복통, Abdominal pain
복통의 종류와 원인
-
소아청소년 환자들의 2~4%가 급성 복통이나 만성 복통으로 외래 소아청소년과에 온다고 한다.
-
복통을 급성 복통 또는 만성 복통으로 분류하기도 하고 기능적 복통 또는 기질적 복통으로 분류하기도 한다. 재발성 복통, 지속성 복통, 또는 간헐성 복통 등으로 분류한다.
-
또 흥분성 위장 증후군에 의한 복통, 기능적 소화불량(Functional dyspepsia)으로 생기는 복통, 복성 편두통으로 인한 복통으로도 분류하기 한다.
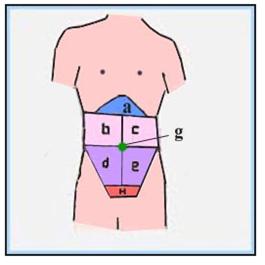
그림 143. 복부의 경계표
a-심와부, b-상 우복부, c-상 좌복부,
d-하 우복부, e-하 좌복부, h-하 복부, g-배꼽
배가 아플 때 그냥 배가 아프다고 의사에게 말하는 대신 복부의 어느 부위가 아프다고 말 하면 의사는 복통의 원인을 더 쉽게 찾아 진단할 수 있다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
① 배가 아픈 것을 복통이라 한다.
② 복통은 어떤 병의 증상이지 병명은 아니다.
③ 복통이 있으면 그 원인이 무엇인지 알아야 복통을 효과적으로 잘 치료할 수 있다. 그렇지만 복통의 원인이 무엇인지 확실히 알 수 없는 경우가 더 많다.
④ 몇 주 이상 오랫동안 계속되는 만성 복통,
⑤ 갑자기 몇 분 내지 몇 시간동안, 또는 며칠 동안 계속되는 급성 복통,
⑥ 아주 경미한 복통, 창자가 끊어질 정도로 아주 심하게 아픈 복통,
⑦ 영유아들에게 주로 생기는 복통,
학령기 아이들이나 사춘기 아이들에게 주로 생기는 복통, 또는 성인들에게 주로 생기는 복통
⑧ 여아들에게 주로 생기는 복통, 남아들에게 주로 생기는 복통
⑨ 충수염 등 복강 내 장기에 생긴 기질적 병으로 생기는 복통
⑩ 폐렴으로 복통이 생길 수 있다. 이와 같이 소화기계통 이외의 다른 계통의 장기에 생긴 기질적 병으로 복통이 생길 수 있다.
⑪ 신체에 기질적 병은 없으나 정서 정신적 문제로 복통이 생길 수 있다. 이런 복통을 기능적 복통(Functional abdominal pain)이라고 한다.
⑫ 또 복강 내의 소화기계통의 기관에 생긴 어떤 질환으로 복통이 생길 수도 있고 소화기계통 이외 다른 계통의 기관에 생긴 즉 흉강 내나 두개강 내 어떤 이상 등으로 복통이 생길 수 있다.
그 외로
⑬ 음식물 알레르기로 생긴 복통,
⑭ 음식물 과식으로 생긴 복통,
⑮ 나이와 체질에 맞지 않는 음식물을 섭취해서 생긴 복통,
⑯ 유당분해 효소 결핍증으로 생긴 유당 불내증으로 생긴 복통,
⑰ 흥분성 위장관 증후군으로 생긴 복통,
⑱ 복성 편두통으로 인한 복통,
⑲ 변비로 생긴 복통,
⑳ 위궤양(소화성 위궤양이나 십이지장 궤양)으로 생긴 복통
㉑ 담석증으로 생긴 복통,
㉒ 요석증, 또는 요로 감염 등으로 생긴 복통 등이 있다. 사춘기 여아들의 월경, 임신 등으로 복통이 생길 수 있다.
㉓ 정신 정서적 문제,
㉔ 변비
㉕ 우유나 우유성분이 든 음식물을 먹은 후 유당 불내증이나 위장관 알레르기로 소아청소년들에게 복통이 생긴다.
㉖ 이와 같이 아이들의 복통의 원인은 아주 많기 때문에 복통의 원인을 한 권의 책에 다 열거할 수 없을 정도이다.
㉗ 여기서는 좀 더 흔히 볼 수 있는 소아청소년들의 복통의 원인과 그 증상 그리고 진단에 대해 설명하기로 한다. [부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다–소아가정간호백과]-제1권 소아청소년 응급의료–급성 복부 질환 참조.
신생아들과 첫 돌 이전 영아들의 복통의 원인
신생아들과 영아들의 복통의 원인은 다음과 같이 상당히 많다.
