발목 염좌(발목 삠), Ankle sprains
발목 염좌의 개요
- 어떤 관절이 갑자기 비틀려 관절을 형성하고 있는 인대(Ligaments)의 일부나 전부가 찢어진 상처를 염좌, 삠, 또는 염전이라고 한다.
- 발목 관절이 갑자기 비틀려 거기에 있는 인대가 째진 상처를 발목 염좌, 발목 삠, 또는 “발목이 삐었다”라고 표현 한다.
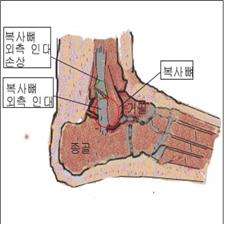
그림 1-17. 발목 측면과 외측발목 인대 손상
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
발목 염좌의 원인
- 관절이 정상적으로 움직일 수 있는 운동의 범위 이상으로 움직여 그 관절에 붙어있는 인대(靭帶)의 일부, 또는 전부가 찢어진 상처를 염좌 또는 삠이라고 한다.
- 장난을 치다가나 달리기 등 운동을 하다가, 사고로 발목, 무릎, 팔꿈치, 어깨, 손가락 등의 관절이 삘 수 있다.
- 특히 울퉁불퉁한 길바닥에서 달일 때 발목 염좌가 더 잘 생길 수 있고 발이 내번 될 때 추골(Malleus)의 외 인대가 가장 잘 손상될 수 있다.
- 신체에 있는 거의 모든 관절이 삘 수 있지만 특히 발목 관절은 신체의 전 체중을 지탱하는 기능을 하고 많이 쓰이는 관절이기 때문에 더 자주 삘 수 있다.
- 또 어깨 관절도 상대적으로 많이 쓰는 관절이기 때문에 신체에 있는 다른 관절에 비해서 더 쉽게 삘 수 있고 더 자주 삘 수 있다
- 발목 염좌는 여자농구 선수들에게 흔히 생긴다. 과거에 한번 발목 염좌가 생겼던 병력이 있으면 발목 염좌 재발성이 높다.
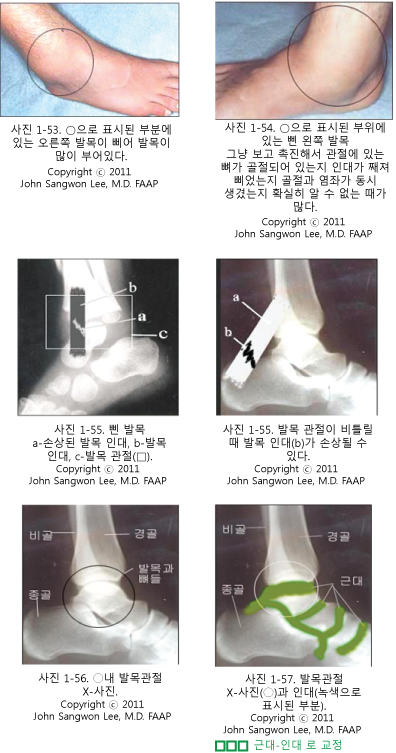
발목 염좌(발목삠)의 증상 징후
-
발목 관절이 삐었을 때 생길 수 있는 증상 징후는 발목 관절 속에 있는 비골, 경골, 족근골 등 관절 뼈가 골절될 때나, 발목 관절 속에 있는 비골 두부, 경골 두부(骨頭)가 탈구될 때 생길 수 있는 증상 징후와 거의 비슷할 수 있다.
발목 염좌(발목 삠)의 급수
-
발목관절을 이루고 있는 여러 종류의 인대들 중 어떤 인대가 얼마나 손상 입었나에 따라, 발목 염좌의 증상 징후 등에 따라 발목 염좌를
1. 1급 발목 염좌
2. 2급 발목 염좌
3. 3급 발목 염좌 등 3급 발목 염좌로 나눈다.
- 발목 염좌의 급수에 따라 증상 징후가 다르다.
- 관절이 삐면 삔 관절이 아프고,
-
째진 인대부분을 만지면 아프고 붓고,
-
정상적으로 잘 움직일 수 없다.
-
특히 발목이 삔 후 즉시 아플 수 있고, 그 후 얼마간 상당히 아플 수 있다.
