백내장 Cataract
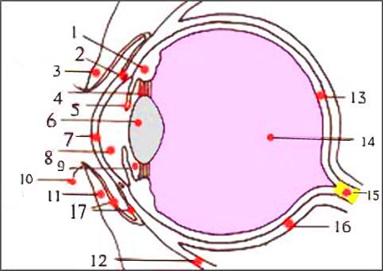
그림 94. 눈의 해부도
1-모양체,
2-쉴렘관,
3-윗 눈꺼풀,
4-렌즈 소대(지지인대),
5-홍채,
6-수정체(렌즈),
7-각막,
8-전방,
9-후방,
10-눈썹,
11-아랫 눈꺼풀,
12-안구 하직근,
13-망막,
14-초자체,
15-시각신경,
16-공막,
17-아래 결막
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
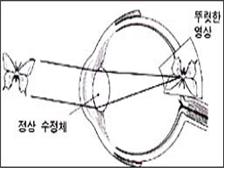
그림 95. 정상 눈으로 본 나비영상
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
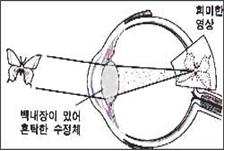
그림 96. 백내장이 있는 눈으로 본 나비 영상
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D. FAAP

그림 97. 정상 눈으로 볼 때
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
그림 98. 심한 백내장이 있는 눈으로 볼 때
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
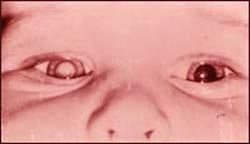
사진 99. 오른쪽 눈에 백내장이 생겨 있다
Courtesey of Dr. Maynard B. Wheeler 제공
백내장의 원인
-
한개 안구 속에는 한 개의 수정체가 들어 있다.
-
수정체(렌즈)는 정상적으로 투명하고 맑다.
-
어떤 원인으로 눈의 렌즈가 혼탁 된 상태를 백내장이라 한다.
-
렌즈의 전면의 바로 앞에는 후방, 그 다음으로 전방, 그리고 각막 등이 있고,
-
렌즈의 후면에는 초자체가 있다(그림 94참조).
-
렌즈는 안구 밖에서 들어오는 물체의 영상을 적절히 굴절시켜 안구의 맨 뒤에 있는 망막에 영상을 보내는 역할을 한다.
-
안구로 들어온 영상이 투명하고 맑은 렌즈를 통과해야 뚜렷한 영상이 망막에 정상적으로 만들어지게 된다.
-
그러나 혼탁 된 렌즈가 있을 때는 안구로 들어온 영상이 혼탁 된 렌즈를 통과한 후 망막에 희미한 영상이 만들어 지게 된다.
-
백내장으로 렌즈의 일부나 대부분이 혼탁 될 수 있다. 그래서 영상의 일부나 전부가 희미하게 될 수 있다.
-
백내장이 렌즈의 일부에만 있을 때는 대부분의 렌즈는 혼탁 되어 있지 않고 렌즈의 일부만 혼탁 되어 있다.
-
때문에 백내장이 있을 때 백내장으로 시력의 일부만 상실되든지 시력에 아무런 지장을 주지 않을 수 있다.
-
한쪽 눈에 생긴 백내장이 다른 쪽 눈으로 번지지 않지만 백내장이 양쪽 눈에 동시에 생길 수 있다.
-
대부분의 백내장은 몇 개월 내지 몇 년을 두고 서서히 생기는 것이 보통이다.
-
백내장의 원인은 노쇠, 눈의 외상, 눈 이 외 신체 다른 부위에 생긴 병, 유전 등이다.
-
생화학 물질이나 단백질이 렌즈에 침적되어 백내장이 생기기도 한다.
-
임신 첫 3개월 동안 임산부가 풍진을 앓을 때 풍진 바이러스가 태아에게 감염되면 태아가 풍진 증후군에 걸릴 수 있다.
-
이 때 태아의 렌즈에 백내장이 생길 수 있다.
-
출생 이후 눈에 타박상, 열상, 천공, 그 외 다른 종류의 외상이 눈에 생길 때, 화학 물질 등으로 눈이 데었을 때, 또는 당뇨병이 있을 때, 병원체 감염으로 생긴 안구염 등으로 백내장이 생길 수 있다.
백내장의 증상 징후
-
