선천성 고관절 탈구와 관절 이형성증 Congenital dislocation of hip and Hip dysplasia
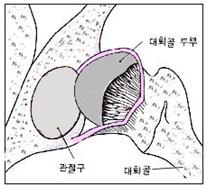
그림 121. 고관절 탈구
왼쪽 고관절 속에 있던 대퇴골 골두가 고관절 관절낭 속에서 빠져 탈구되었다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D.. FAAP
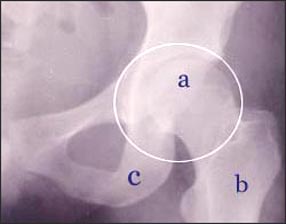
사진 122. ◯내 고관절
◯내에 있는 관절이 고관절이다.
a-대퇴골 두부, b-대퇴골 간, c-좌골
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D.. FAAP
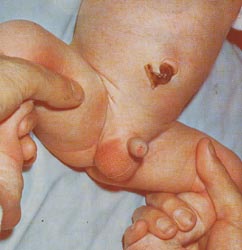
사진 123. 선천성 고관절 탈구가 있나 진찰한다.
출처:Reproduced with permission from Mead Jhonson Nutritional과 소아가정간호 백과
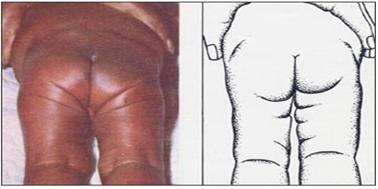
사진 125. 선천성 고관절 탈구가 있는 신생아나 영아의 양쪽 허벅다리의 피부 주름살의 수와 모양이 다를 수 있다. Reproduced with permission from courtsy of Mead Johnson Nutrional Divition
- 대퇴골 두부와 좌골에 있는 관절구가 서로 연결되는 관절을 고관절이라 한다(그림 A, B). 고관절은 한쪽 가랑이 속에 각각 하나씩 모두 두개가 있다.
- 가랑이 속에 있는 한쪽, 또는 양쪽의 고관절을 둘러싸고 있는 관절낭, 대퇴골 두부가 들어있는 관절구, 대퇴골 두부, 그 고관절을 구성하고 있는 근육이나 건, 인대들 중 하나, 둘, 또는 전부가 선천적으로 제대로 발육되지 않아 대퇴골 두부가 고관절 낭 속에서 일부 또는 전부 빠져 나와서 생기는 병을 선천성 고관절 탈구, 고관절 선천성 형성장애(Congenital dysplasia of the hip, or CDH), 또는 고관절 발육 형성장애(Developmental dysplasia of the hip, or DDH)라 한다.
- 형성장애란 말 대신 이형성증이란 말도 쓴다( 탈구, 선천성 고관절 탈구, 일과성 활막염 참조).
선천성 고관절 탈구의 원인
- 원인, 병태생리, 자연 경과, 진단, 치료 등에 관해 아직도 확실히 모르는 점이 많다.
- 고관절 탈구는 자연분만으로 태어난 신생아에게도 생길 수 있다.
- 특히 둔위 분만으로 태어날 때 입은 고관절 상처로 인해 고관절 탈구가 생길 수 있다.
- 이 병의 가족 병력이 있는 집안에게서 태어난 신생아에게 이 병이 있을 확률이 더 높다. 이 병은 첨내반족이나 고관절 이외 다른 뼈의 기형과 함께 생길 수도 있다.
- 자궁 내 태아의 자세(태위)나 모체의 호르몬의 영향을 받아 생긴다는 설도 있다.
- 어떤 고관절 발육 형성장애는 후천성 원인에 의해서도 생긴다.
선천성 고관절 탈구의 증상 징후
- 선천성 고관절 탈구는 1천 명의 신생아들 중 1명이 생긴다.
- 첫 번째 난 신생아,
- 양수 결핍증이 있었던 임신에서 태어난 신생아,
- 또는 둔위 분만으로 태어난 신생아에게 이 병이 더 잘 생긴다.
- 이 병이 있는 신생아나 영유아의 다리가 정상 같이 보일 수도 있고,
- 양쪽 다리의 길이와 모양이 서로 다를 수도 있다.
- 기저귀를 채우기 위해 탈구된 고관절에 있는 허벅다리를 몸통 바깥쪽으로 젖힐 때 고관절 탈구가 있는 쪽의 허벅다리가 정상 고관절이 있는 쪽의 허벅다리를 몸통 바깥쪽으로 벌릴 때보다 덜 젖혀질 수 있다.
