대장균성 설사, E. coli diarrhea
(You may visit www.drleepediatrics.com – Volume 7,
Pediatric Adolescent Infectious Diseases or제 7권, 소아 청소년 감염병 질환 웹사이트)
대장균성 설사의 개요 및 원인
- 대장균에는 여러 균종이 있지만 그 중 주로 5가지 균종 감염으로 대장균성 대장염이 생길 수 있고 그로 인해 설사를 할 수 있다. 식중독 참조.
-
그 5가지 대장균 균종 감염에 의해 다음과 1~5 대장염이 생길 수 있다.
1. 시가 균독을 만들어 내는 시가 독소 형성 대장균 감염병에 의한 설사 Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli(STEC) infectious diarrhea
-
대장균 중 STEC 균종에 감염되면
-
출혈성 결장염,
-
용혈성 요독 증후군,
-
설사 후 혈전증,
-
혈소판 감소증 등이 생길 수 있다.
-
-
STEC균 감염으로 대장염이 생길 때 초기에는 혈이 없는 설사를 하다가 설사가 진행되면서 육안으로 볼 수 있는 혈변 설사 내지 잠혈 설사를 할 수 있고 심한 복통을 호소할 수 있고 환자 중 ⅓에게 열이 난다.
-
심한 출혈성 결장염이 생길 수 있다.
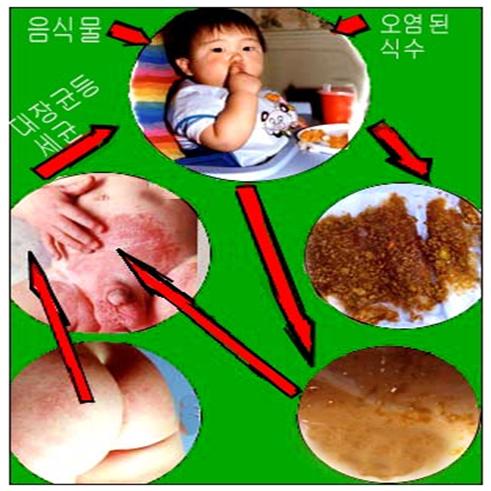
사진 2-148. 대장균성 위장염은 불결한 손과 오염 음식물을 통해 세균감염으로 생긴다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
2. 장질환 발현성 대장균 감염병에 의한 설사 Enteropathogenic E. coli (EPEC) infectious diarrhea
-
대장균의 EPEC 균종에 감염되어 급성 장염이 생기면 물 설사를 심하게 하고 탈수가 심해져 사망 할 수 있다.
-
만성으로 생기면 지속적 설사를 하고 성장지연이 생길 수 있다.
-
이 병은 경제적으로 빈곤하고 위생시설이 부적절한 지방 신생아들이나 2세 이하 영유아들에게 더 잘 생길 수 있다.
3. 장관 독 생성성 대장균 감염병에 의한 설사 Enterotoxigenic E. coli(ETEC)
-
대장균의 ETEC 균종에 감염되면 자기 한정성 물 설사를 1~5일 정도 할 수 있다. 복통이 동반될 수 있다.
4. 장관 장벽 침입성 대장균 감염병에 의한 설사 Enterotoinvasive E. coli(EIEC) infectious diarrhea
-
대장균의 EIEC 균종에 감염되면 대장균이 장벽의 점막층 상피를 침범해서 세균성 이질과 비슷한 설사를 한다. 피나 점액이 섞이지 않은 설사를 하고 열이 나는 것이 보통이다.
5. 장관 집합성 대장균 감염병에 의한 설사 Enteroaggregative E. coli(EAEC) infectious diarrhea
-
대장균의 EAEC 균종 감염은 불결하고 빈곤층 영아들과 유아들에게 주로 생기고 2주 이상 물 설사를 하는 것이 보통이다.
-
때로는 피 섞인 설사도 한다.
-
설사를 경미하게 할 수 있고 성장지연이 생길 수 있다.
-
잠복기는 10시간 내지 6일이다.
대장균성 설사의 진단
-
병력, 증상 징후, 진찰 등을 종합해서 진단하는 것이 보통이다.
-
대장균(E. coli) 0157: H7 균종을 제외하고 대부분의 대장균 균종은 대변 세균 배양검사로 검출하기가 쉽지 않다.
-
그러나 대장균 설사 등을 한다고 의심하면 일단 대변 세균검사를 해서 어떤 종류의 세균 감염으로 설사를 하는지 알아보는 것이 이상적이다. 속성 효소면역 분석검사로 시겔라 감염병과 감별진단한다.
대장균성 설사의 치료
-
일반적으로 항생제 치료에 별로 효과가 없다.
-
심한 경우, 주로 탈수와 전해질 불균형을 포도당 전해질용액 정맥 주사로 재수화치료와 현상 유지 수화 치료를 적극적으로 하고 경미할 때는 경구용 포도당 전해질용액으로 재수화 치료를 할 수 있다. 필요에 따라 대증 치료를 한다.
-
경우에 따라 항생제로 치료한다.
-
장관 독 생성성 대장균(EIEC)성 설사는 셉트라(Septra) 등으로 치료한다.
-
여행자 대장 감염성 설사병은 셉트라, Doxycycline, 또는 Ciprofloxacin 등 항생제로 치료할 수 있다.