백내장이 렌즈의 일부 또는 전체에 생겨 있는지, 렌즈 혼탁의 정도, 렌즈 혼탁이 렌즈의 어느 부위에 생겨 있는지 등에 따라 증상 징후가 다르다.
-
렌즈 혼탁이 렌즈의 가장자리에만 조금 있을 때는 시력 장애가 조금 생기든지 거의 생기지 않는다.
-
그렇지만 렌즈의 중앙 부위에 백내장이 조금 있어도 렌즈에 혼탁이 생겨 시력 장애가 심하게 생길 수 있다.
-
렌즈의 일부가 혼탁 되서 생긴 백내장의 초기에는 시력 장애가 경미하미하게 생길 수 있고 렌즈의 혼탁이 점점 더 심해질 때는 그 정도에 따라 시력 장애가 점점 더 심해질 수 있다.
-
백내장이 있으면 하나의 물체가 둘로 보일 수 있고 눈이 불빛에 과민하고, 책을 눈앞에 바짝 대고 읽는 경향이 있다.
-
정상적으로 까맣던 눈동자의 색이 노랗거나 하얗게 변할 수 있다.
백내장의 진단
-
병력·증상 징후와 진찰소견 등을 종합해서 진단한다.
-
백내장이 경미할 때는 아무 증상도 없고 시력 장애도 거의 없다.
-
이 때 정밀 눈 검사를 하지 않고서 백내장이 있는지 알 수 없다.
-
어떤 경미한 백내장은 몇 달 내지 몇 년을 두고 아주 서서히 생긴다.
-
백내장이 심할 때는 육안으로 보아도 백내장이 있는지 알 수 있지만 백내장이 경미할 때는 백내장이 있는지 없는지 육안으로 보고 쉽게 알 수 없다.
-
아이들에 시력 장애가 있든지 무엇을 잘 볼 수 없을 때는 안과 전문의나 소아청소년과 전문의의 시력과 눈 검사를 받고 백내장 등이 있는지 알아봐야 한다.
-
안과 전문의는 경미한 초기 백내장이 있을 때도 특수 안과 의료기구로 조기에 백내장을 쉽게 진단할 수 있다.
백내장의 치료
-
백내장의 원인과 백내장의 정도에 따라 치료한다.
-
스테로이드제를 장기간 복용하거나 눈에 바르면 백내장이 생길 수 있다.
-
어떤 경우든 스테로이드제는 의사의 처방에 따라서 써야 한다.
-
우유섭취가 백내장의 원인이 될 수 있다. 이때는 우유를 더 이상 먹지 말아야 한다.
-
백내장이 심할 때는 혼탁 렌즈를 수술로 제거해서 백내장을 치료할 수 있다.
-
혼탁 렌즈를 제거한 후 인공렌즈나 콘택트렌즈 또는 안경 등으로 치료할 수 있다.
-
시력에 큰 지장을 주지 않는 경미한 백내장은 의사의 지시에 따라 정기적으로 시력과 눈 검사를 받으면서 백내장의 진행 정도를 면밀히 관찰한다.
Cataract 백내장

Figure 94. Anatomy of the eye 1 – ciliary body, 2 – Schlemm’s Hall, 3 – upper eyelid, 4-lens platoon (support ligament), 5 – iris, 6 – lens (lens), 7 – cornea, 8 – anterior, 9 – rear, 10 – eyebrows, 11 – lower eyelid, 12 – inferior rectus eye muscle, 13 – retina, 14 – vitreous, 15 – optic nerve, 16 – sclera, 17 – lower conjunctiva Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP

Figure 95. Butterfly image seen with normal eyes Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP

Figure 96. Image of a butterfly seen with a cataracted eye Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D. FAAP

