디프테리아와 디프테리아 인두염, Diphtheria and Diphtheria pharyngitis
(You may visit www.drleepediatrics.com – Chapter 7,
Pediatric Adolescent Infectious Diseases or제 7권, 소아 청소년 감염병 질환 웹사이트)
디프테리아와 디프테리아 인두염의 원인
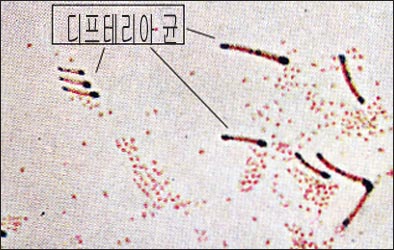
사진 2-78. 디프테리아균. 출처:Practical bacteriology, hematology and Parasitology, Stitt, Clough, Branham
-
디프테리아라는 디프테리아균(Corynebacterium diphtheriae) 감염으로 생기는 급성 감염병의 일종이다.
-
디프테리아균이 비강·인두·후두·기관·피부 등에 감염되어 그 부위에 디프테리아 감염병이 생길 수 있다.
-
디프테리아균 면역체가 조금도 없는 아이가 디프테리아 병소에서 나온 분비물에 접촉되거나 디프테리아균 보균자와 접촉될 때 디프테리아균에 감염될 수 있다.
-
디프테리아균 감염으로 생긴 눈·코·인두·피부 등에 생긴 디프테리아 병소에서 나온 점액 등을 통해서 디프테리아균이 다른 사람에게 감염될 수 있다.
-
DTaP 백신 예방접종을 한 번도 받지 않았거나 권장한 대로 DTaP 백신 예방접종 배열을 적기에 받지 않은 아이들은 디프테리아에 걸릴 수 있다.
-
잠복기는 약 2∼6일이다.
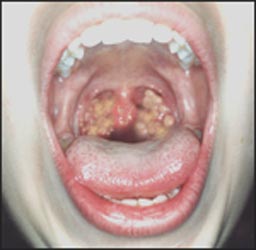
사진 2-80. 디프테리아성 인두 편도염
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
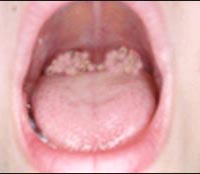
사진 2-79. 디프테리아성 인두 편도염
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
디프테리아와 디프테리아 인두염의 증상 징후
-
디프테리아균 감염병이 신체의 어느 국소에 있느냐, 디프테리아의 병일, 병세의 중증도 등에 따라 증상 징후가 다르다.
-
디프테리아균이 신체의 어느 부위에 감염되면 그 부위 디프테리아균 감염병이 생기고 감염된 디프테리아균 균독이 만들어지고 그 균독이 전신으로 퍼져 혈소판 감소증이 생길 수 있고 디프테리아성 심장염과 디프테리아성 신경마비가 생길 수 있다.
-
디프테리아로 인한 그 외 다른 여러 가지의 증상 징후가 생길 수 있다.
-
디프테리아균이 비강, 인두에 감염되어 위막(僞膜)이 만들어지고 디프테리아성 비인후염이 생길 수 있고 후두와 기관에 감염되어 디프레티아성 폐쇄성 후두 기관염이 생길 수 있다.
-
더 진전되어 디프테리아성 후두 기관 기관지염이 생길 수 있다.
-
이렇게 해서 생긴 후두 기관지염을 디프테리아성 크루프이라고 한다. [부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다–소아가정간호백과]-제8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환–급성 크루프, 바이러스성 급성 후두염 참조.
-
디프테리아성 크루프가 생기면 호흡곤란이 극히 심해질 수 있고 적절한 치료를 응급으로 해주지 않으면 질식 사망할 수 있다.
-
디프테리아성 비인후염의 초기에는 코와 인두가 아프고, 미열 내지 고열 등 여러 가지 증상 징후가 나타날 수 있다.
-
디프테리아균 후두 기관 기관지염으로 디프테리아성 크루프가 생길 때는 물개 짖는 소리처럼 컹컹 소리를 내면서 기침 한다. 흡기성 협착음이 생긴다.
-
드물게는 디프테리아균이 피부나 질, 외이도 또는 결막 등에도 감염되어 그 부위에 디프테리아균 피부염, 디프테리아균 질염, 또는 디프테리아균 결막염 등이 생길 수 있다.
