선천성 갑상선 기능 저하증 Congenital hypothyroidism
-
갑상선 형성 부전,
-
갑상선 불 형성,
- 이소성 갑상선,
- 선천성 갑상선 호르몬 합성 이상,
- 옥도결핍 등으로 갑상선 기능 저하증이 생길 수 있다.
- 선천성 갑상선 질환으로 인하여 갑상선 호르몬이 아주 분비되지 않거나 정상 이하로 분비될 때 생기는 갑상선 질환을 선천성 갑상선 기능 저하증이라 한다1.
선천성 갑상선 기능 저하증의 원인
- 선천성 갑상선 기능 저하증이 있는 아이들의 90%에게는 선천적 갑상선 발육 부전이 있고
- 나머지는 갑상선이 흔적만 있든지
- 태어날 때부터 비정상적으로 아주 작은 갑상선이 발견된다.
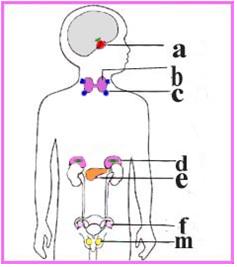
그림 1-34. 갑상선과 그 외 내분비선 해부도
a-뇌하수체, b- 갑상선, c-부갑상선, d-췌장, e-부신, f-난소, m-고환 등은 내분비선들이다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
- 그로 인해 갑상선 호르몬이 아주 분비되지 않거나 몸에서 필요로 하는 만큼 충분한 량의 갑상선 호르몬이 분비되지 않을 때
- 선천성 갑상선 기능저하증이 생길 수 있다.
- 위에서 설명한 것같이 갑상선은 있지만 갑상선의 크기가 비정상적으로 아주 작아서 신체가 필요로 하는 만큼 갑상선 호르몬의 분비 양이 충분치 않을 수 있다.
- 이때도 갑상선 기능 저하증이 생길 수 있다.
- 갑상선의 크기는 정상적이지만 뇌하수체에서 분비되는 갑상선 자극호르몬(TSH) 결핍으로 갑상선이 신체가 필요로 하는 만큼 갑상선 호르몬 양을 충분히 분비 할 수 없을 때
- 갑상선의 크기도 정상이고, 뇌하수체도 정상이지만 갑상선 세포에 이상이 있어 갑상선 호르몬 합성을 정상적으로 할 수 없을 때
- 임신부에게 있는 갑상선 기능 항진증을 치료하기 위해 쓴 항 갑상선 치료약으로 인해 태어난 아기에게 갑상선 기능 저하증이 일시적으로 나타날 때
- 임신 중 자가 면역성 갑상선 질환 등으로 생긴 갑상선 항체로 인해 갑상선 자극 호르몬이 갑상선 세포의 수용체와 결합되지 못하게 방해되어 그 임신부로부터 태어난 아기에게 갑상선 호르몬이 정상적으로 만들어지지 않을 때
- 설 갑상선, 설하 갑상선, 또는 이소성 갑상선 등으로 선천성 갑상선 기능저 하증이 생길 수 있다.
- 그 외 원인으로
선천성 갑상선 기능 저하증의 증상 징후
- 선천성 갑상선 기능 저하증의 원인과 중증도에 따라 증상 징후가 다르다.
- 선천성 갑상선 기능 저하증이 출생 후 몇 주 내 아주 심하게 나타날 수 있고 때로는 경미하게 나타날 수 있다.
- 태어날 때부터 선천적 갑상선 발육부전으로 갑상선이 아주 없으면 증상 징후가 출생 후 몇 주 내 곧 나타날 수 있다.
- 비정상적으로 갑상선 크기가 작을 때는 출생 후 몇 달 내지 몇 년을 두고 증상 징후가 서서히 나타날 수 있다.
- 태어날 때부터 갑상선이 아주 없기 때문에 생긴 선천성 갑상선 기능 저하증의 전형적인 증상 징후는 다음과 같다.
- 출생 전 태아는 갑상선 호르몬을 필요로 하는 만큼 모체로부터 충분히 공급받는다.
- 신생아들과 영유아들은 모체로부터 갑상선 호르몬을 더 이상 공급받지 못하기 때문에 자기 자신의 갑상선에서 분비되는 갑상선 호르몬으로 성장 발육 할 수 없다.
