동상, Frostbites
동상의 개요와 원인
-
손가락, 발가락, 코, 귓바퀴, 얼굴 등 신체의 일부분이나 전신이 심한 한랭 공기나 아주 찬 물체에 노출될 때 노출된 신체의 일부분이나 신체의 여러 계통의 기관, 조직이 손상되는 외상을 동상이라 한다.
-
동상 입은 신체의 부위의 혈관이 비정상적으로 수축되고 혈액 순환 장애가 생길 수 있다.
-
특히 영유아들은 학령기 아이들이나 사춘기 아이들, 성인들에 비해 유약하고 사리판단을 잘 할 수 없어 동상에 더 쉽게 걸릴 수 있다.
-
영유아들은 신체의 일부에 동상을 입어도 자신에게 동상이 생기는지 잘 분간 할 수 없다. 그래서 더 심한 동상에 걸릴 수 있다.
-
추운 겨울에 얼음 물 속에 빠지거나 등산 갔다가 폭설과 한랭에 노출되거나 추운 일기에 적절히 대처하지 않고 스키 등 동기 스포츠를 하다가 동상을 입을 수 있다.
-
찬 한랭 기온이나 물체에 노출될 때 습도, 한랭 바람의 정도, 한랭 온도, 찬 공기에 노출된 기간, 옷을 얼마나 적절히 입었는지, 운동 상태 등에 따라 동상의 정도가 다를 수 있다.
-
손발 등 신체의 일부가 동상을 입었을 때 손발의 조직과 혈관이 손상될 수 있다.
-
동상의 정도에 따라 혈관이 수축되고, 혈관 속 피가 응고되어 혈관 속에 혈전이 생기고, 혈전으로 혈관 속 혈류가 차단되고 동상이 생긴 신체 부위의 혈액순환 장애가 생길 수 있다.
-
이때 손상된 혈관을 통해 피를 공급 받는 말단 기관과 조직이 손상될 수 있고, 동상이 심할 때는 동상 입은 조직이 괴사될 수 있다.
동상의 증상 징후
-
동상의 중증도, 동상을 입은 신체의 부위에 따라 증상 징후가 다르다.
-
전신 동상을 입었을 때는 처음 얼마동안 추워서 몸이 떨리고, 기운이 없고, 의식을 잃고, 맨 나중에는 혼수상태에 빠지고 사망한다.
-
화상을 분류하는 것과 거의 같게 동상의 정도에 따라 동상을 1~4도 동상으로 분류한다.

▴ 사진 1-27. 특히 어린이들을 추운 겨울철에 동상을 입지 않도록 잘 보살펴 줘야 한다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
1. 1도 동상
-
신체의 어떤 국소에 경미하게 생긴 동상을 1도 동상이라 한다.
-
1도 동상을 입은 피부는 붉고 붓고 화끈거리고 따끔따끔 아플 수 있다.
-
이런 증상 징후는 동상 입은 후 24~48시간이 됐을 때 가장 심하게 나타나고, 그 후 1~2 주 동안 계속 될 수 있다.
2. 2도 동상
피부에 동상 습포가 생기고 동상 입은 피부의 감각이 둔해지거나 없어진다.
3. 3도 동상
3도 동상을 입었을 때는 동상 입은 부위의 전 피부층과 피하 조직이 붓고 괴사되고 피부에 궤양이 생길 수 있다.
4. 4도 동상
-
4도 동상을 입었을 때는 동상 입은 부위의 피부층과 피하 조직이 얼고 거기에 수포, 궤양, 괴사 등이 생기고 그 신체 부위가 떨어져나갈 수 있다. 동상 입은 피부가 창백하거나 하얗거나 파랗게 변화되고 팽팽하게 붓는다.
-
1~2도 동상을 입은 직후, 동상을 입은 신체 부위를 따뜻하게 녹여 주면 피부가 다시 붉어지고, 반점이 생기며, 붓고, 아픈 것이 보통이다.
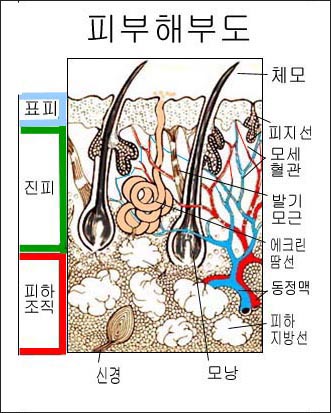
▴ 그림 1-8. 피부층의 구조
피부층에 있는 에크린 땀에서 땀이 나서 피부의 습도가 적절히 유지시키고 피지선에서 피지가 분비되어 피부가 윤활해 지는 것이 정상이다.
너무 씻고 닦으면 피부건강에 해롭다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
-
전 피부층과 피하층까지 동상을 입을 때 즉, 4도 동상을 입었을 때, 즉시 적절히 치료하지 않으면 동상을 입은 신체 부위에 혈액순환이 잘 되지 않아 동상 입은 신체 부위가 상실될 수 있다.
-
그 외 저혈당증, 부정맥, 저산소증, 산혈증, 췌장염, 위장 출혈, 저 체온증, 신장 부전증 등이 생길 수 있다. 그로 인해 여러 증상 징후가 생길 수 있다.