-
때로는 삔 후 처음 한두 시간 동안은 많이 붓지도 않고 심하게 아프지 않을 수 있다. 그렇지만 그 후 시간이 점점 더 지나가면서 삔 관절이 점점 더 붓고 은근히 더 아플 수 있다.
-
삔 후 1~2일 정도 지나면 삔 관절 부분의 피부가 멍들 수 있고, 그 관절에 통증이 은근히 생기고 아파서 그 관절을 움직이기도 힘들 수 있다.
표 22. 발목 염좌 급수 분류 Classification of ankle sprains
|
발목 염좌의 정도 Degree of ankle sprain Ankle |
앞 발목 종아리 인대(전거 인대) 이완 정도
Calf ligament (motor ligament) degree of relaxation |
반상 출혈
Ecchyno mosis, bleeding |
부종
Edema |
발목을 정상으로 움직여 쓸 수 있는 기간
The period during which the ankle can be moved to normal |
| 1급 발목 염좌
Grade 1 ankle sprain |
없다
No |
없다
No |
약간 있다 Some | 2~1일
2~1 days |
| 2급 발목 염좌Grade 2 ankle sprain | 경도
Mild |
조금 있을 수 있다
May have a little mildness |
경도로 있다Mildness | 2~4주
Mild, 2-4 weeks |
| 3급 발목 염좌Grade3 ankle sprain | 상당이 생긴다
Quite a lot |
확실히 있다
Definitely |
많이 생긴다 Much | 4~6주
Many occur 4 to 6 weeks |
출처 및 참조문헌 Sources and references. Sports Med Connecticut State Medical Society, Winter, 2008 p.8
발목 염좌(발목 삠)의 진단
- 병력, 증상 증후와 진찰소견 등을 종합해서 발목 관절이 삐었다고 의심되면 삔 관절 X선 사진 검사 등으로 진단할 수 있다.
- 때로는 발목 관절에 생긴 골절, 탈구, 염좌 등 말목 관절 외상은 발목 X선 사진 검사를 하지 않고 그냥 시진, 촉진, 타진(視珍, 觸診, 打診) 등의 진찰만 해서 확실히 감별 진단하기가 쉽지 않다.

발목 염좌(발목 삠)의 치료
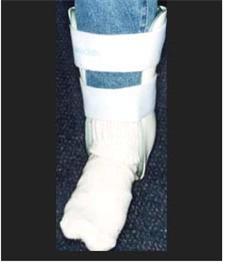
사진 1-60. 삔 발목과 그 부위에 부목을 대어
응급치료 할 수 있다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
- 어떤 발목 관절이 삐었는지, 어느 정도로 삐었는지, 또 어떤 종류의 합병증이 있는지, 나이 등에 따라 치료를 다르게 할 수 있다.
- 교통사고나 안전사고 등으로 발목 관절이 삐었을 경우, 신체의 다른 부위에 찰과상, 절상, 자상 등을 동시 입었을 수 있다.
- 교통사고로 발목 관절이 삐었을 때, 삔 발목 관절을 적절히 응급 치료를 해 주는 것도 중요하지만 호흡곤란이 있는지, 발목 염좌 이외 발목 골절이나 발목 탈구 등 다른 외상이 있는지 알아보고, 있으면 그것도 동시 적절히 응급 치료해야 한다.
- 호흡곤란이 있으면 기도를 확보 해 숨을 제대로 쉴 수 있게 우선 처치해야 한다.
- 통증이 있으면 진통시킨다.
- 상황에 따라 의료구급대, 병원 응급실, 단골 소아청소년과에 긴급으로 전화해서 그들의 전화 지시에 따라 구급차, 적절한 다른 교통수단으로 환아를 적절한 병원으로 빨리 이송한다.
- 교통사고나 안전사고 등으로 발목 염좌가 생기고 크게 다쳤을 때는 단골 소아청소년과 의사, 의료구급대, 구급차가 사고 현장에 도착할 때까지, 또는 그 응급 상황에서 의사로부터 발목 염좌 응급처치에 관한 지시가 없을 때는 가능한 한 처음 발견됐을 때의 환아의 신체 자세 그대로 계속 유지한다. 즉 가능하면, 환아를 사고 현장에서 다른 장소로 함부로 옮기지 말아야 한다. 특히 도와주는 사람이 삔 발목 관절을 함부로 수동적으로 이리 저리 움직이지 말아야 한다.
