박테리아 결막염 (박테리아성 결막염) Bacterial conjunctivitis
박테리아 결막염의 원인
- 결막에 박테리아 감염이 생기면 급성 박테리아 결막염이 생길 수 있다.
- 임질균 감염으로 생긴 결막염도 일종의 박테리아 결막염이지만 여기서는 임질균성 결막염을 제외한 다른 박테리아 감염으로 생긴 결막염에 관해 설명한다.
- 폐렴연쇄상구균, 황색 포도상구균, B군 헤모필러스 인플루엔자균(히비균), A군 베타 용혈성 연쇄상구균이나 B군 용혈성 연쇄상구균 등의 박테리아가 결막에 감염되면 급성 박테리아 결막염이 생길 수 있다.
- 중이염, 부비동염, 감기, 감기 이 외 바이러스 상·하 기도염, 또는 박테리아 상·하 기도염을 앓을 때 급성 박테리아 결막염이 2차 박테리아 감염병으로 생기는 경우가 많다.
- 그렇지만 급성 박테리아 결막염만 따로 생기기도 한다.
박테리아 결막염의 증상 징후
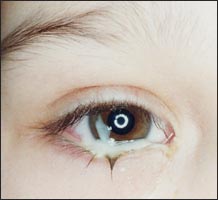
사진 66. 급성 박테리아 결막염
폐렴연쇄상구균 감염으로 급성 박테리아 결막염이 생길 수 있다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
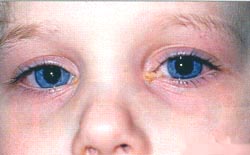
사진 67. 히브 박테리아 감염으로 인한 급성 결막염
소스; Rudolph s, Wagner,M.D.
- 급성 박테리아 결막염을 일으킨 박테리아의 종류, 결막염의 정도, 합병증의 유무 등에 따라 증상 징후가 다르다.
- 박테리아가 결막에 감염되서 급성으로 결막염을 일으키면 결막이 빨갛게 충혈되고 눈꺼풀이 붓고 노란 눈곱이 낀다. (사진 참조)
- 박테리아 결막염이 심할 때는 눈을 뜨지 못할 정도로 눈꺼풀과 눈두덩이도 붓는다.
- 결막염은 한쪽 눈에만 생길 수 있고 양쪽 눈에 동시 생길 수 있다.
- 급성 결막염으로 생긴 증상 징후가 결막염과 같이 있는 중이염이나 축농증 등으로 생긴 증상 징후와 함께 있을 수 있다.
박테리아 결막염의 진단
- 병력, 증상 징후와 진찰소견 등을 종합하여 진단한다.
- 급성 박테리아 결막염이 있다고 의심되면 결막염이 있는 눈의 결막에서 피검 물용 고름을 면봉으로 채취해 그람 염색 현미경 세균검사, 세균배양검사 등을 하고 어떤 종류의 박테리아 감염으로 이 병이 생겼나 알아볼 수 있다.
- 그러나 이 병을 진단하기 위해 세균배양검사를 꼭 하지 않고 증상 징후와 검진 소견 등으로 진단할 때가 더 많다.
- 급성 박테리아 결막염은 중이염이나 부비동염 등과 같이 있을 때가 많기 때문에 급성 박테리아 결막염이 있을 때는 중이염이나 부비동염이 있나 꼭 진찰 받는 것이 좋다.
- 표 2 박테리아 , 바이러스 , 알레르기 결막염의 감별 진단 참조
박테리아 결막염의 치료
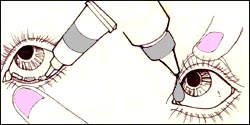
사진 68. 눈에 안약을 넣는 방법
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
- 박테리아 결막염의 정도, 원인, 합병증의 유무에 따라 치료한다.
- 박테리아 결막염으로 생긴 고름으로 세균배양검사를 해서 무슨 박테리아가 결막염을 일으켰나 알아보면서 동시 적절한 항생제 안연고나 항생제 안 점적약제로 치료를 시작하는 것이 이상적이다.
- 그람 염색 현미경 세균검사, 세균 배양검사 등에서 알아낸 박테리아의 종류에 따라, 또는 항균제 감수성 검사로 알아낸 항생제들 중 원인 박테리아를 죽일 수 있는 가장 효과적인 항생제를 선택해서 치료한다.
- 이런 검사를 하지 않고 경험에 토대를 두고 가장 치료효과가 있는 경구용 항생제를 선택해서 치료하든지, 또는 항생제 안점적약제로 치료하든지, 또는 항생제 안점적약제와 경구용 항생제로 동시 치료할 수 있다.
