발목 관절 뼈 골절과 발 뼈 골절, Ankle fractures and Foot fractures
운동, 장난, 또는 안전사고 등으로 발목 관절(족관절) 뼈나 발뼈 등의 일부 또는 전부가 골절될 수 있다.
발목 관절은
-
- 경골 원위 골단,
- 비골의 원위 골단,
- 내 복사뼈,
- 외 복사뼈와 거골, 종골 등 7개의 족근골,
- 연골,
- 인대,
- 근육,
- 건,
- 혈관 등으로 구성되어 있다.
- 발목 관절에 있는 뼈의 일부나 전부가 골절 될 수 있고, 연골이나 인대가 손상되어 발목이 삘 수 있고 뼈가 전위되어 탈구될 수 있다.
X 선 사진으로 보는 발목 관절, 발 뼈와 발 뼈 골절
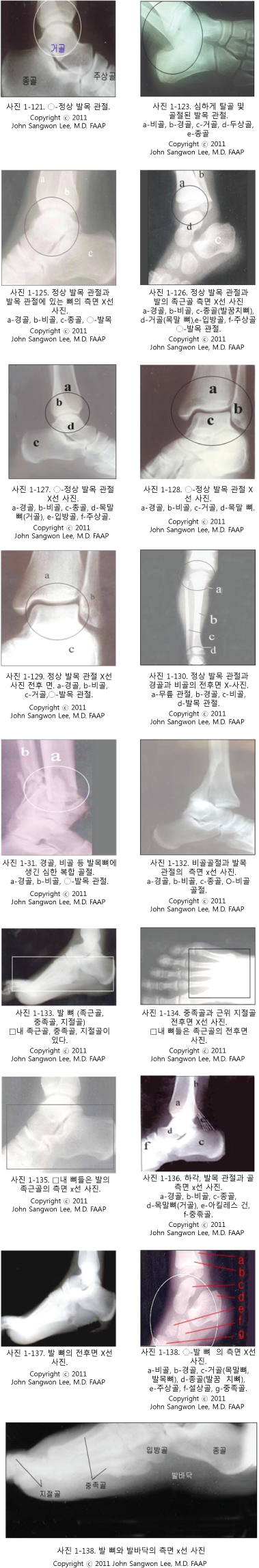
- 발목 관절 속에 있는 뼈가 골절될 때 한 개의 뼈만 골절 될 수도 있지만 발목 관절을 구성하고 있는 다른 종류의 뼈들 중 한 개나 그 이상 여러 개의 뼈가 동시 골절될 수 있다. 그리고 인대, 연골, 근육, 건 등도 동시 손상될 수 있다.
- 발목관절이 삘 때 외과(외측 복사뼈)가 제일 흔히 골절된다. 여기서는 발 뼈 골절이나, 발목 뼈 골절의 관해 주로 설명한다.
발목 관절뼈나 발뼈 골절의 증상 징후
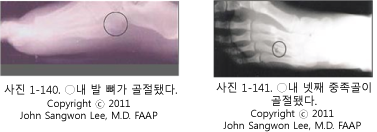
- 발목 관절뼈 골절이나 발 뼈의 골절의 정도, 그 중 어느 뼈에 골절이 생겼는지에 따라, 발목 관절을 이루고 있는 연골, 인대, 혈관, 신경 등의 손상에 따라 증상 징후가 다르다.
- 발목 관절 뼈나 발 뼈의 골절로 생기는 증상 징후는 발목이나 발이 삐었을 때나 발목 관절 뼈가 탈골될 때 생길 수 있는 증상 징후와 거의 비슷한 증상 징후가 생길 수 있다.
- 일반적으로 골절된 뼈가 있는 발목 관절 부위나 발의 부위가 더 붓고 더 아프고 그쪽 발목 관절이나 발의 기능의 이상이 생길 수 있다.
- 발목 관절이나 발을 능동적으로 움직이기 싫어한다.
- 정상적으로 움직일 수 있는 운동 범위가 제한된다.수동적으로 발목이나 발을 움직일 때 아파한다.
- 골절된 관절 부위를 손으로 누르면 더 아프고 환아 자신이나 다른 사람이 골절된 발목 관절 뼈가 있는 발의 부위나 골절된 발목 관절 뼈가 있는 발목관절 부위로 움직이면 그 부위가 더 아플 수 있다.
