물집(수포/포진) Blister(Skin blister, Bullae, Vesicles)
물집(피부에 물집이 잡혔을 때/수포/포진)의 원인
-
피부에 생긴 물집을 수포, 또는 포진이라 한다.
-
물집은 급성으로도 생길 수 있고 만성으로 생길 수 있다.
-
여러 가지 원인으로 생길 수 있다.
-
다음과 같은 경우 물집이 급성으로 생길 수 있다.
-
뜨거운 물이나 불로 생긴 2도 이상 화상으로 화상성 물집
-
어떤 물체에 피부를 심하게 문질러서 생긴 마찰성 물집
-
수두나 헤르페스바이러스 감염 등 바이러스 감염병으로 생긴 물집
-
농가진 등 박테리아 감염병으로 생긴 물집
-
유전성 질환으로 생긴 물집
-
2도 이상의 동상으로 생긴 물집
-
옻 접촉성 피부염 등으로 생긴 물집
-
모기 등 곤충에 물려 생긴 물집
-
화학물질 접촉성 피부염으로 생긴 물집
-
다발 삼출성홍반으로 생긴 물집
-
포도상구균 열탕성 피부염으로 생긴 물집
-
수족 구병으로 생긴 물집
-
매독으로 생긴 물집
-
화상 피부 증후군으로 생긴 물집
-
수포성 피부병 Chronic bullous dermatosis
-
수포성 표피박리증 Epidemolysis bullosa
-
천포창(펨피구스) Pemphigus
-
유천포창(펨피고이드) Pemphigoid
-
편평태선 Lichen planus
-
선천성 각화부전증 Dyskeratosis congenita
-
크론병 Crohn’s disease
-
셀리악 병 Celiac disease
-
장병성 선단피부염 Acrodermatitis enteropathica
-
베체트 병 Behcet’s Disease
-
전신 홍반성 낭창 Systemic lupus erythematosus, SLE
-
포르피리아(포르피리아증) Porphyria
-
콕삭키바이러스 감염병 Coxsackievirus infection
-
식물성 광 피부염 Phytophotodermatitis
-
그 외 다른 여러 원인으로 피부에 물집이 잡힐 수 있다.
-
요약하면 불, 뜨건 물체, 화학물질, 햇볕, 끓는 물, 피부 외상, 박테리아 감염, 또는 바이러스 감염, 2도 이상의 동상, 그 외 다른 원인으로 피부에 물집이 잡힐 수 있다
-
참조문헌 NEJM October 2008 p.1718
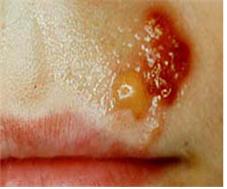
사진 600. 헤르페스바이러스 피부감염으로 인한 물집.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
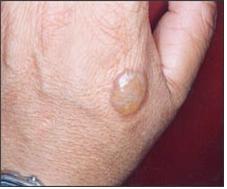
사진 599. 벌레에 물리거나 쏘였을 때 물집이 잡힐 수 있다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
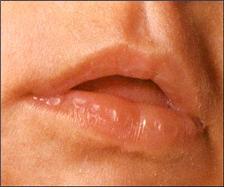
사진 601. 신생아의 아래 입술에 생긴 흡인성 수포(물집).
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee,MD.,FAAP
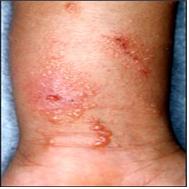
사진 602. 옻나무 접촉으로 인한 접촉성 피부염으로 생긴 물집.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
물집 치료
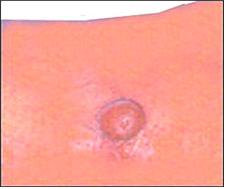
사진603. 곤충에 물려 생긴 물집.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD.F AAP
-
물집의 원인과 물집의 정도에 따라 치료한다.
-
박테리아 감염병이나 바이러스 감염병으로 피부에 생긴 물집은 의사의 지시에 따라 치료한다.