그 중,
① 영아산통,
② 음식물, 특히 우유 단백질이 든 음식물로 생기는 위장관 알레르기 질환,
③ 바이러스 감염이나 박테리아 감염으로 생긴 위장염으로 복통이 생길 수 있고,
④ 소화기계통의 복강 내 장기 이외 신체 다른 부위에 있는 다른 계통의 장기에 생기는 바이러스 감염병이나 박테리아 감염병으로 복통이 생길 수 있다.
⑤ 드물게는 맹장염, 장중적증(장중첩증), 위장이나 신장, 간장의 외상 등으로 복통이 생길 수 있다.
⑥ 에리스로마이신이나 그 외 다른 종류의 항생제 치료, 또는 다른 종류의 약물 치료를 받을 때,
⑦ 정신적으로 불안할 때,
⑧ 나이에 적절치 않은 이유식을 먹을 때,
⑨ 이유식을 너무 많이 먹을 때 복통이 생길 수 있다.
⑩ 정신적으로 불안한 엄마의 젖을 먹는 신생아들이나 영유아들에게도 복통이 생길 수 있다.
첫 돌 이후부터 학령기 전 유아들에게 생기는 복통의 원인
① 바이러스 위장염이나 박테리아 위장염,
② 우유, 초콜릿 또는 그 외 다른 음식물 섭취로 생긴 위장관 음식물(식품) 알레르기,
③ 정신적 불안,
④ 변비증,
⑤ 흥분성 위장관 증후군,
⑥ 소화기계통의 복강 내 장기 이외 신체 다른 부위에 있는 다른 계통의 장기에 생긴 여러 종류의 바이러스 감염병이나 박테리아 감염병으로 복통이 생길 수 있다.
⑦ 폐렴, 편도염, 맹장염, 장중첩증, 비장 파열, 위장 파열, 간염, 췌장염, 신장염, 류마티스 열, 당뇨병, 약물 중독, 식중독, 요석증 등으로 복통이 생길 수 있다.
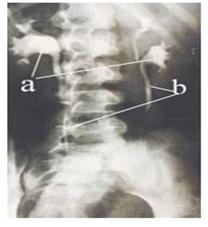
사진 144. 특히 소아가 배가 아프면 요로에 생긴 어떤 이상으로 배가 아픈지 의심해 본다.
a-신장, b-요관.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
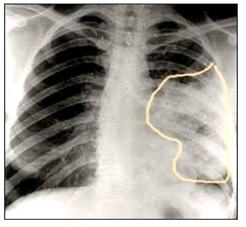
사진 145. 배가 아프면서 기침할 때는 폐렴 등 호흡기 이상으로 배가 아픈지 의심해 본다. 왼쪽 폐(선으로 표시한 부분)에 폐렴이 있다. 폐렴이 있어도 배가 아프다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
학령기 아이들이나 사춘기 아이들에게 생길 수 있는 복통
① 바이러스 위장염이나 박테리아 위장염,
② 음식물로 생긴 위장관 음식물 알레르기,
③ 변비증,
④ 흥분성 위장관 증후군,
⑤ 정신적 불안,
⑥ 소화기계통의 복강 내 장기 이외 신체의 다른 계통의 장기에 생기는 바이러스 감염병이나 박테리아 감염병 등이 복통의 주원인이 될 수 있다.
⑦ 사춘기 여아들의 복통의 주원인은 월경통(생리통)이다.
⑧ 드물게는 복성 편두통으로 인한 복통이 사춘기 아이들에게 있을 수 있다.
⑨ 임신
⑩ 자궁 내막증
⑪ 그 외
복통의 증상 징후
-
복통은 어떤 병의 증상 징후이지 병명은 아니다. 복통을 일으킨 원인에 따라 복통의 정도와 증상 징후가 다르다.
-
영유아들은 배가 아프다는 것을 말로 정확히 표현할 수 없다. 그 대신 배가 아프면 울고 보채고 모유나 인공영양 등을 조금 먹든지 조금도 먹지 않을 수 있다. 배만 아플 수 있고 구토 설사 열 등을 동반할 수 있다.
-
전에 자녀를 양육했던 경험이 있는 부모들은 어려서 의사를 말로 표현할 수 없는 영유아들이 무슨 이유로든 울 때 울음소리의 음색과 음량을 듣고 또 그들의 신체 언어를 통해 어디가 아파서 우는 지, 배가 고파서 우는 지, 또는 다른 이유로 우는 지를 대략 짐작할 수 있다.
