납 중독, Lead poisoning
납 중독의 개요
- 납은 일종의 중금속이다.
- 납은 호흡기계통, 소화기계통, 또는 피부계통 등을 통해 체내로 흡수된 후 뼈, 근육, 혈액, 모발 등에 축적되었다가 대소변 등을 통해 체외로 서서히 배출된다.
- 납 성분이 신생아들, 영유아들, 학령기 아이들, 사춘기 아이들, 성인들의 혈액과 체액에 극소량 정상적으로 있다.
- 혈중 납 농도가 정상 이상 더 높으면 납 중독에 걸릴 수 있다.
- 납 중독의 증상 징후는 혈중 납 농도에 따라 다르다.
- 1990년 미국의 한 연구에 의하면, 6세 이하 영유아 3백만 여명의 혈중 납 농도가 정상 농도 보다 더 높았고, 혈중 납 농도가 정상 농도 보다 더 높은 영유아들의 지능과 성장 발육이 정상 혈중 납 농도를 가진 영유아들의 지능과 성장 발육 비해서 더 떨어졌다.
- 1991년 10월 이전 혈중 납 농도가 25㎍/㎗ 이하이면 정상 혈중 납 농도로 간주했었다. 1991년 10월 미국 CDC(미국 질병통계국)는 혈중 납 농도는 10㎍/㎗ 이하이여야 정상 납 농도라고 정했다.
- 소아청소년들의 납 중독은 될 수 있는 한 조기에 진단해서 조기에 적절히 치료해야 하고, 납 중독을 예방하기 위해 모든 미국 영유아들의 혈중 납 농도를 주기적으로 검사하라고 미 소아청소년과학회는 권장했다 [부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다-소아가정간호백과]-제2권 소아청소년들 질병과 안전사고의 예방-납 중독 예방 참조.
납 중독의 원인
- 우리가 평소 숨 쉬는 공기 속에도, 우리가 사는 주위의 흙 속에도 극소량의 납이 있다.
- 1970년 이전에는 납이 든 휘발유를 많이 썼기 때문에 그 당시의 공기 속에는 요즘의 공기보다 훨씬 더 많은 납이 섞여 있었다.
- 최근에는 거의 모든 나라에서 납이 들어 있지 않은 휘발유를 쓰지만 요즘에도 공기 속에 납이 극소량 들어있다.
- 1970년 이후부터 납이 섞인 페인트를 법적으로 더 이상 사용할 수 없지만 1970년 이전에는 많은 종류의 페인트 속에 납 성분이 들어 있었다. 납 성분이 들어 있는 페인트를 실내 벽에 칠할 때 페인트 속 납이 체내로 흡수될 수 있고, 납이 든 페인트를 칠했던 실내 벽이나 가구 등에서 벗긴 마른 페인트 조각을 태우거나 긁어 벗길 때도 납이 체내로 흡수될 수 있고 납 중독에 걸릴 수 있다.
- 이미증(異味症/이식증)([부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다-소아가정간호백과]-제12권 소아청소년 신경, 정신, 정서, 행동, 수면 문제-이미증 참조)의 증상 징후를 가지고 있는 영유아가 납 성분이 든 페인트를 칠한 벽에서 페인트 조각을 긁어먹거나, 찬바람이 들어오지 못하게 창문 틈을 막는 물질(납 성분이 든)을 떼어먹을 때에 납 중독에 걸릴 수 있다.
- 납 성분이 든 유약을 칠한 멕시코 질그릇을 사용해 납 중독에 걸릴 수 있다.
- 납이 든 탄환이 몸속에 오랫동안 박혀 있을 때,
- 잘못해서 삼킨 납봉이 위장관 내 오랫동안 있을 때,
- 납이든 전지를 태울 때,
- 납으로 만든 가구를 사용할 때,
- 납으로 만든 수도 파이프를 통해 나온 수돗물을 장기간 마실 때 납 중독에 걸릴 수 있다.