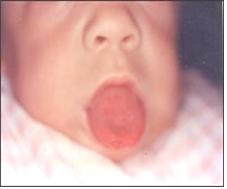
그림 3-35. 선천성 갑상선 기능저하증으로 혀를 비정상으로 내밀고 있다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
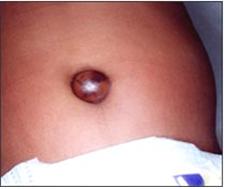
그림 3-36. 선천성 갑상선 기능저하증이 있을 때 배꼽 탈장증이 생길 수 있다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
- 생후 첫 몇 주 동안 자기 자신이 필요로 하는 만큼의 갑상선 호르몬을 충분히 분비할 수 없어도 태어나기 전 모체로부터 공급받았던 갑상선 호르몬의 영향으로 별 지장 없이 정상적으로 자랄 수 있는 것이 보통이다.
- 때문에 갑상선이 선천성으로 없어도 선천성 갑상선 기능 저하증의 증상 징후가 생후 첫 몇 주 동안 현저하게 나타나지 않는 것이 보통이다.
- 그렇지만 생후 3~8주경부터 선천성 갑상선 기능 저하증의 증상 징후가 현저하게 나타나기 시작한다.
- 선천성 갑상선 기능 저하증이 있는 신생아들의 출생 시 체중은 건강한 동성 신생아들의 체중보다 좀 더 나갈 수 있다.
- 그렇지만 신생아들의 체중은 각 신생아에 따라 상당히 차이가 날 수 있기 때문에 출생 시 체중이 좀 더 많이 나간다고 해서 선천성 갑상선 기능저하증이 있다고 진단할 수 없다.
- 선천성 갑상선 기능 저하증을 갖고 태어난 어떤 신생아들에게는 신생아 생리적 황달이 정상 갑상선을 가진 신생아들 보다 더 잘 생기고 그 황달의 정도가 더 심할 수 있고 더 오래 갈 수 있다.
- 선천성 갑상선 기능 저하증을 가진 신생아들은 아주 순한 아기들처럼 잠을 더 많이 자고,
- 배가 고파도 깨서 먹겠다고 잘 울지도 않고, 잘 먹지도 않고 때로는 계속 잠만 잘 수 있다.
- 모유나 인공영양을 먹다 자주 사레들고, 코가 막혀 호흡곤란이 자주 생길 수 있다.
- 별다른 이유 없이 아기의 행동이 느린 감이 있다.
- 배가 불쑥 나오고 부르다.
- 배꼽 탈장이 있을 수 있다.
- 변비가 잘 생긴다.
- 이 병을 조기에 진단해서 적절히 치료하지 않으면 전반적 소아기 성장 발육이 현저히 늦어지고 저능아가 될 수 있다.
- 태어날 때부터 갑상선이 조금 기능할 수 있지만 갑상선의 크기가 비정상적으로 아주 작을 때는 신체가 필요로 하는 만큼 갑상선 호르몬이 충분히 분비되지 않아 선천성 갑상선 기능저하증이 서서히 경미하게 나타나다가 그 후 점점 더 심하게 나타날 수 있다.
선천성 갑상선 기능 저하증의 진단
- 요즘, 신생아가 태어 난 후 신생아실에서 집으로 퇴원하기 전 갑상선 기능검사를 기본적으로 해 선천성 갑상선 기능 저하증을 출생 후 바로 조기 진단하고 있다.
- 병력, 증상 징후와 진찰소견 등을 종합해서 이 병이 있다고 의심되면 혈중 갑상선 호르몬(T4), (유리 T4), T3, 유리 트리요오드타이토닌(Free T3)과 뇌하수체에서 나오는 갑상선 자극 호르몬(TSH)농도, 갑상선 글로불린(Tg), 혈중 티록신 결합글로불린(TBG) 농도 등을 검사하고, 방사핵종 스캔검사, 갑상선 초음파검사, 신피그래피 검사 등으로 갑상선의 유무와 기능 등을 알아서 확진한다.
- 필요에 따라 방사능 옥도 섭취 검사로 진단할 수 있다.
- 그 중 T4, T3, 갑상선자극 호르몬(TSH)의 농도, 방사핵종 스캔검사 등으로 확진할 수 있다.
- 요즘 선천성 갑상선 기능 저하증을 신생아기에 조기 진단하기 위해 갓 태어난 모든 신생아들의 피를 뽑아 혈중 갑상선 호르몬 농도를 통상적으로 검사한다.
선천성 갑상선 기능 저하증의 치료
- 선천성 갑상선 기능 저하증의 원인과 정도에 따라 다르게 치료한다.