-
말로 어느 정도 자기들의 의사를 표현할 수 있는 유아들은 배가 아프면 배 어디가 아프다고 또 어떻게 아픈지 어느 정도로 정확히 알려줄 수 있다.
-
그러나 어떤 유아들은 배가 아픈 것과 배가 고픈 것을 확실히 분별할 수 없다.
-
부모의 사랑과 집중적 관심적 보살핌을 충분히 받지 못하고 자라는 아이들의 일부는 부모의 사랑, 보살핌과 관심사를 더 얻기 위해 정신적으로 심리적으로 배가 아프다고 호소할 수 있다. 이런 경우를 꾀병을 한다고 어떤 부모들은 말한다. 그렇지만 꾀병을 한다고 해서 그대로 놓아두어서는 안 된다. 꾀병하는 이유가 꼭 있기 때문에 그 이유를 알아서 그에 대처해야 그 아픈 것이 낫기 때문이다.
-
어떤 이유로든 등교하기 싫어하거나 공부하기를 싫어하면 무의식적으로 배가 아플 수 있다.
-
배가 고프지도 않을 때나 먹기 싫을 때 음식물을 먹으라고 강요당할 때도 배가 아프다고 호소할 수 있다.
-
어떤 아이는 정신적으로 육체적으로 아주 건강하지만 배가 아프다고 자주 호소하면서 음식물을 평소와 같이 잘 먹고 잘 뛰어 놀기도 한다.
-
바이러스나 박테리아, 또는 그 외 다른 병원체의 감염으로 생긴 위장염으로 복통, 구역질, 구토, 설사, 열 등이 생길 수 있다.
-
충수염의 초기에는 오목가슴이 조금 아프다가 시간이 지나면 오른쪽의 아래 복부가 더 심하게 아픈 것이 특징이다.
-
위장, 신장, 비장, 간장 등 복강 내 기관에 생긴 외상이나 내상으로 심한 복통이 생길 수 있다.
-
류마티스 열, 류마티스 관절염 등으로 복통이 생길 수 있고 류마티스 열이나 류마티스 관절염으로 복통이 생길 때는 류마티스 열이나 류마티스 관절염으로 생기는 공존 증상들과 함께 있는 것이 보통이다.
-
당뇨병으로도 복통이 생길 수 있다. 이때는 음식물을 많이 먹고, 음료수를 많이 마시고, 소변을 자주 많이 보는 증상이 동반된다.
-
변비증으로 생긴 복통은 변비 변을 본 후에는 그 복통이 사라지는 것이 보통이다.
-
우유, 초콜릿 또는 달걀 등의 음식물을 먹고 위장관 음식물 알레르기로 복통이 생길 수 있다. 이때는 알레르기를 일으켰던 음식물을 먹을 때마다 복통이 더하거나 재발되는 것이 보통이다. 그리고 알레르기를 일으킨 음식물을 더 이상 먹지 않으면 복통이 더 이상 생기지 않는 것이 보통이다.
-
위장관 음식물 알레르기로 배가 자주 아픈 아이들에게는 기관지 천식이나 알레르기 비염 , 또는 아토피성 피부염 등 다른 종류의 알레르기 질환이 신체 다른 기관이나 장기에 동시에 있을 수 있다.
복통의 진단
-
복통이 얼마나 오랫동안 지속되는지, 배가 아플 때 다른 증상 징후의 유무, 과거에도 비슷한 복통의 병력, 진찰소견 등을 종합해서 복통의 원인을 찾아본다.
-
다음과 같은 복통에 관한 증상 징후의 정보를 많이 가능한 한 정확하게 의사에게 알리면 복통의 원인을 더 쉽게 찾고 더 정확하게 진단해서 효과적으로 치료할 수 있다.