- 납 성분이 공장 굴뚝이나 자동차 배기관에서 나오는 연기 속에도 조금 섞여 있을 수 있고 그 연기를 오랫동안 흡입하면 납 중독에 걸릴 수 있다.
- 보통 먹는 음식물 속에도 납이 극소량 들어 있을 수 있다.
- 영유아들이 납이 들어 있는 장난감이나 물건을 빨거나 납 성분에 오염된 공기를 장기간 마실 때 납 중독에 걸릴 수 있다.
- 최근 베토벤의 유골의 납 농도가 비정상적으로 상당히 높았고 아마도 납 중독으로 사망했는지 추정했다.
표 10. 납 성분이 있는 출처 Common source of lead
| 납 성분이 아주 많이 들어 있는 출처 | 납 성분이 어느 정도 많이 들어 있는 출처 | 납 성분이 소량 들어 있는 출처 |
| 주택의 외부나 내부에 칠한 납 든 페인트 | 집안 먼지, 집안 내부에 쓴 물질, 납이 오염된 흙 | 음식물, 집 주위 공기, 식수 |
출처와 참조문헌 Handbook oh Common Poisonings in Children. American Academy of Pediatrics p.206
납 중독의 증상 징후
- 혈중 납 농도에 따라서 납 중독의 증상 징후가 다르다.
- 혈중 납 농도가 10㎍/㎗(1㎍=0.000001g, 1㎗=0.1ℓ) 이하면 건강상 해가 생기지 않는다.
- 혈중 납 농도가 정상 농도 보다 조금 더 높다고 해서 반드시 납 중독의 증상 징후가 현저하게 나타나지 않는다.
- 연구에 의하면, 혈중 납 농도가 40∼60㎍/㎗ 이하일 때는 경도 납 중독의 증상 징후가 현저하게 나타나지 않을 수 있다.
- 경도 납 중독에 걸리면 납 중독의 증상 징후가 서서히 나타날 수 있고 과도 활동 장애, 주의력 결핍 장애, 학습부진, 발육부진 등이 경미하게 나타날 수 있다.
- 경도 납 중독에 걸린 소아청소년들의 ⅓정도는 앞서 설명한 증상 징후 이외 다른 여러 가지 증상 징후가 나타낼 수 있다.
- 혈중 납 농도가 60㎍/㎗이거나 그 이상일 때는 생명에 위험한 납 중독의 증상 징후가 다양하게 나타 날 수 있다.
- 혈중 납 농도가 100∼150㎍/㎗ 이면 식욕감퇴, 빈혈, 구토, 변비, 신경질환, 전신 경련, 과도 활동 장애, 주의력 결핍 장애, 언어와 발육 퇴행증, 반신마비, 실명, 그 외 다른 여러 가지 증상 징후가 나타날 수 있고 심지어는 사망 할 수 있다.
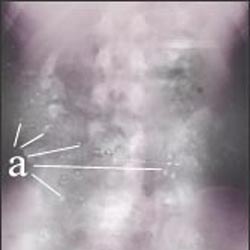
사진 1-30. 납 중독에 걸린 환아의 복부 X선 사진
납 성분이 든 페인트 부스러기를 먹은 아이들의 복부 X선 사진 검사를 해 보면 위장관에 들어 있는
작고 흰 페인트 조각들(a)이 복부 X선 사진 검사에 나타날 수 있다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
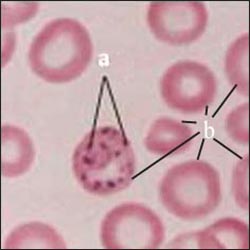
그림 1-31. 납 중독에 걸린 환아의 CBC 혈액 검사
a-납 중독에 걸린 환아의 CBC 혈액 검사에서 적혈구 속에 있는 염기성 반점들
b-적혈구 혈 중 납 농도를 측정해서 확실히 진단할 수 있다. 헤모글로빈 농도가 비 정상적으로 낮을 수 있다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
납 중독의 진단
- 병력, 증상 징후와 진찰소견 등을 종합해서 납 중독이 있다고 의심되면 혈 중 납 농도를 측정하고 CBC 혈액 검사 등 다른 검사를 해서 이 병을 진단할 수 있다. 이미증이 있는 영유아가 납이 든 페인트 조각을 벗겨 먹고 납 중독에 걸릴 수 있다.
