대퇴골 골절, Femur fractures(Femoral fractures/Thighbone fractures/Fractures of the femur)
대퇴골 골절의 개요
-
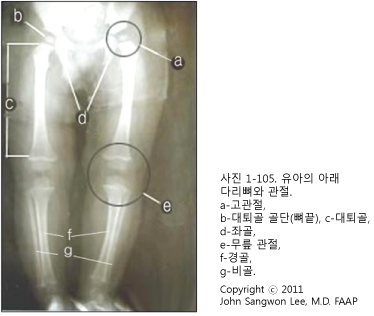
대퇴골은 고관절(엉덩 관절)과 무릎 관절을 연결시키고 허벅다리 속에 있는 뼈이다.
-
인체의 모든 뼈들 중 가장 길고 가장 크고 가장 강한 뼈다(쇄골 골절, 쇄골 골절 참조).
- 여기서 대퇴골 골절에 관해 알아보자.
| 골단(뼈끝)=관절 연골+해면 뼈+골단 판으로 구성되어 있다. |
대퇴골 골절의 원인
-
운동이나 장난, 또는 교통사고 등으로 대퇴골이 골절될 수 있다.
-
드물게 아동 학대(소아 학대)로 대퇴골이 골절될 수 있다.
대퇴골 골절의 증상 징후
- 대퇴골은 골두, 골간, 대퇴골 경, 대퇴골 내측 상과, 대퇴골 외측 상과, 대전자, 소전자 등으로 구성된다.
- 대퇴골 골절의 정도, 골절된 상태와 대퇴골의 어느 부분이 골절 됐느냐에 따라 증상 징후가 다르다.
- 대퇴골이 심하게 골절되면 대퇴골 골절의 골절된 끝 부분 뼈로 골절된 대퇴골의 주위에 있는 혈관, 말초 신경, 근육 등이 손상될 수 있다. 날카로운 골절 뼈끝이 피부층을 뚫고 피부 밖으로 솟아나올 수 있다.
- 대퇴골이 골절되면서 골절된 대퇴골 끝 부분으로 대퇴골 골절 주위에 있는 큰 혈관이 짤리거나 짤린 혈관에서 넓적다리 속으로 피가 많이 날 수 있고, 그로 인해 급성 출혈성 빈혈이 심하게 생길 수 있고 심지어는 쇼크에 빠질 수 있다.
- 대퇴골이 심하게 골절될 때는 골절된 대퇴골이 있는 대퇴부가 비정상적으로 구부러지든지 뒤틀리기도 하고, 골절된 대퇴골이 있는 다리의 길이가 정상 길이보다 더 짧아질 수도 있고 더 길어질 수도 있다.
- 대퇴골 골절이 생긴 대퇴부가 현저히 붓고 손으로 만지면 몹시 아프다.
- 부모가 버릇을 고친다고 준 체벌로, 또는 아동학대로 대퇴골이나 그 외 뼈가 골절될 수 있다. 이런 경우 아동 신체적 학대(소아 신체학대)를 당한 환아의 피부에는 최근에 입은 상흔 및, 또는 오래 전에 입은 상흔이 발견될 수 있다. 또 피부 상흔뿐만 아니라 대퇴골이나 다른 뼈가 최근에 골절된 상흔 또는 오래 전에 골절된 상흔을 찾아볼 수 있다.
대퇴골 골절의 진단
-
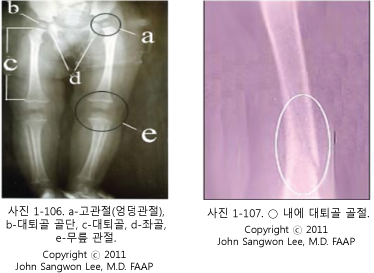
병력, 증상 징후와 진찰소견 등을 종합해서 대퇴골이 골절됐다고 의심되면 대퇴골 X-선 사진 검사 등으로 진단한다.
대퇴골 골절의 치료
- 대퇴골의 골절의 정도와 대퇴골의 어느 부위가 골절됐는지, 골절의 원인, 환아의 나이, 합병증 등에 따라 치료 한다.
