두개 강 내 출혈, Intracranial bleeding
사진1-202. 두부 X-선 사진으로 두개골 골절을 진단할 수 있다. Copyright ⓒ 2012 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
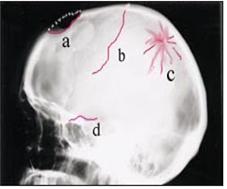
사진1-203. 여러 종류의 두개골 골절. a-함몰 두개골 골절, b-선상 두개골 골절, c-분쇄 두개골 골절, d-두개골 저 골절. ▴ Copyright ⓒ 2012 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
- 머리를 어디에 세게 부딪치거나 머리가 강타 당할 때, 또는 다른 방법으로 두부(머리) 외상을 입을 때 두개 강 내 출혈이 생길 수 있다.
- 뇌 좌상이 있을 때는 뇌 속의 일부의 혈관이 손상되어 뇌 실질 속에 피가 맺히는 정도로 미세한 뇌출혈이 생길 수 있고,
- 경막외 출혈, 경막하 출혈, 또는 뇌 실질 속 출혈이 생길 수 있고 그로 인해 여러 종류의 두개 강 내 혈종이 두개 강 내에 생길 수 있다.
- 심한 두부 외상이 생기면 뇌진탕만 생길 수 있고 또 뇌 좌상만 생길 수도 있고,
- 뇌진탕과 뇌 좌상이 동시 생길 때 경막 외면과 두개골 내면의 사이에 출혈이 생길 수도 있다. 이런 출혈을 경막외 출혈(硬膜外出血)이라 한다.
- 경막외 출혈로 경막외 공간에 피 덩어리가 생길 수 있다. 이것을 경막외 혈종(硬膜外血腫)이라 한다.
- 경막 내면과 지주막 외면 사이에 있는 공간에 피가 나면 경막하 출혈이라 하고, 거기에 생긴 피 덩어리를 경막하 혈종(硬膜下血腫)이라 하고,
- 지주막하에 생긴 출혈을 지주막하 출혈이라고 한다.
- 뇌 실질 속에 생긴 출혈을 뇌출혈이라도 하고 뇌 실질 속에 생긴 피 덩어리를 뇌 혈종이라고 한다. 이런 여러 종류의 출혈을 통틀어 두개 강 내 출혈이라 한다.
- 이런 두개 강 내 출혈이나 혈종을 적절히 치료하지 않으면 생명이 위험할 수 있다.
- 물론 중뇌 교뇌(뇌교), 연수에도 출혈이 생길 수 있다.
- 심한 두부 외상을 입었을 때는 의료구급대, 병원 응급실, 또는 단골 소아청소년과의 지시에 따라 병원 응급실로 급히 데리고 가 뇌 진탕, 뇌 좌상, 또는 그 외 다른 뇌 외상이나 두개 강 내 출혈이 있나 알아보고 적절한 응급 치료를 받아야 한다.
- 두부 외상을 심하게 입었던 당시 두개 강 내 출혈의 증상 징후가 현저히 나타나지 않아도 1~2일 동안 병원에 입원 관찰 치료를 받아야 하는 것이 보통이다.
- 병원에서 퇴원한 후 집에서 관찰 치료를 하는 중 구토하거나 잠을 계속 자거나, 정신이 혼동되거나, 시력이나 다른 감각 기관에 이상이 있거나, 전신 경련을 하거나 머리가 심하게 아프면 의사의 지시에 따라 병원 응급실로 즉시 다시 데리고 가야 한다.
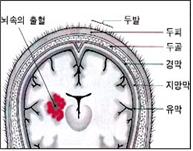
그림1-204. 뇌 실질 속 출혈. Copyright ⓒ 2012 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
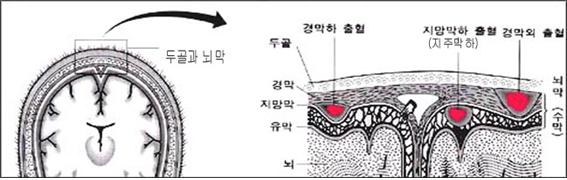
그림1-205. 경막외 출혈, 지망막(지주막)하 출혈과 경막하 출혈.Copyright ⓒ 2012 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
Intracranial bleeding 두개 강 내 출혈

Photo 1-202. A skull fracture can be diagnosed with an X-ray of the head. Copyright ⓒ 2012 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Photo 1-203. Several types of skull fractures. a-depressed skull fracture, b-linear skull fracture, c-crushed skull fracture, d-cranial base fracture.
Copyright ⓒ 2012 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
- Intracranial bleeding can occur when the head is hit hard, when the head is struck, or when a head trauma occurs in another way.
- When there is a brain contusion, some blood vessels in the brain may be damaged, resulting in microscopic cerebral hemorrhage, which causes blood to form in the brain parenchyma.
- Epidural hemorrhage, subdural hemorrhage, or cerebral parenchymal hemorrhage may occur, resulting in several types of intracranial hematomas occurring in the cranial cavity. When severe head trauma occurs, only concussion may occur, and only brain concussion may occur.
- When concussions occur simultaneously, bleeding may occur between the dura’s outer and the skull’s inner surfaces. This bleeding is called epidural hemorrhage (硬膜外出血).
- Epidural hemorrhage can lead to blood clots in the epidural space. This is called epidural hematoma (硬膜外血腫).
- If blood bleeds in the space between the inner surface of the dura mater and the outer surface of the arachnoid, it is called subdural hemorrhage, and the lump of blood generated there is called a subdural hematoma.
- Subarachnoid hemorrhage is a hemorrhge under a subarachnoidal pcse.
- The hemorrhage in the brain parenchyma is called a cerebral hemorrhage, and a lump of blood in the brain parenchyma is called a brain hematoma. Together, these types of bleeding are called intracranial bleeding.
- These intracranial hemorrhages or hematomas can be life-threatening if not properly treated.
- Of course, bleeding can occur in the midbrain and medulla.
- In case of severe head trauma, follow the instructions of a medical paramedic, hospital emergency room, or regular pediatrics department to promptly take them to the hospital emergency room to see if there is a concussion, brain strain, or other brain trauma or intracranial bleeding, and appropriate emergency treatment.
- At the time of severe head trauma, even if the symptoms of intracranial bleeding do not appear remarkable, it is common to be hospitalized for 1 to 2 days for observational treatment.
- If your child is vomiting, continues to sleep, is confused, has an abnormal vision or other sensory organs has general convulsions or has severe headaches during observational treatment at home after you are discharged from the hospital, go to the hospital emergency room as directed by your doctor.
- You must take it back immediately.

- Figure 1-204. Hemorrhage in the brain parenchyma. Copyright ⓒ 2012 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

- Figure 1-205. Epidural hemorrhage, subretinal (arachnoid) hemorrhage and subdural hemorrhage. Copyright ⓒ 2012 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
제12권. 소아청소년 신경 정신 질환, 행동 수면 문제Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
Emergency care, Harvey grant, and Robert Murray
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
Manual of Emergency Care
응급환자관리 정담미디어
소아가정간호백과-부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원 저
The pregnancy Bible. By Joan stone, MD. Keith Eddleman, MD
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
임신에서 신생아 돌보기까지. 이상원
Breastfeeding. by Ruth Lawrence and Robert Lawrence
The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 18th edition
Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th-2st Edition
Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
Growth and Development of Children, George H. Lowrey 8th edition
소아과학 대한교과서
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”