류마티스 열 Rheumatic fever
- A군 베타 용혈성 연쇄상구균을 편의상 여기서 A군 연쇄상구균이라 한다.
- A군 연쇄상구균 감염으로 생긴 편도염, 인두편도염, 인두염, 중이염 또는 성홍열 등 A군 연쇄상구균 감염병을 앓는 중이나 다 나은 조금 후 A군 연쇄상구균 항원 항체 이상반응으로 체내 결합조직이나 심장 등 신체 여러 계통의 여러 장기에 생기는 염증을 류마티스 열 또는 류머티스성 열이라고 한다.
류마티스 열의 원인
-
A군 연쇄상구균 급성 편도염이나 인두 편도염, 임두염 또는 다른 여러 가지 A군 연쇄상구균 감염병이 신체 어떤 부위에 있을 때 A군 연쇄상구균 항원 항체 이상반응으로 염증이 결합조직에 생겨 류마티스 열이 생긴다고 믿고 있다.
-
류마티스 열이 발병하기 바로 전이나 발병될 당시 신체의 어느 부위에 A군 연쇄상구균(사슬알균) 감염에 의한 전염병이 있는 것이 보통이다. 드물게 류마티스 열이 발생됐을 때 A군 연쇄상구균에 의한 전염병을 최근에 앓은 적도 없고 또 그 당시 앓고 있지 않을 수 있다. [부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다–소아가정간호백과]-제7권 소아청소년 감염병-A군 연쇄상구균에 의한 전염병,
-
제15권 소아청소년 알레르기 및 자가면역질환–연소성 류마티스양 관절염 참조.
류마티스 열의 증상 징후
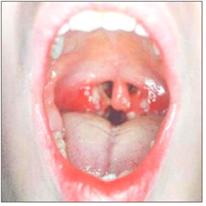
- 류마티스 열의 주증(동반 질환)에 따라, 류마티스 열의 진행 과정, 합병증의 유무, A군 연쇄상구균 감염에 의한 전염병의 종류 등에 따라 증상 징후가 많이 다르다.
-
류마티스 열에 걸렸을 때
-
류마티스 심장염,
-
류마티스 관절염,
-
류마티스 피부 발진,
-
유주성 홍반(가장자리 홍반),
-
류마티스 무도증,
-
류마티스 결절(피하 결절),
-
류마티스 폐렴 등 주 동반 질환이 생길 수 있다.
-
-
앞서 열거한 이런 류마티스 열로 생긴 류마티스 심장염, 류마티스 관절염, 류마티스 피부 발진(유주성 홍반), 류마티스 무도증, 류마티스 결절을 류마티스 열의 주 동반 질환 또는 류마티스 열의 주증 이라고 한다.
-
류마티스 열을 앓을 때 언제든지 이런 류마티스 열의 주 동반 질환이 한꺼번에 다 나타나는 것이 아니다.
-
그 중 한 가지 주 동반 질환이나 몇 가지 또는 거의 모든 류마티스 열의 주 동반 질환이 다 나타날 수 있다.
-
류마티스 열은 A군 연쇄상구균 감염에 의해 생기는 인두염, 편도염, 인두편도염, 성홍열 등이 더 잘 발생되는 겨울철과 봄철에 더 많이 나타난다.
-
A군 연쇄상구균에는 여러 균종이 있는데 그 중 류마티스 열을 일으키는 균종이 따로 있다.
-
3세 이전 영유아들이나 3세 이후 유아들, 학령기 아이들이나 사춘기 아이들, 성인들도 류마티스 열에 걸릴 수 있지만 5∼15세 연령층 소아청소년이 더 잘 걸릴 수 있다.
-
또 위생시설이 불결한 환경에서 사는 아이들이나 협소 거주지에서 사는 소아청소년들이 이 병에 더 잘 걸릴 수 있다.
-
A군 연쇄상구균 감염병을 앓는 환아들의 3%에서 류마티스 열이 발생할 수 있다고 하나 일정한 시기와 장소 등에 따라 집중적으로 더 많이 발생될 수 있다.
-
그래서 류마티스 열의 전반적인 발생 율은 0.3%에 불과하다고 한다.
-
대부분 A군 연쇄상구균 감염에 의한 전염병을 앓은 후 약 1∼5주일 경에 류마티스 열의 주 동반 질환(주증) 중 하나 또는 하나 이상 여러 개 주 동반 질환이 발생되는 것이 보통이다.
-
그렇지만 류마티스 무도증은 A군 연쇄상구균 감염에 의한 전염병을 앓은 후 2∼6개월이 지난 후에도 발생될 수 있다.
-
A군 연쇄상구균 감염에 의한 인두염이나 편도염 등에 의해서 생기는 증상 징후와 류마티스 열에 의해서 생기는 증상 징후가 같이 나타날 수 있다.
-
또 류마티스 열을 앓을 때 어떤 종류의 주 동반 질환에 따라 증상 징후가 다르다.
-
류마티스 관절염, 류마티스 무도증, 류마티스 심장염, 류마티스 결절 등에서 생기는 증상 징후가 동시에 나타날 수 있다.