-
화상이나 외상으로 물집이 잡혔을 때 물집을 덮고 있는 피부에 박테리아 감염이 생기지 않게 치료한다.
-
심한 화상으로 물집이 많이 생길 때는 혈관 내 단백질, 전해질, 체액이 물집을 통해서 체외로 소실되지 않게 예방하고 치료해야 한다.
-
화상으로 생긴 물집은 곪지 않은 한 터트리지 말고 그대로 놓고 관찰할 수 있다.
-
화상으로 생긴 물집은 덮고 있는 피부가 괴사되지도 않고 재생될 수 있다.
-
화상이나 외상으로 생긴 물집이 터지지 않았을 때는 박테리아 감염이 생기지 않도록 물집을 터트리지 말고 실버데인 크림(Sliverdane cream) 등 화상치료용 크림을 바르거나 소독된 거즈나 일회용 반창고로 물집을 덮어 치료한다.
-
물집이 화학물질로 잡혔을 때 바로 접촉된 피부를 수도 물로 깨끗이 씻고 물집은 터트리지 말고 그대로 두고 관찰할 수 있다.
-
터진 물집이 불결하면 비눗물로 깨끗이 씻은 후 베타다인 살균 액이나 다른 종류의 살균 약으로 소독한다.
-
물집이 이미 터졌거나, 물집을 덮었던 피부가 괴사됐거나 물집이 곪았을 때는 소독된 가위로 물집을 덮은 피부를 조심스럽게 잘라낸 후 물집이 있는 부위를 살균된 거즈로 덮고 의사의 지시에 따라 치료한다.
-
물집이 터지기는 했지만 물집이 불결하지 않고 박테리아 감염이 되지 않았을 때는 터진 물집을 베타다인 살균 액이나 다른 종류의 살균제액으로 살균 한 후 일회용 반창고나 거즈로 덮고 관찰 치료한다.
-
원인이 무엇인지 모르거나, 물집을 어떻게 치료할지 잘 모르면 병원 응급실이나 의사의 지시에 따라 치료한다.
-
그리고 물집이 심할 때는 병원으로 환아를 곧 데리고 간다.
-
물집이 생기면 권장한 대로 파상풍 백신 예방접종을 한다.
-
물집이 생긴 부위가 붓고 아프면 얼음물 찜질이나 찬물 찜질을 하든지 타이레놀이나 모트린으로 진통시킨다.
-
터진 물집에 박테리아 감염이 생겨 곪으면 적절한 항생제로 치료한다.
- 그 외 물집이 생기게 한 원인에 따라 치료한다.
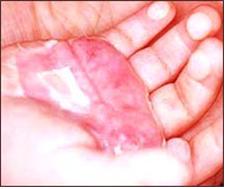
사진 604. 2도 화상으로 손가락에 생긴 물집.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD.,FAAP
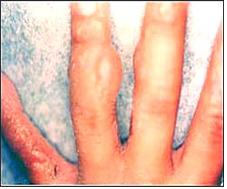
사진 605. 덩굴 옻나무 접촉성 피부염으로 생긴 물집.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
Blister (Skin blister, Bullae, Vesicles) 물집(수포/포진)
Causes of blisters (skin blisters/vesicles)
• Blisters on the skin are called blisters or herpes.
• Blisters can be acute or chronic.
• It can be caused by a number of reasons.