디프테리아와 디프테리아 인두염의 진단
-
병력·증상 징후·진찰소견 등을 종합하여 디프테리아가 의심되면, 인두, 비강, 피부 등에 있는 디프테리아 병소에서 분비물을 채취하여 디프테리아균 세균 배양 검사를 하고 적절한 혈액검사를 해서 디프테리아를 진단할 수 있다.
디프테리아와 디프테리아 인두염의 치료
-
디프테리아가 의심되면 의사의 진단·치료를 급히 받아야 한다.
-
이 병으로 비강·인두·후두·기관 등 상·하 기도에 위막이 생겨 기도가 막혀 그로 인해 질식사망할 수 있다.
-
디프테리아균 신경마비가 생길 수 있다.
-
이런 이유로 디프테리아 환아는 입원 치료를 받아야 한다.
-
체내 디프테리아균 독소를 디프테리아균 항독소(Antitoxin) 혈청주사로 해독 시킨다.
-
디프테리아균을 보균한 사람에게는 에리스로마이신이나 다른 적절한 항생제로 치료한다.
-
디프테리아균 피부염으로 생긴 증상 징후가 경미할지라도 피부염을 일으킨 디프테리아균에서 생성되는 디프테리아균 독소로 인해 디프테리아균 심장염 또는 디프테리아균 신경염 등이 생길 수 있다.
-
증상 징후가 경미하더라도 디프테리아성 피부염이 완치될 때까지 안정해야 한다.
-
디프테리아성 인두염·디프테리아성 비인두염 또는 디프테리아균 후두 기관 기관지염으로 호흡곤란이 심하게 생기면 기관절개수술 치료를 한다.
-
이 때 절개된 기관 구멍을 통해 숨을 쉬게 한다.
-
입을 통하여 기관 속에 넣은 기관내관을 통해서 숨을 쉬게 치료 할 때도 있다. 체내에 이미 만들어진 디프테리아균 독소는 항생제 치료로 해독될 수 없지만 디프테리아균이 죽을 수 있다.
-
페니실린이나 에리스로마이신 등의 항생제로 디프테리아를 치료한다.
디프테리아와 디프테리아 인두염 환아의 격리
-
디프테리아를 적절한 항생제로 치료하기 시작한 날로부터 10일 정도까지 환아를 격리시켜야 한다.
-
비강과 인두 그리고 기관 등 상·하 기도에서 나온 분비물에 디프테리아균이 더 이상 배양되지 않을 때까지 환아를 격리해야 한다.
디프테리아와 디프테리아 인두염 환아와 접촉한 경우
-
디프테리아를 앓는 환자와 접촉한 건강한 아이나 성인에게는 디프테리아에 걸리지 않게 다음과 같이 예방 한다.
-
디프테리아의 증상 징후가 조금도 없고 데프테리아 백신으로 예방접종을 과거에 한 번도 받지 않은 아이, 예방접종을 적기에 받지 않아서 디프테리아균 감염에 완전히 면역되어 있는지를 확실히 알 수 없는 아이에게는 에리스로마이신이나 페니실린 등 항생제로 디프테리아를 예방적 치료를 한다.
-
나이에 따라 DTaP 백신이나 Td 백신으로 예방접종을 하고 디프테리아가 발병되는지 약 7일 동안 관찰 치료한다.
-
디프테리아의 증상 징후가 하나도 나타나지 않고 디프테리아가 발병되는지 계속 관찰할 수 없는 경우나, 디프테리아 백신으로 과거에 한 번도 예방접종을 받지 않은 아이에게는 페니실린이나 적절한 다른 항생제로 예방적 치료를 시작하고, 나이에 따라 DTaP 백신이나 Td 백신으로 디프테리아 예방접종을 해준다.
디프테리아 백신 예방접종
- 2014년 1월 미 소아청소년과학회에서 권장하는 0~6세 소아 감염병 예방접종 스케줄 참조
- 생후 2·4·6·18개월에 DTaP 백신으로 각각 1차, 2차, 3차, 4차로 총 4차 디프테리아 파상풍, 백일해 백신으로 예방접종을 해 주고, 유치원에 들어갈 때쯤, 또는 4∼7세경에 5차 디프테리아 백신으로 5차 예방접종을 해 주면 디프테리아에 거의 완전히 면역된다.
