기도 내 이물(2), Foreign bodies in the airways(2)
병원 밖에서 아이의 기도 내 이물이 들어갔을 때는 다음과 같은 처치 방법으로 기본 생명유지를 위한 기본 심폐 소생술을 할 수 있다
여기에 제시하는 기도 내 이물 제거 응급처치법은 현재 가장 적절한 응급처치법이다.
|
가. 이물이 기도 내로 들어갔으나 거의 정상적으로 숨을 쉴 수 있고 의식이 있는 경우의 기도 내 이물 제거 처치법

▴ 사진 1-220. 다른 사람은 병원 응급실이나 의사의 도움을 전화로 청한다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

▴ 사진 1-221. 의사의 지시에 따라 응급치료를 사고 현장에서 시작하면서 구급차로 병원으로 데리고 간다. 관찰은 좋은 치료방법 중 하나이다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
-
이물이 기도의 일부 내로 흡인된 것 같으나 숨을 거의 정상적으로 쉴 수 있고, 의식이 있고 호흡곤란이 경미하게 생길 때는 얼굴을 바닥에 대고 엎드린 자세로 환아를 눕히고 안정시킨다.
-
그와 동시 주위 사람의 도움을 구하면서 의료구급대, 병원 응급실이나 단골 소아청소년과 의사의 도움을 전화로 긴급히 청하고 그들의 지시에 따라 응급처치를 사고 현장에서 시작한다.
-
의료구급대, 단골 소아청소년과 의사. 응급실의 도움을 받을 수 없는 상황에서는 환아의 얼굴을 바닥에 대고 엎드린 자세로 눕히고 구급차나 다른 적절한 교통수단을 이용해 병원 응급실로 급히 데리고 간다.
나. 이물이 기도 내로 흡인된 후 숨을 제대로 쉬지 못하고 거의 질식된 상태에 있지만 의식이 아직 있을 때 기도 내 이물 제거 방법
-
인두 부분 기도 내나 기관 부분 기도 내 이물로 호흡곤란이 심하게 생기고, 병원 응급실로 데리고 갈 상황도 못 되고, 의료구급대가 사고 현장으로 와서 기도 내 이물 제거 응급 처치법을 할 수 있는 시간 여유도 없고, 기도 내 이물로 기도가 완전히 막혀, 또는 거의 완전히 막혀 생명이 위험하다고 판단될 때는 사고 현장에서 다음과 같이 기도 내 이물 제거 응급 처치법을 시작한다.
-
환아의 턱과 혓바닥과 혀뿌리를 한쪽 손의 엄지와 인지로 잡아 혀가 입안 위 앞쪽으로 올리고 입을 크게 벌린 후 이물이 인두 부분 기도 내에 있나 찾아본다.
-
인두 부분 기도 내에서 이물이 보이고, 그 이물을 손가락으로 쉽게 꺼낼 수 있을 것 같으면, 다른 쪽 손가락으로 이물을 꺼낸다. 이렇게 꺼낼 때 인두 부분 기도 내 이물을 인두 부분 기도 내에서 후두 부분 기도 있는 쪽으로 더 깊숙이 밀어 넣을 수 있다. 그래서 기도가 더 완전히 막힐 수 있다.
-
따라서 처음부터 이 방법으로 응급처치를 하지 않고 1세 이전 영아들의 경우는, 기도 내 이물 제거 등치기 처치법을 실행한다. 즉 5번 기도 내 이물 제거 등치기 응급 처치법을 하든지, 기도 내 이물 제거 가슴 밀기 응급처지 법을 하든지,
-
1~8세 아이들의 경우, 기도 내 이물 제거 오목가슴 밀기 응급 처치법(하임리크 응급 처치법) 등으로 기도 내 이물을 제거한다.
-
보이는 인두 부분 기도 내 이물을 손가락으로 후벼 꺼내는 처치 방법으로 꺼낼 수 없다고 판단되면
-
1세 이전 영아들의 경우는, 기도 내 이물 제거 등치기 응급처치법 및, 또는 가슴 밀기 응급처치법,
-
1~8세 아이들의 경우는, 기도 내 이물 제거 오목가슴 밀기 처치법(하임리크 처치법) 등의 응급처치법으로 기도 내 이물을 제거한다.
-
주위에 있는 사람의 도움을 청하고, 의료구급대, 병원 응급실, 또는 소아청소년과 의사에게 응급으로 전화해 그들의 지시에 따라 구급차나 다른 적절한 교통수단으로 병원 응급실로 긴급히 이송한다.
-
호흡이 정지되거나 심장 박동이 정지되면 기본 생명유지를 위한 기본 심폐 소생술 응급 처치법을 시작한다. ( 호흡곤란 참조).
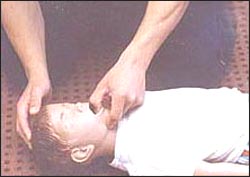
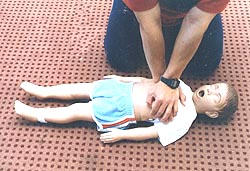
▴ 사진 1-222. 이물이 인두 부분 기도 속에 있는지 알아보기 위해 입안을 들여다본다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
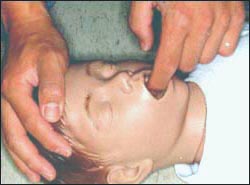
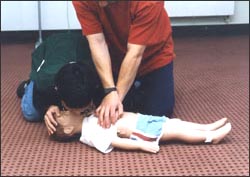
▴ 사진 1-223. 이물이 인두 부분 기도 속에서 보이고 꺼낼 수 있으면 이물을 손가락으로 꺼낸다. 이때 잘못하면 인두 부분 기도 내 이물을 후두 부분 기도 속이나 기관 부분 기도 속으로 깊숙이 밀어 넣을 수 있다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
다. 이물이 영아의 기도 속으로 갑자기 들어가 기도가 완전히 막혀서 숨을 제대로 쉬지 못하지만 의식이 있는 순간 기도 내 이물 제거 응급처치법
-
다음과 같이 기도 내 이물 제거 응급처치를 바로 시작하면서 주위에 있는 사람의 도움을 청한다.
-