• Blisters can develop acutely if:
• Burn blisters from second-degree burns caused by hot water or fire
• Abrasive blisters caused by heavy rubbing of the skin against an object
• Blisters caused by a viral infection, such as chickenpox or herpesvirus infection • Blisters caused by bacterial infections such as impetigo • Blisters caused by hereditary disorders • Blisters from 2nd degree or greater frostbite • Blisters caused by poison ivy contact dermatitis
• Blisters caused by insect bites such as mosquitoes
• Blisters from chemical contact dermatitis
• Blisters with multiple erythema exudative
• blisters caused by staphylococcal scalding dermatitis
• blisters caused by hand, foot and mouth disease
• blisters caused by syphilis
• Blisters caused by burn skin syndrome
• Chronic bullous dermatosis
• Epidemolysis bullosa
• Pemphigus
• Pemphigoid
• Lichen planus
• Dyskeratosis congenita
• Crohn’s disease
• Celiac disease
• Acrodermatitis enteropathica
• Behcet’s Disease
• Systemic lupus erythematosus, SLE
• Porphyria (porphyria)
• Coxsackievirus infection
• Phytophotodermatitis, vegetable photodermatitis
• There are many other causes of blisters on your skin.
• In summary, blisters on the skin can be caused by fire, hot objects, chemicals, sunlight, boiling water, skin trauma, bacterial or viral infection, second degree or higher frostbite, or other causes. • References NEJM October 2008 p.1718

Picture 600. Blisters caused by a herpesvirus skin infection. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Picture 599. Blisters can be formed when bitten or stung by an insect. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Picture 601. Aspiration blisters (blisters) on the lower lip of a newborn. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Picture 602. Blisters resulting from contact dermatitis caused by contact with poison ivy. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
Blister treatment

Picture 603. Blisters caused by insect bites. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD.F AAP
• Treatment depends on the cause and severity of the blister.
• Treat blisters on the skin caused by bacterial or viral infections according to the doctor’s instructions.
• Treat blisters from burns or trauma to avoid bacterial infection on the skin covering the blisters.
• When a large number of blisters are formed due to severe burns, it is necessary to prevent and treat the loss of intravascular proteins, electrolytes, and body fluids through the blisters.
• Blisters caused by burns can be observed without popping them as long as they are not scalded.
• Blisters from burns can regenerate without necrosis of the overlying skin.
• If a blister caused by burns or trauma does not burst, do not open the blister to prevent bacterial infection, but apply a burn treatment cream such as Silverdane cream or cover the blister with sterile gauze or a disposable bandage.
• When blisters are caught with chemicals, immediately wash the skin in contact with tap water and leave the blisters intact for observation.
• If the opened blister is dirty, wash it thoroughly with soapy water and then disinfect it with betadyne sterilizing solution or other sterilizing agent.
• If the blister has already ruptured, the skin that covered the blister is necrotic, or the blister has become blistered, carefully cut off the skin covering the blister with sterile scissors and cover the blistered area with sterile gauze .
• If a blister has burst, but the blister is not dirty and there is no bacterial infection, sterilize the blister with betadine sterilizing solution or other disinfectant solution, then cover it with a disposable band-aid or gauze and observe and treat.
• If you do not know what the cause is or how to treat the blister, treat it as directed by a hospital emergency room or doctor.
• And if the blisters are severe, take them to the hospital right away.
• If blisters occur, get a tetanus vaccine as recommended.
• If the blistered area is swollen and painful, use ice or cold water or Tylenol or Motrin for pain relief.
• Bacterial infection in the ruptured blisters should be treated with appropriate antibiotics
• Treat other blisters depending on the cause.

Picture 604. Blisters on fingers from second-degree burns Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Picture 605. Blisters from poison ivy contact dermatitis. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy of Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com제6권 신생아 성장 발육 육아 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제9권 소아청소년 소화기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제10권. 소아청소년 신장 비뇨 생식기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제11권. 소아청소년 심장 혈관계 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제12권. 소아청소년 신경 정신 질환, 행동 수면 문제
- www.drleepediatrics.com제13권. 소아청소년 혈액, 림프, 종양 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제14권. 소아청소년 내분비, 유전, 염색체, 대사, 희귀병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제15권. 소아청소년 알레르기, 자가 면역질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제17권. 소아청소년 피부 질환
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th — 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
-
Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, Harvey grant, and Robert Murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
-
The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
-
Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care
-
응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
-
Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
-
Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
-
Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
-
소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”