- 5차 DTaP 백신으로 디프테리아를 예방접종을 해 준 후에 디프테리아와 파상풍을 Td 백신으로매 10년마다 1회씩 예방접종을 한다.
- 사춘기 아이들과 성인들에게 디프테리아, 파상풍, 백일해를 예방접종할 수 있는 새로운 2 종류의 Dtap 백신이 있다. 하나는 GlaxoSmithKline 제약회사에서 만든 Boostrix (dTpa/) Vaccine이고 다른 하나는 Sanofi Pasteur제약회사에서 만든 Adacel 백신((Tetanus Toxoid, Reduced Diphtheria Toxoid and Acellular Pertussis Vaccine Adsorbed)이다. Boostrix (dTpa/Tdap) Vaccine 백신은 10~18세사춘기 아이들과 성인들에게 1 회 접종할 수 있고 Adacel dTap 백신은 11~64세 아이들과 성인들에게 1회 접종할 수 있다. 그래서 DTaP 예방접종을 받은 후 매 10년마다 Td 백신으로 예방접종을 해주는 것보다 Adacel 백신이나 Boostrix 백신으로 예방접종을 할 수 있다.
- DTaP 백신 예방접종, 예방접종 기록 카드 참조.
2014년 1월 이후 권장 미 0~18세 소아청소년 기본 예방접종 Recommended immunization schedule for 0~18 year old Americal children in Jan 1st 2013
|
☞ 각 나라에 따라 권장 기본 예방접종 스케줄이 다를 수 있다. |
2013년 1월 이후 권장 미 0~18세 소아청소년 기본 예방접종 스케줄과 표 1A
Recommended immunization schedule for persons aged 0 through 18 years since January 2013
| 예방접종 백신 종류/ 예방해 주는 감염병 | 출생 후 바로 | 생후 1개월 |
생후 2개월 |
생후 4개월 |
생후 6개월 |
생후 9개궐 |
생후 12개월 |
생후 15개월 |
생후 18개월 |
생후 19~23개월 |
생후 2~3세 |
생후 4~6세 |
생후 7~10세 |
생후 11~12세 |
생후 13~15세 |
생후 16~18세 |
||||||
| Hepatitis B¹ (HepB) /b 형 간염 | ←1차 접종 | ←2차 접종→ | ←3차 접종→ | |||||||||||||||||||
| Rotavirus²(RV) RV-1(2회분 배열 접종); RV-5(3 회분 배열 접종)/ 로타바이러스 감염병 | ←1차 접종→ | ←2차 접종→ | 각주 2 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Diphtheria, Tetanus, acellular Pertussis³(DTaP;<7세)/파상풍, 디프테리아, 백일 해 | ←1차 접종→ | →2차 접종→ | ←3차 접종→ | ←4차 접종→ | ←5차 접종→ | |||||||||||||||||
| Tetanus, Diphtheria, acellular Pertussis⁴ (DTap;7세나 >7세 파상풍, 디프테리아, 백일 해 | (Tdap) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Haemophilus influenzae type b⁵(HIb)/ 히브 감염병 | ←1차 접종→ | ←2차 접종→ | 각주 5 | ←3차 또는 4차 접종 → 각주 5 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Pneumococcal conjugate⁶a, c (PCV13)/폐렴연쇄상구균 감염병 | ←1차 접종→ | ←2차 접종→ | ←3차 접종→ | ←4차 접종→ | ||||||||||||||||||
| Pneumococcal polysaccharide⁶bc (PPSV23) /폐렴연쇄상구균 감염병 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Inactivated Poliovirus⁷(IPV)(<18 세)/소아마비 | ←1차 접종→ | ←2차 접종→ | ←3차 접종→ | ←4차 접종→ | ||||||||||||||||||
| 예방 접종 백신 종류/예방해 주는 감염병 | 출생 후 바로 | 생후 1개월 |