- 발목 관절 뼈나 발 뼈가 골절 됐을 때 골절되어 있는 발로 정상적으로 서고 걷지 못한다.
- 그쪽 발에 체중을 지탱하게 하거나 힘주고 서기를 싫어한다.
- 골절된 후 2~3일정도 지나면 골절된 발목 관절 부위가 더 심하게 붓고 멍이 더 들 수 있다.
- 국소에 따뜻한 촉감을 줄 수는 있지만 전신 열은 나지 않는다.
발목 관절뼈나 발뼈 골절의 진단
- 병력, 증상 징후와 진찰소견 등을 종합해 발목 관절 뼈나 발 뼈가 골절됐다고 의심되면 발 뼈 X선 사진 검사나 발목 관절 뼈 X선 사진 검사로 진단한다.
- 발 뼈나 발목 관절 뼈 골절은 다음과 같은 외상과 감별진단 해야 한다
-
- 발이나 발목관절 타박상,
- 발목 관절 삠,
- 발목 관절 탈구
- 발목 관절염 등.
발목 관절뼈나 발뼈 골절의 치료
-
발목 관절뼈가 골절되었다고 의심되면 그쪽 발이나 발목관절로 더 이상 걷지 않게 하고 환아를 안정시킨다.
- 의료구급대, 단골 소아청소년과나 병원 응급실에 전화해 그들의 지시에 따라 사고 현장에서 응급치료를 시작한다.
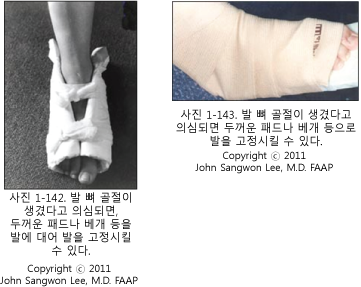
- 의료구급대, 단골 소아청소년과 의사가 사고 현장으로 올 수 없는 경우에는 큰 베개나 스펀지 등으로 발목 관절 뼈가 골절되었다고 의심되는 쪽의 발, 발목 관절과 아랫다리 전체를 적절히 받치고 고정시킨다.
- 골절 된 쪽 발이나 발목관절을 더 이상 움직이지 못하게 부목으로 고정시킨 후 구급차나 다른 적절한 교통수단을 이용해 병원 응급실이나 근처 적절한 병원으로 급이 이송한다.
- 골절된 발목 관절 뼈가 있는 발목관절이나 그쪽 발을 당기거나 밀거나 비틀지 말고 가능한 한 처음 목격한 자세 그대로 계속 유지하면서 골절된 발목이나 발에 부목을 댄다. 이때도 의사의 지시대로 응급처치를 한다.
- 발 뼈나 발목 관절 뼈가 골절되었을 때 가능하면 발이나 아랫다리의 혈액순환이 정상적인지 말초 신경도 정상적인지 체크해보고 단골 소아청소년과 의사의 지시대로 응급처치를 한다.
- 골절된 발목 관절 뼈가 있는 쪽의 발톱 밑의 혈색이 정상인지 발등 동맥 맥박이 정상적으로 뛰는지를 체크해서 발과 발목관절의 혈액순환이 정상인지 알아보고 필요에 따라 단골 소아청소년과 의사에게 보고한다.
- 발등 동맥 맥박이 뛰지 않거나 발톱 밑 혈색이 파랗거나 창백할 때는 단골 소아청소년과 의사나 의료구급대, 병원 응급실에 긴급으로 전화 해 그들의 지시에 따라 구급차 등을 이용해 응급실로 급히 이송한다.
Ankle fractures and foot fractures 발목 관절 뼈 골절과 발 뼈 골절
- Part or all of the ankle joint (ankle) bone or foot bone may be fractured due to exercise, play, or safety accident.
The ankle joint is conssited with
- Distal tibia epiphysis,
- Distal epiphysis of the fibula,
- Inner ankle,
- 7 ankles, including the external ankle,talus, and calcaneus,
- Cartilage,
- Ligament,
- Muscle,
- Tendon,
- It consists of blood vessels and the like.
- Part or all of the bones in the ankle joint may be fractured, cartilage or ligaments may be damaged, resulting in sprained ankles, and dislocation of the bones may result.
Fracture of ankle joint, foot bone, and foot bone as seen by X-ray image

- When a bone in the ankle joint is fractured, only one bone may be fractured, but one or more of the different types of bones that make up the ankle joint may fracture simultaneously.
