, and when a part of the esophageal duct is partially blocked and there is an obstruction of the esophageal duct connected to the stomach, the part of the esophageal obstruction in which the breast fed or artificial nutrition is incompletely blocked.
It can pass through and go down into the stomach, and another portion of the food can pass through the fistula (ru) between the esophagus and trachea and into the lungs.
Diagnosis of congenital esophageal obstruction and tracheoesophageal fistula (congenital esophageal atresia/tracheoesophageal fistula)
• If the disease is suspected by taking the medical history, symptoms, signs, examination findings, etc., it can be diagnosed with an X-ray picture of the chest and abdomen, an ultrasound of the chest and abdomen, an X-ray of the barium esophagus, a tracheoscopy, an esophagus and gastroscopy, etc.
Treatment of congenital esophageal obstruction and tracheoesophageal fistula (congenital esophageal atresia/tracheoesophageal fistula)
• Treatment varies depending on the type and severity of esophageal obstruction.
• If you suspect this disease, you should not take any food orally until you have a positive diagnosis.
• You will need to be admitted soon to the neonatal intensive care unit to ensure that diagnostic treatment is available.
• After diagnosis, selective surgical treatment is performed at an appropriate time.
• The prognosis is different depending on the type of malformation. • Children with severe esophageal obstruction have also undergone surgical treatment and have been seen growing and developing normally.
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제9권 소아청소년 소화기 질환
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th — 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
-
Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, Harvey grant, and Robert Murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
-
The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
-
Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care
-
응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
-
Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
-
Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
-
Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
-
소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”