- 이 병은 신생아기에 조기 진단해 조기에 적절히 치료를 시작하지 않으면 저능아가 될 수 있기 때문에 신생아기에 치료를 일찍 시작하는 것이 대단히 중요하다.
- 만일 진단을 늦게 해 저능아가 된 후 저능아의 안녕복지를 일생동안 부모나 국가가 책임지고 한다면 적어도 $1,014,000 정도 양육비가 든다고 한다(2003년 통계)12.
- 적어도 생 후 6주 이전 적절한 치료를 시작하면 거의가 정상적으로 성장 발육될 수 있다.
- 그러나 그보다 늦게 진단해서 치료를 늦게 시작하면 거의가 저능아가 될 수 있다.
- 선천성 갑상선 기능 저하증은 경구용 소디움-L-사이록신(타이록신) 갑상선 호르몬을 일생 동안 매일 복용 치료한다.
- 주기적으로 혈 중 T4, T3, 갑상선자극호르몬 농도 검사로 치료가 잘 되나 알아본다.
|
다음은“갑상선호르몬 수치가 높다고 하는데요, 갑상선 기능 저하증”에 관한 인터넷 소아청소년 건강상담 질의응답의 예 입니다. |
Q&A. 갑상선호르몬 수치가 높다고 하는데요
Q.
- 선천성대사검사결과 갑상선 호르몬 수치가 높다고 해서 오늘 다시 재검했습니다.
- 출생한지 4주 되었는데요..갑상선기능저하증이라고 결과가 나오면 치료방법은? 또 증세는 어떤가요?
- 지금 모유나 우유도 잘 먹고 정상적으로 크고 있는 것 같거든요?
- 걱정이 많이 됩니다.
A.
- ddd님
- 안녕하세요. 질문해 주셔서 감사합니다. 좋은 질문입니다.
- 자녀의 나이, 성별, 과거 병력, 가족 병력, 진찰소견, 임상검사 등의 정보를 많이 알수록 답변을 드리는데 도움이 더 됩니다. 주신 정보를 토대로 해서 답변을 드리겠습니다.
- “선천성 대사 이상 검사의 결과 중, 갑상선 호르몬 수치가 높아서 다시 검사했다“고 하셨는데 여러 종류의 선천성 대사 이상이 있을 수 있고 선천성 대사 이상 여부를 알아보는 검사에는 여러 가지가 있습니다.
- 갑상선 기능이 정상인지 비정상인지 알아보기 위해 뇌하수체에서 분비되는 갑상선 자극호르몬(TSH)을 검사하기도 합니다.
- 갑상선 자극호르몬은 갑상선 호르몬이 분비되도록 갑상선을 자극하는 뇌하수체 전엽 호르몬들 중 하나입니다.
- “갑상선 호르몬 수치가 높다“고 하신 말씀은 아마도 혈중 갑상선 자극호르몬의 수치가 정상 이상으로 높다는 것 같습니다.
- 그 수치가 비정상으로 상당히 높으면 갑상선 기능 저하증을 의심해 볼 수 있지만 약간 높은 경우에는 트라이요오도타이로닌(T3), 티록신(T4), 갑상선 자극호르몬(TSH) 등의 호르몬을 다시 검사해서 그 검사의 결과에 따라 갑상선 기능이 비정상인지 정상인지 알아보는 것이 보통입니다.
- 그 임상 검사의 결과가 여러 가지 이유로 정확하게 나타나지 않을 수 있습니다.
- 검사의 결과가 비정상치이지만 거의 정상수치에 가까울 때는 같은 검사를 다시 검사해서 그 검사의 결과가 정확했었는지 정확하지 않았었는지 알아보는 것이 중요합니다.
- 때로는 검사실에서 검사를 잘못해서 검사 결과가 잘못 나올 수 있습니다. 그래서 다시 검사해서 진단하는 것이 좋습니다.
- 소아청소년과에서 이 문제에 관해 상담하시기 바랍니다.
- [부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다–소아가정간호백과] 제2권 소아청소년 질병 안전사고 예방–태어나서 성인이 될 때까지 정기 건강검진을 다음 표와 같이 한다.
- 선천성 갑상선 기능저하증,
- 후천성 갑상선 기능저하증 등을 참조하시기 바랍니다.
- 질문이 더 있으시면 다시 연락 주시기 바랍니다. 감사합니다. 이상원 드림
Congenital hypothyroidism 선천성 갑상선 기능 저하증
• hypothyroidism,
• thyroid fire formation,
• ectopic thyroid gland,
• congenital thyroid hormone synthesis abnormalities,
• Hypothyroidism may occur due to iodine deficiency or the like.