- 가능한 한 환아를 안정시키고 처음 목격한 대퇴골 골절 자세에서 더 이상 움직이지 말아야 한다.
- 단골 소아청소년과 의사나 의료구급대가 사고 현장에 도착하기 전, 병원 응급실로 데리고 가기 전 골절된 사고 현장에서 가능 하면, 다른 장소로 환아를 함부로 옮겨서는 안 된다.
- 의료구급대, 병원 응급실, 또는 단골 소아청소년과에 긴급으로 전화해 그들의 지시에 따라 응급 처치를 사고 현장에서 시작하고 구급차나 다른 적절한 교통수단으로 종합 병원 응급실로 이송한다.
- 가능한 한 대퇴골 골절이 생긴 다리의 피부를 전체적으로 살펴보고 그쪽 다리의 발등 동맥 맥박이 정상적으로 뛰는지 체크해본다.
- 골절된 대퇴골이 있는 넓적다리와 그쪽 아랫다리의 혈액순환이 정상으로 되는지 알아보기 위해 그쪽 발의 발톱 밑 혈색을 체크한다.
- 필요에 따라 체크한 결과를 의사에게 보고하면서 사고 현장에서나 병원으로 이송하는 중 응급처치 한다.
- 대퇴골 골절이 있는 다리의 말초 신경이 잘려 신경마비가 있는지 알아보기 위해 그쪽 다리의 발가락을 환아 자신이 능동적으로 움직일 수 있는지 체크해보고 가능하면 아픈 감각도 정상적으로 있는지 빨리 체크한다.
- 필요에 따라 아랫바지를 조심히 벗기든지 가위나 칼로 잘라 벗긴다.
- 옷을 벗길 때나 부목을 댈 때 골절된 다리를 끌거나 밀거나 당기거나 뒤틀어서는 절대로 안 된다. 벗긴 옷을 부목을 댈 때 이용할 수 있다.
- 쇼크에 빠져 있을 때는 상체를 하체보다 15도 정도 더 낮게 눕힌다. 가급적이면 응급실이나 단골 소아청소년과의 지시에 따라 이런 처치도 한다.
- 의료구급대, 단골 소아청소년과 의사가 사고 현장에 와서 환아를 병원으로 이송하기 전에 헤어(Hare) 견인 부목, 반구부목(半球部木), 또는 적절한 판자 부목으로 대퇴골 골절이 있는 쪽 발끝에서 허리까지 고정처치를 한다.
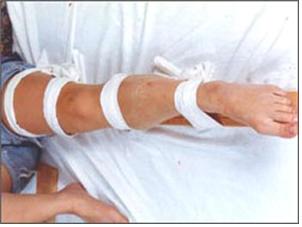
▴ 사진 1-108. 대퇴골이 골절됐다고 의심되면 그쪽의
상하다리와 허리 부위까지 부목을 댄다.
대퇴골이 골절됐다고 의심되면 그 부위를
누르지도 밀지도, 당기거나 틀지도 말고
최초 목격한 그 상태에서 부목을 대고 병원으로 이송한다. Copyright ⓒ 2013 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
Femur fractures(Femoral fractures/Thighbone fractures/Fractures of femur) 대퇴골 골절

Overview of femur fracture
- The femur connects the hip joint and the knee joint and is the bone in the thigh.
- It is the longest, largest, and strongest of all bones in the human body (see clavicle fracture, clavicle fracture).
- Here’s a look at femur fractures.
- Epiphysis (end of the bone) = It is composed of joint cartilage + cancellous bone + epiphysis plate.
Causes of femur fracture
- The femur may be fractured due to exercise, playing, or traffic accident.
- Rarely, child abuse (child abuse) can result in a fracture of the femur.
Symptoms, signs of a femur fracture
- The femur is composed of a head, a bone stem, a femur neck, a femur medial epicondyle, a femur lateral epicondyle, a large trochanter, and a small trochanter.
- Symptoms and signs differ depending on the degree of femur fracture, the condition of the fracture, and which part of the femur is fractured.