의료구급대, 병원 응급실, 또는 단골 소아청소년과 의사에게 긴급 전화를 해 그들의 지시에 따라 응급처치를 사고 현장에서 시작한다.
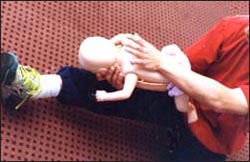
▴ 사진 127. 영아의 얼굴을 바닥으로 향하게 하고 처치자의 무릎 위에 영아를 눕힌다. 이때 처치자의 한쪽 손바닥으로 영아의 턱을 꼭 받친다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
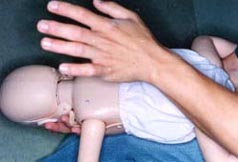
▴ 사진 128. 처치자의 다른 쪽 손바닥으로 영아의 양어깨 견갑골 사이 중간 등 부분을 5번 정도 연달아 세게 친다. 그러나 상처를 낼 정도로 너무 세게 쳐서는 안 된다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
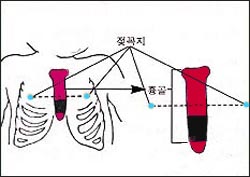
▴ 그림 129. 양쪽 젖꼭지 사이를 잇는 횡선과 앞가슴 밀기 응급처치를 할 부분.
■ 로 표시된 흉골 부분을 흉강 속으로 밀어 기도 내 이물 제거 앞가슴 밀기 응급처치를 한다.
참조문헌 Textbook of Neonatal과 소아가정간후백과 Resuscitation. 1987
▴ 사진 130. 사진과 같이 처치한다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
▴ 사진 131. 구조자의 입을 영아의 입이나 입과 콧구멍에 동시 대고 두 번 공기를 기도 속으로 불어넣은 후 계속 같은 방법으로 인공호흡을 한다. 기본 생명유지를 위한 기본 심폐 소생술을 할 때 심장 마사지를 5번하고 인공호흡을 한 번 한다. 나이에 따라 이공호흡수와 심장 마사지수가 다르다
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
▴ 사진 131. 구조자의 입을 영아의 입이나 입과 콧구멍에 동시 대고 두 번 공기를 기도 속으로 불어넣은 후 계속 같은 방법으로 인공호흡을 한다. 기본 생명유지를 위한 기본 심폐 소생술을 할 때 심장 마사지를 5번하고 인공호흡을 한 번 한다. 나이에 따라 이공호흡수와 심장 마사지수가 다르다. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
-
영아의 얼굴을 바닥으로 향하게 하고 처치자의 무릎 위에 영아를 눕힌다. 이때 처치자의 한쪽 손바닥으로 영아의 턱을 꼭 받친다.
-
이때 영아의 얼굴에서 목, 앞가슴, 복부까지 그쪽의 손과 팔로 받친다.
-
영아를 받친 처치자의 팔과 영아를 처치자의 무릎 위에 함께 올려놓는다.
-
영아의 두 다리를 양쪽으로 벌린다.
-
영아의 머리를 몸통보다 조금 낮추고 처치자의 다른 쪽의 손바닥으로 영아의 양어깨 견갑골 사이 있는 등 중간 부분을 5번 정도 연달아 상처가 나지 않을 정도로 세게 친다. 즉 기도 내 이물제거 등치기 응급 처치법을 5번 한다.
-
이 때 기도 속을 막았던 이물이 기도 내에서 입안이나 입 밖으로 나오면 이 처치를 중지한다.
-
이상 설명한 기도 내 이물 제거 등치기 응급 처치법을 실행 한 후에도 기도 내를 막은 이물이 기도 내 에 그대로 있고 아직도 숨을 제대로 쉴 수 없을 때는 다음과 같이 응급처치를 계속 할 수 있다.
-
영아의 등을 쳤던 손으로 영아의 뒤통수를 받쳐 잡고 그 팔로 영아의 등과 엉덩이에 댄다. 즉 이때 양쪽 손과 앞 팔로 영아를 샌드위치와 같이 잡는다.
-
즉, 한쪽 손과 앞 팔로 영아의 턱, 목, 가슴, 배를 받치고, 다른 쪽 손과 앞 팔로 영아의 뒤통수, 등, 허리, 엉덩이를 잡는다.
-
그 다음 영아의 등을 바닥으로 향하게 하고 처치자의 무릎에 영아를 눕힌다. 이때 영아의 머리, 목, 몸통을 잘 받친다.
-
영아의 얼굴과 머리는 몸통보다 좀 낮은 자세로 눕힌다.
-
위의 사진 130 과 같이 영아의 양쪽 젖꼭지 사이를 잇는 횡선에서 처치자의 손가락 하나 넓이만큼 배꼽이 있는 쪽으로 떨어진 흉골 위 부분에 처치자의 집게 손가락과 가운데 손가락의 끝마디로 심장 마사지하는 방법과 똑같은 방법으로 영아의 앞가슴(그림 129 ■로 표시된 부분)을 등뼈 있는 쪽을 향해서 세게(그러나 상처입지 않게) 5번 연달아 민다.
-
기도 내 이물이 입 안이나 입 밖으로 나올 때까지, 또는 숨을 정상적으로 쉴 때까지 기도내 이물 제거 등 치기 응급 처치법과 앞가슴 밀기 응급 처치법을 반복한다.
-
이렇게 처치 할 때 기도 내 이물이 나오지 않고, 영아가 의식을 완전히 잃었을 때는 한쪽 가운데 손가락과 집게손가락을 이용해서 영아의 혓바닥, 혀뿌리와 턱을 함께 싸잡고 입을 크게 벌리고 인두강 속에 이물이 있나 찾아볼 수 있다.
-
이때 이물이 목구멍 속에서 보이고 꺼낼 수 있으면 손가락으로 후벼 꺼낼 수 있다. 전에도 설명한 바와 같이 인두 부분 기도 내에 있는 이물을 손으로 꺼낼 때 이물을 후두 부분 기도 속, 또는 그 이하에 있는 기도 속으로 깊숙이 밀어 넣을 위험성이 있다. 따라서 극히 조심히 이 응급 처치법을 실행한다. 어떤 의사는 아예 손가락으로 인두 강 속 이물을 손으로 꺼내지 말라고 권장 한다.
-
