선천성 담도 폐쇄로 생기는 신생아 황달(선천성 담도 폐쇄증), Neonatal jaundice due to bile duct obstruction
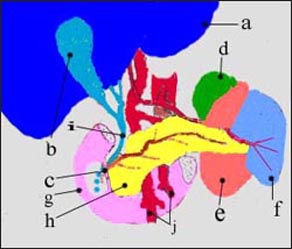
그림 2-367. 총수 담관(담도)이 선천성으로 막히면 신생아에게 황달이 생길 수 있다.
a-간, b-담낭, c-십이지장 유두(담즙과 췌장액이 분비되는 출구), d-부신, 선천성 담도 폐쇄증 e-좌 신장, f-지라, g-십이지장, h-췌장, i-총수 담관, j-혈관. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
- 담즙은 간장에서 분비된다.
- 그 담즙이 십이지장 속으로 흐르는 관을 담도라고 한다.
- 담도는 간에서 시작해서 십이지장관에 연결된다.
- 드물게 어떤 신생아의 담도가 선천성으로 완전히 막힐 수 있다.
- 이렇게 선천성으로 완전히 막힌 담도를 선천성 담도 폐쇄라고 한다.
- 담도가 완전히 막혔을 때는 간에서 만들어진 담즙이 십이지장 속으로 흘러 내려갈 수가 없다.
- 그리고 간에서 분비되는 담즙이 막힌 담도 부위까지만 흘러 내려갔다가 막힌 담도 부분 이하로 더 이상 내려갈 수가 없다.
- 그 대신 답즙이 역류돼서 간장 속으로 들어간다.
- 결국 그 담즙이 핏속으로 흡수된다. 핏속으로 흡수된 담즙으로 인해 황달이 생긴다.
- 그 담즙 속에는 직접형 빌리루빈이 들어있다. 이때 혈액에 직접형 빌리루빈 농도가 증가된다. 선천성 담도 폐쇄가 생기는 원인은 아직도 확실히 모른다([부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다-소아가정간호 백과]-제 5권 인공영양, 이유식, 비타민, 미네랄, 지방, 단백질-비타민 A 결핍증).
선천성 담도 폐쇄로 생기는 신생아 황달(선천성 담도 폐쇄증)의 증상 징후
- 막힌 담도의 부분, 막힌 정도, 담도가 막힌 후 경과된 기간 등에 따라 증상 징후가 다르다.
- 전형적인 선천성 담도 폐쇄증의 증상 징후는 다음과 같다.
- 보통 생후 처음 몇 주 동안은 아무 증상 징후가 없을 수 있다.
- 생후 3~8주 정도 지나면 눈 흰자위와 피부에 황달기가 현저하게 나타나기 시작하고 피부와 눈이 노랗고 간장이 붓고 커질 수 있다.
- 선천성 담도 폐쇄를 조기에 적절히 치료해주지 않고 오랫동안 방치하면 황달은 점점 더 심해진다.
- 이때 핏속에 직접형 빌리루빈과 간접형 빌리루빈의 농도가 비정상적으로 동시 증가된다.
- 그러나 담도폐쇄만 있을 때는 핏속의 간접형 빌리루빈의 농도가 20mg/dl 이상 증가되지 않는 것이 통예이다.
- 시간이 더 경과돼서 병이 계속 진행되면 소화장애, 혈액응고 장애, 성장 장애 등이 현저히 나타날 수 있다.
- 소변색이 노랗고 대변색이 백토색과 같이 회백색이 될 수 있다.
- 담도가 완전히 폐쇄됐을 때는 수술로 새 담도를 만들어 주는 치료를 하거나 간 이식 수술 치료를 받지 않으면 1년 이내에 사망하는 것이 보통이다.
선천성 담도 폐쇄로 생기는 신생아 황달(선천성 담도 폐쇄증)의 진단
- 병력, 증상 징후, 진찰소견 등을 종합해서 이 병이 의심되면 핏속에 있는 직접형 빌리루빈과 간접형 빌리루빈의 농도, 간 기능검사, 간과 담관의 초음파 검사, 간과 담관의 CT 스캔 검사 등으로 이 병을 확진할 수 있다.
- 담도 울트라 사운드 검사에 Triangular cord sign이 있으면 이 병을 진단하는 데 많은 도움이 된다고 한다.
선천성 담도 폐쇄로 생기는 신생아 황달(선천성 담도 폐쇄증)의 치료
- 증상 징후, 담도 폐쇄의 정도, 합병증의 유무 등에 따라 치료할 수 있다.