생후 2개월 |
생후 4개월 |
생후 6개월 |
생후 9개궐 |
생후 12개월 |
생후 15개월 |
생후 18개월 |
생후 19~23개월 |
생후 2~3세 |
생후 4~6세 |
생후 7~10세 |
생후 11~12세 |
생후 13~15세 |
생후 16~18세 |
||
| Influenza⁸(IIV; LAIV) 1부에게는 2회분,각주 8 /인플루엔자 | ←매해 마다 접종 받는다 (11V 만)→ | ←매해 마다 접종 받는다 (II V 또는 LAIV)→ | ||||||||||||||||
| Measles, Mumps, Rubella⁹(MMR)/ 홍역, 풍진, 유행성 이하선염 | ←1차 접종→ | ←2차 접종→ | ||||||||||||||||
| Varicella ¹⁰ (VAR) /수두 | ←1 차 접종→ | ←2차 접종→ | ||||||||||||||||
| Hepatitis A¹¹ (HepA)/A형 간염 | ←2 회분→ 주서 11 | |||||||||||||||||
| (Human papillomavirus¹² (HPV2; 여성에게만 (HPV4; 여성과 남성 에게)/사람유두종 바이러스 감염병 | ←3회 분 배열 접종→ | |||||||||||||||||
| Meningococcal¹³ (MenACWY-D 생후 9 개월이나 그후후. MenACWY-CRM-D는 생후 2개월이나 그 이후. MenACWY-TT는 은 생후 2세나 그 이후. /수막구균 뇌막염과 그 외 감염병
—————————- Meningococcal B 백신에는 MenB-4C, Bexsero, MenB-FHbp, Trumenba 백신이 있다. 10세나 그 이상에 접조한다. Bexsero백신은 2회 접종하고 Trumenba 백신은 총 3회 접종한다. 위험도다 없는 사춘기아이들이나 청년들은 16-23세에 접종받는다. 소스: CDC, AAP News 3/2021 |
←주서 13→ | ←1차 접종→ | 추가 접종 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
접종을 권장 하는 나이의 범위, | ||
|
|
건강상 고 위험 군 아이들에게 접종을 권장하는 나이 |
디프테리아, 백일해, 파상풍을 예방하는 DTaP 예방접종 백신 DTaP vaccine (Diphtheria, Tetanus Acellular Pertussis Immunization)
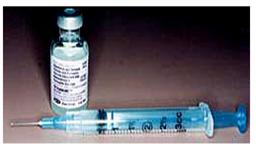
사진 2-81. DTaP 백신 백신과 주사기
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
- DTaP 백신은 디프테리아, 백일해, 파상풍을 예방할 때 쓰는 종합 예방접종 백신이다. DTaP 백신의 D는 디프테리아(Diphtheria), T는 파상풍(Tetanus), A는 무세포(Acellular), P는 백일해(Pertussis)의 영어의 머리 글자를 따서 만든 약자다. 경구용 DTaP 예방접종 백신은 아직 개발되어 있지 않다.
디프테리아 백신 예방 접종의 연령
- DTaP 백신은 생후 2, 4, 6, 18개월과 4~6세에 각각 1차, 2차, 3차, 4차, 5차 접종해서 총 5차 접종한다. 마지막 DTaP 예방접종을 받은 날로부터 10년마다 파상풍과 디프테리아를 예방하기 위해 Tdap 백신으로 예방접종을 받는다.
- 그러나 테트라뮨 히부, Pediatrix 백신, Adacel 백신, Boostrix 백신 등 백일해 백신 성분이 든 종합 예방접종 백신들도 있다. 그리고 그 종합 예방접종 백신으로 접종하는 방법이 각각 다르므로 의사의 지시에 따라 백일해백신을 예방접종해야 한다.
- 사춘기 아이들과 성인들에게 예방접종할 수 있는 2종류의 dTap 종합 백신이 FDA의 승인됐다. 하나는 GlaxoSmithKline 제약회사에서 만든 Boostrix 백신이고 다른 하나는 Sanofi Pasteur제약회사에서 만든 Adacel dTap 백신이다. Boostrix dTap 백신은 10~18세사춘기 아이들과 성인들에게 1차 접종할 수 있고 Adacel dTap 종합 백신은 11~64세 아이들과 성인들에게 1회 접종할 수 있다.