이물이 입 속이나 인두 속에서 보이지 않으면 영아의 머리를 뒤로 살짝 젖히고 목을 옆으로 살짝 돌려 기도(숨통)속이 최대한도로 열리게 한다. 구조자의 입을 영아의 입이나 입과 콧구멍에 대고 인공호흡을 시작하고 심장 마사지를 해서 기본 생명유지를 위한 기본 심폐 소생술을 한다.
-
생명유지를 위한 기본 심폐 소생술을 할 때 맨 처음은 처치자가 공기를 영아의 기도 속으로 두 번 불어넣는다. 이때 영아의 기도가 완전히 막혀 있으면 불어넣은 공기가 막힌 부분의 기도까지 들어갈 수 있고 그 이상 숨통(기도)을 통과해서 폐 속으로 들어갈 수 없기 때문에 공기를 입으로 불어넣는데 저항이 생기는 것을 느낄 수 있고 또 영아의 폐포가 펴지지 않기 때문에 앞가슴도 숨 쉴 때와 같이 올라오지 않는 것이 보통이다.
라. 이물이 영아의 기도 속으로 들어간 직후 호흡이 정지되고 심장 박동이 없고 의식을 완전히 잃은 순간 기도 내 이물 제거 응급처치 법
- 다음과 같이 기도 내 이물 제거 응급처치를 즉시 시작하면서 가능하면 주위 사람의 도움을 청한다.
- 그리고 의료 구급대, 병원응급실, 또는 단골 소아청소년과 의사에게 긴급으로 전화해 그들의 지시에 따라 응급처치를 사고 현장에서 시작한다.
① 기도 내 이물로 의식을 완전히 잃었을 때는 영아의 혓바닥, 혀뿌리와 턱을 한쪽 엄지손가락과 집게손가락으로 싸잡아 혀뿌리를 위로 앞으로 올려서 인두 강 속에 이물이 있나 찾아본다.
② 이물이 인두 강 속에서 보이면 다른 손가락으로 이물을 후벼 꺼낼 수 있다. 보이지도 않거나 보이지만 꺼낼 수 없고 숨이 정지되어 있을 때는 양쪽 견갑골 사이에 있는 등 부분을 5번 손바닥으로 연달아 치는 기도 내 이물 제거 등치기 응급처치를 한다.
③ 처치자의 입을 환아의 입과 콧구멍에 동시에 대고 또는 입에 대고 콧구멍을 막고 인공호흡을 하면서 심장 마사지도 한다. 최초로 2번 공기를 환아의 숨통(기도)을 통과해서 폐 속으로 불어 넣는다. 심장 마사지는 5번 한다. 기도 내 이물로 기도가 완전히 막혔을 때는 불어넣은 공기가 폐 속으로 들어갈 수 없기 때문에 영아의 앞가슴이 숨 쉴 때와 같이 올라오지 않는 것을 볼 수 있고, 기도 속으로 불어넣는 공기가 기도 속으로 흘러들어 가는데 저항이 있는 것을 느낄 수 있다.
④ 만약 ③ 처치를 한 후에도 기도 내 이물로 숨을 쉬지 못하면 머리와 얼굴을 옆으로 돌리고 목을 뒤로 살짝 젖혀 기도(숨통)가 열리게 다시 시도한다.
⑤ 그래도 기도 내 이물로 숨을 쉬지 못하면 기도 내 이물 제거 앞가슴 밀기 처치를 5번 연달아 또 한다.
⑥ 이물이 후두 내나 기관 내에서 구강이나 입 밖으로 나오지 않고 의식이 계속 없을 때는 ① 의 손가락 이물 제거 처치를 또 다시 시행 할 수 있다.
⑦ 이물이 기도 속에서 완전히 나올 때까지 ②~⑤ 처치를 반복할 수 있다.
⑧ 기도 속 이물이 기도 밖으로 나오고 정상적으로 숨을 쉬기 시작한 후 단골 소아청소년과 의사나 의료구급대, 구급차가 사고 현장에 도착해 그들의 치료를 받을 때까지 계속 관찰한다.
마. 기도 내 이물 제거 하임리크 처치법 Heimlich maneuver
-
이물이 영아의 인두 부분 기도 내, 후두 부분 기도 내, 또는 기관 부분 기도 내에 들어가 호흡곤란이 심하게 생길 때 기도 내 이물 제거 등치기 처치법이나 앞가슴 밀기 처치법, 또는 오목가슴 밀기 처치법 등의 응급 처치를 할 수 있고,
-
1세 이후 유아들이나 8세 이전 유아들과 학령기 아이들의 인두 부분 기도 속, 후두 부분 기도 속, 또는 기관 속에 이물이 들어가 호흡곤란이 심하게 생길 때 기도 내 이물 제거 등치기 응급처치법, 또는 오목가슴 밀기 응급 처치법 (하임리크 처치법) 등으로 기도 내 이물이 제거하는 응급처치를 할 수 있다.
-
기도 내 이물 제거 오목가슴 밀기(하임리크) 응급처치는 환아가 선 자세에서도 할 수도 있고 누워있는 자세에서도 할 수 있다.
-
하임리크 처치 방법에 관해 다음 더 구체적으로 설명한다.
1) 이물이 기도 내로 흡인되어 이물로 기도가 막혔으나 유아, 학령기 아이, 사춘기 아이, 또는 성인이 아직 서 있거나, 또는 누워있는 자세에서 기도 내 이물 제거 오목가슴 밀기 응급처치법(하임리크 처치법)
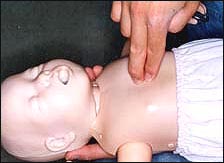
① 기도 내 이물로 호흡곤란 상태에 빠져 있고 아직 서 있는 아이를 목격 했을 때는 처치자가 그 아이의 등 뒤에 서서 처치자의 두 팔을 환아의 양쪽 겨드랑이 밑에 넣고 두 팔로 아이의 가슴을 둘러싼다(사진 133 참조).
② 아이의 배꼽의 바로 위, 흉골 검상돌기의 맨 아래 끝에 있는 복부 부위(오목가슴)에 처치자의 한쪽 주먹을 댄다. 그리고 처치자의 다른 쪽 손으로 복부에 댄 주먹을 싸잡는다. 아이의 오목가슴에 주먹을 댈 때 엄지가 있는 쪽의 주먹을 오목 가슴에 먼저 댄다.
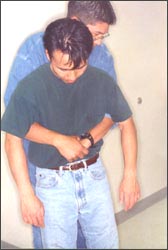
▴ 사진 133. ①~⑥에서 설명한 것과 같이 하임리크 처치법을 실시한다. 아이의 오목가슴에 주먹을 댈 때 엄지가 있는 쪽의 주먹을 아이의 오목 가슴에 먼저 댄다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