대장균성 설사의 예방
-
대장균(E. coli) 0157:H7 균종 감염은 잘 익히지 않은 쇠고기, 생우유, 사과 주스, 식수 및 연못 물 등에서 감염될 수 있고 잘 익히지 않은 시금치, 양파, 또는 상추 등을 섭취한 후 감염될 수 있다.
-
어린이집 아이들이나 집단생활을 하는 고아원 등에게 이병이 더 잘 생길 수 있다.
-
여행자 대장균성 감염성 설사병은 오염된 물, 음식물, 장관 독 생성성 대장균, 장관 집합성 대장균, 또는 장관 장벽 침입성 대장균의 감염으로 생길 수 있다.
E. coli diarrhea 대장균성 설사
Overview and causes of Escherichia coli diarrhea
• There are several species of E. coli, but five of them can cause E. coli colitis, which can lead to diarrhea. See food poisoning.
• The following 1~5 colitis can be caused by infections of the 5 E. coli species. 1. Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli(STEC) infectious diarrhea
• If you are infected with STEC species of E. coli, o hemorrhagic colitis, o hemolytic uremic syndrome, o thrombosis after diarrhea, o Thrombocytopenia may occur.
• When colitis occurs due to STEC infection, diarrhea without blood may occur initially, but as diarrhea progresses, it may cause bloody diarrhea or occult blood diarrhea, which can be seen with the naked eye, and may complain of severe abdominal pain, and ⅓ of the patient has a fever.
• Severe hemorrhagic colitis may develop.

Photo 2-148. Escherichia coli gastroenteritis is caused by bacterial infection through dirty hands and contaminated food. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
2. Enteropathogenic E. coli (EPEC) infectious diarrhea caused by intestinal disease-expressing Escherichia coli infectious disease
• If acute enteritis occurs due to infection with E. coli EPEC species, watery diarrhea may be severe and dehydration may become severe, resulting in death.
• If it is chronic, you may have persistent diarrhea and delayed growth.
• The disease can be more prevalent in local newborns or infants under the age of 2 who are economically impoverished and inadequate sanitation.
3. Enterotoxigenic E. coli(ETEC) diarrhea caused by intestinal poisonous E. coli infectious disease
• If you are infected with the ETEC strain of E. coli, you may have self-limiting water diarrhea for 1 to 5 days. It may be accompanied by abdominal pain.
4. Enterotoinvasive E. coli (EIEC) infectious diarrhea caused by intestinal barrier invasive Escherichia coli infectious disease
• When infected with EIEC species of E. coli, E. coli invades the epithelium of the intestinal mucosa, causing diarrhea similar to bacterial dysentery. It is common to have diarrhea that does not contain blood or mucus and has a fever.
5. Enteroaggregative E. coli (EAEC) infectious diarrhea caused by intestinal collective E. coli infectious disease
• EAEC fungal infection of E. coli is common among unclean and poor infants and infants, and watery diarrhea is common for more than two weeks.
• Sometimes bloody diarrhea.
• Diarrhea may be mild and growth delay may occur.
• The incubation period is 10 hours to 6 days.
Diagnosis of Escherichia coli diarrhea
• It is common to comprehensively diagnose medical history, symptoms, symptoms, and medical examination.
• E. coli 0157: Except for the H7 strain, most of the E. coli strains are difficult to detect by stool culture tests.
• However, if you suspect that you have E. coli diarrhea, it is ideal to do a stool bacteriological test to find out what type of bacterial infection you are causing diarrhea. It is differentially diagnosed from Shigella infectious diseases by rapid enzyme immunity assay
Treatment of Escherichia coli diarrhea
• In general, antibiotic therapy is not very effective.
• In severe cases, dehydration and electrolyte imbalance can be treated actively with intravenous glucose electrolyte solution intravenous injection and active rehydration treatment and, in mild cases, rehydration treatment with an oral glucose electrolyte solution. Treat symptomatic treatment as needed.
• Sometimes treated with antibiotics.
• Intestinal venom-producing E. coli (EIEC) diarrhea is treated with Septra or the like. • Traveler’s colon infectious diarrhea can be treated with antibiotics such as Septra, Doxycycline, or Ciprofloxacin.
Prevention of Escherichia coli diarrhea
• E. coli 0157:H7 fungal infection can be infected from poorly cooked beef, raw milk, apple juice, drinking water and pond water, and after eating poorly cooked spinach, onions, or lettuce.
• Children in daycare centers and orphanages where they live in groups are more likely to develop morbidity.
• Traveler E. coli infectious diarrhea can be caused by infection with contaminated water, food, intestinal toxic E. coli, intestinal collective E. coli, or intestinal barrier invasive E. coli.
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권. 소아청소년 감염병
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th – 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
-
식중독,
-
포도상구균 식중독,
-
보툴리즘,
-
세균성 이질,
-
파라티푸스 열,
-
파라티푸스 식중독,
-
파라티푸스 위장염,
-
캄필로박터균(Campylobacter jejuni) 감염병,
-
리스테리아증, p.00 대장균(E. COLI O157:H7) 감염, p.00 비브리오균 감염병, p.00 A형 간염, p.00 노로바이러스(Noroviruses) 감염병,
-
캄필로박터 감염병(Campylobacter infections)
-
E.coli: Prevention is the best cure, Pediatric News, 11/06
-
Red book, 2012.
-
Textbook pediatrics, Nelson
-
Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, Harvey grant, and Robert Murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
-
The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
-
Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care
-
응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
-
Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
-
Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
-
Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
-
소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”