발작성 빈박, 발작성 심방 빈박, 발작성 방실 결절 빈박, 발작성 심실 빈박 Paroxysmal tachycardia, Paroxysmal atrial tachycardia, Paroxysmal atrioventricular tachycardia, Paroxysmal ventricular tachycardia
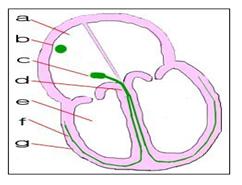
그림 66. 정상 심장 자극 전도계
a-심방, b-동방 결절, c-방실 결절, d-히스 속, e- 심실, f-푸르키니에 망상섬유, g-심근
Copyright ⓒ 2013 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
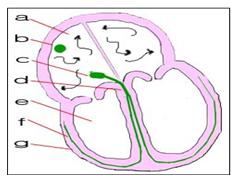
그림 67. 발작성 심방 빈박
a-심방, b-동방 결절, c-방실 결절, d-히스 속, e- 심실, f-푸르키니에 망상섬유, g-심근 이소성 자극전도
Copyright ⓒ 2013 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
-
심장 자극 전도계는 정상적으로 동방 결절(Sinus node)에서 시작되고 그 전도가 방실 결절(A-V node)⟶히스 속(His bundle)⟶심실 중격 심실 자극 전도계의 좌우 다발 가지를 거쳐 푸르키니에 망상섬유(Purkinj’s reticular fiber)로 퍼져 심장 전체로 자극이 전파되고 그로 인해 정상적으로 심방과 심실이 조화를 이루면서 수축 이완되는 것이 정상이다.
-
심장 자극 전도가 동방결절에서 시작되고 전체의 정상 심장 자극 전도계를 통과해서 심장전체에 전도될 때는 동성 박동이 정상적으로 생기지만 심장 자극전도가 동방결절에서 시작되지 않고 심방의 엉뚱한 부분이나, 방실 결절 부위, 또는 심실의 어떤 한 부분에서 이소성 심장 자극전도가 갑자기 시작되고 그로 인해 이소성 심장 박동이 빠르게 몇 분 동안, 몇 시간, 또는 몇 일간 지속되는 빈박을 발작성 빈박(Paroxysmal tachycardia)이라고 한다.
-
심장 자극전도가 동방 결절에서 시작되지 않고 심방의 다른 한 부분에서 시작돼서 생긴 발작성 빈박을 발작성 심방 빈박(Paroxysmal atrial tachycardia)이라 하고, 방실 결절 부위에서 이소성 심장 박동이 시작돼서 생긴 발작성 빈박을 발작성 방실 결절 빈박(Paroxysmal atrioventricular tachycardia)이라고 한다. 심실의 어떤 한 부분에서 이소성 심장 박동이 시작되어 생긴 발작성 빈박을 발작성 심실 빈박(Paroxysmal ventricular tachycardia)이라고 한다.
발작성 빈박, 발작성 심방 빈박, 발작성 방실 결절 빈박, 발작성 심실 빈박의 원인
-
대부분의 발작성 빈박의 원인은 확실히 모른다.
-
그렇지만 선천성 심장혈관 기형이나 류마티스 심장염, 또는 그 밖에 다른 종류의 심장 질환이 있거나, 약물 중독, 심장 수술 치료를 받은 후에 발작성 빈박이 생길 수 있다.
발작성 빈박, 발작성 심방 빈박, 발작성 방실 결절 빈박, 발작성 심실 빈박의 증상 징후
-
말로 잘 표현할 수 있는 학령기 전 유아들, 학령기 아이들, 사춘기 아이들에게 발작성 빈박이 갑자기 생기면 왼쪽 앞가슴이 두근거린다고 부모에게 호소한다.
-
발작성 빈박이 갑자기 멈추고 정상적으로 심장이 뛰기 시작하면 가슴이 두근거리던 것도 그친다.
-
이런 발작성 빈박이 불과 몇 초 동안 지속될 때도 있고, 몇 분 내지 몇 시간, 며칠 또는 몇 주 동안 계속 지속적으로 뛸 수 있다.
-
발작성 빈박이 있을 때 심장이 일 분 당 1백80~3백 번 정도까지 뛸 수 있다.
-
발작성 빈박이 계속 지속되면 왼쪽 앞가슴이 불편하다.
-
또 심장이 비정상적으로 빨리 수축됐다 이완되었다 해서 심장 내 피를 전신으로 정상적으로 펌프할 수 없기 때문에 심장이 쇠약해지고 심장부전증이 생길 수 있다.
발작성 빈박, 발작성 심방 빈박, 발작성 방실 결절 빈박, 발작성 심실 빈박의 진단
-
병력, 증상 징후와 진찰소견 등을 종합하여 이 병이 의심되면 심전도 검사, 가슴 X-선 사진 검사, 심초음파 검사, 피 검사 등으로 진단한다.
발작성 빈박, 발작성 심방 빈박, 발작성 방실 결절 빈박, 발작성 심실 빈박의 치료
-
발작성 빈박을 일으킨 원인을 찾아 그 원인에 따라 치료한다.
-
심장 자체에 어떤 병도 없고 원인을 확실히 모르는 발작성 빈박은 다음과 같이 임시 응급 치료를 할 수 있다.
-
의사 지시에 따라 한쪽 안구를 한쪽 손으로 잠시 동안 살짝 누르면 발작성 빈박이 그칠 수 있다.
-
또는 목에 있는 경동맥을 손으로 잠시 동안 살짝 눌러도 발작성 빈박이 그치고 심장박동이 정상적으로 돌아갈 수 있다.
