부종 Edema
부종의 개요와 원인
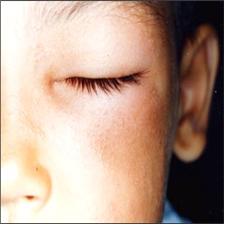
사진 550. 얼굴이 덩굴 옻나무 피부염으로 부었다. 신증후군으로 얼굴이 부으면 대개 전신도 붓는 것이 보통이다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD.,FAAP
-
체액(Body fluid)이 신체의 한 국소의 간질 조직이나, 또는 전신의 간질조직에 비정상적으로 많이 축적되어 붓는 것을 부종이라 한다.
-
부종은 신체의 일부분에 생기는 국소적 부종과 전신에 생기는 전신 부종으로 나눌 수 있다.
-
급성으로 생기는 부종과 만성으로 생기는 부종으로 나눌 수 있다.
-
육안으로 볼 수 있게 피부가 부은 부종, 피부와 근육에 동시에 생긴 부종도 있고 뇌나 간, 위장, 폐 등 그 외 내장 기관에만 생기는 내장 부종도 있다.
-
전신에 부종이 경도로 서서히 생길 때는 몸이 부었는지 확실히 알 수 없을 때도 있으나 점차로 더 심하게 부으면 체중이 비정상적으로 증가되고 몸이 부어 있는 것을 육안으로 쉽게 보고 알 수 있다.
-
신장염, 신증후군, 심장 부전증, 또는 무 알부민증 등으로 전신에 부종이 생길 수 있다.
-
신증후군으로 부종이 생기면 얼굴에 더 현저하게 부종이 나타날 수 있다.
-
심장 부전증으로 부종이 생기면 다리에 더 현저히 부종이 나타나는 것이 일반적이다.
신생아 부종
-
출생 체중이 1.3kg 이하이거나 그 보다 더 작은 미숙아들에게 전신 부종이 생길 수 있다. 그들의 손발에 생긴 부종을 흔히 볼 수 있다.
-
그 원인은 확실치 않다. 원인을 알아보면.
-
비타민 E 결핍증,
-
심한 빈혈,
-
1차성 림프수종(밀로리 병),
-
선천성 림프수종,
-
난소발육 부전증,
-
항이뇨호르몬(ADH 호르몬) 분비 이상,
-
선천성 무 알부민증,
-
심한 단백질 결핍증,
-
공피증,
-
매독,
-
선천성 혈관신경성 부종,
-
당뇨병을 앓는 엄마로부터 태어난 신생아,
-
고 알도스테른증,
-
단백질 소실 위장병,
-
가락토즈증,
-
유미 복막증,
-
거대세포 간염,
-
C형 간염,
-
B형 간염,
-
사이토메가로바이러스 감염병,
-
톡소프라스마증, 신
-
진대사 이상 등으로 인해 부종이 생길 수 있다.
신생아 부종과 복수 원인
-
체액이 복강 내에 비정상적으로 축적되는 현상을 복수라고 한다.
-
신증후군,
-
신장염,
-
신생아 요로 폐쇄증,
-
유미 복막증,
-
복강내 낭종파열,
-
담관 폐쇄증,
-
태변성 복막염,
-
담즙 복막염,
-
감염병 등으로 복수가 생길 수 있다.
신생아기 이후 소아들에게 생기는 부종의 원인
|
|
원인에 따라 치료한다.
Edema 부종
Overview and Causes of Edema

Picture 550. The face is swollen with poison ivy dermatitis. When the face is swollen with nephrotic syndrome, it is usually the whole body as well. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
• Edema is when body fluid accumulates abnormally in one local interstitial tissue or in interstitial tissue throughout the body.
• Edema can be divided into local edema occurring in a part of the body and systemic edema occurring throughout the body.
• It can be divided into acute edema and chronic edema.
• Swelling of the skin visible to the naked eye, swelling of the skin and muscles simultaneously, and visceral edema that occurs only in other internal organs such as the brain, liver, stomach, and lungs.
• When edema develops slowly and mildly throughout the body, it is not always clear whether the body is swollen or not, but as the swelling becomes more severe, the bodyweight increases abnormally and the swelling can be easily seen with the naked eye.
• Nephritis, nephrotic syndrome, heart failure, or albuminosis can cause swelling throughout the body.
• If nephrotic syndrome causes edema, edema may appear more prominently on the face.
• When edema is caused by heart failure, it is common to see more marked edema in the legs.
Neonatal edema
• Systemic edema may occur in premature infants weighing less than or equal to 1.3 kg at birth. Edema on their limbs is common.