- 때로는 복부 X선과 뼈 X선 검사가 납 중독을 진단하는데 도움 된다. 그 외 혈액, 두발, 타액, 소변 등의 납 농도를 측정해서 납 중독을 진단할 수 있다.
- 소아청소년, 특히 영유아들이 정기 건강검진을 받을 때 손가락에서 한두 방울의 피를 뽑아 그 피를 검사용 여과지에 묻혀 혈중 납 농도 검사를 해 납 중독을 조기에 진단할 수 있다.
납 중독의 분류와 치료
- 혈중 납 농도에 따라, 납이 체내에 들어온 경로에 따라 치료 방법이 다르다.
- 혈중 납 농도가 10∼40㎍/㎗일 때는 균형 잡힌 음식물을 충분히 먹고 적절한 기간을 두고 혈중 납 농도를 반복 추적 측정해서 혈중 납 농도치가 점점 더 증가되는지 감소되는지를 알아보는 정도의 관찰 치료를 한다.
- 이때 혈중 납 농도가 계속 더 증가되면 증가되는 원인을 찾아 원인 제거 치료를 한다. 납이 언제 어디서, 어떻게 해서 체내로 들어왔는지를 알아내 더 이상 체내에 들어오지 않도록 처치한다.
표 11. 납 중독의 분류와 치료 Classification of blood lead levels in children and treatment plans
| 혈중 납 농도(단위=㎍/㎗) | 납 중독 중증도의 분류 | 납 중독의 치료 |
| 9이나 그 이상 | I | 치료를 할 필요가 없다. |
| 10~14 | IIa | 동사무소와 공동으로 대치한다. 약물로 치료하지 않는다. 3개월 후 추적 혈중 납 농도 검사를 한다. |
| 15~19 | IIb | 각 환아에 따라 치료전략을 세운다. 환경치료를 한다. 적절한 영양분을 공급한다. 3개월 마다 추적 혈 중 납 농도 검사를 한다. |
| 20~44 | III | 전문가의 치료를 받는다. 환경조사를 하고 납이 있는 출처에서 납을 제거한다. 영양분 공급을 한다. 약물치료를 공급한다. |
| 45~69 | 1V | 전문가의 치료를 받는다. 환경을 조사하고 납이 있는 출처에서 납을 제거한다. 영양분을 공급한다. 병원 입원 약물치료를 받는다. |
| 70이나 그 이상 | V | 전문가의 치료를 받는다. 환경조사를 하고 납이 있는 출처에서 납을 제거한다. 영양분을 공급한다. 병원입원 약물치료를 받는다. |
출처와 참조문헌 Handbook of Common Poisonings in Children. American Academy of Pediatrics P 206
- 일반적으로 혈중 납 농도가 40㎍/㎗이거나 그 이상일 때는 정상 혈중 납 농도나 그 이하 농도로 떨어질 때까지 약물 치료를 받는다. 이때의 납 중독의 증상 징후, 혈중 납 농도에 따라 칼슘 디소듐 에데테이트(Calcium disodium edetate), 발(BAL), 디-페니실라민(D-Penicillamine) 등의 약물로 납 중독을 치료받을 수 있다.
- 납 중독이 심하면 전신경련이 생길 수 있고, 뇌가 손상될 수 있다. 이런 때는 매니톨(Mannitol), 스테로이드제 등으로 치료한다.
- 두개 강 내 뇌압이 비정상적으로 높을 때는 두개국부 절제술(頭蓋局部切除術) 등으로 치료 한다.
- 납을 다량으로 섭취한 후 납 중독이 급성으로 생겼을 때는 위세척치료도 하고 설사를 하게 해서 위장관 속 납을 대변으로 배출시키는 치료도 한다.
|
다음은 “납 중독”에 관한 인터넷 소아청소년 건강상담 질의응답의 예 입니다. |
Q&A. 납 중독에 관하여 알고 싶습니다.