- In addition, ligaments, cartilage, muscles, and tendons can also be damaged at the same time.
- When the ankle joint is sprained, the lateral part ankle is the most common fracture.
- This section mainly describes the fracture of the foot bone or the fracture of the ankle bone.
Symptoms, signs of an ankle bone or foot bone fracture

- Symptoms, signs differ depending on the degree of fracture of the ankle joint bone or the bone of the foot, and which bone has fractured, depending on the cartilage, ligaments, blood vessels, nerves, etc. that make up the ankle joint.
- Symptoms of a fracture of the ankle joint or foot bones may have almost identical symptoms to those of a sprained ankle or foot, or when an ankle joint bone is dislocated.
- In general, the area of the ankle joint or the foot where the fractured bone is located is more swollen and more painful, and the ankle joint or the function of the foot may be abnormal.
- They don’t like to actively move their ankle joints or feet. The range of motion you can move normally is limited; it hurts when you manually move your ankle or foot.
- If you press the fractured joint with your hand, it will hurt more, and if you or someone else moves to the part of the foot with the fractured ankle joint bone or the ankle joint with the fractured ankle joint bone, that part may be more painful.
- When the ankle joint bone or foot bone is fractured, you cannot stand and walk normally with the fractured foot.
- They don’t like to hold their weight on their feet or to stand on their feet.
- After 2 to 3 days after the fracture, the fractured ankle joint may become more swelling and bruising.
- It can give a warm touch to the topical area, but it does not produce body heat.
Diagnosis of ankle joint bone or foot bone fracture
If you suspect that an ankle joint bone or foot bone has been fractured by combining the medical history, symptoms, signs, and examination findings, it is diagnosed with a foot bone X-ray examination or an ankle joint bone X-ray examination.
Fractures of the bones of the foot or ankle joint should be diagnosed differentially from the following trauma:
- Bruises in the foot or ankle joint,
- sprained ankle joint,
- Ankle dislocation
- Ankle arthritis,
- etc.
Treatment of fractures of the ankle joint or foot bones
- If you suspect that the ankle joint bone is fractured, stop walking with the foot or ankle joint and stabilize the child.
- Call a medical paramedic, a regular pediatrics department or hospital emergency room and follow their instructions to initiate emergency treatment at the accident site.
- If a medical paramedic or regular pediatrician cannot come to the accident site, use a large pillow or sponge to properly support and fix the entire ankle joint and lower leg on the side of the suspected ankle bone fracture.
- The fractured foot or ankle joint is fixed with a splint so that it cannot move any further and transported to the hospital emergency room or nearby appropriate hospital using an ambulance or other suitable means of transportation.
- Fractured Ankle Joint
- Do not pull, push, or twist the ankle joint with bone or its foot, and apply a splint to the fractured ankle or foot while maintaining the position as first sighted as possible. In this case, take first aid according to the doctor’s instructions.
- When the foot bone or ankle joint bone is fractured, check whether the blood circulation in the foot or lower leg is normal and the peripheral nerves are normal, and take first aid as directed by a regular pediatrician.
- Check whether the skin color under the toenail on the side of the fractured ankle joint bone is normal or the instep arterial pulse is beating normally to find out whether the blood circulation in the foot and ankle joint is normal, and report it to a regular pediatrician if necessary.
- If the instep arterial pulse does not beat or the color under the toenail is blue or pale, call a regular pediatrician, medical paramedic, or hospital emergency room in an emergency, and follow their instructions to an emergency room using an ambulance.
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
-
Quick Reference to Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., p.80-81, 164-165
-
Emergency Pediatrics, A guide to ambulatory care, 5th edi. Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen, p.552-555
-
Emergency care and transportation of the sick and injured, 3rd edition, American Academy of orthopedic surgeons. p.134, 163-164, 162-163
- Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, Harvey grant, and Robert Murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care 응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과-부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원 저
-
The pregnancy Bible. By Joan stone, MD. Keith Eddleman, MD
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
-
임신에서 신생아 돌보기까지. 이상원
-
Breastfeeding. by Ruth Lawrence and Robert Lawrence
-
Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics 14~19th ed. Beherman,
-
The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 18~19th edition
-
Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
-
Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th-21st Edition
-
Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
-
Growth and Development of Children, George H. Lowrey 8th edition
-
소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”