▴ 사진 134. ①~⑥에서 설명한 것과 같이 하임리크 처치 법을 서 있는 자세에서 실시한다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
③ 다시 설명하면, 처치자의 다른 쪽 손바닥으로 오목가슴에 먼저 댄 주먹을 싸잡는다. 그 다음은 그 두 주먹으로 아이의 오목가슴을 흉강 내 중앙 부위 쪽으로 연달아 한 번씩 한번 씩 또박또박 5 번 민다.
이때 복강 내 간장 등 다른 장기나 흉곽에 있는 늑골이나 흉골의 검상돌기 등이 손상되지 않게 오목가슴 밀기 처치법(하임리크 처치법)을 실시한다.
④ ③의 처치를 실시할 때 기도 속 이물이 더 잘 나올 수 있게 매번 또박또박 밀어야 한다. 기도 내 이물이 나올 때까지 오목가슴 밀기 응급 처치법(하임리크 처치법)을 계속하든지 기도 내 이물 제거 등치기 응급 처치를 대신 할 수 있다.
⑤ 하임리크 처치를 하는 동안 아이의 의식이 완전히 없을 때는 누워있는 자세에서 한쪽 엄지손가락과 집게손가락으로 혓바닥, 혀뿌리와 턱을 함께 잡아 혀를 위로 앞으로 올리고 인두 강 부분 기도 속에 이물이 있나 찾아본다.
구강 속이나 인두 부분 기도 속에서 이물이 보이고 꺼낼 수 있으면 다른 쪽 손가락으로 이물을 후벼 꺼낼 수 있다.
이미 설명한 바와 같이 인두강 내 이물을 잘못 꺼내면 인두 부분 기도 속 이물이 후두 부분 기도 속으로 들어갈 수 있다.
⑥ 입안이나 인두 부분 기도 내 이물이 보이지 않으면 머리를 뒤로 한 번 더 살짝 젖히고, 얼굴과 목을 옆으로 살짝 돌려 기도 속을 최대한도로 크게 열어준다.
아직도 숨을 쉬지 못하거나, 숨을 겨우 쉬거나, 앞가슴이 숨 쉬는 대로 조금 위아래로 올라왔다 내려왔다 할 때는 또다시 머리를 조금 더 뒤로 젖히고 얼굴, 목을 살짝 옆으로 돌려서 기도가 더 활짝 열리게 해서 숨을 더 잘 쉬게 한 번 더 시도한다.
숨이 멈추고, 심장박동도 없고, 의식도 완전히 없고, 기도 속이 계속 차단된 것 같으면 기도 내 이물 제거 오목가슴 밀기 응급처치법(하임리크 처치법)을 반복 시도한다.
그리고 기본 생명유지를 하기 위한 기본 심폐 소생술 응급 처치법을 적절히 계속 한다.
2) 이물이 1세 이후 유아, 학령기 아이, 또는 사춘기 아이의 기도 속으로 흡인되어 기도 내 이물로 기도가 막혀 의식을 잃는 순간에 처한 아이를 목격한 바로 후, 또는 의식을 잃으려고 할 때 기도 내 이물 제거 오목가슴 밀기 처치법(하임리크 처치법)
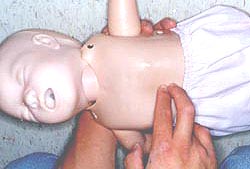
㈀ 등을 편평한 장소에 대고 아이를 눕힌다.
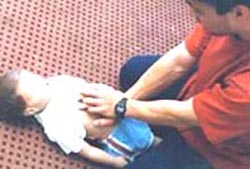
▴ 사진 136. 양쪽 손바닥을 아이의 배꼽 바로 위, 흉골의 검상돌기 바로 아래 복부, 즉 오목 가슴에 올려놓고 기도 내 이물 제거 오목 가슴 밀기 하임리크 응급처치법을 실시한다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
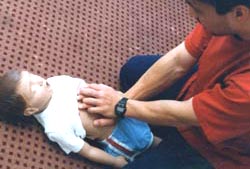
▴ 사진 135. 양쪽 손바닥을 아이의 배꼽 바로 위, 흉골의 검상돌기의 맨 끝 부분의 바로 아래에 있는 복부(오목 가슴)에 올려놓고 기도 내 이물 제거 오목 가슴 밀기 응급처치법(하임리크 처치법)을 실시한다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
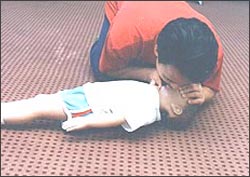
▴ 사진 137. 두 손 가락으로 아이의 코 구멍을 막고 처치자의 입을 아이의 입에 대고 인공호흡을 한다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
▴ 사진 138. 심장 마사지를 한다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
㈁ 이물이 기도 내로 흡인된 바로 후 의식을 잃고 쓰러지는 아이를 목격할 때는 처치자의 한쪽 엄지와 인지로 혓바닥, 혀뿌리와 턱을 싸잡아 혀를 위쪽으로 끌어 올려 인두 부분 기도 속에 이물이 있나 찾아보고, 있으면 꺼낼 수 있다.
이물이 보이고 꺼낼 수 있으면 다른 손가락으로 후벼 꺼낼 수 있다. 그러나 이런 처치방법으로 이물을 꺼낼 때 인두 강 내 이물이 인두 부분 기도의 아래에 있는 후두 부분 기도 속으로 깊숙이 들어갈 수 있다. 따라서 이 방법을 인두 강 내 이물을 제거하는 방법을 권장하지 않는 의사들도 있다.
㈂ ㈁을 시도했으나 이물을 꺼낼 수 없고 숨을 쉬지 않으면 ㈃에서 ㈇까지의 이물 제거 응급처치법을 반복한다.
▴ 사진 139. 두 사람이 있을 때는 한 사람은 인공호흡을 하고, 다른 사람은 심장마사지를 한다. 한 사람만 있으면, 혼자서 인공호흡도 하고 심장마사지도 해야 한다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
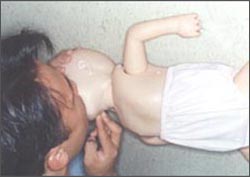
㈃ 처치자의 두 다리를 양쪽으로 쫙 벌리고 아이의 넓적다리 위쪽에서 두 무릎을 꿇든지(사진 134, 135 참조), 그 아이의 엉덩이의 한쪽 옆에서 아이의 얼굴을 향해 두 무릎을 꿇고 쭈그리고 앉는다. (사진 139 참조).
㈄ 처치자의 한쪽의 손바닥을 아이의 배꼽 바로 위쪽, 흉골의 검상돌기 바로 아래 복부, 오목가슴에 올려놓는다. 그 한쪽 손바닥 위에다 다른 쪽 손바닥을 올려놓는다. 이때 늑골이나 흉골 검상돌기 위부위에 손바닥을 대서는 안 된다.
㈅ 두 손바닥으로 흉강 내 중앙부위 쪽을 향하여 오목가슴을 힘 있게 또박또박 5번 연달아 민다. 이때 오목가슴 이외 다른 부위의 복부를 밀거나 오목가슴의 옆쪽으로 아래쪽으로 밀어서는 안 된다.
㈆ ㈅의 처치를 한 후 기도 내 이물이 나오지 않으면 혓바닥, 혀뿌리와 턱을 엄지와 둘째손가락으로 싸잡아 혀를 위 앞쪽으로 올리면서 이물이 인두 부분 기도 내로 나와 있나 본다. 이물이 있으면 손가락으로 후벼 꺼낸다.
㈇ 숨을 계속 쉬지 못하면 ㈃∼㈆의 처치를 반복한다.
질식과 기도 내 이물 예방
-
기도 내 이물의 75∼80%는 4세 이전 영유들에게 생긴다.
-
부모들은 특히 영유아 자녀들의 기도 속으로 이물을 흡인되지 않게 잘 예방해야 한다. 특히 어린 영유아들의 일부는 어떤 것이든 입 속에 넣고 빨고 먹고 놀지 않게 해야 한다.
-
영유가 입에 넣고 빨고 놀 수 있는 것은 무엇이든지 기도 속으로 쉽게 흡인될 가능성이 있다. 입 에 넣고 놀 수 있는 작은 장난감, 옷핀 또는 쇠붙이 장난감을 갖고 놀지 않게 안전한 장소에 잘 보관해야 한다.
-
기도 내로 쉽게 흡인 해 들어갈 수 있을 정도로 작은 것은 영유아들이 가지고 놀지 않게 하고, 땅콩, 알사탕 등이 기도 내로 들어가지 않게 감독한다.
-
냉장고 안에 들어가 놀지 않도록 주의한다. 영유들이 가지고 노는 작은 장난감은 기도 내로 들어가지 않게 입 안에 넣을 수 없는 큰 것만 사준다.
-
직경이 1½인치 보다 더 작은 장난감은 사주지 않는다. 창문에 매단 코드로 질식사고가 생길 수 있으므로 영유아들의 손에 닿지 않게 코드를 설치한다.
-
크립 측면 스래트 간격이 2⅜인치 간격보다 더 좁아야 한다. 영유아들의 크립에 너무 부드러운 베딩을 될 수 있는 한 피한다.
-
부모는 기본 생명유지를 위한 기본 심폐 소생술을 평소에 배운다.
5대 독자 3세 유아 자녀가 땅콩을 먹다가 땅콩이 자녀의 기도 속으로 흡인해 들어가 기도가 차단되어 숨을 못 쉬고 얼굴이 파라지면서 죽어 가는 것을 목격했다고 가정하면
|
Foreign bodies in the airways(2) 기도 내 이물(2)
- When a foreign object enters the child’s airways outside the hospital, basic CPR for basic life maintenance can be performed with the following treatment methods.
The first aid method for removing foreign objects in the airways presented here is currently the most appropriate first aid method.
- However, there may be new first aid measures other than this one.
- Readers should follow the latest first aid measures obtained from regular pediatricians or from emergency medical reference books.
- At that time, you should check frequently to see if it is the most up-to-date and most appropriate treatment.
- The first aid method for removing foreign bodies in the airways presented here cannot be applied uniformly in all situations.
- When a foreign body enters the airways of an infant under the age of 1, but is able to breathe properly and is conscious
- When a foreign body is aspirated into the airways of an infant under the age of 1 and is almost suffocated due to the inability to breathe,
- but there is a sense of consciousness
- A foreign body suddenly enters the airway of an infant under the age of 1, and the airway is completely blocked, making it difficult to breathe properly, but at the moment of consciousness
- In the case of witnessing a complete loss of consciousness immediately after a foreign object enters an infant’s airway under 1 year of age.
- Do Heimlich maneuver
1. When a foreign body enters the airways of an infant after the age of 1, a school-age child, or a child or adult after the school-age removes the foreign body in the airway while the child or adult is conscious.
2. You witnessed the loss of consciousness by entering the airway of a school-age child. Immediately after or at the moment of loss of consciousness, remove foreign objects in the airway.
(A) How to remove a foreign body from the airways when a foreign body has entered the airway but can breathe almost normally and is conscious