- 이전에는 5~6세에 마지막 DTaP 백신으로 예방접종을 해준 후 그 후 10년이 될 때 Td 백신으로 디프테리아와 파상풍을 예방해 주도록 권장했고 백일해를 예방하는 예방접종은 5~6세 이후 더 이상 권장하지 않았다.
- 과거에 권장한 대로 DTaP 백신으로 백일해 예방접종을 7 세 전에 받았던 사춘기 아이들과 성인들에게 백일해가 발생될 수 있기 때문에 최근에는 사춘기 아이들과 성인들에게 dTap 종합 예방접종 백신인 Adacel 백신이나 Boostrix 백신으로 예방접종을 해 주도록 권장한다.
- 10~18세 이상 아이들이나 성인들에게 Td 백신으로 예방접종을 해 주어야 할 때는 Td 백신 대신에 dTap 백신의 일종인 Adacel dTap 백신이나 Boostrix dTap 백신으로 예방접종을 해야 할 때가 왔다. 따라서 10~18세 이상 아이들에게 디프테리아와 파상풍백신 예방접종을 받아야 할 때는 의사와 꼭 상의해서 결정한다.
디프테리아 백신 예방접종의 방법
- 소아청소년 건강검진을 받고 체온을 재서 열이 나는지 알아본다. 열이 나지 않고 DTaP 백신으로 예방접종을 받아서는 안 될 금기 조건이 없으면 DTaP 백신 0.5cc를 허벅다리나 상박부 근육 주사로 접종한다.
- 급성 발열성 감염병을 앓을 때는 DTaP 백신으로 예방접종 받지 않는 것이 좋다. 그리고 그 병이 다 나은 후에 접종받는다.
- 감기를 경미하게 앓을 때나 감기 이외 다른 종류의 바이러스성 호흡기 질환 등을 경미하게 앓을 때도 의사의 지시에 따라 DTaP 백신으로 예방접종을 받을 수 있다.
- 과거에 예방접종을 받은 후 DTaP 백신으로 인해 섭씨 40도 이상의 고열이 났거나, 그 외 다른 부작용이 심하게 생긴 예방 접종 병력이 있으면 그 다음 DTaP 백신으로 접종할 수 없다.
- 과거에 DTaP 백신으로 예방접종을 받은 후 어떤 종류든 부작용이 발생했으면 그 DTaP 백신 부작용을 의사에게 자세히 알려야 한다.
박테리아 감염병과 바이러스성 감염병 종합 백신
-
Pediarix(Diphtheria, Tetanus Toxoids, Acellular Pertussis Adsorbed, Hepatitis B (Recombinant), Inactivated Poliovirus Vaccine Combined) 백신은 디프테리아, 파상풍, 백일해, B형 간염, 소아마비 등 5가지 감염병은 동시에 예방해 줄 수 있는 종합 백신의 일종이다.
- 이전에는 디프테리아, 백일해, 파상풍, 소아마비, B형 간염을 1번 예방접종을 하기 위해 3번 주사로 예방접종을 받았던 것을 Pediarix 백신으로 접종 받으면 3번 주사를 맞는 대신 한번 주사를 맞아 5 종류의 감염병을 한 번에 예방접종 받을 수 있다.
- 생후 2, 4, 6 개월에 Pediarix 백신으로 1차, 2차, 3차로 접종받을 수 있다. 생후 7세 이후 아이들에게는 Pediarix 백신으로 접종 받을 수 없다.
디프테리아 백신 예방접종의 부작용
- 예방접종 백신의 종류에 따라 부작용이 다르게 나타날 수 있다. 주사 맞은 국소가 아프고 발적되고 부을 수 있다. 열이 날 수 있고 보챌 수 있다.
디프테리아 백신 예방접종의 금기
-
백신의 종류에 따라 금기 조건이 다를 수 있다. 종합백신의 성분 중 이스트(곰팡이), Neomycin, Polymyxin B 등의 성분에 알레르기가 있는 아이들은 이 종합백신으로 예방접종을 받을 수 없다.
- 더 자세한 정보는 www.aapnews.org
경미한 부작용
- DTaP 백신으로 예방접종을 받은 후 그 종합접종백신으로 인하여 심한 부작용이 잘 생기지는 않으나 다음과 같은 경미한 부작용은 비교적 흔히 생긴다.