• A thyroid disorder that occurs when the thyroid hormone is not secreted or secreted below normal due to congenital thyroid disease is called congenital hypothyroidism1.
Causes of congenital hypothyroidism
• 90% of children with congenital hypothyroidism have congenital hypothyroidism
• The rest are only traces of the thyroid gland.
• From birth, abnormally tiny thyroid glands are found.

Figure 1-34. Anatomy of the thyroid gland and other endocrine glands The a-pituitary gland, b-thyroid gland, c-parathyroid gland, d-pancreas, e-adrenal, f-ovary, m-testis are endocrine glands. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
• As a result, thyroid hormone is not secreted very much, or when the body does not produce enough thyroid hormone as needed.
• Congenital hypothyroidism may develop.
• As described above, you have a thyroid gland, but the size of the thyroid gland is abnormally very small, so the amount of thyroid hormone secretion may not be sufficient as the body needs it.
• Hypothyroidism can also develop at this time.
• When the thyroid gland is normal in size, but due to a deficiency of thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) secreted by the pituitary gland, the thyroid gland cannot secrete enough thyroid hormone as the body needs.
• When the size of the thyroid gland is normal and the pituitary gland is also normal, but the thyroid gland cells are abnormal and the thyroid hormone cannot be synthesized normally.
• Temporary hypothyroidism in babies born from antithyroid medications used to treat hyperthyroidism in pregnant women.
• When thyroid stimulating hormone is prevented from binding to thyroid cell receptors due to thyroid antibodies caused by autoimmune thyroid disease during pregnancy, and thyroid hormones are not produced normally in babies born from the pregnant woman.
• Congenital hypothyroidism may occur due to the hypothyroidism of the gland, a sublingual thyroid, or an ectopic thyroid.
• For other reasons
Symptoms signs of congenital hypothyroidism
• Symptoms differ depending on the cause and severity of congenital hypothyroidism. • Congenital hypothyroidism can develop very severely and sometimes mildly within weeks after birth.
• If the thyroid gland is very absent from birth due to congenital hypoplasia, symptoms may appear soon after birth within a few weeks.
• When the thyroid gland is abnormally small, symptoms may appear gradually, months to years after birth.
• Typical symptomatic signs of congenital hypothyroidism caused by a very low thyroid gland from birth are as follows.
• Before birth, the fetus receives enough from the mother to need thyroid hormones.
• Newborns and infants are unable to grow and develop with thyroid hormones secreted by their own thyroid gland because they no longer receive thyroid hormones from their mother.

Figure 3-35. Congenital hypothyroidism, protruding the tongue abnormally. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Figure 3-36. Umbilical hernia can develop when congenital hypothyroidism is present. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
• In the first few weeks of life, it is common for people to not be able to secrete enough thyroid hormones as needed by themselves, but can grow normally without any problems due to the influence of thyroid hormones supplied by the mother before birth.
• Because of this, symptoms of congenital hypothyroidism usually do not appear significantly during the first few weeks of life, even if the thyroid gland is not congenital. • However, symptoms of congenital hypothyroidism begin to appear remarkably from 3 to 8 weeks of age.
• Newborns with congenital hypothyroidism may weigh a little more than the weight of healthy same-sex newborns at birth. • However, since the weight of newborns can vary considerably from one newborn to another, it is not possible to diagnose congenital hypothyroidism just because they weigh a little more at birth.
• In some newborns born with congenital hypothyroidism, neonatal physiological jaundice is more likely than newborns with normal thyroid gland, and the degree of jaundice may be more severe and may last longer.
• Newborns with congenital hypothyroidism sleep more like very mild babies,
• Even when I’m hungry, I don’t cry well to eat, I don’t eat well, and sometimes I can only sleep.
• You often die while eating breast milk or artificial nutrition, and you may have trouble breathing frequently due to a stuffy nose.
• The baby’s behavior is slow for no apparent reason.
• The boat pops out and calls.
• You may have an umbilical hernia.
• Constipation is good.
• If the disease is diagnosed early and not properly treated, overall childhood growth and development may be significantly delayed and the child may become impaired.
• The thyroid gland may function slightly from birth, but when the size of the thyroid gland is abnormally very small, the thyroid hormone is not secreted enough as the body needs, and congenital hypothyroidism may appear gradually and mildly, and then become more and more severe. have.