▴ Photo 1-220. Others call for help from a hospital emergency room or doctor. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

▴ Photo 1-221. Following the doctor’s instructions, emergency treatment begins
at the scene of the accident and takes them to the hospital by ambulance.
Observation is one of the best treatment options. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John
Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
- When a foreign body seems to have been aspirated into a part of the airway, but can breathe almost normally, and when there is consciousness and difficulty breathing slightly, lay the child on the floor in a prone position and stabilize it.
- At the same time, urgently call for help from medical paramedics, hospital emergency rooms, or regular pediatricians by phone while seeking help from people around them, and initiate first aid at the accident site according to their instructions.
- Medical paramedics, regular pediatricians. In situations where emergency room assistance is not available, lay the child’s face on the floor in a prone position and take the child to the hospital emergency room using an ambulance or other appropriate means of transportation.
(B) How to remove a foreign body from the airways when a foreign body is aspirated into the airway and is in a state of almost choking without proper breathing, but is still conscious
- There are severe breathing difficulties due to foreign objects in the pharyngeal airway or trachea airways, and it is not possible to take them to the hospital emergency room.
- When the airway is completely blocked or almost completely blocked by a foreign body and it is judged that life is in danger, start the first aid method to remove the foreign body in the airway at the accident site as follows.
- Hold the child’s chin, tongue, and root of the tongue with the thumb and finger of one hand, raise the tongue to the front of the mouth, open the mouth wide, and look for a foreign body in the pharyngeal airway.
- If a foreign body is visible in the pharyngeal airway and it seems that the foreign body can be easily removed with a finger, remove the foreign body with the other finger.
- When pulling out in this way, the foreign body in the pharyngeal airway can be pushed deeper into the laryngeal airway within the pharyngeal airway. So the airway can be more completely blocked.
- Therefore, in the case of infants before the age of 1, without first aid in this way from the beginning, perform the countermeasure to remove foreign objects in the airway. In other words, whether you are using the first aid method to remove foreign objects in the airway 5 times-back blows, or the first aid method to remove foreign objects in the airway, push the chest,
- In the case of children aged 1-8, remove foreign objects in the airways with the first aid method for pushing the Epigastric region(Heimlik first aid method), etc., to remove foreign objects in the airways.
- If it is judged that the foreign body in the visible pharyngeal part of the airway cannot be pulled out with a finger, In the case of infants before the age of 1, the first aid method for removing foreign objects in the airways and the first aid method for back blowing 5 times, In the case of children aged 1 to 8, remove foreign objects in the airways with first aid measures such as removing foreign objects in the airways and pushing the epigastrium region(Heimlik treatment method).
- Ask for help from people around you, call a medical paramedic, hospital emergency room, or pediatrician as an emergency, and follow their instructions to urgently transfer them to the hospital emergency room by ambulance or other appropriate means of transportation.
- When breathing is stopped or the heartbeat is stopped, basic CPR first aid to maintain basic life is initiated. (See Difficulty breathing).