▴ 사진 1-28. 동상을 입지 않게 옷을 잘 입히고 부모가 잘 관찰 한다. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
동상 치료
-
동상을 입었을 때나 동상을 입었다고 의심되면 서슴지 말고 다음과 같이 치료한다.
-
동상 입은 환아를 따뜻한 장소로 옮긴다. 담요 등으로 따뜻하게 싸 보온한다.
-
동상의 정도에 따라 치료에 차이가 많다. 단골 소아청소년과, 병원 응급실, 의료구급대의 전화 지시에 따라 1차 응급치료를 현장에서 시작한다.
-
동상 입은 신체의 국소만 따뜻하게 처치하지 말고 몸 전체(전신)를 따뜻하게 보온한다. 젖은 옷은 마른 옷으로 갈아입힌다.
-
동상을 입은 신체 부위를 히팅 패드(Heating pad)로 따뜻하게 치료 하지 않는다.
-
감각이 정상으로 되돌아 올 때까지 더운물(섭씨 37.8~40.6 도, 화씨 100~105도) 속에 20분 동안 동상 입은 신체 부위를 담가 녹이든지,
-
의사의 지시에 따라 따뜻한 물로 목욕해서 서서히 녹인다.
-
동상을 입어 찬 신체 부위를 정상 체온으로 올릴 때는 한 시간 동안에 섭씨 0.5~2.0도 정도씩 서서히 올리는 식으로 국소에 생긴 동상을 치료하기도 한다. 이런 동상 치료도 가능한 한 어디까지 의사의 지시에 따라 한다.
-
동상을 입은 신체의 부위가 아프면 아이브프로펜(Ibuprophen), 타이레놀(Tylenol)이나 아편제 등 적절한 진통제로 의사의 지시에 따라 진통시킨다.
-
동상 입은 신체의 부위를 마사지하거나 문질러서는 절대로 안 된다.
-
의사의 처방에 따라 헤파린(Heparin)제 주사 치료로 혈관 속 혈전을 녹이고 앞으로 더 혈전이 생기 않게 치료할 수 있다.
-
동상으로 생긴 물집은 터트리지 말고 그대로 놓고 관찰 치료 한다. 이 치료방법에 찬반이 있다
-
손발에 동상이 생겼을 때는 손발가락 사이에 깨끗한 솜 덩어리(면구)나 거즈를 끼어 넣는다. 더 이상 상처가 생기지 않도록 동상 입은 부위를 조심히 관찰 치료 한다.
-
필요에 따라 파상풍 백신 예방접종을 받는다.
-
정도에 따라 포도당 전해질 용액 정맥주사, 산소호흡 치료, 투석치료를 받는다.
-
가능하면, 따듯한 음료수를 마신다.
-
일반적으로 동상 입은 신체 부분을 녹이는 치료를 시작한 후 24~48시간에 동상의 정도를 재평가 받는다. 1주일 경 동상 입은 신체 부분의 조직 손상의 정도와 그 부분을 절단 치료를 할 것인가를 테크늄 영상검사로 결정한다.
-
Plasminogen activator제 주사치료를 한 결과 절단 치료 필요성이 감소됐다고 한다(출처; NEJM September 2008 p.1037).
-
일반적으로 동상의 진단 치료는 복잡하기 때문에 동상을 입었다고 의심되거나 진단이 나면 의사의 지시에 따라 적극적으로 치료받아야 한다.