- 탈구된 고관절을 손으로 만지면서 진찰을 할 때(사진 123 참조) 대퇴골 두부가 고관절낭 속으로 들어갔다 나왔다 하면서 소리가 날 수 있고,
- 또 탈구된 대퇴골 두부가 고관절낭 속에서 빠져 나오는 느낌을 검진자의 손에 감지될 수 있다. 모든 의사들이 이런 검진을 쉽게 할 수는 없다.
- 함부로 이런 검진을 하면 고관절 손상을 더 입힐 수 있다.
- 양쪽 허벅다리에 생긴 피부 주름살의 수나 모양이 서로 다를 수 있다.
- 그러나 양쪽 고관절이 정상일 때도 두 허벅다리의 피부 주름살이 똑같지 않을 수 있다.
- 선천성 고관절 탈구를 조기에 진단해서 적절히 치료해주지 않았을 때는 고관절 탈구가 있는 신생아가 자라서 영유아가 된 후 서고 걷기 시작할 때 고관절 탈구가 있는 쪽 다리를 저는 것이 보통이다.
- 그리고 그쪽 다리가 다른 쪽 다리보다 더 길 수 있고 더 짧을 수 있다.
- 걷기 시작하면 오리가 걷는 것같이 기우뚱거리면서 걷기도 한다.
- 이 병을 제때에 적절히 치료해주지 않으면 일생동안 절름발이 장애자가 된다.
- 그러나 선천성 고관절 탈구를 조기에 적절히 치료해도 완치가 되지 않는 경우도 있고 일생동안 절름발이 장애자가 될 수도 있다.
- 이 병이 있어도 고관절에 통증은 생기지 않는다.
- 조기에 확진을 받지 않고 사춘기에 이르면 고관절 발육 형성장애가 있는 고관절에 관절염이 더 잘 생길 수 있다.
- 그래서 모든 신생아의 고관절을 초음파 검사를 해서 조기 진단 치료를 해야 한다는 연구도 있다.
선천성 고관절 탈구의 진단 치료
- 이병의 진단 치료에 관해 학계에 이론이 많다.
- 병력·증상 징후와 검진 소견 등을 종합해서 이 병이 의심되면 양쪽 고관절 X선 사진 검사·초음파 검사나 CT 스캔 검사 등으로 진단한다.
- 생후 4개월 이전에는 고관절 초음파 사진 검사로 이 병을 진단하는 것이 가장 좋고,
- 생후 4개월 이후에는 고관절 X선 사진 검사로 진단하는 것이 가장 좋다.
- 갓 태어났을 때부터 정기 건강검진을 받을 때마다 고관절 탈구가 있는지 없는지 통상적으로 알아보는 것이 일반적이다.
- 가족 중 누군가가 이 병을 가진 가족 병력이 있는 집안에서 태어난 신생아, 둔위 분만으로 태어난 신생아는 이 병에 더 잘 걸릴 수 있다.
- 이 병의 중증도, 고관절을 형성하는 여러 조직들 중 어느 부위에 이상이 있느냐,
- 처음 진단받을 때 아이의 연령 등에 따라 치료와 예후가 다르다.
- 이 병이 의심되거나 진단 받았을 때는 정형외과 전문의 치료를 곧 받아야 한다.
- 선천성 고관절 탈구가 생후 2~3개월 이전에 확진되었을 때는 2~3개의 기저귀를 포개어 채워주면 양쪽 허벅다리가 몸통 좌우 바깥으로 넓게 벌어져 치료된다고 한다.
- 그러나 이 치료의 신빙성은 적다.
- 고관절낭 속에서 빠져나온 대퇴골 두부를 고관절구 속에 넣는 수술 치료를 한 다음 석고 붕대로 고정시켜 치료해주거나 파블릭 장치(Pavlik harness)로 치료 한다.
- 브레이스, 스트랩, 벨코 등으로도 치료한다. 이런 치료는 가능하면 많은 경험이 있는 소아 정형외과 전문의에게 맡기는 것이 바람직스럽다.
Congenital dislocation of hip and Hip dysplasia

Figure 121. Hip dislocation The femoral head in the left hip joint was dislocated from the hip joint capsule. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D.. FAAP

Picture 122. ◯My hip joint ◯The inner joint is the hip joint. a – femoral head, b – liver of the femur, c – ischial bone Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D. FAAP

Photo 123. Examine for congenital hip dislocation. Source: Reproduced with permission from Mead Jhonson Nutritional and Encyclopedia of Pediatric and Family Nursing

Picture 125. In newborns or infants with congenital hip dislocation, the number and shape of skin folds on both thighs may be different. Reproduced with permission from courtsy of Mead Johnson Nutrial Divition
• The joint in which the femur head and the articular ball in the ischial bone are connected is called the hip joint (Fig. A, B). There are two hip joints, one in each crotch.