▴ Photo 1-222. Look inside your child’s mouth to see if the foreign body is in his pharyngeal airway. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

▴ Photo 1-223. If the foreign body is visible in the pharyngeal airway and can be removed, remove the foreign body with your finger. At this time, if wrongly done, the foreign body in the pharyngeal airway may be pushed deep into the laryngeal airway or the tracheal airway. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
(C). A foreign body suddenly enters the infant’s airway and the airway is completely blocked, so it is impossible to breathe properly.
- However, when there is consciousness, the foreign body in the airway is removed. Immediately start first aid to remove foreign bodies in the airways as follows, and ask for help from people around you.
- Make an emergency call to a medical paramedic, hospital emergency room, or a regular pediatrician and follow their instructions to initiate first aid at the accident site.

▴ Photo 127. Place the infant with the infant’s face facing the floor and lay the infant on the person’s lap. At this time, support the infant’s chin tightly with the palm of one of the therapists. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

▴ Photo 128. Back-blowing the middle back between the infant’s shoulder blades with the other palm of the person in a row about 5 times in succession. But don’t hit it too hard enough to hurt you. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

▴ Figure 129. A horizontal line connecting the nipples and a part for first aid by pushing the front chest. Push the sternum area marked with ■ into the chest cavity to remove foreign objects from the airways.
References: Textbook of Neonatal and Resuscitation. 1987

▴Photograph 130-1.
Treat as shown in Photograph 130.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

▴ Photo 131. Press the rescuer’s mouth to the infant’s mouth or mouth and nostrils at the same time, blow air into the airway twice, and continue to perform artificial respiration in the same way. When performing basic cardiopulmonary resuscitation to maintain basic life, do heart massage 5 times and artificial respiration once. The number of breathing and heart massages differs according to age. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