▴ 사진 1-29 동상을 입지 않게 예방 한다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
Update. 6/9/2022. NEJM-p 2213. Treated with Iloprost, hyperbaric oxygen, Antibiotics, Dextran, Nonsteroid anti-inflammatory drugs, Heparin and etc.
Frostbites
Overview and causes
- Frostbite is a trauma in which parts of the body such as fingers, toes, nose, auricles, face, etc., or parts of the body are exposed when the whole body is exposed to severe cold air or very cold objects, damages various organs and tissues of the body.
- Blood vessels in areas of the body that are frostbite may contract abnormally and blood circulation may be impaired.
- In particular, infants and toddlers are more susceptible to frostbite than school-age children, adolescents, and adults because they are weaker and can’t make good judgments about self-satisfaction.
- Even if infants and toddlers wear frostbite on a part of their body, they can’t tell if they’re getting frostbite.
- So your child can get more severe frostbite.
- Your child may get frostbite while falling in icy water in the cold winter, going for mountain climbing and then being exposed to heavy snow and cold, or playing synchronous sports such as skiing without adequately coping with the cold weather.
- The degree of frostbite may vary depending on the humidity, the degree of cold wind when exposed to cold or cold air, the cold temperature, the period of exposure to cold air, how properly dressed, and exercise conditions.
- When parts of the body such as limbs are frostbite, the tissues and blood vessels of the limbs can be damaged.
- Depending on the degree of frostbite, blood vessels are constricted, blood clots in blood vessels, blood clots are formed in blood vessels, blood flow in blood vessels is blocked by blood clots, and blood circulation disorders in areas of the body where frostbite is formed can occur.
- At this time, terminal organs and tissues supplied with blood through damaged blood vessels may be damaged, and when frostbite is severe, the frostbite tissue may be necrotic.
Symptoms, signs of frostbite
- Symptoms and signs differ depending on the severity of the frostbite and the part of the body where the frostbite was inflicted.
- When wearing full-body frostbite, the first time it is cold for some time, so that the body trembles, feels incapacitated, loses consciousness, and finally falls into a coma and dies.
- It is almost the same as classifying burns, and it classifies statues into 1-4 degrees of frostbite according to the degree of frostbite.

▴ Picture 1-27.
In particular, children should be taken care of so that they do not get frostbite in the cold winter. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
- First-degree Frostbite
- Slight frostbite on a certain part of the body is called the first-degree frostbite.
- First-degree frostbite skin can be red, swollen, burning, and tingling.
- Signs of these symptoms are most severe 24 to 48 hours after the frostbite and may continue for a week or two after that.
- 2nd-degree Frostbite
- Frostbite poultices form on the skin, and the sensation of the frostbitten skin becomes dull or disappears
- Third-degree Frostbite
- When third-degree frostbite is worn, the entire skin layer and subcutaneous tissue of the frostbitten area are swollen and necrosis and ulcers may occur on the skin.
- 4th-degree Frostbite
- When 4-degree frostbite is worn, the skin layer and subcutaneous tissue of the frostbite area freezes, blisters, ulcers, necrosis, etc. may form there, and the body part may fall off.
- Frostbite skin turns pale, white, or blue and swells tightly. Immediately after 1-2 degrees of frostbite, the skin becomes red, spots, swelling, and soreness are common if you warmly melt the affected body part.