Q.
2세 된 남아인데 페인트 조각을 주어먹습니다. 납 중독에 걸렸는지 걱정이 됩니다. 좋은 답변을 기다리겠습니다.
A.
아무개님
안녕하십니까. 질문해 주셔서 감사합니다.
자녀의 나이와 성별, 과거 현재 가족의 병력, 증상 징후와 진찰소견, 적절한 임상검사 등의 결과를 종합해서 진단 치료하는 것이 이상적이지만 주신 정보를 참작해서 답변을 드립니다.
[부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다–소아가정간호백과]-제2권 소아청소년 질병과 안전사고 예방– “납 중독 예방” 및“납 중독” 등을 참조하시기 바랍니다. 그리고 소아청소년과에서 진찰 진단 치료를 받고 상담하시기 바랍니다.
질문이 더 있으시면 다시 연락 주세요. 감사합니다. 이상원 드림
Lead poisoning 납중독
Overview of lead poisoning
- Lead is a heavy metal.
- Lead is absorbed into the body through the respiratory system, digestive system, or skin system, then accumulates in bones, muscles, blood, hair, etc., and is slowly discharged out of the body through feces and the like.
- Lead is normally found in very small amounts in the blood and body fluids of newborns, infants, school-age children, adolescent children, and adults.
- If your blood lead level is higher than normal, you can lead to lead poisoning.
- Symptoms, signs of lead poisoning depend on the level of lead in the blood.
- A 1990 study in the United States found that 3 million infants and younger children under the age of 6 had higher blood lead levels than normal, and the intelligence and growth of infants and toddlers with higher than normal blood lead levels were found to have normal blood lead levels.
- Their intelligence and growth fell further compared to their development.
- Before October 1991, if the blood lead concentration was less than 25㎍/㎗, it was considered normal blood lead concentration. In October 1991, the US CDC (American Centers for Disease Control and Prevention) determined that the blood lead concentration should be less than 10㎍/㎗ as the normal lead concentration.
- The American Academy of Pediatrics and Adolescents recommended that lead poisoning in children and adolescents should be diagnosed as early as possible and appropriately treated as early as possible.
- To prevent lead poisoning, the American Academy of Pediatrics and Adolescents recommended that all US infants and toddlers should regularly test their blood lead levels.
- You must be a teacher-Child and Family Nursing Encyclopedia]-Volume 2 Prevention of diseases and safety accidents among children and adolescents-Refer to the prevention of lead poisoning.
Causes of lead poisoning
- There is a very small amount of lead in the air we usually breathe and in the soil around us. Before 1970, a lot of lead-based gasoline was used, so the air at that time contained much more lead than today’s air.
- Recently, almost all countries use lead-free gasoline, but even these days, the air contains very little lead.
- Since 1970, lead-based paints are no longer legally available, but before 1970, many types of paint contained lead.
- When lead-based paint is applied to an interior wall, lead in the paint may be absorbed into the body, and lead is absorbed into the body when burning or scraping a piece of dry paint peeled off from the interior wall or furniture where the lead-based paint was applied.
- Can be and lead to lead poisoning. Infants and toddlers with symptoms of miosis
- Your child can get lead poisoning when your child scrapes a piece of paint off a painted wall with an ingredient, or when your child takes away a material (which contains lead) that closes the window gaps to keep the cold air out.
- Your child can get lead poisoning by using Mexican earthenware glazed with lead content.
- When a bullet containing lead is stuck in the body for a long time When an accidentally swallowed lead stick is in the gastrointestinal tract for a long time When burning a lead or battery,
- When using lead furniture, prolonged drinking of tap water from lead water pipes can lead to lead poisoning.
- Lead can be a little mixed in smoke from factory chimneys or automobile exhaust pipes, and long inhalation of the smoke can lead to lead poisoning.