▴ Photo 131. Press the rescuer’s mouth to the infant’s mouth or mouth and nostrils at the same time, blow air into the airway twice, and continue to perform artificial respiration in the same way. When performing basic cardiopulmonary resuscitation to maintain basic life, do heart massage 5 times and artificial respiration once. Depending on the age, the number of breathing and heart massages is different. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
- With the infant’s face facing the floor, lay the infant on the person’s lap. At this time, support the infant’s chin tightly with the palm of one of the therapists.
- At this time, support the infant’s face to the neck, front chest, and abdomen with their hands and arms.
- The arm of the caregiver supporting the infant and the infant are placed together on the caregiver’s lap.
- The infant’s legs are spread to both sides. Lower the infant’s head slightly below the torso and hit the middle part of the infant’s shoulder blades between the infant’s shoulder blades with the palm of the other side of the caregiver 5 times in a row so that it does not hurt.
- That is, the first aid method for removing foreign objects in the airway is performed 5 times.
- At this time, if the foreign body that blocked the airway comes out of the mouth or out of the airway, stop this treatment.
- If the foreign body that has blocked the airway remains in the airway and still cannot breathe properly after performing the above-described first aid method for removing foreign body in the airway, first aid can be continued as follows. Hold the infant’s back with the hand that struck(blowing) the infant’s back, and place the arm on the infant’s back and hips.
- That is, at this time, hold the infant like a sandwich with both hands and front arms. That is, support the infant’s chin, neck, chest, and stomach with one hand and front arm, and hold the infant’s back, back, waist, and buttocks with the other hand and front arm.
- Then, with the infant’s back facing the floor, lay the infant on the person’s lap. At this time, support the infant’s head, neck, and body well.
- The infant’s face and head are laid down in a lower position than the torso.
- As shown in the above picture (130-1), the infant’s heart is massaged in the same way as the method of heart massage with the tip of the forefinger and the middle finger on the upper part of the sternum, which is the width of the doctor’s finger as much as the width of the belly button in the horizontal line between the infant’s nipples.
- Push the sternum area marked with ■ the part marked in Figure 129) firmly (but not hurt) 5 times in succession toward the side of the spine.
- Repeat first aid measures such as removing foreign bodies from the airways and first aid measures by pushing the chest until foreign bodies in the airways come out of the mouth or out of the mouth, or until you breathe normally.
- When treated in this way, the foreign body in the airway does not come out, and when the infant is completely unconscious, you can use one middle finger and forefinger to wrap the infant’s tongue, the root of the tongue, and chin together, open the mouth wide and look for foreign objects in the pharyngeal cavity.
- At this time, if the foreign body is visible in the throat and can be pulled out, it can be pulled out with a finger.
- As explained before, when a foreign body in the pharyngeal airway is pulled out by hand, there is a risk of pushing the foreign body deep into the airway in the occipital region or below.
- Therefore, implement this first aid method with extreme care. Some doctors recommend that you don’t use your fingers to pull foreign objects out of the pharyngeal cavity with your hand.
- If the foreign body is not visible in the mouth or pharynx, tilt the infant’s head slightly back and turn the neck slightly to the side to open the airway (breathing) to the maximum.
- Put the rescuer’s mouth on the infant’s mouth or mouth and nostrils, start artificial respiration and do cardiac massage to perform basic CPR to maintain basic life.
- When performing basic CPR for life support, the first time the practitioner blows air into the infant’s airway twice.
- At this time, if the infant’s airway is completely blocked, you can feel the resistance to blowing air into your mouth because the blown air can enter the airway in the obstructed part, and you cannot pass through the breather (airway) and into the lungs anymore. Since the infant’s alveoli do not open, it is common that the prothorax does not rise as well as when breathing.
(D) Immediately after the foreign body enters the infant’s airway, breathing stops, there is no heartbeat, and the moment the person completely loses consciousness, remove the foreign body from the airway. Immediately start first aid to remove foreign bodies in the airways as follows, and seek help from people around you, if possible.
Then, urgently call a medical paramedic, hospital emergency room, or a regular pediatrician and follow their instructions to initiate first aid at the accident site.
① When the child’s tongue, the root of the tongue, and chin are wrapped with one thumb and forefinger, when the child’s tongue, the root of the tongue, and chin are wrapped with one thumb and forefinger, raise the root of the tongue upward and forward to look for a foreign object in the pharynx.
②You can pull out the foreign body with it. If it is invisible or visible but cannot be taken out and breath is stopped, perform first aid to remove foreign objects in the airways by striking the back part between the shoulder blades with the palm of the 5th hand.
③ Place the person’s mouth into the child’s mouth and nostrils at the same time. Place your nostrils on your face or mouth, and do heart massage while doing artificial respiration.
For the first time, air No. 2 is blown into the lungs after passing through the child’s breath (airway). Do heart massage 5 times.
When the airway is completely blocked by a foreign body in the airway, it is possible to see that the infant’s chest does not rise up as when breathing, because the blown air cannot enter the lungs, and the air blown into the airway flows into the airway. You can feel there is resistance.
④ If you cannot breathe with a foreign body in the airway after taking the treatment, try again to open the airway (breathing) by turning your head and face to the side and tilting your neck slightly back.
⑤ If you are unable to breathe, remove the foreign body in the airway, and perform another procedure for pushing the chest five times in a row.
⑥ When the foreign body does not come out of the mouth or mouth in the larynx or inside the trachea and there is no consciousness, the finger foreign body removal treatment in ① can be performed again.
⑦ You can repeat the measures ② to ⑤ until the foreign body comes out of the airway completely.
⑧ After the foreign body in the airway comes out of the airway and starts to breathe normally, a regular pediatrician, medical paramedic, or ambulance can go to the accident site.
Continue to observe until you arrive and receive their treatment. hemp.
(E) How to remove foreign bodies in the airways by Heimlich maneuver
- When a foreign body enters the pharyngeal airway, laryngeal airway, or tracheal airway of infants and causes severe breathing difficulties, emergency treatment such as removal of the foreign body in the airway, backstroke treatment, push on the front chest, or push on the concave chest may be performed.
- There is, When a foreign body enters the pharyngeal airways, larynx airways, or trachea of infants
- after the age of 1, infants before the age of 8, and children with severe breathing difficulties, remove the foreign body from the airways, first aid measures, or push the concave chest emergency First aid measures can be taken to remove foreign objects in the airways with the treatment method (Heimlik treatment method).
- Removal of foreign objects in the airway Pushing the concave chest (Heimlique): First aid can be done in a standing position or in a lying position.
1) A foreign body was aspirated into the airway and the airway was blocked with a foreign body, but an infant, school-age child, adolescent child, or an adult was still standing or lying in the airway. The treatment method of Heimlik will be described in more detail below.

