바이러스 심근염 Viral myocarditis
바이러스 심근염의 원인
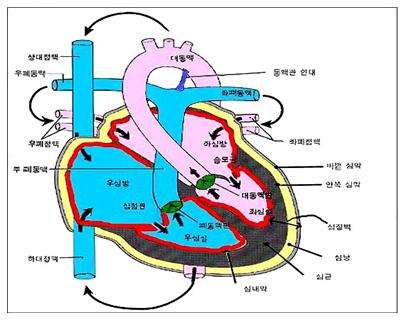
그림 95. 심장과 심장벽
화살표(→)는 혈액이 흐르는 방향
검은 색으로 표시된 부위가 심장 근육(심근)
소스; Used with permission from Ross Laboratories Columbus, OH, USA
-
콕삭키바이러스, 에코바이러스, 풍진바이러스, 수두바이러스 등 바이러스 감염이 신체의 다른 계통의 장기에 감염되어 그 장기에 바이러스 전염병을 1차적으로 일으키는 동시 심근에도 1차적으로 직접 감염되어 바이러스 심근염을 일으킬 수 있다.
-
때로는 심근에만 1차적으로 바이러스가 감염되어 바이러스성 심근염만 일으킬 수 있다.
-
이렇게 바이러스 감염에 의해서 생긴 심근염을 바이러스 심근염이라고 한다(가와사키 병 참조).
바이러스 심근염의 증상 징후
-
심근염을 일으킨 바이러스의 종류, 다른 계통의 장기에 생긴 바이러스 감염병의 증상 징후, 심근염의 중증도 등에 따라 증상 징후가 다르다.
-
바이러스성 심근염의 전형적인 증상은 호흡곤란, 무기력, 피부 창백, 왼쪽 앞가슴 통증, 맥박이 비정상적으로 빠르거나 늦은 증상 징후 등이다.
-
바이러스 심근염이 심할 때는 기외수축 부정맥, 방실 차단성 부정맥, 울혈성 심장부전증 등 생명에 위험한 합병증이 생길 수 있고 심지어는 사망 할 수 있다.
-
때로는 바이러스 심근염으로 인해 증상 징후는 거의 없고 다른 계통의 장기에 생긴 바이러스성 전염병에 의한 증상 징후만 주로 나타날 수 있다.
바이러스 심근염의 진단
-
병력, 증상 징후와 진찰소견 등을 종합해서 이 병이 의심되면 가슴 X-선 사진검사, 심장 초음파 검사, 심전도 검사, 피 검사와 그 외 다른 여러 가지 검사로 진단할 수 있다.
-
가슴 X-선 사진 검사에 심장이 비정상적으로 커져 있을 수 있다.
-
심장이 커질 수 있는 다른 병들과 감별 진단해야 한다.
-
바이러스 배양검사, 바이러스 항원 항체 검사 등으로 진단할 수 있다.
바이러스 심근염의 치료
-
바이러스 심근염 치료에는 항생제치료에는 효력이 없다.
-
그때그때 생긴 증상 징후에 따라 대증치료를 한다.
-
정신적, 육체적 안정을 취하고 충분한 영양분과 수분을 섭취한다.
-
필요에 따라 디기탈리스제로 치료한다.
Viral myocarditis 바이러스 심근염
Causes of viral myocarditis

Figure 95. Heart and heart wall Arrow (→) is the direction in which blood flows The area marked in black is the heart muscle (myocardium) sauce; Used with permission from Ross Laboratories Columbus, OH, USA
• Viral infections such as coxsackie virus, ecovirus, rubella virus, chickenpox virus, etc. infect other organs of the body and cause viral infectious diseases in those organs. have.
• Sometimes the virus is infected primarily only in the myocardium, which can cause only viral myocarditis.
• Myocarditis caused by this viral infection is called viral myocarditis (see Kawasaki disease).
Symptoms, signs of viral myocarditis
• Symptoms differ depending on the type of virus that caused myocarditis, the symptoms of viral infectious diseases in other organs, and the severity of myocarditis.
• Typical symptoms of viral myocarditis are shortness of breath, lethargy, pale skin, pain in the left anterior chest, and signs of abnormally fast or late pulse.
• Severe viral myocarditis can lead to life-threatening complications such as ectopic arrhythmia, atrioventricular arrhythmia, and congestive heart failure, and even death.
• Sometimes there are few symptoms due to viral myocarditis, and only symptomatic symptoms due to viral infectious diseases in other organs are present.
Diagnosis of viral myocarditis
• If the disease is suspected by taking the medical history, symptoms, signs, and examination findings together, it can be diagnosed by chest X-ray examination, echocardiography, electrocardiogram, blood test, and many other tests.
• A chest x-ray may show an abnormally enlarged heart.
• Diagnosis should be differentiated from other diseases that can cause enlarged heart.
• It can be diagnosed by virus culture test, virus antigen antibody test, etc.
Treatment of viral myocarditis
• Antibiotic therapy is not effective for the treatment of viral myocarditis.
• Treat symptomatic treatment according to the symptoms and symptoms that occurred then. • Get mental and physical stability and get enough nutrients and fluids.
• Treat with digitalis as needed.
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com제11권. 소아청소년 심장 혈관계 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th — 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
-
Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, Harvey grant, and Robert Murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
-
The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
-
Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care
-
응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
-
Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
-
Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
-
Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
-
Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
-
소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”