- 의사의 처방에 따라 여러 종류의 항생제 안연고나 항생제 안점적약제 중 한 종류를 선택해서 10일 정도 눈에 넣어 치료하기도 한다.
- 요즘 4세대 세팔로스포린 항생제 Fluoroquinolones 안약, 비가목스(Vigamox, Moxifloxacin) 안약, 안점적약제로 박테리아 결막염을 치료하기도 한다.
- 포비돈-아이오다인(Povidone-Iodine) 안약으로 박테리아 결막염이나 클라미디아 결막염을 치료한다.
- 박테리아 결막염이 한쪽 눈에만 있어도 처음 며칠 동안은 안연고나 안 점적약제를 양쪽 눈에 넣어 치료하다가 나중 며칠 동안은 결막염이 있는 눈에만 발라 치료할 수 있다.
- 박테리아 결막염을 일으킨 박테리아가 눈에만 침입하지 않고 중이나 부비강 등에 동시 침입하여 결막염과 중이염 및, 또는 부비강염이 동시 생길 수 있다. 그러므로 박테리아 급성 결막염을 앓을 때는 중이염이나 축농증 등이 함께 있나 알아보고 그에 따라 적절히 치료한다.
- 눈에 안연고 약이든 안 점적약제를 넣어 치료할 때 영유아들은 싫어하고 잘 울 수 있다.
- 영유아들의 대부분은 눈에 액체로 된 안약을 넣은 직후 울 수 있다.
- 그때 넣은 액체 안약이 눈물과 같이 금방 쉽게 씻겨 나올 수 있다.
- 따라서 영유아들의 결막염은 액체 안약으로 치료해 주는 대신 가능한 한 연고 안약으로 치료해 주는 것이 낫다.
- 연고 안약이나 액체 안약으로 박테리아 결막염을 치료할 때 눈이 쓰리고 잠시 동안 잘 보이지 않는다고 울 때도 있다.
- 안약 자체로 약물 알레르기가 생겨 쓰리고 아프고 눈이 붓을 수도 있다.
- 눈에 안약, 안 점적약제를 넣을 때 환아가 싫어하면 안약 자체로 약물 알레르기 반응이나 부작용이 생기는지 잘 살펴보아야 한다.
- 안약의 부작용이나 알레르기가 생기지 않는 한 안약을 처방 따라 계속 넣어 치료한다.
- 치료 중 질문이 있으면 의사에게 문의해야 한다. 부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다-소아가장간호백과-제 21권 눈에 안 점적약제나 안연고를 넣는 방법 참조.
- www.vigamox.com.
- 아이들에게 흔히 볼 수 있는 결막염 참조
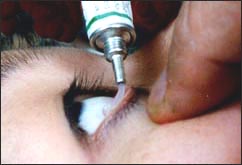
사진 69. 눈에 안연고를 넣는다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D. FAAP
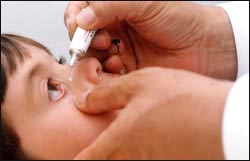
사진 70. 눈에 안연고를 넣는다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D. FAAP
박테리아 결막염을 치료할 때 흔히 쓸 수 있는 항생제 안연고나 안점적약
Bacterial conjunctivitis 박테리아 결막염 (박테리아성 결막염)Causes of bacterial conjunctivitis • A bacterial infection of the conjunctiva can cause acute bacterial conjunctivitis. • Conjunctivitis caused by a gonorrhea infection is also a type of bacterial conjunctivitis, but conjunctivitis caused by a bacterial infection other than gonococcal conjunctivitis is discussed here. • Acute bacterial conjunctivitis can occur when bacteria such as Streptococcus pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus, Group B Haemophilus influenzae (Hibi), Group A beta-hemolytic streptococci or Group B hemolytic streptococci infect the conjunctiva. • Acute bacterial conjunctivitis often occurs as a secondary bacterial infection when you have otitis media, sinusitis, cold, or other viral upper and lower respiratory tract infections, or bacterial upper and lower respiratory tract infections. • However, only acute bacterial conjunctivitis may occur on its own. Symptoms, signs of bacterial conjunctivitis
Photo 66. Acute bacterial conjunctivitis Streptococcus pneumoniae infection can lead to acute bacterial conjunctivitis. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
Photo 67. Acute conjunctivitis due to infection with Heb. sauce; Rudolph s, Wagner, M.D. • Symptoms vary depending on the type of bacteria causing acute bacterial conjunctivitis, the degree of conjunctivitis, and the presence or absence of complications. • When bacteria infect the conjunctiva and cause acute conjunctivitis, the conjunctiva becomes red and congested, the eyelids swell, and yellow mucus is formed. (see photo) • When bacterial conjunctivitis is severe, the eyelids and eyelids swell to the point that you cannot open your eyes. • Conjunctivitis can occur in only one eye or in both eyes at the same time. • Symptomatic signs of acute conjunctivitis may be present together with symptoms of otitis media or sinusitis with conjunctivitis. Diagnosis of bacterial conjunctivitis • Diagnosis is made by combining medical history, symptoms, signs, and examination findings. • If acute bacterial conjunctivitis is suspected, pus from the conjunctiva of the eye with conjunctivitis is collected with a cotton swab and subjected to Gram-stained microscopic bacteriological examination and bacterial culture to determine what kind of bacterial infection caused the disease. • However, in order to diagnose this disease, there are more cases when a bacterial culture test is not necessary and diagnosis is made based on symptoms and examination findings. • Since acute bacterial conjunctivitis often coexists with otitis media or sinusitis, it is recommended to check for otitis media or sinusitis when acute bacterial conjunctivitis occurs. • See Table 2 Differential Diagnosis of Bacterial, Virus, and Allergic Conjunctivitis treatment of bacterial conjunctivitis