- DTaP 백신을 주사로 맞은 국소가 조금 붓고 아플 수 있다. 종합접종백신을 주사로 맞은 다리가 1~3일 동안 제대로 움직일 수 없을 정도로 아프고 또 미열이 나면서 보챌 수 있다.
디프테리아 백신 예방접종의 심한 부작용
-
DTaP 백신으로 예방접종을 받은 후 다음과 같은 부작용이 생기면 심한 DTaP 백신 부작용이라 한다.
-
섭씨 40도(화씨 104도)나 그 이상의 고열이 나거나
-
DTaP 백신으로 접종을 받은 후 어떤 방법으로도 도저히 달랠 수 없이 3시간이나 그 이상 계속 심하게 울거나
-
쇼크에 빠지거나
-
전신경련을 하거나
-
뇌염이 생기거나
-
아나필락시가 생기거나
-
혈소판이나 적혈구가 파괴되거나
-
그 외
Diphtheria and Diphtheria pharyngitis 디프테리아와 디프테리아 인두염
Causes of diphtheria and diphtheria pharyngitis

Photo 2-78. Diphtheria. Source: Practical bacteriology, hematology and Parasitology, Stitt, Clough, Branham
• Diphtheria is a type of acute infectious disease caused by infection with Corynebacterium diphtheriae.
• Diphtheria bacteria can infect the nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea, skin, etc.
and a diphtheria infection may occur in the other area.
• A child with no diphtheria immunity can become infected with diphtheria when they come into contact with secretions from diphtheria lesions or with a diphtheria carrier.
• Diphtheria can infect other people through mucus from diphtheria lesions in the eyes, nose, pharynx, and skin caused by diphtheria infection.
• Children who have never received DTaP vaccination or have not received the DTaP vaccination arrangement in a timely manner as recommended may develop diphtheria.
• The incubation period is about 2-6 days.

Photo 2-80. Diphtheria pharyngeal tonsillitis. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Photo 2-79. Diphtheria pharyngeal tonsillitis. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
Symptoms, signs of diphtheria and diphtheria pharyngitis
• Symptoms and signs differ depending on where the diphtheria infectious disease is located in the body, the condition of diphtheria, and the severity of the disease.
• When diphtheria is infected in any part of the body, a diphtheria infectious disease occurs in that area, an infected diphtheria bacteria toxin is produced, and the toxin spreads throughout the body, resulting in thrombocytopenia, and diphtheria carditis and diphtheria nerve palsy may occur.
• Diphtheria can cause many other signs, symptoms.
• Diphtheria bacteria are infected in the nasal cavity and pharynx, forming a pseudomembrane, diphtheria nasopharyngitis, and infection of the larynx and trachea, resulting in diaphoretic obstructive laryngeal tracheitis.
• It may develop further, resulting in diphtheria laryngeal bronchitis.
• The resulting laryngeal bronchitis is called diphtheria croup. www.drleepediatrics.com-Volume 8 Children and adolescent respiratory diseases-Acute Croup, Viral acute laryngitis.
• Diphtheria croup can make breathing extremely difficult and can lead to suffocation and death if appropriate treatment is not given as an emergency.
• In the early stages of diphtheria nasopharyngitis, the nose and pharynx may be sore, and various symptoms such as mild to high fever may appear.
• When diphtheria-laryngeal bronchitis develops diphtheria croup, cough with a squeaking sound like a seal barking. Inspiratory stricture sounds occur.
• In rare cases, diphtheria can also be infected with the skin, vagina, external ear canal, or conjunctiva, causing diphtheria dermatitis, diphtheria vaginitis, or diphtheria conjunctivitis.
Diagnosis of diphtheria and diphtheria pharyngitis
• If diphtheria is suspected by synthesizing the medical history, symptoms, and examination findings, diphtheria can be diagnosed by collecting secretions from diphtheria lesions in the pharynx, nasal cavity, and skin, performing a diphtheria bacterial culture test, and performing an appropriate blood test.
Treatment of diphtheria and diphtheria pharyngitis
• If diphtheria is suspected, seek medical attention and treatment immediately.
• This disease causes pseudomembranes to form in the upper and lower airways such as the nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, and trachea, which can block the airways, resulting in suffocation and death.
• Diphtheria nerve palsy may develop.
