림프부종과 밀로리 병 Lymphedema and Milroy disease
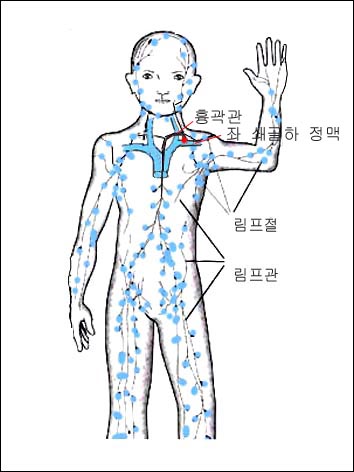
그림 1-13. 전신에 분포된 림프관과 림프절
거의 대부분의 전신에서 돌아온 림프액은 쇄골 하 정맥 속으로 들어간다. 빨간 점으로 표시한 부분에서 핌프액이 정맥 속으로 들어간다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
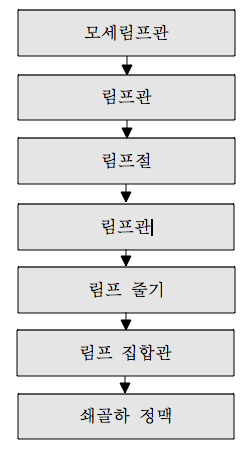
림프액의 흐름
- 림프관의 일부가 선천성으로 또는 후천성으로 일시적으로 또는 장기적으로 막혀 림프액 순환장애가 생기면 막힌 림프관 부위 이하 말단 신체 부위에 림프액 등이 비정상적으로 증가되고 거기다가 체액이 고이고 결과적으로 국소적 신체 부위가 부어있는 상태를 림프부종이라고 한다.
- 림프부종이 국소적으로 장기적으로 생기면 섬유아세포가 림프부종이 있는 그 부위에 비정상으로 증가되고 결과적으로 결합조직이 비정상적으로 많이 형성되고 증가된다.
-
그래서 림프 부종이 있는 국소를 손으로 만지면 마치 나무판자를 만지는 것같이 굳은 촉감이 있다.
림프부종과 밀로리 병의 원인
-
국소적 만성 감염으로도 림프부종이 생길 수 있다.
-
수술 후 합병증으로 림프부종이 생길 수 있다. 이런 경우를 2차 림프부종이라고 한다. 유방수술 후 국소적 림프부종이 흔히 생길 수 있다.
-
밀로리 병(Milroy disease)이나 마이그 병(Meige disease) 등으로 림프부종이 생길 수 있다. 이 두 병은 1차 림프부종에 속한다. 밀로리 병은 상염색체 우성으로 유전되는 선천성 질환으로서 출생 시부터 나타나있는 것이 보통이다.
-
국소적으로 림프부종이 나있는 신체부위에 A군 연쇄상구균감염이나 황색 포도상구균성 감염이 더 잘 생길 수 있다. 그런 종류의 감염으로 인해 그 부위의 림프관에 병적 변화가 생겨 림프부종이 더 심해질 수 있다.
-
남녀에게 다 같이 생길 수 있으나 70~80%는 여성에게 생긴다.
-
우 하지에 더 잘 생기고 무릎 이하 부위까지 생기지 않는 것이 보통이다.
-
림프부종이 있는 국소 부분을 손가락 끝으로 눌렀다 바로 떼면 누른 자국이 생기지 않는 것이 비림프 부종과 림프부종이 점이다.
림프부종과 밀로리 병의 진단
-
증상 징후 병력 진찰소견을 종합해서 밀로리 병이 의심되면 림프부종이 있는 신체 부위 초음파 검사를 해서 동맥 정맥 누관이 있는지 알아본다.
-
그 부위 X-선 검사로 그 부위에 있는 뼈의 이상 유무를 알아본다.
-
그 후 검사에 이상이 없으면 그 부위 피하층에 색소 주입 검사를 해서 림프관 연상검사를 해서 진단할 수 있다.
-
때로는 MRI 검사로 진단할 수 있고 그 부위의 생체 조직검사를 해서 진단할 수 있다.
림프부종과 밀로리 병의 치료
-
밀로리 병으로 림프부종이 있으면 그 부위 체위를 조금 더 높이는 물리치료, 마사지 치료 등을 할 수 있다.
-
박테리아성 감염이 생기지 않도록 특별히 예방하고 일단 생기면 적절히 항셍제로 치료한다.
-
필요에 따라 탄력붕대로나 보통 붕대로 감아주는 치료 등 내과적 치료를 하고 필요에 따라 수술 치료를 하기도 한다.
Lymphedema and Milroy disease 림프부종과 밀로리 병

Figure 1-13. Lymphatic vessels and lymph nodes throughout the body The lymph fluid that has returned from most of the body enters the subclavian vein. In the area marked with a red dot, the pimp fluid enters the vein. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
Lymph flow

• When a part of the lymphatic vessel is congenital or acquired temporarily or for a long period of time, and lymphatic circulation is impaired, the lymphatic fluid is abnormally increased in the distal body area below the blocked lymphatic vessel area, and the body fluid accumulates as a result, and as a result, the local body area is swollen. Is called lymphedema.
• When lymphedema develops locally and long-term, fibroblasts increase abnormally in the area where lymphedema is present, resulting in abnormal formation and increase in connective tissue.
• So, if you touch the area with lymphedema with your hands, it has a firm touch as if you were touching a wooden board.
Causes of lymphedema and Milori’s disease
• Localized chronic infection can also lead to lymphedema.
• Lymphedema may develop as a complication after surgery. This case is called secondary lymphedema. Localized lymphedema is common after breast surgery.
• Lymphedema can occur due to Milroy disease or Meige disease. These two diseases belong to primary lymphedema. Milori’s disease is a congenital disease inherited by autosomal dominance and is usually present from birth.
• Group A streptococcal infections or Staphylococcal infections are more likely to develop in areas of the body with localized lymphedema. That kind of infection can lead to pathological changes in the lymphatic vessels in the area, making lymphedema more severe.
• It can occur in both men and women, but 70-80% occurs in women.
• It is more common in the right lower extremities and less than the knees.
• Non-lymphatic edema and lymphedema do not form when the local area with lymphedema is pressed with the tip of a finger and then immediately released.
Diagnosis of lymphedema and Milori’s disease
• Symptoms Signs Combined the medical history findings and suspected of Milori’s disease, perform an ultrasound examination of the part of the body with lymphedema to find out if there is an arterial vein fistula.
• X-ray the area to check for any abnormalities in the bones in the area.
• If there is no abnormality in the test after that, you can diagnose by performing a lymphatic tube association test by injecting pigment into the subcutaneous layer of the area.
• Sometimes it can be diagnosed with an MRI scan and a biopsy of the area can be done.
Treatment of lymphedema and Milori’s disease
• If you have lymphedema due to Milory’s disease, you can do physical therapy or massage therapy to raise the position of the area a little bit.
• Specially prevent bacterial infections from occurring and, once they do, treat them with antibiotics appropriately.
• If necessary, medical treatment, such as treatment with an elastic bandage or a normal bandage, may be performed, and surgical treatment may be performed if necessary.
처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com제13권. 소아청소년 혈액, 림프, 종양 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th — 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
-
Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, Harvey grant, and Robert Murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
-
The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
-
Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care
-
응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
-
Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
-
Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
-
Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
-
소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”