눈 화학물질 화상, Chemical burns in the eyes
화학물질로 인한 눈 화상(화학물질 눈 화상)의 개요 Chemical burns in the eyes
 |
 |
|
| ▴ 사진 1-18. 눈 화학물질 화상으로
인한 결막염. 초산은 안약이나 안 항생제 등 화학물질로 눈병을 치료 받을 때나 예방할 때, 화학물질이 안전사고로 눈으로 들어가면 눈 화학물질 화상이 생길 수 있고 결막이 붓고 붉어지면서 화학물질성 결막염이 생길 수 있다. Used with permission from Mead-Johnson Co. |
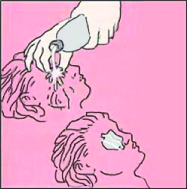
▴ 그림 1-6. 화학물질이 눈에 들어가면 지체말고 용기에 떠놓은 맑은 물이나 흐르는 수돗물로 눈을 적어도 5-15분 이상 흠뻑 씻고 닦아주면서 의사의 도움을 바로 받는다. 시간을 절약하기 위해 필요에 따라 옷을 입은 채로 샤워 물로 눈을 씻을 수 있다. 참조문헌:Emergency care and transportation of the sick and injured by the AAOS |
-
독극물, 약물, 머리 염색약 등 화학물질이 눈에 들어가면 눈 화학물질 화상이 생길 수 있다 (눈의 화상 참조).
-
화학물질이 사고로 눈에 들어갔을 때는 조금도 지체 말고 사고 현장에서 흐르는 수돗물이나 깨끗한 맑은 물을 손으로 떠서 또는 컵으로 떠서 눈을 여러 번 충분히 씻는다.
-
응급처치를 잘못 하거나 응급 치료를 지체하면 실명할 수 있다.
-
눈을 깨끗한 물로 씻을 때 머리를 낮추고, 가능하면 눈을 반복적으로 크게 떴다 감았다 한다.
-
가능하면 아래위 눈꺼풀을 뒤집어 까고 충분한 물로 결막을 여러 번 흠뻑 씻어준다.
-
알칼리성 화학물질이 눈에 들어가면 눈 화학물질 화상이 더 쉽게 생길 수 있다. 그래서 더 적극적으로 오랫동안 물로 눈을 씻어야 한다. 참고로, 때로는 눈물의 pH 지수가 산성으로 변화될 때까지 물로 씻어야 한다.
-
동시에 독극물 중독치료 센터, 의료구급대, 병원 응급실, 단골 소아청소년과의 지시에 따라 치료한다.
-
구급차나 다른 적절한 교통수단으로 병원 응급실, 안과, 또는 단골 소아청소년과로 환아를 데리고 갈 때는 화학물질이나 독극물을 담은 용기를 가지고 간다.
-
눈에 들어간 화학물질을 담은 용기나 상자에 쓰여 있는 응급 치료법을 참조한다.
Overview of chemical burns in the eyes (chemical eye burns)

Photo 1-18. With eye chemical burns Caused by conjunctivitis.

Acetate is an eye drop or an antibiotic, etc.
- When treating or preventing eye diseases with chemical substances, If chemicals enter the eyes due to safety accidents, chemical burns in the eyes may occur.
- And the conjunctiva becomes swollen and red Chemical conjunctivitis can develop.
- Used with permission from Mead-Johnson Co. Figure 1-6.
- When chemicals get into your child’s eyes
- Without delay, the clear water in the container
- Eyes at least 5-15 minutes with running tap water
- After washing and wiping the abnormality,
- Get help right away.
- Don’t spend time undressing for a shower to wash the eyes.
- You can wash your child’s eyes with water.
- Reference: Emergency care and transportation of the sick and injured by the AAOS
- If chemicals such as poisons, drugs, hair dyes, etc. get into the eyes, eye chemical burns may occur (see Eye Burns).
- If a chemical substance gets into your child’s eyes in an accident, do not delay at all and wash your child’s eyes several times with tap water or clean clear water flowing from the accident site with your hands or with a cup.
- Incorrect first aid or delay in emergency treatment can lead to blindness.
- When washing your child’s eyes with clean water, lower your child’s head and, if possible, open and close your child’s eyes repeatedly.
- If possible, flip the upper and lower eyelids upside down and drench the conjunctiva several times with plenty of water.
- Eye chemical burns are more likely to occur if alkaline chemicals get into your eyes.
- So, you should wash your child’s eyes with water more aggressively for a long time.
- For reference, sometimes your child needs to rinse with water until the pH index of his tears changes to acidic.
- At the same time, treatment is performed according to the instructions of the poison poisoning treatment center, medical emergency department, hospital emergency room, and regular pediatrician.
- When taking the child to the hospital’s emergency room, ophthalmology, or regular pediatrician or other appropriate means of transportation, bring a container of chemicals or poison.
- Refer to the first aid treatment written on the container or box containing the chemical in the eye.
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
-
Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, Harvey grant, and Robert Murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
-
The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
-
Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care 응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
-
Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
-
Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
-
Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
-
Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics 14th ed. Beherman,
-
The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 18th edition
-
Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
-
Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th-21st Edition
-
Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
-
소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”