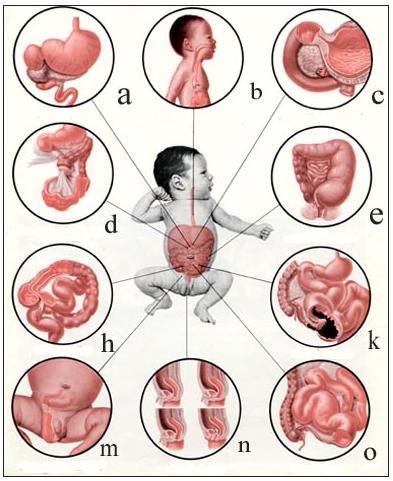
그림 146. 신생아들과 신생아기 이후 영아들에게 생길 수 있는 장 폐쇄의 원인
a-윤상 췌장, b-선천성 식도폐쇄증과 기관 식도 누관, c-비후성 유문 협착증, d-장축염증, e-선천성 거대결장, h-장중첩증, k-태변성 장폐색증, l-감돈 된 오른쪽 서혜부 탈장증, m-여러 종류의 쇄항증, n-소장폐쇄증. Used with permission from Ross Laboratories, Columbus, Ohio 43216 와 소아가정간호백과
① 배가 얼마 동안 아팠는지, 갑자기, 또는 서서히 아프기 시작했는지
② 음식물을 먹기 전부터, 또는 음식물을 먹는 중 배가 아팠는지, 아니면 먹고 난 후 배가 아프기 시작했는지, 특정 음식물을 먹으면 배가 더 아픈지
③ 간헐적으로 배가 아픈지, 또는 지속적으로 배가 아픈지
④ 배가 조금 아픈지 또는 심하게 아픈지
⑤ 신체 다른 계통의 어느 부위는 하나도 아프지 않고 소화기계통에 속한 배만 아픈지, 아니면 배와 신체 다른 부위가 동시 아픈지
⑥ 배가 아프면서 감기나 다른 계통에 있는 호흡기의 어딘가에 질환 등 앓는지
⑦ 구토와 설사와 열 등의 증상이 함께 있으면서 배가 아픈지, 변비증이 있으면서 배가 아픈지
⑧ 소변을 자주 보면서 또는 소변을 볼 때 힘들고 아프면서 배가 아픈지
⑨ 복부 타박상을 입은 후에 배가 아픈지
⑩ 부모나 자녀 자신이 정신적으로 불안하면서 배가 아픈지
⑪ 기능적 복통은 우울증이 있거나 정신이 불안한 아이들에게 더 잘 생기고 그들의 엄마에게도 거의 같은 복통의 현재나 과거 병력이 있는 경우가 많다.
아이가 배가 아프면서 다음과 같은 병력이 있는지.
⑫ 항생제나 다른 어떤 약물을 쓸 때 배가 아픈지
⑬ 월경 이상(생리 이상)이 있는지
⑭ 비정상 질 분비물이 있으면서 복통이 있는지
⑮ 성교한 후 복통이 있는지
⑯ 규칙적으로 하던 월경을 몇 달 거르면서 복통이 있는지
⑰ 그 외 복통에 관련된 증상 징후 정보 등을 의사에게 알리면 복통의 원인을 더 쉽게 찾아낼 수 있고 진단 치료를 더 효율적으로 할 수 있다.
위에 열거한 복통에 관련된 여러 가지 사항과 복통의 특징 등에 관한 정보, 진찰소견, 여성의 내진 결과 등을 종합하여 복통의 원인을 진단한다.
때에 따라 피, 대소변 검사, 가슴이나 위장관 X-선 사진, 복강 내 기관들의 초음파검사, CT 스캔 검사, MRI 검사 등으로 복통의 원인을 진단할 수 있다.
복통의 치료
-
생명에 위험한 병으로 복통이 생길 수 있고, 또 생명에 위험하지 않은 병으로도 복통이 생길 수 있다.
-
그러므로 복통의 원인을 확실히 찾아 치료해 주어야 한다.
-
복통의 원인과 정도에 따라 치료한다.
-
때로는 신체검사와 임상 검사를 여러 번 반복해도 복통의 원인을 확실히 찾지 못할 수 있다.
-
그와 반대로 아무런 치료를 해 주지 않아도 저절로 낫는 복통도 많다.
-
기능적 복통은 Peppermint oil로 치료하고, 흥분성 위장 증후군으로 생기는 복통은 Hyosycamine이나 Dicyclomin(Bentyl)제로 치료하고 변비로 생기는 복통은 변비 치료약으로, 설사로 생기는 복통은 Loperaminde(Immodium)제 등으로 대증 치료를 할 수 있다.
-
기능적 소화불량은 Ranitidine(Zantac)이나 Lansoprazole(Prevacid)제 등으로 치료하고
-
복성 편두통은 Cyproheptadine (Periactin)나 Propranol (Inderal)제 등으로 치료한다. 급성 복부질환의 감별진단 Diferencial diagnosis of acute abdomen 참조
|
다음은“복통, 열 ”에 관한 인터넷 소아청소년 건강상담 질의응답의 예 입니다. |
Q&A. 복통, 열에 대하여
Q.
35개월 된 남자아이의 아빠입니다.
지난 토요일 13일 오후에 점심에 냉면을 조금 먹은 후부터 배가 심하게 아프다고 합니다.