- The food you normally eat can contain very little lead. Infants and toddlers can develop lead poisoning when they suck on toys or objects that contain lead or when they breathe lead-contaminated air for a long time.
- Recently, it was estimated that the lead levels in Beethoven’s remains were unusually high, and probably died of lead poisoning.
Table 10. A common source of lead
| 납 성분이 아주 많이 들어 있는 출처
Sources with a high level of lead |
납 성분이 어느 정도 많이 들어 있는 출처
Sources with a certain amount of lead |
납 성분이 소량 들어 있는 출처
Sources with a small amount of lea |
| 주택의 외부나 내부에 칠한 납 든 페인트
Leaded paint on the exterior or interior of the house |
집안 먼지, 집안 내부에 쓴 물질, 납이 오염된 흙
Dust inside the house, the material used inside the house, soil |
음식물, 집 주위 공기, 식수
|
Sources and references-Handbook oh Common Poisonings in Children. American Academy of Pediatrics p.206
Symptoms, signs of lead poisoning
- Symptoms, signs of lead poisoning differ according to the level of lead in the blood. If the blood lead concentration is less than 10㎍/㎗ (1㎍=0.000001g, 1㎗=0.1ℓ), there is no harm to health.
- Slightly higher blood lead levels than normal do not necessarily show significant signs of lead poisoning.‘
- Studies have shown that when blood lead levels are less than 40-60 µg/dL, symptoms of mild lead poisoning may not appear significantly.
- If you have mild lead poisoning, symptoms, signs of lead poisoning may appear gradually, and hyperactivity disorder, attention deficit disorder, poor learning, and poor growth may appear mildly.
- In children and adolescents with mild lead poisoning, degree ⅓ may have a number of symptoms other than those described above.
- When the blood lead level is 60㎍/㎗ or higher, various signs, symptoms of life-threatening lead poisoning can appear.
- Loss of appetite, anemia, vomiting, constipation, neurological diseases, systemic convulsions, hyperactivity disorder, attention deficit disorder, speech and developmental degeneration, hemiplegia, blindness, and many other things when the blood lead concentration is 100∼150㎍/㎗.
- Symptoms may appear and even death may occur.

Photo 1-30.
X-ray of the abdomen of a child with lead poisoning
An x-ray scan of the abdomen of children who ate lead-based paint crumbs shows that the gastrointestinal tract, Small pieces of white paint (a) may appear on an abdominal x-ray examination.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Figure 1-31.
CBC blood test for a child with lead poisoning.
Basophilic spots in red blood cells on a CBC blood test in a child with a-lead poisoning
b-erythrocytes,
blood lead levels can be measured and diagnosed with certainty.
Hemoglobin concentration may be abnormally low.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
Diagnosis of lead poisoning
- If you suspect that your child has lead poisoning by combining your child’s medical history, symptoms, and medical examination findings, you can diagnose the disease by measuring the lead level in your child’s blood and performing other tests, such as a CBC blood test.
- Infants and toddlers with image disease can develop lead poisoning by peeling off pieces of lead-containing paint.
- Sometimes abdominal x-rays and bone x-rays can help diagnose lead poisoning.
- In addition, lead poisoning can be diagnosed by measuring the concentration of lead in blood, hair, saliva, and urine.
- When children and adolescents, especially infants, have regular health check-ups, take one or two drops of blood from their fingers and put the blood on a test filter paper to test for lead concentration in the blood, so lead poisoning can be diagnosed early.
Classification and treatment of lead poisoning
- Depending on the concentration of lead in the blood, the treatment method differs depending on the path through which the lead entered the body.
- When the blood lead concentration is 10-40㎍/㎗, a balanced diet is eaten, and the blood lead concentration is repeatedly followed up for an appropriate period of time to determine whether the blood lead concentration increases or decreases.
- At this time, if the blood lead concentration continues to increase, find the cause of the increase and treat it to remove the cause.
- Find out when, where, and how lead got into the body and treat it so that it no longer enters the body.