- 팔다리에 있는 어떤 관절이 조금 삐었을 때는 삔 관절을 몸통보다 조금 더 높게 받쳐 올려놓으면 덜 아플 수 있고 덜 부을 수 있다.
- 의사가 진찰 하고 발목 X선 사진 등으로 검사해도 발목 관절의 어느 부분이 손상됐는지 확실히 알 수 없을 때도 있다. 더군다나 부모가 그냥 시진하고 촉진해서 발목 어디가 손상됐다고 쉽게 진단할 수 없다.
- 상황에 따라 베개나 둘둘 만 담요, 또는 판자 등으로 삔 발목 관절 부위와 그 부위의 위아래에 있는 성한 아랫다리와 발까지 부목을 대고 병원 응급실이나 단골 소아청소년과 의사에게 데리고 갈 수 있다.
- 이때도 가능한 한 삔 발목 관절을 함부로 움직여서는 안 된다.
- 가능한 한, 삔 발목 관절을 처음 목격한 자세 그대로 유지하고 삔 발목 관절에 부목을 적절히 댈 수 있다.
- 삔 관절이 붓고 아플 때는 삔 발목 관절을 얼음 덩어리 물 주머니로 찬찜질을 할 수 있다.
- 1급 발목 염좌가 있는 발목, 단순히 삔 발목 관절을 약 7∼14일 동안 쓰지 않고 안정을 취하고 쉬면 잘 낫는 것이 보통이다.
- 발목 관절이 다쳤을 때 발목 관절이 삐기만 했는지, 발목 관절에 탈구가 되었는지, 발목 관절을 이루고 있는 뼈의 일부가 골절되었는지, 염좌와 골절이 함께 동시 있는지 의사도 누구도 겉으로 그냥 보고 확실히 금방 감별 진단할 수 없는 경우가 많다.
- 따라서 발목 관절이 삐었다고 의심할 때는 발목 관절 X선 사진 검사 등을 하고 의사의 진단 치료를 받는 것이 이상적 치료이다.
- 발목 관절을 이루는 뼈가 골절되거나 탈구되지 않고 조금 삐기만 했을 때는 의사의 지시에 따라 삔 발목 관절과 그 부위를 탄력붕대 등으로 감아주고 1∼2주 동안 삔 발목 관절을 쓰지 않고 관찰하면 대개 잘 치료될 수 있다.
- 발목 관절이 좀 심하게 삐었을 때도 삔 발목 관절을 탄력붕대로 감아주거나 부목을 대고 삔 발목 관절을 일정 기간 동안 쓰지 않고 쉬면서 치료 될 수 있다([부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다-소아가정간호백과]-제21권 소아청소년 가정 학교 간호-탄력붕대 참조).
- 발목이 삐었을 때 삔 발목 관절이 많이 아프고 부으면 다 나을 때까지 삔 발목 관절을 절대로 쓰지 말아야 한다.
- 부득이 걸어야 할 때는 목발을 이용해 걸을 수 있지만 삔 발목 관절과 발에는 체중과 힘을 가해서는 안 된다.
- 심하게 발목 관절을 삐었을 경우, 수술 치료를 한다. 대부분의 발목 관절 염좌는 2∼3주일 정도 지나면 완치되는 것이 보통이다.
- 발목 염좌는 정형외과에서 치료 받는 것이 이상적이다.
- 1~2급 발목 관절 삠은 RICE-보호 즉 레스트(resting/안정), 얼음 찜질(ice pack), 압박 붕대 치료(Electric bandage treatment), 거상(Elevation)으로 치료한다.
Ankle sprains 발목 염좌(발목 삠)
Overview of ankle sprains
-
A wound in which a joint is suddenly twisted and part or all of the ligaments forming the joint is torn is called a sprain or torsion.
-
Ankle sprains sprained ankles, or “sprained ankles” are described as ankle sprains, sprained ankles, and slit ligaments.
Figure 1-17. Injuries to the sides of the ankle and lateral ankle ligaments. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
Causes of ankle sprains
-
A wound in which part or all of the ligaments attached to the joint is torn by moving beyond the range of motion in which the joint can move normally is called a sprain.