병원에서는 자세한 설명 없이 장에 가스가 차서 그렇다고 하며 약을 주었지만 호전되지 않아서 이렇게 상담드립니다.
혹시 맹장염이 아닌 지 걱정도 되고 신문에서 봤던 복통감기가 아닌가도 의심이 됩니다.
증상은 39.9도까지 가는 고열이 나고 배가 아프다고 합니다.
열이 나서 해열제를 먹이면 괜찮아지고 또 얼마 후에 열이 납니다.
맹장염과 복통감기의 증상에 대하여 알고 싶고 자세한 대처방안도 알려 주십시오.
A.
숙이님
안녕하세요. 질문해 주셔서 감사합니다. 좋은 질문입니다.
나이, 성별, 과거 병력, 가족 병력, 진찰소견, 임상검사 등의 정보를 많이 알수록 답변을 드리는데 도움이 됩니다. 주신 정보를 토대로 해서 답변을 드리겠습니다.
이미 문제를 해결하셨을 줄 믿습니다마는 참고로 말씀드리겠습니다.
열이 나면서 배가 아픈 증상이 있는 병은 숫하게 많습니다. 그런 복통이 여러 종류의 질병으로도 생길 수 있습니다. (p.000 복통 참조)
가령 박테리아 감염, 바이러스 감염, 또는 캠프로백터 감염 등으로 인한 위장염을 비롯해서 편도염, 폐렴, 뇌막염 등으로 배가 아프고 열이 날 수 있습니다.
식중독, 요로 감염, 간염, 류마티스 열 등으로 배가 아프고 열이 날 수 있습니다.
그 외 더 많은 원인으로 인해 배가 아프고 열이 날 수 있습니다.
맹장염이란 말은 충수염을 말하시는 줄로 압니다. 충수염이 있을 때도 배가 아프고 열이 날 수 있습니다. 복통 감기는 무엇인지 잘 몰라 답변드릴 수 없습니다.
소아청소년과에서 진단을 받으시고 이런 문제에 관해서 상담하시기 바랍니다.
복통, 맹장염, 위장염. [부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다–소아가정간호백과]-제22권 아들 딸 이렇게 사랑해 키우세요–열 등을 참조하시기 바랍니다.
질문이 더 있으면 다시 연락해 주시기 바랍니다. 감사합니다. 이상원 드림
Abdominal pain 복통
Types and causes of abdominal pain
• It is said that 2-4% of pediatric and adolescent patients come to the outpatient pediatrics department with acute abdominal pain or chronic abdominal pain.
• Abdominal pain may be classified as acute or chronic abdominal pain, or functional abdominal pain or organic abdominal pain. It is classified as recurrent abdominal pain, persistent abdominal pain, or intermittent abdominal pain.
• It is also classified as abdominal pain due to excitable gastrointestinal syndrome, abdominal pain due to functional dyspepsia, and abdominal pain due to abdominal migraine.

Figure 143. Abdominal landmarks a-apical region, b-upper right abdomen, c-upper left abdomen, d-lower right abdomen, e-lower left abdomen, h-lower abdomen, g-belly If you have a stomach ache, instead of just telling your doctor that your stomach hurts, you can tell your doctor that something in your stomach hurts, so your doctor can more easily find and diagnose the cause of your stomach pain. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
① Pain in the stomach is called abdominal pain.
② Abdominal pain is a symptom of a disease, not a disease name.
③ If you have abdominal pain, you need to know what the cause is so that you can effectively treat abdominal pain. However, more often than not, it is not clear what causes abdominal pain.
④ Chronic abdominal pain that lasts for several weeks or longer,
⑤ Suddenly, acute abdominal pain that lasts for minutes to hours, or for several days, ⑥ Very mild abdominal pain, abdominal pain very severely painful enough to break the intestines,
⑦ Abdominal pain that occurs mainly in infants and toddlers, Abdominal pain that occurs primarily in school-age children or adolescent children, or abdominal pain that occurs primarily in adults
⑧ Abdominal pain that occurs mainly in girls and abdominal pain that occurs mainly in boys
⑨ Abdominal pain caused by organic diseases in the abdominal cavity such as appendicitis
⑩ Pneumonia can cause abdominal pain. In this way, abdominal pain can occur due to an organic disease that occurs in organs other than the digestive system.
⑪ There is no organic illness in the body, but abdominal pain can occur due to emotional and mental problems. This abdominal pain is called functional abdominal pain.
