박테리아성 고관절염 Bacterial arthritis of hip(Septic hip arthritis)
박테리아성 고관절염의 원인
- 세균(박테리아)이 고관절에 감염되어 고관절이 곪고 거기에 염증이 생긴 관절염을 박테리아 고관절염이라 한다.
- 고관절염을 일으키는 박테리아(세균)의 종류가 많이 있다.
- 결핵균 감염으로 생긴 고관절염은 제외하고 다른 종류의 박테리아 고관절염에 관해서 주로 설명한다.
- 나이에 따라 박테리아성 고관절염을 일으키는 세균의 종류가 다를 수 있다.
- 폐렴연쇄상구균, B형 헤모필러스 인플루엔자균(히브균), A군 β 용혈성 연쇄상구균, B군 용혈성 연쇄상구균, 황색 포도상구균들 중 한 종류의 세균 감염에 의해서 박테리아성 고관절염이 생길 수 있다.
- 이 중에서 고관절염이 황색 포도상구균 감염으로 소아들에게 더 잘 생길 수 있다.
박테리아성 고관절염의 증상 징후
- 열이 나고 관절염이 생긴 고관절이 붓고 만지면 아프고 그쪽 다리로 디디고 설 수 없다.
- 박테리아성 고관절염이 있는 다리를 구부리고, 또 그쪽 다리를 몸통 바깥쪽으로 젖힌 자세를 취하는 것이 보통이다.
- 박테리아성 관절염이 신생아에게 생기면 아무 것도 먹지 않고 열이 나고 몹시 보채고 잠을 많이 자는 증상 징후가 생길 수 있다.
박테리아성 고관절염의 진단 치료
- 병력, 진찰소견, 증상 증후, 적혈구 침강속도(ESR) 증가 검사, CBC 피 검사와 총 백혈구 수 증가 검사, 고관절 X선 사진 검사, 고관절 MRI 검사, 고관절 CT 스캔 검사 등으로 진단하고 고관절 속에서 고름을 채취해 그 피검물로 그람 염색 현미경 세균 검사 및 세균 배양검사를 해서 어떤 종류의 세균 감염으로 고관절염이 생겼는지 알아본다.
- 전해질 포도당 액 혈관주사로 탈수를 치료하고 경험 토대로 선택한 항생제나 항균제 감수성 검사의 결과에 따라 적절한 항생제를 선택해 항생제 혈관주사 치료를 하면서 고관절 속에 든 고름을 외과적 수술로 빼준다.
박테리아성 고관절염의 후유증
- 백테리라성 고관절염이 생겨 있던 쪽 대퇴골 성장판의 일부, 또는 전부가 파괴될 수 있다.
- 대퇴골 골단의 두부와 경부가 완전히 없어지거나 고관절 두부가 탈구되어 일생동안 절름발이 장애자가 될 수 있다.
박테리아성 고관절염의 감별 진단
- 골수염 Osteomyelitis
- 급성 관절염과 패혈성 관절염(감염성 관절염) Acute arthritis and Septic arthritis
- 연소성 류마토이드 관절염 Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis
- 결핵균성 척추염 Tuberculosis spondylitis
- 결핵균성 관절염 Tuberculosis arthritis
- 일과성 활막염 Transient synovitis (Toxic synovitis)
사진 141. Kingella kingae 세균
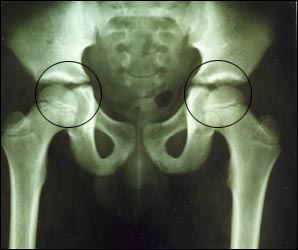
사진 143. 양쪽 고관절(◯으로 표시된 부분)
고관절에 생긴 염증을 고관절염이라고 한다.
세균(박테리아) 감염으로 생긴 고관절염을 박테리
아성 고관절염이라 한다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
|
다음은“5살된 여아 엉덩이뼈에 물이 차는데요, 고관절염.”에 관한 인터넷 소아청소년 건강상담 질의응답의 예 입니다. |
Q&A. 5살된 여아 엉덩이뼈에 물이 차는데요, 고관절염.