-
류마티스 열이 있을 때 맹장염의 증상 징후와 비슷한 복통이 생길 수 있고, 또 미열이나 고열 등 증상 징후가 생길 수 있다.
-
이런 증상 징후는 거의가 급성으로 오는 것이 보통이지만 때로는 서서히 만성으로 나타나기도 한다.
-
류마티스 열의 각 동반 질환에 관해 다음 각항에서 더 자세히 설명한다.
Rheumatic fever 류마티스 열
• Group A beta hemolytic streptococcus is referred to here as group A streptococcus for convenience.
• Group A streptococcal antigen antibody adverse reactions caused by group A streptococcal antigen antibody adverse reactions in the body’s connective tissues, heart, etc., such as tonsillitis, pharyngeal tonsillitis, pharyngitis, otitis media, otitis media, or scarlet fever. Inflammation in many organs is called rheumatic fever or rheumatic fever.
Causes of rheumatic fever
• It is believed that when group A streptococcal tonsillitis, pharyngeal tonsillitis, pharyngitis, or several other group A streptococcal infectious diseases are present in any part of the body, an adverse reaction to the group A streptococcal antigen antibody results in inflammation in the connective tissue, resulting in rheumatic fever.
• It is common to have an infectious disease caused by a group A streptococcus (chain bacterium) infection in any part of the body just before or at the time of the onset of rheumatic fever. Rarely, when rheumatic fever occurs, you may not have recently suffered from an infectious disease caused by group A streptococcus, and you may not have suffered at that time.www.drleepediatrics.com-Volume 7 Child and Adolescent Infectious Diseases-Infectious diseases caused by group A streptococcus,
• See Volume 15 Child and Adolescent Allergy and Autoimmune Diseases-Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis.
Symptoms, signs of rheumatic fever

Picture 77. Group A beta hemolytic streptococcal tonsillitis Rheumatic fever can occur when suffering from pharyngitis or tonsillitis. Copyright ⓒ 2013 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
• Depending on the main symptom of rheumatic fever (combined disease), symptoms and signs vary greatly depending on the progression of rheumatic fever, the presence or absence of complications, and the type of infectious disease caused by group A streptococcal infection.
o When you have rheumatic fever
o rheumatic heart disease, o rheumatoid arthritis,
o rheumatic skin rash,
o Mimic erythema (erythema at the edges),
o Rheumatoid chorea,
o rheumatic nodules (subcutaneous nodules),
o Major comorbidities such as rheumatoid pneumonia may occur.
• Rheumatoid heart disease, rheumatoid arthritis, rheumatoid skin rash (proliferative erythema), rheumatoid chorea, and rheumatic nodules caused by these rheumatic fevers listed above are called the main comorbidities of rheumatic fever or the main symptoms of rheumatic fever.
• Whenever you have rheumatic fever, the main comorbidities of rheumatic fever do not appear all at once.
• One of the major comorbidities, several or almost all of the major comorbidities of rheumatic fever may appear.
• Rheumatic fever is more common in winter and spring, when pharyngitis, tonsillitis, pharyngeal tonsillitis, and scarlet fever caused by group A streptococcal infection are more common.
• There are several species of streptococcus in group A, of which there is another one that causes rheumatic fever.
• Infants and young children before 3 years of age, infants after 3 years of age, school-age children, adolescents, and adults can also get rheumatic fever, but children and adolescents aged 5 to 15 may be more susceptible to it.
• In addition, children living in poorly sanitized environments or children living in confined settlements may be more susceptible to the disease.
• It is said that 3% of children with group A streptococcal infection may develop rheumatic fever, but it may develop more intensively depending on certain times and places.
• Therefore, the overall incidence of rheumatic fever is said to be only 0.3%.
• It is common to develop one or more of one or more major comorbidities of rheumatic fever approximately 1 to 5 weeks after suffering from infectious diseases caused by most group A streptococcal infections.
• However, rheumatoid chorea can develop 2 to 6 months after suffering from an infectious disease caused by a group A streptococcal infection.
• Symptoms caused by pharyngitis or tonsillitis caused by group A streptococcal infection and symptoms caused by rheumatic fever may appear at the same time.
• Also, when you have rheumatic fever, the symptoms and signs differ depending on the type of primary comorbidity.
• Symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis, rheumatoid chorea, rheumatoid heart disease, rheumatoid nodules, etc. may appear at the same time.
• When you have rheumatic fever, abdominal pain similar to the symptoms of appendicitis may occur, and symptoms such as mild fever or high fever may occur.
• Most of the signs of these symptoms are usually acute, but sometimes gradually become chronic. • Each comorbidity of rheumatic fever is described in more detail in the following sections.
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
-
Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, Harvey grant and Robert Murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
-
The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
-
Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care
-
응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
-
Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
-
Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
-
Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
-
Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics 14th ed. Beherman,
-
The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 18th edition
-
Red book 29th edition 2012
-
Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th Edition
-
Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gerhon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
-
소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”