⑫ Also, abdominal pain may occur due to a disease in the organs of the digestive system in the abdominal cavity, or abdominal pain may occur due to an abnormality in the chest cavity or cranial cavity that occurs in an organ other than the digestive system. To others
⑬ abdominal pain caused by food allergy, ⑭ Abdominal pain caused by overeating of food, ⑮ Abdominal pain caused by eating foods that do not fit your age and constitution, ⑯ Abdominal pain caused by lactose intolerance caused by a lack of lactose-degrading enzymes,
⑰ abdominal pain caused by excitatory gastrointestinal syndrome, ⑱ abdominal pain due to abdominal migraine,
⑲ abdominal pain caused by constipation,
⑳ Abdominal pain caused by gastric ulcer (peptic gastric ulcer or duodenal ulcer)
㉑ abdominal pain caused by cholelithiasis,
㉒ urolithiasis or abdominal pain caused by urinary tract infections. Adolescent girls can experience abdominal pain due to menstruation and pregnancy.
㉓ mental-emotional problems,
㉔ constipation
㉕ Children and adolescents have abdominal pain due to lactose intolerance or gastrointestinal allergy after eating milk or foods containing milk.
㉖ There are so many causes of abdominal pain in children, so it is impossible to list all of the causes of abdominal pain in one book.
㉗ Here, we will explain the more common causes of abdominal pain in children and adolescents, their symptoms, and the diagnosis.
www.drleepediatrics.com-Volume 1 Children and Adolescent Emergency Medical Services-Refer to Acute Abdominal Disease. Causes of abdominal pain in newborns and pre-first-birth infants
There are many causes of abdominal pain in newborns and infants, including: them,
① Infant colic,
② Allergic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract caused by food, especially food containing milk protein,
③ Abdominal pain may occur due to gastroenteritis caused by viral infection or bacterial infection,
④ Abdominal pain may occur due to viral infections or bacterial infections that occur in organs of other systems in other parts of the body other than the organs in the abdominal cavity of the digestive system. ⑤ In rare cases, abdominal pain may occur due to appendicitis, intestinal dysphoria (intestinal overlap), trauma to the stomach, kidneys, and liver.
⑥ When receiving erythromycin or other types of antibiotic treatment, or other types of drugs,
⑦ When you are mentally anxious,
⑧ When eating baby food that is not appropriate for your age,
⑨ Eating too much baby food can cause abdominal pain.
⑩ Newborns and infants who feed on the mother’s mentally unstable mother may also have abdominal pain.
Causes of abdominal pain in infants from the first birthday to preschool age
① viral gastroenteritis or bacterial gastroenteritis,
② Allergies to food (food) in the gastrointestinal tract caused by ingestion of milk, chocolate or other foods,
③ mental anxiety,
④ constipation,
⑤ excitable gastrointestinal syndrome,
⑥ Abdominal pain can occur due to various types of viral infections or bacterial infections that occur in organs of other systems in other parts of the body other than the organs in the abdominal cavity of the digestive system.
⑦ Pneumonia, tonsillitis, appendicitis, intestinal overlap, spleen rupture, gastrointestinal rupture, hepatitis, pancreatitis, nephritis, rheumatic fever, diabetes, drug addiction, food poisoning, urolithiasis, etc. can cause abdominal pain.

Picture 144. Especially, if a child has a stomachache, try to suspect something of a stomach ache caused by an abnormality in the urinary tract. a-kidney, b-ureter. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Photo 145. When coughing while having a stomachache, try to suspect whether the stomach hurts due to respiratory abnormalities such as pneumonia. There is pneumonia in the left lung (marked with a line). Even with pneumonia, the stomach hurts. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
Abdominal pain that can occur in school-age or adolescent children
① viral gastroenteritis or bacterial gastroenteritis,
② Gastrointestinal food allergy caused by food,
③ constipation,
④ excitable gastrointestinal syndrome,
⑤ mental anxiety,
⑥ Viral infections or bacterial infections that occur in organs of the body other than the organs in the abdominal cavity of the digestive system can be the main cause of abdominal pain.
⑦ The main cause of abdominal pain in adolescent girls is menstrual pain (menstrual pain).
⑧ Rarely, abdominal pain due to abdominal migraine may be present in adolescent children. ⑨ pregnancy ⑩ endometriosis
⑪ Others
Symptoms signs of abdominal pain
• Abdominal pain is a symptom of a disease, not a disease name. The severity and symptoms of abdominal pain differ depending on the cause of the abdominal pain.
• Infants and toddlers cannot accurately describe in words that they have a stomachache. Instead, if your stomach hurts, you may cry and feel sick, and you may eat a little breast milk or artificial nutrition, or not eat at all. It can only cause stomach pain and can be accompanied by vomiting, diarrhea, and fever.