Table 11 Classification of blood lead levels in children and treatment plans
| 혈중 납 농도(단위=㎍/㎗)
Blood lead concentration (unit = ㎍/㎗) |
납 중독 중증도의 분류
Classification of lead poisoning severity |
납 중독의 치료
Treatment of lead poisoning |
| 9 or more | I | 치료를 할 필요가 없다.
Do not need treatment |
| 10~14 | IIa | 동사무소와 공동으로 대치한다. 약물로 치료하지 않는다. 3개월 후 추적 혈중 납 농도 검사를 한다.
Confronted jointly with the town office. Not treated with drugs. After 3 months, a follow-up blood lead level test is performed |
| 15~19 | IIb | 각 환아에 따라 치료전략을 세운다. 환경치료를 한다. 적절한 영양분을 공급한다. 3개월 마다 추적 혈 중 납 농도 검사를 한다.
Establish a treatment strategy for each patient. Do environmental treatment. Provide adequate nutrients. Follow-up blood lead levels are tested every 3 months |
| 20~44 | III | 전문가의 치료를 받는다. 환경조사를 하고 납이 있는 출처에서 납을 제거한다. 영양분 공급을 한다. 약물치료를 공급한다.
Seek professional treatment. Do environmental research and remove lead from sources where lead is present. Provide nutrients. Supply medication. |
| 45~69 | 1V | 전문가의 치료를 받는다. 환경을 조사하고 납이 있는 출처에서 납을 제거한다. 영양분을 공급한다. 병원 입원 약물치료를 받는다.
Get professional treatment. Investigate the environment and remove lead from sources where lead is present. Supply nutrients. Get hospitalized medication. |
| 70 and more | V | 전문가의 치료를 받는다. 환경조사를 하고 납이 있는 출처에서 납을 제거한다. 영양분을 공급한다. 병원입원 약물치료를 받는다.
Get professional treatment. Do environmental research and remove lead from sources where lead is present. Supply nutrients. Get hospitalized medication. |
Sources and references Handbook of Common Poisonings in Children. American Academy of Pediatrics P 206
- In general, when the blood lead concentration is 40㎍/㎗ or higher, the drug is treated until the blood lead concentration drops to or below the normal blood lead concentration.
- Lead poisoning can be treated with drugs such as calcium disodium edetate, BAL, and D-Penicillamine, depending on the symptoms of lead poisoning at this time and the concentration of lead in the blood.
- Severe lead poisoning can lead to systemic cramps and damage to the brain.
- In this case, it is treated with Mannitol or steroids.
- When the brain pressure in the cranial cavity is abnormally high, it is treated with a cranial section resection (頭蓋局部切除術).
- When lead poisoning occurs acutely after ingesting a large amount of lead, gastrointestinal lavage treatment and diarrhea are also performed to expel lead in the gastrointestinal tract through feces.
The following is an example of an Internet pediatric and adolescent health consultation question and answer on “lead poisoning”
Q&A.
‘I want to know about lead poisoning’.
Q.
My child is a 2-year-old boy, and he took a piece of paint.
I am worried if I have lead poisoning.
I look forward to your good answer.
A.
Hello.
Thanks for asking.
It is ideal to provide diagnostic treatment by combining the results of the child’s age and sex, past and present family medical history, symptom signs and examination findings, and appropriate clinical tests.
[Parents should also be at least a half-doctor-Child and Family Nursing Encyclopedia]-Volume 2 Prevention of pediatric and adolescent diseases and safety accidents-Refer to “Prevention of Lead Poisoning” and “Lead Poisoning”. Also, please consult with the Department of Pediatrics and Adolescents after receiving medical examination and treatment. If you have more questions, please contact us again. Thank you. Lee Sang-won dream.
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
- Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
- Emergency care, Harvey Grant and Robert Murray
- Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
- Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
- Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
- The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
- Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
- Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
- Manual of Emergency Care 응급환자관리 정담미디어
- 소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
- Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
- Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
- Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
- Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
- Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics 14th ed. Beherman,
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 18th edition
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th-21st Edition
- Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
- 소아과학 대한교과서
- 제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
- Other
- Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
- “부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
- “The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”