-
While playing or exercising, such as running, joints such as ankles, knees, elbows, shoulders, and fingers may be sprained in an accident.
-
In particular, ankle sprains are more likely to occur when running on the bumpy road, and the external ligaments of the malleus are most likely to be damaged when the foot is inverted.
-
Almost any joint in the body can be sprained, but the ankle joint in particular can be sprained more often because it functions to support the entire body’s weight and is a popular joint.
-
Also, since the shoulder joint is a relatively common joint, it can be sprained more easily and more often than other joints in the body.
-
Ankle sprains are common among female basketball players.
-
If you have a history of having an ankle sprain once in the past, the recurrence of an ankle sprain is high.
Symptoms, Signs of an ankle sprain (sprained ankle)
-
Symptoms, signs that may occur when the ankle joint is sprained are symptoms that may occur when joint bones such as the fibula, tibia, and ankle bones in the ankle joint are fractured, or when the fibula head and tibia head in the ankle joints are dislocated.
-
Among the various types of ligaments that make up the ankle joint, depending on which ligament has been damaged and how much, the ankle sprain is caused by the symptoms of an ankle sprain.
Grade of ankle sprain
-
Grade 1 ankle sprain
-
Grade 2 ankle sprain
-
Class 3 ankle sprains, etc.
- Symptoms, signs vary depending on the number of ankle sprains.
-
If the joint is sprained, the sprained joint hurts,
-
Touching the slit ligament causes pain and swelling,
-
Can’t move well normally.
-
In particular, the ankle can hurt immediately after a sprain,
-
and it can be quite painful for some time thereafter.
-
Sometimes, during the first hour or two after a sprain, you may not have a lot of swelling and may not get very sick.
-
However, as time passes after that, the sprained joint may become more and more swollen and slightly more painful.
-
About 1-2 days after the sprain, the skin of the sprained joint may be bruised, and the joint may be painfully painful and difficult to move.
Table 22. Classification of ankle sprains
|
발목 염좌의 정도 Degree of ankle sprain Ankle |
앞 발목 종아리 인대(전거 인대) 이완 정도 calf ligament (motor ligament) degree of relaxation | 반상 출혈Ecchyno mosis, bleeding | 부종Edema | 발목을 정상으로 움직여 쓸 수 있는 기간 Period during which the ankle can be moved to normal |
| 1급 발목 염좌
Grade 1 ankle sprain |
없다
No |
없다
No |
약간 있다 Some | 2~1일 2~1 days |
| 2급 발목 염좌Grade 2 ankle sprain | 경도
mild |
조금 있을 수 있다 May have a little mildness | 경도로 있다mildness | 2~4주 mild 2-4 weeks |
| 3급 발목 염좌Grade3 ankle sprain | 상당이 생긴다
Quit a lot |
확실히 있다 Definitely | 많이 생긴다 much | 4~6주 Many occur
4 to 6 weeks |
Sources and references
Sports Med Connecticut State Medical Society, Winter, 2008 p.8
Diagnosis of ankle sprain
• If it is suspected that the ankle joint is sprained by combining the medical history, symptoms, and examination findings, it can be diagnosed with a sprained joint X-ray examination.
• Sometimes, it is easy to make a definitive differential diagnosis by simply examining, palpation, percussion, etc. without performing an X-ray examination of the ankle for extremity joint trauma such as fractures, dislocations, and sprains in the ankle joint.

Treatment of an ankle sprain (sprained ankle)
-
Photo 1-60. Splint the sprained ankle and the area Emergency treatment can be performed. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
-
Treatment can be done differently depending on which ankle joint is sprained, to what extent it is sprained, what kind of complications are present, and age.
-
If your ankle joint is strained due to a traffic accident or safety accident, you may have suffered abrasions, and cuts on other parts of the body at the same time.
-
When the ankle joint is strained due to a traffic accident, it is important to provide appropriate emergency treatment for the sprained ankle joint, but it is important to find out if there is any other trauma such as ankle fracture or ankle dislocation other than an ankle sprain, and if there is any, it is also necessary to provide appropriate emergency treatment at the same time.
-
If your child has difficulty breathing, you should first take care of securing an airway so that your child can breathe properly.