• For this reason, children with diphtheria should be treated in hospital.
• Detoxify diphtheria toxin in the body with diphtheria antitoxin (Antitoxin) serum injection.
• People with diphtheria are treated with erythromycin or other appropriate antibiotics.
• Although the symptoms of diphtheria dermatitis are mild, diphtheria toxins produced by the diphtheria bacteria that cause dermatitis can cause diphtheria carditis or diphtheria neuritis.
• Even if the symptoms are mild, they should remain stable until the diphtheria dermatitis is cured.
• If you have severe breathing difficulties due to diphtheria pharyngitis
• Diphtheria nasopharyngitis or diphtheria laryngeal bronchitis, tracheostomy treatment is performed.
• At this time, breathe through the incised tracheal opening.
• In some cases, breathing is performed through an endotracheal tube inserted into the trachea through the mouth. Diphtheria toxins already made in the body cannot be detoxified with antibiotic treatment, but the diphtheria bacteria can die.
• Treat diphtheria with antibiotics such as penicillin or erythromycin.
Isolation of diphtheria and children with diphtheria pharyngitis
• Children should be isolated for up to 10 days from the start of treatment for diphtheria with appropriate antibiotics.
• Patients should be isolated until no more diphtheria are cultured in secretions from the upper and lower airways such as the nasal cavity, pharynx, and trachea.
Contactant with a child with diphtheria and diphtheria pharyngitis
• Prevent diphtheria in healthy children or adults who have come into contact with a patient with diphtheria.
• Erythromycin or penicillin for children who have no signs of symptoms of diphtheria and have never been vaccinated with a diphtheria vaccine in the past, or children who are not fully immunized against diphtheria infection because they have not been vaccinated in a timely manner. Antibiotics are used to treat diphtheria prophylactically.
• Depending on your age, vaccinate with DTaP vaccine or Td vaccine, and observe and treat diphtheria for about 7 days.
• If there are no signs of diphtheria and it is not possible to continue to observe if diphtheria develops, or if a child who has not been vaccinated with a diphtheria vaccine in the past, prophylactic treatment with penicillin or other appropriate antibiotics is started, and at age. Therefore, they are vaccinated against diphtheria with either the DTaP vaccine or the Td vaccine.
Diphtheria Vaccination
• Refer to the infectious disease vaccination schedule for children aged 0-6 recommended by the American Academy of Pediatrics and Adolescents in January 2014.
• At 2, 4,6,18 months of age, vaccinated with a total of 4th diphtheria tetanus and pertussis vaccines at the first, second, third, and fourth doses of DTaP vaccine, respectively, by the time they enter kindergarten or 4-7 If you give the 5th vaccination with the 5th diphtheria vaccine at age, you are almost completely immunized against diphtheria.
• After vaccinating diphtheria with the 5th DTaP vaccine, vaccination against diphtheria and tetanus with Td vaccine is given once every 10 years.
• There are two new Dtap vaccines to immunize adolescent children and adults against diphtheria, tetanus and whooping cough.
One is Boostrix (dTpa) Vaccine by GlaxoSmithKline Pharmaceuticals, and the other is Adacel Vaccine ((Tetanus Toxoid, Reduced Diphtheria Toxoid and Acellular Pertussis Vaccine Adsorbed) by Sanofi Pasteur Pharmaceuticals.
Boostrix (dTpa/Tdap) Vaccine vaccine is Adacel dTap vaccine can be given once to adolescent children and adults aged 10 to 18 years, and Adacel dTap vaccine can be given to children and adults aged 11 to 64 years. Vaccination can be done with the Adacel vaccine or Boostrix vaccine rather than vaccination.
• DTaP vaccination, see vaccination record card.