▴ Figure 1-8.
The structure of the skin layer It is normal for the skin to be lubricated as sebum is secreted from the sebaceous glands and properly maintains the humidity of the skin due to sweating from the eccrine sweat in the skin layer.
Washing and wiping too much is harmful to skin health.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
- When frostbite up to the entire skin layer and subcutaneous layer is inflicted, i.e., when fourth-degree frostbite is worn, if not treated properly immediately, blood circulation to the frostbite body part may be poor and the frostbite body part may be lost.
- In addition, hypoglycemia, arrhythmia, hypoxia, acidemia, pancreatitis, gastrointestinal bleeding, hypothermia, and kidney failure may occur.
- This can lead to several symptomatic signs.

▴ Photo 1-28.
Dress well to avoid frostbite, and parents should observe.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
Frostbite treatment
- When you have frostbite or if you suspect you have frostbite, do not hesitate to treat it as follows.
- Move the frostbite patient to a warm place.
- Keep warm by wrapping it warmly with a blanket or the like.
- There are many differences in treatment depending on the degree of frostbite.
- First emergency treatment is initiated on-site according to the telephone instructions of the regular pediatric and adolescent department, hospital emergency room, and medical paramedics.
- Do not warmly treat only the areas of the body where you are wearing frostbite, but keep the whole body warm (whole-body).
- Change wet clothes to dry clothes.
- Do not warmly treat frostbite areas with a heating pad.
- Either soak the frostbitten body part for 20 minutes in hot water (37.8-40.6 degrees Celsius, 100-105 degrees Fahrenheit) until the sensation returns to normal and dissolves, As directed by your doctor, take a warm bath and dissolve slowly.
- When raising a cold body part from frostbite to normal body temperature, local frostbite may be treated by gradually raising it by 0.5 to 2.0 degrees Celsius for an hour.
- Treatment of such frostbite should be done according to the doctor’s instructions to the extent possible.
- If the area of the body in the frostbite is sore, it is given an appropriate pain reliever, such as Ibuprophen, Tylenol, or opiates, according to the doctor’s instructions.
- You should never massage or rub any part of the body that is frostbite. According to the doctor’s prescription, heparin injection treatment can dissolve blood clots in blood vessels and treat them so that no more blood clots occur in the future.
- Do not burst the blister caused by frostbite, but leave it as it is and conduct observational treatment.
- There are pros and cons to this treatment method.
- When frostbite occurs on the limbs, put a clean cotton ball or gauze between the limbs.
- Carefully observe and treat the frostbitten area so that no further wounds occur.
- Get vaccinated against tetanus vaccine as needed.
- The degree of intravenous injection of glucose electrolyte solution, oxygen respiration treatment, and dialysis treatment are given.
- If possible, drink warm beverages.
- In general, the degree of frostbite is reevaluated 24 to 48 hours after starting the treatment to dissolve the body part of the frostbite.
- Around one week, the degree of tissue damage to the frostbitten part of the body and whether to perform amputation treatment for that part is determined by a technetium imaging test.
- It is reported that the need for amputation treatment decreased as a result of injection treatment with plasminogen activator (Source; NEJM September 2008 p.1037).
- In general, the diagnosis and treatment of frostbite is complicated, so if you suspect that you have frostbite or are diagnosed, you should actively receive treatment according to the doctor’s instructions.

▴ Photo 1-29 Prevent frostbite.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
Update. 6/9/2022. NEJM-p 2213. Treated with Iloprost, hyperbaric oxygen, Antibiotics, Dextran, Nonsteroid anti-inflammatory drugs, Heparin and etc.
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
-
Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, Harvey grant, and Robert Murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
-
The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
-
Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care 응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
-
Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
-
Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
-
Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
-
Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics 14th ed. Beherman,
-
The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 18th edition
-
Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
-
Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th-21st Edition
-
Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
-
소아과학 안효섭 외 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”