Q.
- 5살 된 여아입니다. 오른쪽 무릎이 아파서 병원엘 갔는데 의사 선생님이 x-레이를 찍어 보시고는 엉덩이뼈에 물이 차서 그렇다고 합니다. 지금 일주일 분의 약을 먹고 상태는 호전 되었는데 아직도 무릎 위쪽이 조금 아프다고 합니다. 병명을 말씀하셨는데 잘 들어 보지 못한 병명이라 잘 모르겠구요. 걸어 다니지 말고 안정을 취해야 한다고 하시더군요. 약물로 치료가 된다고 하셨는데 커가면서 또 이런 현상이 나타날 수가 있는지요. 계속 뛰지도 못하고 심한 움직임을 할 수 없는지요.
- –답답한 엄마가
A.
- 미선님
- 안녕하세요. 질문해 주셔서 감사합니다. 좋은 질문입니다. 휴가로 답변이 늦어 죄송합니다.
- 자녀의 나이, 성별, 과거 병력, 가족 병력, 진찰소견, 임상검사 등의 정보를 많이 알수록 답변을 드리는데 도움이 됩니다. 주신 정보를 토대로 해서 답변을 드리겠습니다.
- 대퇴골, 고관절, 경골, 비골, 무릎관절(슬관절) 등에 생긴 골절,
- 바이러스성 고관절염
- 박테리아성 고관절염,
- 결핵성 고관절염,
- 대퇴골 등에 생긴 골수염,
- 레그퍼세스 병,
- 고관절 활막염,
- 연소성 류마토이드 관절염 등으로 무릎이나 고관절이 아플 수 있습니다.
- 어떤 원인으로 고관절에 체액이 잡혀있는지 확실히 모르기 때문에 질문에 답변을 정확히 드릴 수 없습니다.
- 아직도 증상 징후가 계속되고 의문이 있으면 이 문제에 대해서 단골 소아청소년과 의사와 상담하시기 바랍니다.
- 그리고 가능하면 정형외과 전문의 치료를 받으시기 바랍니다.
- “활액 검사로 관절염을 감별 진단할 수 있다” 참조
- 다리를 절고 아플 때,
- 고관절염,
- 결핵성 고관절 염,
- 대퇴골 등에 생긴 골수염,
- 레그퍼세스 병,
- 고관절 활막염,
- 연소성 류마토이드 관절염 등을 참조하시기 바랍니다.
- 질문이 더 있으면 다시 연락해 주시기 바랍니다. 감사합니다. 이상원 드림
Bacterial arthritis of hip (Septic hip arthritis) 박테리아성 고관절염
Causes of Bacterial Hip Arthritis
• Bacterial (bacterial) infection of the hip joint causes the hip joint to become sore and inflamed. It is called bacterial hip arthritis.
• There are many types of bacteria (bacteria) that cause hip arthritis.
• Except for hip arthritis caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection, other types of bacterial hip arthritis are mainly discussed.
• Depending on the age, the types of bacteria that cause bacterial hip arthritis may differ.
• Bacterial hip arthritis can be caused by infection with one of the following bacterial infections: Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae type B (H. pneumoniae), group A β hemolytic streptococci, group B hemolytic streptococci, and Staphylococcus aureus.
• Of these, hip arthritis is more likely to occur in children due to Staphylococcus aureus infection.
Symptoms, signs of Bacterial Hip Arthritis
• Fever, arthritic hip joint is swollen and painful to the touch and cannot stand with that leg.
• It is common to assume a position with the leg with bacterial hip arthritis with the leg bent and that leg extended out of the torso.
• Newborns with bacterial arthritis may develop symptoms of not eating, a fever, irritability, and sleeping a lot.