• The cause is unclear. If you find out the cause.
• Vitamin E deficiency; • severe anemia;
• primary lymphedema (Millory’s disease);
• Congenital lymphedema;
• ovarian hypoplasia;
• Abnormal secretion of antidiuretic hormone (ADH hormone);
• Congenital aalbuminosis;
• severe protein deficiency;
• scleroderma;
• Syphilis;
• Congenital angioneurotic edema;
• Newborns born to mothers with diabetes;
• hyperaldosteronism;
• protein loss gastrointestinal disease;
•Galactosis;
• chyloperitonosis;
• giant cell hepatitis;
• Hepatitis C;
• Hepatitis B;
• cytomegalovirus infections;
• Toxoplasmosis, renal
• Edema may occur due to metabolic abnormalities.
Neonatal edema and ascites causes
• Abnormal accumulation of body fluid in the abdominal cavity is called ascites.
• Nephrotic Syndrome;
• Nephritis;
• Neonatal urinary tract atresia;
• chyloperitonosis;
• Intra-abdominal cyst rupture;
• bile duct atresia;
• meconium peritonitis;
• biliary peritonitis;
• Ascites may occur due to infectious diseases, etc.
Causes of edema in children after the neonatal period
• scarlet fever;
• whooping cough;
• Rocky Mountain Spotted Column;
• diphtheria;
• Staphylococcal dermatitis;
• Bacterial infectious diseases such as graveyard disease
• Roseola
• Infectious mononucleosis;
• Viral infectious diseases such as mumps
• Connective dermatitis; • allergic dermatitis;
• insect bites;
• bee stings;
• drug addiction;
• Hives from inhaled substances;
• Allergic reactions such as food (food) allergy
• Henoch’s purpura, serum sickness,
• Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis;
• Kawasaki disease;
• Steven-Johnson syndrome;
• Systemic lupus erythematosus, dermatomyositis,
• progressive systemic sclerosis;
• Connective tissue diseases such as polyarteritis • albuminosis,
• Trypsinogen deficiency;
• Garactosis, etc.
• heart failure;
• Arterial venous fistula, etc.
• Contractile carditis, etc.
• chronic allergic gastroenteritis;
• ulcerative colitis;
• Protein-losing gastroenteritis;
• Gastrointestinal lymphangiectasia;
• Celiac disease (gluten-induced enteritis);
• Gastrointestinal infections, etc.
• Meigs’ Ovary
• Fibroma;
• Turners’ syndrome;
• Noonan syndrome, etc.
• filariasis, trichinella, etc.
• burn,
• Surgery, etc.
• primary tumors;
• metastatic tumors;
• Neuroblastoma;
• Postperitoneal fibrosis
• Myxedema;
• scurvy;
• beriberi;
• Vitamin E deficiency;
• Hyperthyroidism,
• hypothyroidism;
• Pancreatitis;
• Eosinophilic cellulitis
• pulmonary edema;
• diabetic cerebral edema;
• Reye’s syndrome;
• hypoxia;
• Laryngeal edema, etc.
• Nephrotic Syndrome;
• Nephritis;
• hereditary nephritis;
• Infectious nephritis;
• drug-induced
• Nephritis;
• Immune Nephritis
• cirrhosis of the liver;
• Hepatocellular insufficiency
• wasting
• Lymphangitis
• Etc
Treat according to the cause.
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy of Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com제6권 신생아 성장 발육 육아 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제9권 소아청소년 소화기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제10권. 소아청소년 신장 비뇨 생식기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제11권. 소아청소년 심장 혈관계 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제12권. 소아청소년 신경 정신 질환, 행동 수면 문제
- www.drleepediatrics.com제13권. 소아청소년 혈액, 림프, 종양 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제14권. 소아청소년 내분비, 유전, 염색체, 대사, 희귀병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제15권. 소아청소년 알레르기, 자가 면역질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제17권. 소아청소년 피부 질환
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th — 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
-
Current Pediatric Therapy, Gellis and Kagan
-
Clinical Pediatric Dermatology, Sidney Hurwitz
-
Infectious Diseases In Children, 2002
-
Manual of Skin Diseases, Gordon G. Sauer
-
Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics
-
Neonatology, BEHRMAN
-
Pediatric and Adolescent Gynecology, S. Jean Herriot Emans, M.D., Donald Peter Goldstein, M.D.
-
Sign and Symptoms in Pediatrics, Walter W. Tunnessen, Jr.
-
Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, Harvey grant, and Robert Murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
-
The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
-
Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care
-
응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
-
Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
-
Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
-
Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
-
소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD,, FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”