-
또 숨을 크게 깊이 들이 마신 후 참을 수 있을 때까지 잠간동안 참다가 내 쉰다.
-
이와 같은 방법으로 숨쉬기 운동을 잠시 동안 반복하면 발작성 빈박이 그칠 수 있다.
-
어떤 때는 얼음 덩어리를 깨물어 먹으면 발작성 빈박이 그칠 수 있다.
- 응급요법으로 치료가 안 되면 디기탈리스제나 프로프라노롤(Propranolol/Inderal)제 또는 그 밖에 다른 여러 종류의 약물로 치료한다.
그림 70. 동방성 발작성 빈박
Copyright ⓒ 2013 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
Paroxysmal tachycardia, paroxysmal atrial tachycardia, paroxysmal atrioventricular tachycardia, paroxysmal ventricular tachycardia발작성 빈박, 발작성 심방 빈박, 발작성 방실 결절 빈박, 발작성 심실 빈박
Paroxysmal atrioventricular tachycardia, Paroxysmal ventricular tachycardia Paroxysmal tachycardia, paroxysmal atrial tachycardia, paroxysmal atrioventricular tachycardia, paroxysmal ventricular tachycardia, Paroxysmal atrioventricular tachycardia, Paroxysmal ventricular tachycardia

Figure 66. Normal cardiac stimulation conduction system a-atrium, b-eastern nodule, c-atrioventricular nodule, d-heather, e-ventricle, f-Purkinje reticular fiber, g-myocardium Copyright ⓒ 2013 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Figure 67. Paroxysmal atrial tachycardia a-atrium, b-eastern nodule, c-atrioventricular nodule, d-heather, e-ventricle, f-purkinie reticular fiber, g-myocardial ectopic stimulation conduction Copyright ⓒ 2013 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
• The cardiac stimulation conduction system normally starts at the Sinus node, and conduction proceeds through the left and right bundle branches of the AV node⟶His bundle⟶ventricular septum ventricular stimulation conduction system (Purkinj’s reticular fiber) spreads to the entire heart, and impulses are propagated throughout the heart, and it is normal for the atrium and ventricle to contract and relax as they normally harmonize.
• When cardiac stimulation conduction begins at the sinus node and passes through the entire normal cardiac stimulation conduction system and conducts to the entire heart, the same-sex beating occurs normally. An ectopic heart impulse conduction abruptly begins at a site or in some part of the ventricle, resulting in an ectopic heartbeat that rapidly lasts for minutes, hours, or even days, called paroxysmal tachycardia.
• Paroxysmal atrial tachycardia is called paroxysmal atrial tachycardia, and paroxysmal atrial tachycardia is called paroxysmal atrial tachycardia. It is called paroxysmal atrioventricular tachycardia. Paroxysmal ventricular tachycardia is called paroxysmal ventricular tachycardia.
Causes of paroxysmal tachycardia, paroxysmal atrial tachycardia, paroxysmal atrioventricular tachycardia, paroxysmal ventricular tachycardia
• The cause of most paroxysmal freckles is not clear.
• However, you may have congenital cardiovascular malformations, rheumatoid carditis, or other types of heart disease, or you may develop paroxysmal tachycardia after drug addiction or cardiac surgery.
Symptoms, signs of paroxysmal tachycardia, paroxysmal atrial tachycardia, paroxysmal atrioventricular nodule tachycardia, paroxysmal ventricular tachycardia
• Infants of preschool age, school-age children, and adolescents who can be well expressed in words, complain to their parents that the left front chest is pounding when they suddenly have a paroxysmal tachycardia.
• When the paroxysmal frequency stops suddenly and the heart starts beating normally, the heartbeat stops.
• Sometimes this paroxysmal frequency lasts only a few seconds, and it can continue running for minutes to hours, days, or weeks.
• When there is a paroxysmal frequency, the heart can beat 180 to 300 times per minute.
• If paroxysmal tachycardia persists, the left anterior chest is uncomfortable.
• In addition, because the heart contracts abnormally quickly and then relaxes, the blood inside the heart cannot be pumped normally throughout the body, which can lead to weakness and heart failure.
Diagnosis of paroxysmal tachycardia, paroxysmal atrial tachycardia, paroxysmal atrioventricular nodule tachycardia, paroxysmal ventricular tachycardia
• Comprehensive medical history, symptoms, and examination findings. If this disease is suspected, it is diagnosed by electrocardiography, chest X-ray examination, echocardiography, and blood tests.
Treatment of paroxysmal tachycardia, paroxysmal atrial tachycardia, paroxysmal atrioventricular tachycardia, paroxysmal ventricular tachycardia
• Find the cause of paroxysmal freckles and treat them according to the cause.
• For paroxysmal freckles without any disease in the heart itself and the cause of which is unknown, temporary emergency treatment may be provided as follows.
• As directed by your doctor, briefly pressing one eye with one hand for a while may stop paroxysmal frequency.
• Or, even if you gently press the carotid artery in the neck with your hand for a while, the paroxysmal frequency stops and the heart rate can return to normal.
• Take a deep breath and hold it for a while until you can hold it, then exhale.
• Repeating the breathing exercise in this way for a while may stop seizure frequency. • Sometimes, biting a block of ice can stop the paroxysmal frequency.
• If emergency therapy does not help, treat with digitalis or propranolol (Propranolol/Inderal) drugs or other drugs.

Figure 70. Orthotropic paroxysmal frequency Copyright ⓒ 2013 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
출처 및 참조문헌
- www.drleepediatrics.com제11권. 소아청소년 심장 혈관계 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th — 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
-
Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, Harvey grant, and Robert Murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
-
The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
-
Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care
-
응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
-
Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
-
Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
-
Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
-
소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”