- If the femur is severely fractured, blood vessels, peripheral nerves, and muscles around the fractured femur may be damaged by the fractured end bone of the femur fracture.
- Sharp fractured bone tips can penetrate the skin layer and protrude out of the skin.
- When the femur is fractured, a large blood vessel around the femoral fracture can be cut off at the end of the fractured femur, or a lot of blood can bleed into the thigh from the cut blood vessel, which can lead to severe acute hemorrhagic anemia and even shock have.
- When the femur is severely fractured, the femur with the fractured femur may be bent or twisted abnormally, and the length of the leg with the fractured femur may be shorter or longer than the normal length.
- The femur fractured femur is markedly swollen and very painful when touched with the hand.
- Fractures of the femur or other bones can be caused by corporal punishment given by parents to cure habits or through child abuse.
- In this case, the skin of a patient who has suffered physical abuse of a child (child physical abuse) may have a recently worn scar or a long-ago wound.
- In addition to skin scars, scars of recent fractures of the femur or other bones or scars that have been fractured long ago can be found.

Diagnosis of femur fracture
- If it is suspected that the femur has been fractured by synthesizing the medical history, symptoms, and examination findings, it is diagnosed with an X-ray photograph of the femur.
Treatment of femur fractures
- Treatment is performed according to the degree of fracture of the femur, which part of the femur is fractured, the cause of the fracture, the age of the patient, and complications.
- As much as possible, the child should be stabilized and no further movement in the posture of the first observed femur fracture.
- Before a regular pediatrician or medical paramedic arrives at the site of the accident, before taking it to the hospital emergency room, at the site of the fractured accident, if possible, the child should not be relocated to another location.
- Emergency calls to a medical paramedic, hospital emergency room, or regular pediatrics, follow their instructions, to initiate first aid at the accident site and transfer to the general hospital emergency room by ambulance or other appropriate means of transportation.
- As much as possible, look at the skin of the leg where the femur fracture occurred, and check that the pulse of the instep artery of that leg is beating normally.
- Check the color under the claws of the foot to see if the blood circulation in the thigh and the lower leg with the fractured femur is normal.
- If necessary, take first-aid measures at the accident site or during transfer to a hospital while reporting the results of the check to the doctor.
- To see if the peripheral nerve of the leg with the femur fracture is cut off and there is a nerve paralysis, check if the toe of that leg can be actively moved, and if possible, quickly check if the sore sensation is normal. If necessary, take off the lower pants carefully or cut them off with scissors or a knife.
- Never pull, push, or twist a fractured leg when undressing or applying a splint. It can be used to splint off clothes.
- When in shock, lay your upper body 15 degrees lower than your lower body. If possible, follow the instructions of the emergency room or regular pediatrics department.
- Before a medical paramedic or a regular pediatrician arrives at the accident site and transfers the child to the hospital, fix it from the tip of the toe to the waist on the side of the femur fracture with a traction splint, hemisphere splint, or an appropriate plank splint.

▴ Picture 1-108. If you suspect that your femur is fractured,
Apply a splint to the upper leg and waist.
If you suspect that your femur has been fractured, neither push nor push, pull, or twist At the first sighting, a splint is placed and transported to the hospital. Copyright ⓒ 2013 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
-
Quick Reference to Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., p.
-
Emergency Pediatrics, A guide to ambulatory care, 5th Edi. Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen, p.520, 546-547
-
Emergency care and transportation of the sick and injured, 3rd edition, American Academy of orthopedic surgeons. p.23, 24, 67, 129.130,
- Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, Harvey grant, and Robert Murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care 응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과-부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원 저
-
The pregnancy Bible. By Joan stone, MD. Keith Eddleman, MD
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
-
임신에서 신생아 돌보기까지. 이상원
-
Breastfeeding. by Ruth Lawrence and Robert Lawrence
-
Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics 14th~19th ed. Beherman,
-
The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 18~19th edition
-
Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
-
Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th-21st Edition
-
Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
-
Growth and Development of Children, George H. Lowrey 8th edition
-
소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”