- 담도의 일부가 막혔는지, 전부가 막혔는지, 완전히 또는 불완전하게 막혔는지에 따라, 그리고 막히지 않고 정상적으로 남아 있는 담도의 길이가 얼마나 긴지에 따라, 간에서 나온 막히지 않은 담도를 십이지장관에 연결시키는 수술 치료를 한다.
- 이런 수술 치료를 할 수 없을 때는 다른 사람의 간을 이식해서 치료하기도 한다.
Neonatal jaundice due to bile duct obstruction 선천성 담도 폐쇄로 생기는 신생아 황달(선천성 담도 폐쇄증)

Figure 2-367. Congenital blockage of the common bile duct (biliary tract) can lead to jaundice in newborns. a-liver, b-gallbladder, c-duodenal papilla (exit where bile and pancreatic fluid are secreted), d-adrenal, congenital biliary atresia e-left kidney, f-spinal, g-duodenum, h-pancreas, i-common bile duct, j-vascular. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
• Bile is secreted from the liver.
• The tube through which the bile flows into the duodenum is called the biliary tract.
• The biliary tract starts in the liver and connects to the duodenum.
• Rarely, the biliary tract in some newborns can be congenital and completely blocked.
• Congenital biliary obstruction is called congenital biliary obstruction.
• When the biliary tract is completely blocked, bile produced by the liver cannot flow down into the duodenum. • And the bile secreted from the liver flows down only to the blocked biliary tract and cannot go further below the blocked biliary tract.
• Instead, the bile is refluxed and goes into the soy sauce.
• Eventually, the bile is absorbed into the blood. Jaundice occurs due to bile being absorbed into the blood.
• The bile contains direct bilirubin. At this time, the concentration of direct bilirubin in the blood increases. The cause of congenital biliary obstruction is still unknown ([Parents should also be at least the half-doctors-Encyclopedia of Pediatric Family Nursing]-Volume 5 artificial nutrition, baby food, vitamins, minerals, fat, protein-vitamin A deficiency). Symptoms of neonatal jaundice (congenital biliary atresia) caused by congenital biliary atresia
• Symptoms differ depending on the part of the biliary tract, the degree of blockage, and the length of time that has elapsed since the biliary tract is blocked.
Typical signs of congenital biliary atresia are:
• Usually during the first few weeks of life there may be no signs of symptoms.
• After 3 to 8 weeks of age, jaundice begins to appear remarkably on the whites of the eyes and on the skin, and the skin and eyes are yellow, and the liver may become swollen and enlarged.
• If the congenital biliary obstruction is left untreated for an extended period of time without early and adequate treatment, jaundice becomes more and more severe.
• At this time, the concentration of direct bilirubin and indirect bilirubin increases abnormally at the same time in the blood. • However, when there is only biliary obstruction, it is a common practice that the concentration of indirect bilirubin in the blood does not increase by more than 20mg/dl.
• As time passes and the disease continues to progress, digestive disorders, blood clotting disorders, and growth disorders may be noticeable.
• The color of urine may be yellow and the color of the stool may become grayish-white like white clay.
• When the biliary tract is completely obstructed, it is common to die within a year unless a new biliary tract is created by surgery or if a liver transplant is not treated. Diagnosis of neonatal jaundice (congenital biliary atresia) caused by congenital biliary obstruction
• If the disease is suspected by combining the medical history, symptoms, signs, examination findings, etc., the disease is diagnosed with the concentration of direct and indirect bilirubin in the blood, liver function test, ultrasound of the liver and bile ducts, CT scan of the liver and bile duct Can be confirmed.
• The presence of the Triangular cord sign on the biliary tract ultrasound test is said to be very helpful in diagnosing this disease. Treatment of neonatal jaundice caused by congenital biliary obstruction (congenital biliary atresia)
• It can be treated according to the symptoms of symptoms, the degree of biliary tract obstruction, and the presence or absence of complications.
• Surgery to connect an unblocked biliary tract from the liver to the duodenal canal, depending on whether part of the biliary tract is blocked, all, completely or incompletely blocked, and how long the biliary duct remains normally unblocked Treat it.
• When this type of surgical treatment is not possible, another person’s liver is transplanted to treat it.
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, Harvey grant, and Robert Murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care 응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원 저
-
The pregnancy Bible. By Joan stone, MD. Keith Eddleman, MD
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
-
임신에서 신생아 돌보기까지. 이상원
-
Breastfeeding. by Ruth Lawrence and Robert Lawrence
-
Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics 14th ed. Beherman,
-
The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 18th edition
-
Red book 29th edition 2012
-
Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th Edition
-
Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
-
소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”