Photo 68. How to put eye drops in your eyes Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP • Treatment depends on the severity, cause, and presence of complications of bacterial conjunctivitis. • It is ideal to start treatment with an appropriate antibiotic eye ointment or antibiotic eye drops while performing a bacterial culture test with pus caused by bacterial conjunctivitis to determine which bacteria caused the conjunctivitis. • Select and treat the most effective antibiotic that can kill the causative bacteria from among the antibiotics detected by the antimicrobial susceptibility test or according to the type of bacteria detected by Gram stain microscopic bacteriological examination and bacterial culture examination. • Without these tests, the most effective oral antibiotics can be selected and treated based on experience, treated with antibiotic eye drops, or treated with antibiotic eye drops and oral antibiotics simultaneously. • Depending on your doctor’s prescription, you can select one of several antibiotic eye ointments or antibiotic eye drops and put it in your eyes for 10 days for treatment. • These days, 4th generation cephalosporin antibiotics Fluoroquinolones eye drops, Vigamox (Moxifloxacin) eye drops, and eye drops are sometimes used to treat bacterial conjunctivitis. • Treat bacterial or chlamydial conjunctivitis with Povidone-Iodine eye drops. • Even if bacterial conjunctivitis is only in one eye, for the first few days, you can apply eye ointment or eye drops to both eyes, and then apply it to the affected eye only for a few days. • Bacteria that cause conjunctivitis do not only invade the eyes, but simultaneously invade the middle or sinuses, causing conjunctivitis, otitis media, and/or sinusitis at the same time. Therefore, when you have acute bacterial conjunctivitis, find out if you have otitis media or sinusitis and treat it accordingly. • Infants and young children may not like it and cry easily when they are treated with eye ointment or eye drops. • Most infants and young children may cry immediately after placing liquid eye drops in their eyes. • The liquid eye drops put in at that time can be easily washed out like tears. • Therefore, it is better to treat conjunctivitis in infants and young children with ointment eye drops as much as possible instead of using liquid eye drops. • When treating bacterial conjunctivitis with ointment eye drops or liquid eye drops, the eyes are sore and sometimes cry with difficulty seeing for a while. • The eye drops themselves can cause a drug allergy, which can cause soreness, soreness, and swelling of the eyes. • If the child does not like when eye drops or eye drops are put into the eye, carefully examine whether the eye drops themselves cause allergic reactions or side effects. • As long as there are no side effects or allergies to eye drops, continue to administer eye drops as prescribed. • You should ask your doctor if you have any questions during treatment. www.drleepediatrics.com – Volume 21, How to Put Eye Drops or Ointment into Your Eyes. • www.vigamox.com. • See Conjunctivitis Common in Children
Photo 69. Put the eye ointment in the eye. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D. FAAP
Photo 70. Put an eye ointment into your eyes. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D. FAAP Antibiotic eye ointment or eye drops commonly used to treat bacterial conjunctivitis 1. erythromycin eye ointment, 2. Chloramphenicol eye ointment; 3. sulfa eye ointment, 4. Tobramycin eye ointment (Tobrex), 5. Azithromycin 6. Gentamycin eye ointment 7. Polytrim eye ointment 8. Moxifloxacin (Vigamox) eye drops 9. Becifloxacin Eye Drops 10. Povidone-Iodine Eye Drops 11. Others 출처 및 참조문헌
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP “부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다. “The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.” |