Recommended immunization schedule for persons aged 0 through 18 years since January 2021,
2021년 1월 이후 권장 미 0~18세 소아청소년 기본 예방접종 스케줄과 표 1A
Vaccination type of vaccine/ infectious disease that prevent
| Vaccination type of vaccine/ infectious disease that prevent | Right after birth | After birth 1 month | After birth 4 month | After birth 6 month | After birth 9 month | After birth 12 month | After birth 1 5 month | After birth 18 month | After birth 19~23 month | After birth 2-3 years old | After birth 4-6 years old | After birth 7-10 years old | After birth 11-12 years old | After birth 13-15 years old | After birth 16-18 years old | |||||||
| Hepatitis B¹ (HepB) /b 형 간염 | ←1st vaccination→ | ←2nd vaccination→ | ←←3rd vaccination→→ | |||||||||||||||||||
| Rotavirus² (RV) RV-1 (two batch sequence inoculation); RV-5 (3-batch sequence vaccination)/ Rotavirus infection | ←1st vaccination→ | ←2nd vaccination→ | note 2 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Diphtheria, Tetanus, acellular Pertussis³ (DTaP; <7 years old)/tetanus, diphtheria, pertussis | ←1st vaccination→ | ←2nd vaccination→ | ←3rd vaccination→ | ←4th vaccination→ | ←5th vaccination→ | |||||||||||||||||
| Tetanus, Diphtheria, acellular Pertussis⁴ (DTap; 7 years old> 7 years old tetanus, diphtheria, whooping cough | (Tdap) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Haemophilus influenzae type b⁵(HIb)/ Hib infectious disease | ←1st vaccination→ | ←2nd vaccination→ | note 5 | ←3rd or 4th vaccination→ Footnote 5 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Pneumococcal conjugate⁶a, c (PCV13)/Pneumococcal infection | ←1st vaccination→ | ←2nd vaccination→ | ←3rd vaccination→ | ←4th vaccination→ | ||||||||||||||||||
| Pneumococcal polysaccharide⁶bc (PPSV23) / Streptococcal pneumonia infection | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Inactivated Poliovirus⁷(IPV)(<18 years old)/Polio | ←1st vaccination→ | ←2nd vaccination→ | ←3rd vaccination→ | ←4th vaccination→ | ||||||||||||||||||
| Vaccination type of vaccine/ infectious disease that prevent | Right after birth | After birth 1 month | After birth 2 month | After birth 4 month | After birth 6 month | After birth 9 month | After birth 12 month | After birth 15 month | After birth 18 month | After birth 19-23 month | After birth 2-3 years old | After birth 4-6 years old | After birth 7-10 years old | After birth 11-12 years old | After birth 13-15 years old | After birth 16-18 years old | ||
| Influenza⁸ (IIV; LAIV) for 1 copy, 2 servings, footnote 8 / Influenza | ←Get inoculated every year (11V 만)→ | ←Get inoculated every year(II V or LAIV)→ | ||||||||||||||||
| Measles, Mumps, Rubella⁹(MMR)/ Measles, Rubella, Mumps | ←1st vaccination→ | ←2nd vaccination→ | ||||||||||||||||
| Varicella ¹⁰ (VAR) /Varicella | ←1st vaccination→ | ←2nd vaccination→ | ||||||||||||||||
| Hepatitis A¹¹ (HepA)/Hepatitis A | ←2 doses→ | |||||||||||||||||
| (Human papillomavirus¹² (HPV2; women only (HPV4; women and men))/Human papillomavirus infectious disease | ←3rd vaccination→ | |||||||||||||||||
| Meningococcal¹³ (MenACWY-D 9 months or later. MenACWY-CRM-D is 2 months or later. MenACWY-TT is 2 years old or later. / Meningococcal meningitis and other infectious diseases) —————————- Meningococcal B vaccines include MenB-4C, Bexsero, MenB-FHbp, and Trumenba vaccines. We touch on 10 years of age or older. The Bexsero vaccine is inoculated twice and the Trumenba vaccine has inoculated a total of three times. Adolescents and young adults with no risk are vaccinated at age 16-23. Source: CDC, AAP News 3/2021 | ←1st vaccination→ | Booster vaccination | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
The age range for which vaccination is recommended, | ||
|
|
Age recommending vaccination for children in the high risk group |
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
-
www.drleepediatrics.com제7권. 소아청소년 감염병
-
Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
-
Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th- 21st Edition
-
The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
-
Report of the Committee on Infectious Diseases, 20th Edition, American Academy of Pediatrics 및 소아가정간호백과
-
Report of the Committee on Infectious Diseases, 27th Edition, American Academy of Pediatrics
-
Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, Harvey grant, and Robert Murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
-
The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
-
Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care
-
응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
-
Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
-
Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
-
Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
-
소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”