• The joint capsule surrounding one or both hip joints in the crotch, the articular bulb containing the femoral head, the femur head, and one, two, or all of the muscles, tendons, and ligaments that make up the hip joint are congenitally properly developed Congenital dysplasia of the hip (or CDH), or Developmental dysplasia of the hip, or DDH ) is called
• Use dysplasia instead of dysplasia (see dislocation, congenital hip dislocation, and transient synovitis).
Causes of Congenital Hip Dislocation
• There are still many uncertainties about the cause, pathophysiology, natural course, diagnosis, and treatment.
• Hip dislocation can also occur in newborns born through vaginal delivery. • Hip dislocations can be caused by hip injuries, particularly at birth through gluteal delivery.
• Newborns born to families with a family history of the disease are more likely to have the disease. This disease may also occur with deformities of the cavities or other bones other than the hip joint.
• There is also the theory that it is caused by the influence of the fetus’s posture in the womb (fetal position) or the hormones of the mother.
• Some hip dysplasia can also be caused by acquired causes.
Symptoms of Congenital Hip Dislocation
• Congenital hip dislocation occurs in 1 in 1,000 newborns.
• First-born newborns;
• Newborns born to pregnancies with amniotic fluid deficiency;
• Newborns born to gluteal delivery are more likely to develop the disease.
• Newborns or infants with this disease may have normal legs,
• Both legs may be of different lengths and shapes.
• When the dislocated thigh is tilted out of the torso to fill the diaper, the thigh on the dislocated side may tilt less than when the normal hip is spread outward.
• When examining the dislocated hip joint with your hand (see photo 123), a sound may be heard as the femur head moves in and out of the hip joint capsule
• In addition, the examiner’s hand can sense the feeling of the dislocated femur head coming out of the hip joint capsule. Not all doctors can easily perform these tests.
• Doing these examinations carelessly can cause more hip joint damage.
• The number and shape of skin folds on both thighs may be different.
• However, even when both hip joints are normal, the skin folds on the two thighs may not be the same.
• If congenital hip dislocation is not diagnosed early and treated appropriately, it is common for newborns with hip dislocation to limp when they begin to stand and walk after they grow up and become infants.
• And one leg may be longer or shorter than the other. • When it starts to walk, it staggers and walks like a duck.
• If the disease is not treated in a timely manner, it can be life-long crippled.
• However, there are cases where congenital hip dislocation cannot be cured even if treated early and adequately, and it can lead to lifelong lameness.
• There is no pain in the hip joint even with this disease.
• If you reach puberty without being diagnosed early, you may be more likely to develop arthritis in the hip joint with hip dysplasia.
• Therefore, some studies suggest that early diagnosis and treatment should be performed by ultrasound examination of the hip joint of all newborns.
Diagnosis, treatment of congenital hip dislocation
• There are many theories in academia regarding the diagnosis and treatment of this disease.
• If the disease is suspected by combining the medical history, symptoms, and examination findings, it is diagnosed by X-ray examination of both hip joints, ultrasound examination or CT scan examination.
• It is best to diagnose this disease by ultrasonography of the hip before 4 months of age,
• After 4 months of age, it is best to diagnose with an X-ray of the hip joint.
• It is common to check whether there is a hip dislocation or not at every regular health checkup since birth.
• Newborns born in a household where someone in the family has a family history of the disease, and newborns born in a gluteal delivery, are more likely to get the disease.
• The severity of the disease, which part of the various tissues that form the hip joint is abnormal;
• When first diagnosed, treatment and prognosis are different depending on the age of the child.
• If this disease is suspected or diagnosed, you should seek immediate medical attention from an orthopedic surgeon.
• When a congenital hip dislocation is confirmed before 2-3 months of age, it is said that if 2-3 diapers are stacked and filled, both thighs spread wide to the left and right of the torso and are treated. • However, the reliability of this treatment is low.
• After surgical treatment, the femoral head, which has come out from the hip joint capsule, is put into the hip joint, and then fixed with a plaster bandage or treated with a Pavlik harness.
• Treat with braces, straps, or Velco. If possible, it is desirable to entrust such treatment to an experienced pediatric orthopedic surgeon.
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제16권 소아청소년 정형외과 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제9권 소아청소년 소화기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제10권. 소아청소년 신장 비뇨 생식기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제11권. 소아청소년 심장 혈관계 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제12권. 소아청소년 신경 정신 질환, 행동 수면 문제
- www.drleepediatrics.com제13권. 소아청소년 혈액, 림프, 종양 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제14권. 소아청소년 내분비, 유전, 염색체, 대사, 희귀병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제15권. 소아청소년 알레르기, 자가 면역질환
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th — 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
-
Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, Harvey grant, and Robert Murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
-
The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
-
Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care
-
응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
-
Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
-
Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
-
Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
-
소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”