무지 외반족과 팔자걸음 Out-toeing(Outtoeing)
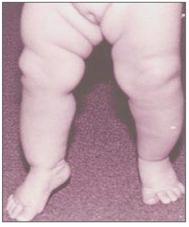
사진 112. 오른쪽 생리적 무지외반
발도 정상이고 아랫다리도 정상인데 대퇴골 상단에 있는 대퇴골 두부가 몸통 바깥쪽으로 조금 돌아가면 대퇴골 상단 두부 외경이 생긴다. 그로 인해 생긴 무지 외반을 생리적 영아 무지외반이라고 한다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
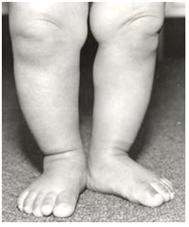
사진 113. 양쪽 발에 생긴 생리적 무지외반
발도 정상이고 아랫다리도 정상인데 양쪽 대퇴골 상단 두부가 몸통 바깥쪽으로 조금 돌아가서 생기는 대퇴골 상단 두부 외경으로 생긴 양쪽 무지외반
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
-
무지 외반족은 무지 내반족 보다 아주 드물게 생긴다.
-
대개는 생후 1~2세에 나타난 것이 보통이다.
-
대부분의 무지 외반족은 자연히 나을 수 있다.
-
한쪽 또는 양쪽의 엄지발가락이나 발 끝부분이 몸통의 바깥쪽을 향하는 발을 무지 외반족이라 한다. 무지 외반족이 있는 아이는 팔자걸음을 걸을 수 있다
-
무지 외반족은 무지 내반족이 생기는 빈도보다 훨씬 낮다.
-
한쪽이나 양쪽의 아랫다리의 정강이뼈(경골과 비골)가 몸통 바깥쪽으로 비틀릴 때,
-
한쪽 또는 양쪽의 아랫다리는 정상이지만 발 자체가 몸통 바깥쪽으로 향하든지,
-
발도 아랫다리도 정상인데 고관절 이상으로 대퇴골이 몸통 바깥쪽으로 비틀리면서 무지외반족이 생길 수 있다.
-
엄지발가락이 무지 외반족으로 몸통 바깥쪽으로 향할 때는 평소 보통으로 걸을 때는 별 지장이 생기지 않을 수 있다.
-
무지 외반족이 있는 발과 그 쪽 다리 전체가 무지 외반족이 있는 쪽으로 향할 때가 많다.
-
경미한 무지 외반족은 자연히 나을 수 있다(팔과 다리 참조).
-
좀 심한 경우, 수동 손 운동 물리치료를 해주면 더 쉽게 낫는 것이 보통이다.
-
아주 심한 무지 외반족이 있을 때는 단골 소아청소년과 전문의의 의뢰를 받아 정형외과 전문의에게 문의, 진단, 치료 받는다.
Out-toeing (Outtoeing) with the ignorant hallux 무지 외반족과 팔자걸음

Photo 112. Right physiological hallux valgus Even though the feet are normal and the lower legs are also normal, when the femur head at the top of the femur rotates slightly to the outside of the body, the outer diameter of the upper head of the femur occurs. The resulting valgus valgus is called physiological valgus valgus of infants. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP

Picture 113. Physiological hallux valgus on both feet The feet are normal and the lower legs are also normal, but both valgus caused by the outer diameter of the upper head of the femur, which is caused when the upper heads of both femurs are slightly turned to the outside of the torso Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
• The ignorant hallux is much rarer than the ignorant hallux.
• It is usually present at 1 or 2 years of age.
• Most ignorant hallux will get better on their own.
• Feet with one or both big toes or toes pointing outward of the body are called hallux valgus. A child with ignorance hallux can walk
• The ignorant hallux is much less frequent than the ignorant hallux.
• When the shinbones (tibia and fibula) of one or both lower legs twist outward of the torso; • One or both lower legs are normal, but the feet themselves point outward of the torso;
• Even though your feet and lower legs are normal, you may develop a hallux valgus when the femur twists outward from the torso beyond the hip joint.
• When the big toe is on the outside of the torso as a hallux valgus, it may not cause any problems when walking normally.
• Often the foot with the ignorant hallux and the entire leg on that side will point toward the ignorant hallux.
• Mild ignorant hallux may heal spontaneously (see Arms and Legs).
• In more severe cases, it is usually easier to get better with manual hand exercise physiotherapy.
• If you have very severe hallux valgus, you will receive a referral from a regular pediatrician and consult with an orthopedic specialist for diagnosis and treatment.
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제16권 소아청소년 정형외과 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제9권 소아청소년 소화기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제10권. 소아청소년 신장 비뇨 생식기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제11권. 소아청소년 심장 혈관계 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제12권. 소아청소년 신경 정신 질환, 행동 수면 문제
- www.drleepediatrics.com제13권. 소아청소년 혈액, 림프, 종양 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제14권. 소아청소년 내분비, 유전, 염색체, 대사, 희귀병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제15권. 소아청소년 알레르기, 자가 면역질환
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th — 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
-
Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, Harvey grant, and Robert Murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
-
The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
-
Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care
-
응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
-
Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
-
Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
-
Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
-
소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”