Figure 97. Normal Eye View Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP

Figure 98. Viewed by an eye with severe cataracts Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP

Picture 99. I have a cataract in my right eye Courtesy of Dr. Courtesy of Maynard B. Wheeler
Causes of Cataracts
• One lens contains one lens.
• The lens (lens) is normally transparent and clear.
• A condition in which the lens of the eye becomes cloudy for some reason is called a cataract.
• Immediately in front of the anterior surface of the lens is the posterior, then the anterior, and the cornea,
• The back of the lens has a vitreous body (see Figure 94).
• The lens properly refracts the image of an object coming from outside the eyeball and sends the image to the retina at the back of the eyeball.
• The image that enters the eye must pass through a transparent and clear lens so that a clear image is normally created on the retina.
• However, when there is a cloudy lens, the image entering the eye passes through the cloudy lens and a faint image is created on the retina.
• Cataracts can cloud part or most of the lens. So some or all of the image may be blurred.
• When the cataract is only part of the lens, most lenses are not cloudy and only part of the lens is cloudy.
• Because of this, when you have a cataract, you may lose only part of your vision or your vision may not be affected.
• Cataracts in one eye do not spread to the other, but cataracts can occur in both eyes at the same time.
• Most cataracts usually develop slowly over months or years.
• The causes of cataracts are aging, eye trauma, diseases other than the eyes, and heredity.
• Biochemicals or proteins can deposit on the lens, causing cataracts.
• If a pregnant woman has rubella during the first three months of pregnancy and the rubella virus infects the fetus, the fetus can develop rubella syndrome.
• At this time, cataracts may develop in the fetal lens.
• After birth, bruises, lacerations, perforations, or other trauma to the eye, chemical burns, diabetes, or cataracts due to pathogenic infections. can Cataract Symptoms Signs • Symptoms vary depending on whether the cataract is part or all of the lens, the degree of lens opacity, and where the lens opacity is located.
• When there is only a small amount of lens opacity at the edge of the lens, there is little or no visual impairment.
• However, even a small amount of cataract in the center of the lens can cause clouding of the lens and cause severe visual impairment.
• In the early stages of cataracts caused by the opacity of a part of the lens, there may be mild visual disturbances, and as the opacity of the lens becomes more severe, the visual impairment may become more severe depending on the severity.
• If you have a cataract, you may see one object as two, your eyes are sensitive to light, and you tend to read books close to your eyes.
• The color of the normally black eyes may change to yellow or white.
Diagnosis of Cataracts
• Diagnosis is made by combining medical history, symptoms, signs, and examination findings.
• When the cataract is mild, there are no symptoms and little or no visual impairment.
• You can’t tell if you have a cataract without doing a thorough eye exam at this time.
• Some mild cataracts develop very slowly over months or years.
• When the cataract is severe, it can be seen with the naked eye, but when the cataract is mild, it is difficult to tell whether or not there is a cataract with the naked eye.
• If your child has a vision impairment or cannot see well, they should have their eyes and eyes checked by an ophthalmologist or pediatrician to see if they have cataracts or the like.
• Ophthalmologists can easily diagnose cataracts at an early stage with special ophthalmic medical instruments, even with mild early cataracts.
Cataract treatment
• Treatment depends on the cause and severity of the cataract.
• Taking steroids for a long time or applying them to the eyes can cause cataracts. • In any case, steroids should be used according to the doctor’s prescription.
• Milk consumption can cause cataracts. At this point, you should no longer drink milk.
• If the cataract is severe, the opacifying lens may be surgically removed to treat the cataract.
• After removing the opaque lens, it can be treated with artificial lenses, contact lenses, or glasses.
For mild cataracts that do not significantly affect vision, follow your doctor’s instructions for regular eye and eye exams and closely monitor the progression of the cataract.
출처 및 참조문헌
-
Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, Harvey grant, and Robert Murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
-
The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
-
Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care
-
응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
-
Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
-
Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
-
Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
-
Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics 14th ed. Beherman,
-
The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 18th edition
-
Red book 29th edition 2012
-
Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th Edition
-
Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
-
소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”