비 유행성 이하선염, Non-mumps parotitis
(You may visit www.drleepediatrics.com – Volume 7,
Pediatric Adolescent Infectious Diseases or제 7권, 소아 청소년 감염병 질환 웹사이트)
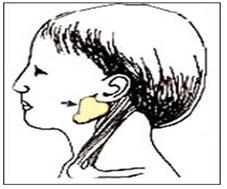
그림 3-95. 화살표시로 표시된 부위에 정상 이하선이 있다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
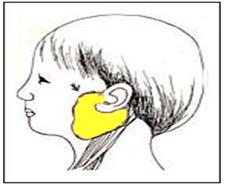
그림 3-96. 화살표시로 표시된 이하선에 이하선염이 생겨 이하선이 부었다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
-
이하선은 침을 만들어 분비하고 아밀라제 효소를 분비하는 외분비선의 일종으로, 외이(外耳)의 바로 앞, 아래 부위에 각각 한 개씩 좌우 양쪽에 있다(그림 3-95~96).
-
이하선염이 유행성 이하선염바이러스 (볼거리바이러스) 감염으로 생기면 유행성 이하선염(볼거리)이라고 한다.
-
그러나 사이토메갈로바이러스, 콕삭기바이러스, 림프구성 맥락뇌막염바이러스, 또는 사람 면역결핍 바이러스 등 비 유행성 이하선염 바이러스 감염으로 생긴 이하선염을 비 유행성 이하선염이라고 한다.
-
재발성 이하선염은 유행성 이하선염바이러스 감염으로 생기지 않고 알레르기로 생기는 비 유행성 이하선염의 일종이다.
-
또 황색 포도상구균 등 화농성 박테리아 감염으로 화농성 이하선염이 생길 수 있다.
-
비 유행성 이하선염이 급성으로 생기면 급성 비 유행성 이하선염,
-
만성으로 생기면 만성 비 유행성 이하선염이라고 한다.
-
비 유행성 이하선염에 대해서 다음에 더 설명하기로 한다. 볼거리 참조. 화농성 이하선염 참조.
비 유행성 이하선염의 원인
- 비 유행성 이하선염을 일으킨 원인을 확실히 알 수 없는 때도 있고 에이즈 등 바이러스 감염, 박테리아 감염, 자가 면역질환, 이하선 외상, 매독, 또는 알레르기 등으로 인해 비 유행성 이하선염이 생길 수 있다.
비 유행성 이하선염의 증상 징후
- 비 유행성 이하선염을 일으킨 원인에 따라 증상 징후가 다르다.
- 또 비 유행성 이하선염이 급성으로 생겼는지 또는 만성으로 생겼는지에 따라 증상 징후가 다르다.
- 비 유행성 이하선염의 종류, 정도, 경과에 따라 증상 징후가 다르다.
- 일반적으로 비 유행성 이하선염이 있는 부위가 붓고 아프며 손으로 누르면 아플 수 있다.
- 미열이나 고열이 날 수 있고 양쪽 볼 안쪽 입 안 점막층에 있는 이하선 분비관의 외도구가 빨갛게 부을 수 있으며 거기서 고름이 나올 수 있다.
비 유행성 이하선염의 진단 치료
- 병력·증상 징후·진찰소견 등을 종합해서 진단한다.
- 비 유행성 이하선염의 원인에 따라 진단할 수 있다.
- 비 유행성 이하선염을 일으킨 원인에 따라 치료한다.
Non-mumps parotitis
(You may visit www.drleepediatrics.com – Chapter 7, Pediatric Adolescent Infectious Diseases (Vol. 7, Child and Adolescent Infectious Diseases website)

Figure 3-95. There is a normal parotid gland in the area indicated by the arrow. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Figure 3-96. Parotiditis occurred in the parotid gland indicated by the arrow, and the parotid gland was swollen. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
• Parotid gland is a kind of exocrine gland that secretes saliva and secretes amylase enzyme and is located right in front of and below the outer ear, one each on the left and right sides (Figure 3-95~96).
• If mumps is caused by mumps virus (mumps virus) infection, it is called mumps.
• However, mumps caused by infection with a non-mumps virus such as cytomegalovirus, coxsackievirus, lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus, or human immunodeficiency virus is called non-mumps. • Recurrent mumps is a type of non-mumps infection that is not caused by mumps virus infection but is caused by allergies.
• Infection with purulent bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus can also cause mumps suppurativa.
• If non-mumps is acute, acute non-mumps, • When it becomes chronic, it is called chronic non-mumps.
• Non-mumps will be further explained next. See sights. See purulent mumps.
Causes of non-mumps
• Sometimes the cause of non-mumps is not known with certainty, and viral infection such as AIDS, bacterial infection, autoimmune disease, parotid trauma, syphilis, or allergy can cause mumps.
Symptoms, Signs of Non-Mumps
• Symptoms and signs differ depending on the cause of non-mumps.
• Also, symptoms differ depending on whether non-mumps are acute or chronic.
Symptoms and signs differ according to the type, severity, and course of non-mumps.
• Typically, the area with non-mumps is swollen and painful and may be painful when pressed with your hand.
• You may have a slight fever or high fever, and the external duct of the parotid gland in the mucous layer of the inner mouth on both cheeks may become red and swollen, and pus may come out of it.
Diagnostic treatment of non-mumps
• Diagnosis is made by combining medical history, symptoms, signs, and examination findings.
• Diagnosis can be made according to the cause of non-mumps.
Treat according to the cause of non-mumps.
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권. 소아청소년 감염병
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th – 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
-
Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, Harvey grant, and Robert Murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
-
The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
-
Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care
-
응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
-
Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
-
Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
-
Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
-
소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”