Diagnosis of congenital hypothyroidism
• Nowadays, the basic thyroid function test is performed after the newborn is born and before discharged home from the neonatal room to diagnose congenital hypothyroidism immediately after birth.
• If you suspect that you have this disease by combining your medical history, symptoms, symptoms, and examination findings, you will be able to find thyroid hormone (T4), (free T4), T3, free triiodothytonin (Free T3) and thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) from the pituitary gland. )Concentration, thyroid globulin (Tg), blood thyroxine-binding globulin (TBG) concentration, etc. are tested, and the presence and function of the thyroid gland are checked by taking a radionuclide scan, an ultrasound of the thyroid gland, and a neophyte.
• If necessary, it can be diagnosed with a radioactive jade intake test. • Among them, T4, T3, thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) concentration, radionuclide scan, etc. can be used to confirm the diagnosis.
• To diagnose congenital hypothyroidism early in the neonatal period these days, blood from all newborns is routinely tested for thyroid hormone levels in the blood.
Treatment of congenital hypothyroidism
• Treat differently depending on the cause and severity of congenital hypothyroidism.
• It is very important to start treatment early in the neonatal period because this disease can be diagnosed early in the neonatal period and, if not properly started, can lead to a low-potential baby.
• If the parent or the state is responsible for the welfare of the child with a disability after being diagnosed with a late diagnosis, it is said that child support costs will be at least $1,014,000 (2003 statistics)12.
• Most people can grow and develop normally if appropriate treatment is initiated before at least 6 weeks of age.
• However, if you diagnose later and start treatment late, most of the babies can become impaired.
• Congenital hypothyroidism is treated by taking oral sodium-L-thyroxine (thyroxine) thyroid hormone daily for life.
• Periodically check if the treatment works well with blood T4, T3, and thyroid-stimulating hormone levels.
The following is an example of a question-and-answer on Internet pediatrics and adolescents health counseling about “the thyroid hormone level is high, hypothyroidism”.
Q&A.
Thyroid hormone levels are said to be high.
Q.
• My congenital metabolism test revealed that my thyroid hormone levels were high, so I retested today.
• It’s been 4 weeks since I was born.. If the result is hypothyroidism, what is the treatment? What about the symptoms?
• You are eating well with breast milk or milk now, and you seem to be getting bigger normally?
• I’m worried a lot.
A.
• ddd
• Good morning. Thanks for asking. That’s a good question.
• The more information you know about your child’s age, gender, past medical history, family medical history, medical examination findings, and clinical examination, the more helpful it is to give you an answer. We will respond based on the information you provided.
• You said, “Of the results of the test for congenital metabolic abnormalities, the thyroid hormone level was high, so I tested again.”
• Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) secreted by the pituitary gland is also tested to see if thyroid function is normal or abnormal.
• Thyroid-stimulating hormone is one of the anterior pituitary hormones that stimulate the thyroid gland to release thyroid hormones.
• When you say “the level of thyroid hormone is high”, it seems that the level of thyroid-stimulating hormone in the blood is higher than normal.
• If the level is abnormally high, hypothyroidism can be suspected, but if it is slightly high, hormones such as triiodothyronine (T3), thyroxine (T4), and thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) are retested and the test Based on the results, it is common to see if thyroid function is abnormal or normal.
• The results of the clinical test may not be accurate for a number of reasons.
• If the test results are abnormal but are close to normal, it is important to retest the same test to see if the test results were correct or incorrect.
• Sometimes, the laboratory tests incorrectly and the results are incorrect. So it’s a good idea to retest and diagnose.
• Talk to the Department of Children and Adolescents on this matter.
• www.drleepediatrics.com-Vol. 2 Prevention of child and adolescent disease safety accidents-Regular health check-ups from birth to adulthood are as shown in the table below.
• congenital hypothyroidism,
• Please refer to acquired hypothyroidism, etc.
• If you have more questions, please contact us again. Thank you. Lee Sang-won.
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- www.drle epediatrics.com제14권. 소아청소년 내분비, 유전, 염색체, 대사, 희귀병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제6권 신생아 성장 발육 육아 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제9권 소아청소년 소화기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제10권. 소아청소년 신장 비뇨 생식기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제11권. 소아청소년 심장 혈관계 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제12권. 소아청소년 신경 정신 질환, 행동 수면 문제
- www.drleepediatrics.com제13권. 소아청소년 혈액, 림프, 종양 질환
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th — 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
-
Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, harvey grant and robert murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
-
The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
-
Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies , Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care
-
응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
-
Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
-
Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
-
Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
-
소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”