• Parents with previous experience raising children can hear the tone and volume of crying when infants and toddlers who are young and unable to verbally express their intentions for any reason and use their body language to see where they are crying for being sick, or crying because of hunger, or You can roughly guess if you are crying for another reason.
• Infants who can express their intentions to some extent in words can tell exactly where and how they hurt when they have a stomach ache.
• However, some infants cannot clearly tell between being hungry and hungry.
• Some of the children who grow up lacking enough parental love and intensive care may complain of mentally and psychologically hunger in order to gain more parental love, care, and interest. Some parents say that they are faking sickness in this case. However, if you are faking a disease, you should not leave it alone. Because there is a reason for faking sickness, you must know the reason and deal with it to heal the pain.
• If you hate to go to school or to study for any reason, you may unconsciously get a stomachache. • You can complain that you are hungry even when you are forced to eat when you are not hungry or when you do not like to eat.
• Some children are very healthy mentally and physically, but often complain that they have a stomachache, eat well and play well as usual.
• Gastroenteritis caused by infection with viruses, bacteria, or other pathogens can cause abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and fever.
• In the early stages of appendicitis, the concave chest hurts a little, but over time, the lower right abdomen hurts more severely.
• Severe abdominal pain may occur due to trauma or internal injuries to organs in the abdominal cavity, such as the stomach, kidneys, spleen, and liver
. • Abdominal pain may occur due to rheumatoid fever or rheumatoid arthritis, and when abdominal pain occurs due to rheumatoid fever or rheumatoid arthritis, it is usually accompanied by coexisting symptoms caused by rheumatoid fever or rheumatoid arthritis. • Diabetes can also cause abdominal pain. This is accompanied by symptoms of eating a lot of food, drinking a lot of beverages, and urinating a lot.
• Abdominal pain caused by constipation usually disappears after seeing constipation.
• Eating foods such as milk, chocolate, or eggs and food allergies in the gastrointestinal tract can cause stomach pain. At this time, it is common for abdominal pain to increase or recur every time the food that caused the allergy is eaten. And if you no longer eat the food that caused the allergy, it is common for abdominal pain to no longer occur.
• Children with frequent stomachaches from gastrointestinal food allergies may have other types of allergic diseases such as bronchial asthma, allergic rhinitis, or atopic dermatitis at the same time in different organs or organs of the body.
Diagnosis of abdominal pain
• Find out the cause of abdominal pain by comparing how long abdominal pain lasts, the presence of other symptoms when the stomach ache, history of similar abdominal pain in the past, and examination findings.
• By giving your doctor as much information as possible about the symptoms and signs of abdominal pain, such as the following, you can find the cause of abdominal pain more easily, diagnose it more accurately, and treat it effectively.

Figure 146. Causes of intestinal obstruction in newborns and postnatal infants a-Critic pancreas, b-congenital esophageal obstruction and tracheal esophageal fistula, c-hypertrophic pyloric stenosis, d-intestinal axial inflammation, e-congenital giant colon, h-intestinal obstruction, k-meconium intestinal obstruction, l-contained right inguinal hernia , m-several types of ataxia, n-small intestinal obstruction. Used with permission from Ross Laboratories, Columbus, Ohio 43216 and Pediatric Home Nursing Encyclopedia
① How long did the stomach hurt, suddenly, or slowly?
② Does the stomach hurt before eating or while eating, whether the stomach started aching after eating, or whether the stomach hurts more when eating certain foods? ③ Whether the stomach hurts intermittently or continuously
④ Whether the stomach hurts a little or severely
⑤ Doesn’t any part of the body hurt, but only the stomach belonging to the digestive system, or does the stomach and other parts of the body hurt at the same time?
⑥ Whether you are suffering from a cold or other diseases of the respiratory system while your stomach hurts
⑦ If symptoms such as vomiting, diarrhea, and fever are present together, does the stomach hurt, constipation and stomach pain?
⑧ Is your stomach ache while urinating often or when you urinate?
⑨ Does the stomach hurt after suffering an abdominal bruise?
⑩ Parents or children themselves are mentally anxious and have a stomachache
⑪ Functional abdominal pain is more common in children with depression or anxiety, and their mothers often have a current or past history of abdominal pain. If the child has a stomachache and has the following medical history:
⑫ Does your stomach hurt when using antibiotics or any other medication?
⑬ Are there any menstrual abnormalities (menstrual abnormalities)?
⑭ Abnormal vaginal discharge and abdominal pain
⑮ If you have abdominal pain after intercourse ⑯ How many months have you skipped your regular menstruation to see if you have abdominal pain?