-
Pain relief if there is pain.
-
Depending on the situation, call the medical paramedics, hospital emergency room, or regular pediatric clinic in an emergency and follow their telephone instructions to quickly transfer the child to the appropriate hospital by ambulance or other appropriate means of transportation.
-
When an ankle sprain occurs due to a traffic accident or a safety accident, etc., and serious injuries, it is possible until a regular pediatrician, medical paramedic, or ambulance arrives at the scene of the accident, or when there is no instruction for emergency treatment of an ankle sprain from a doctor in the emergency.
-
Keep the child’s body posture as it was when it was first discovered. In other words, if possible, don’t move the child from the accident site to another location.
-
In particular, the helper should not move the sprained ankle jointly and passively.
-
If some joints in the limbs are slightly sprained, it may be less painful and less swollen by placing the sprained joint a little higher than the torso.
-
Even if a doctor examines and examines an ankle X-ray, it is sometimes impossible to know for sure which part of the ankle joint is damaged. What’s more, it’s not easy to diagnose that the ankle is injured by parents just by examining and palpating it.
-
Depending on the situation, your child can take the sprained ankle joint with a pillow, blanket, or plank, and take it to the hospital emergency room or a regular pediatrician by applying a splint to the sprained ankle joint and the tender lower leg and foot above and below the area.
-
Even at this time, you should not move the sprained ankle joint as much as possible.
-
As far as possible, you can keep the sprained ankle in the same position as it was first seen and apply a splint to the sprained ankle properly. If the sprained joint is swollen and painful, you can apply a cold compress with an ice cube to the sprained ankle joint.
-
Grade 1 sprained ankle, simply sprained ankle joint for about 7-14 days without using it, taking a rest and rest, it is common to heal well.
-
When the ankle joint is injured, whether the ankle joint is sprained, whether the ankle joint has been dislocated, whether a part of the bones that make up the ankle joint is broken, and whether sprains and fractures are both at the same time, neither doctor nor anyone can diagnose it by looking at it.
-
There are many cases. Therefore, when it is suspected that the ankle joint is sprained, the ideal treatment is to perform an ankle joint X-ray examination and receive diagnostic treatment from a doctor.
-
If the bones that make up the ankle joint are not fractured or dislocated and are only slightly sprained, according to the doctor’s instructions, wrap the sprained ankle joint and the area with an elastic bandage, etc., and observe it without using the sprained ankle joint for 1 to 2 weeks.
-
Even when the ankle joint is slightly sprained, it can be treated by wrapping the sprained ankle joint with an elastic bandage or applying a splint to the sprained ankle joint while resting for a certain period of time. See Volume 21 Child and Adolescent Home School Nursing-Elastic Bandage.
-
If the sprained ankle joint hurts a lot when the ankle is sprained and swollen, you should never use the sprained ankle joint until it is healed. If your child has to walk, your child can use crutches to walk, but your child should not put weight or force on the sprained ankle joint and foot.
-
If the ankle joint is severely sprained, surgical treatment is performed. Most ankle sprains are usually cured after 2-3 weeks. Ideally, an ankle sprain should be treated in an orthopedic clinic.
-
Grade 1~2 sprained ankle joints are treated with RICE i.e. rest (resting/stabilization), ice pack, electric bandage treatment, and elevation.
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
-
Quick Reference to Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D. p.164
-
Emergency Pediatrics, A guide to ambulatory care, 5th edi. Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Emergency care and transportation of the sick and injured, American Academy of orthopedic surgeons.
-
Nelson textbook, 15 edition
-
Signs & Symptoms in Pediatrics 2nd edition
-
The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 18th edition
-
Sports Med Connecticut State Medical Society, Winter, 2008 p.8
-
Contemporary Pediatrics, July 2008. p.46
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, Harvey grant, and Robert Murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care 응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과-부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원 저
-
The pregnancy Bible. By Joan stone, MD. Keith Eddleman, MD
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
-
임신에서 신생아 돌보기까지. 이상원
-
Breastfeeding. by Ruth Lawrence and Robert Lawrence
-
Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics 14th-21st ed. Beherman,
-
The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 19th edition
-
Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
-
Growth and Development of Children, George H. Lowrey 8th edition
-
소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”