Diagnosis, Treatment of Bacterial Hip Arthritis
• Diagnosis by medical history, examination findings, symptomatic symptoms, ESR increase test, CBC blood test and total white blood cell count test, hip X-ray, hip MRI, hip CT scan, etc. , and the specimens are subjected to Gram-stained microscopic bacteriological examination and bacterial culture to find out what kind of bacterial infection caused hip arthritis.
• Dehydration is treated by intravenous injection of electrolyte glucose solution, and the pus in the hip joint is surgically removed while performing antibiotic vascular injection by selecting the appropriate antibiotic according to the results of the antibiotic or antimicrobial susceptibility test selected based on experience.
Sequelae of bacterial hip arthritis
• Part or all of the growth plate of the femur on the side of the hip osteoarthritis may be destroyed.
• Complete loss of the head and neck of the epiphysis of the femur or dislocation of the head of the hip joint can result in lifelong lameness.
Differential diagnosis of bacterial hip arthritis
• Osteomyelitis • Acute arthritis and septic arthritis
• Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis
• Tuberculosis spondylitis
• Tuberculosis arthritis
• Transient synovitis (Toxic synovitis)

Picture 141. Kingella kingae bacteria

Picture 143. Both hip joints (marked with ◯) Inflammation of the hip joint is called hip arthritis. Bacterial (bacterial) infection of the hip joint It’s called sub-arthritis. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
The following is an example of a Q&A on health counseling for children and adolescents on the Internet about “The hip bone of a 5-year-old girl is getting watery, hip arthritis.”
Q&A.
5 year old girl with water on her hip bone, hip arthritis.
Q.
• I am a 5 year old girl. Her right knee hurt, so she went to the hospital, and the doctor took an x-ray and said it was because water was filling up her hip bone. She says now that she has taken a week’s supply of medicine and her condition has improved, she still has a little pain in her upper knee. You mentioned the name of the disease, but I do not know it well because I have not heard of it. She told me not to walk around and she said she should take it easy. She said that it can be treated with drugs, but can this happen again as she grows up? She can’t keep running and can’t make strenuous movements.
• -A bored mother A.
• Mi Seon-nim • Good morning. Thanks for asking. That’s a good question. Sorry for the late reply due to vacation.
• The more information you have, such as your child’s age, gender, past medical history, family history, medical findings, and clinical tests, it will help you answer questions. We will give you an answer based on the information you provided.
• Fractures in the femur, hip joint, tibia, fibula, knee joint (knee joint), etc.;
• Viral hip arthritis
• Bacterial hip arthritis;
• tuberculous hip arthritis;
• Osteomyelitis of the femur, etc.;
• Legpurses’ disease;
• hip synovitis;
• Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis may cause pain in the knee or hip joint.
• We can’t answer your question precisely because we’re not sure what causes fluid to be held in the hip joint.
• If symptoms still persist and if you have any questions, please discuss this with your regular pediatrician.
• And, if possible, see an orthopedic surgeon.
• See “A synovial fluid test can differentially diagnose arthritis” • When your legs hurt and limp,
• Hip arthritis;
• tuberculous hip arthritis;
• Osteomyelitis of the femur, etc.;
• Legpurses’ disease;
• hip synovitis;
• See also Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis.
• If you have more questions, please contact us again.
Thank you. Lee Sang-won .MD
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제16권 소아청소년 정형외과 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제9권 소아청소년 소화기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제10권. 소아청소년 신장 비뇨 생식기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제11권. 소아청소년 심장 혈관계 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제12권. 소아청소년 신경 정신 질환, 행동 수면 문제
- www.drleepediatrics.com제13권. 소아청소년 혈액, 림프, 종양 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제14권. 소아청소년 내분비, 유전, 염색체, 대사, 희귀병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제15권. 소아청소년 알레르기, 자가 면역질환
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th — 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
-
Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, Harvey grant, and Robert Murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
-
The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
-
Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care
-
응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
-
Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
-
Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
-
Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Berverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gerhon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
-
소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”