⑰ If you inform the doctor of other symptoms and signs related to abdominal pain, the cause of abdominal pain can be more easily identified and diagnostic treatment can be performed more efficiently.
The cause of abdominal pain is diagnosed by synthesizing the various items related to abdominal pain listed above, information on the characteristics of abdominal pain, examination findings, and the results of a woman’s seismic examination. Sometimes, blood and urine tests, chest or gastrointestinal X-rays, ultrasound of the abdominal organs, CT scans, MRIs, etc. can diagnose the cause of abdominal pain.
Treatment of abdominal pain
• A life-threatening illness can cause abdominal pain, and a non-life-threatening illness can cause abdominal pain.
• Therefore, it is necessary to find and treat the cause of abdominal pain. • Treat according to the cause and severity of abdominal pain.
• Sometimes physical and clinical tests can be repeated several times and the cause of abdominal pain cannot be determined.
• On the contrary, many abdominal pains heal on their own without any treatment.
• Functional abdominal pain is treated with Peppermint oil, abdominal pain caused by excitable gastrointestinal syndrome is treated with Hyosycamine or Dicyclomin (Bentyl), abdominal pain caused by constipation is treated with constipation medicine, and abdominal pain caused by diarrhea is symptomatic with Loperaminde (Immodium). can do. • Functional indigestion is treated with Ranitidine (Zantac) or Lansoprazole (Prevacid). • Abdominal migraine is treated with Cyproheptadine (Periactin) or Propranol (Inderal). See Differential diagnosis of acute abdomen.
The following is an example of an Internet pediatric and adolescent health counseling question and answer on “Stomach Pain, Fever”.
Q&A. About abdominal pain and fever
Q. This is the father of a 35-month-old boy. After eating a little naengmyeon for lunch on the afternoon of the 13th on Saturday, the stomach is said to be very sick. The hospital said that it was because the intestine was filled with gas without a detailed explanation, and the medicine was given, but it did not improve.
He’s worried about whether it’s appendicitis, and whether it’s the abdominal cold he saw in the newspaper.
Symptoms are said to have a high fever that goes up to 39.9 degrees Celsius and a stomachache. If you take antipyretics because you have a fever, it will be okay, and after a while you will get a fever. You would like to know about the symptoms of appendicitis and abdominal cold, and also provide detailed measures for coping.
A.
Bent Good morning.
Thanks for asking. That’s a good question. The more information you know about age, gender, past medical history, family medical history, medical examination findings, clinical examination, etc., the more helpful it is to give you an answer. We will respond based on the information you provided. I believe you have already solved the problem, but I will tell you for your reference. There are a number of illnesses that have symptoms of stomach pain with fever. Such abdominal pain can also result from many types of illness. (See Abdominal Pain) For example, gastroenteritis due to bacterial infection, viral infection, or campylobacter infection, as well as tonsillitis, pneumonia, meningitis, etc. can cause stomach aches and fever. Food poisoning, urinary tract infections, hepatitis, rheumatic fever, etc. can cause stomach aches and fever.
Many other causes can cause stomach aches and fever. I know that the word appendicitis means appendicitis.
Even with appendicitis, your stomach may ache and have a fever. We can’t answer you because you don’t know what a cold is. Get a diagnosis at the Department of Pediatrics and Adolescents and consult with you about these problems. Abdominal pain, appendicitis, gastroenteritis. www.drleepediatrics.com-Vol. 22 Sons and Daughters So Love and Raise-Please refer to Fever. If you have more questions, please contact us again. Thank you. Lee Sang-won. MD
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제9권 소아청소년 소화기 질환
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th — 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
-
[부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다–소아가정간호백과]-제1권 소아청소년 응급의료–급성 복부 질환(배가 갑자기 아플 때) Acute abdominal pain, Acute abdomen 참조
-
소화불량 Indigestion, Dyspepsia 참조
-
위궤양이나 십이지장 궤양으로 갑자기 배가 아플 때 Acute abdominal pain due to gastric peptic ulcer or duodenal peptic ulcer 참조
-
위나 십이지장 궤양 천공 Perforation of peptic ulcer of stomach or duodenum 참조
-
장 폐쇄증 Intestinal obstruction 참조
-
충수염 Appendicitis 참조
-
비장 파열 Splenic rupture, Ruptured spleen, Rupture of spleen 참조
-
급성 복부질환의 감별진단 Diferencial diagnosis of acute abdomen 참조
-
Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, harvey grant and robert murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
-
The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
-
Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies , Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care
-
응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
-
Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
-
Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
-
Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gerhon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
-
소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”