▴ Photo 133. Perform the Heimleak treatment as described in ①~⑥. When making a fist on the child’s concave chest, first place the fist on the side of the child’s concave chest. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

▴ Photo 134. As described in ①~⑥, perform the Heimlique treatment in a standing position. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
① When a child is in breathing difficulties with a foreign body in the airway and sees a child still standing, the injured person stands behind the child’s back and puts the injured person’s arms under both armpits of the child and covers the child’s chest with both arms (refer to photo 133).
② Put one of the person’s fists into the abdominal area (concave chest) just above the child’s belly button and at the bottom end of the sternum protrusion.
Then, with the other hand of the therapist, hold the fist in the abdomen. When making a fist on the child’s epigastrium, put the fist on the side with the thumb on the epigastrium▴ As described in Photo 133. ①~⑥, implement the Heimlique treatment method. When fisting the child’s epigastrium, place the fist on the side of the child’s concave chest first.
▴ As described in Photo 134. ①~⑥, implement the Heimlique treatment method in a standing position.
③ In other words, use the other palm of the person in charge to hold the fist placed on the concave chest first. Then, with those two fists, push the child’s concave chest toward the central part of the chest cavity one by one, one at a time, five times. At this time, the concave chest pushing treatment (Heim Leak treatment method) is performed to prevent damage to other organs such as the liver in the abdominal cavity or the ribs in the rib cage or the sternum geometries.
④ When carrying out the treatment of ③, you must push it back and forth every time so that the foreign body in the airway can come out better.
The first aid method for pushing the concave chest (Heimlik treatment method) can be continued until the foreign body in the airway comes out, or it can be substituted for the first aid treatment for removing the foreign body in the airway.
⑤ If the child is completely unconscious during the Heimlich treatment, hold the tongue, root of the tongue, and chin together with one thumb and forefinger in a lying position, raising the tongue upward and looking for a foreign object in the trachea of the pharyngeal cavity. If the foreign body is visible in the mouth or in the pharyngeal airway and can be pulled out, the foreign body can be pulled out with the other finger. As already explained, if a foreign body in the pharyngeal cavity is removed incorrectly, the foreign body in the pharyngeal airway may enter the laryngeal airway.
⑥ If you do not see any foreign objects in your mouth or pharyngeal airways, tilt your head back once more, and turn your face and neck slightly to the side to open the airways as wide as possible. If you still can’t breathe, you can barely breathe, or when your front chest rises up and down a little as you breathe, you can turn your head back a little more and turn your face and neck slightly to the side to make the airways open more and breathe.
Try one more time to make it better rest. If breathing is stopped, there is no heartbeat, there is no consciousness, and the inside of the airway seems to be blocked continuously, try the first aid method (Heimlik treatment method) repeatedly to remove the foreign body in the airway and push the concave chest. And, to maintain basic life, continue with the basic CPR first aid method appropriately.
2) Immediately after witnessing a child in the moment of loss of consciousness due to a foreign body being sucked into the airways of an infant after the age of 1, a school-age child, or adolescent child.
- How to remove foreign objects and push the concave chest(Epigasreic region) (Heimlik treatment)
(ㄱ) Place the child on a flat surface and lay the child down.

▴ Picture 136. Put both palms directly above the navel of the child and on the abdomen, that is, the concave chest (epigastric region) just below the sternum, and remove foreign objects in the airways. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

▴ Photo 135. Put both palms on the abdomen (concave chest/epigastric region)
just above the child’s navel, just below the tip of the sternum’s sternum, and perform the first aid method (HeimLick treatment method) to remove foreign objects from the airways. do. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

▴ Photo 137. Clog the child’s nose hole with two fingers, and put your mouth on the child’s mouth to perform artificial respiration. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

▴ Photo 138. Do a heart massage. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
- When a child loses consciousness and falls shortly after a foreign body is aspirated into the airways, hold the tongue, root of the tongue, and the chin with one thumb and cognition of the person to be treated, pull the tongue upwards and look for a foreign body in the pharyngeal airway.
- if any foreign object is visible and can be pulled out, it can be pulled out with another finger.
- However, when the foreign body is removed with this treatment method, the foreign body in the pharyngeal cavity can go deep into the laryngeal airway below the pharyngeal airway.
- Therefore, some doctors do not recommend this method to remove foreign bodies in the pharyngeal cavity.
㈁ but the foreign body cannot be taken out and does not breathe, repeat the first aid method to remove the foreign body from ㈃ to ㈇.

▴ Picture 139. When there are two people, one person performs artificial respiration, and the other person does heart massage. If you only have one person, you should do artificial respiration and heart massage by yourself. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
㈃ Either kneel on the top of the child’s thighs with the her legs wide open on both sides (see photos 134 and 135), or kneel down on one side of the child’s buttocks toward the child’s face and squat. (See photo 139).
㈄ Place the palm of one side of the heron the child’s belly button, the abdomen just below the xiphoid process of her sternum, and her epigastric region. Place the other palm on top of that palm.
At this time, do not place your palm on the upper part of the ribs or sternum sagittal process.
㈅ Push the concave chest with both palms toward the center of the chest cavity and push the concave chest 5 times in succession.
- At this time, do not push the abdomen other than the concave chest or downward to the side of the concave chest.
- If the foreign body in the airway does not come out after the treatment of
㈆ ㈅, wrap the tongue, root of the tongue, and chin with the thumb and second finger, and raise the tongue upwards and forwards, and see if the foreign body is coming out of the pharyngeal airway.
- If there is a foreign object, pull it out with your finger.
- If you cannot keep breathing, repeat the treatment
Prevention of suffocation and foreign bodies in the airways
- 75-80% of foreign matter in airway occurs in young children before the age of 4 years.
- Parents, in particular, should prevent foreign objects from being sucked into the airways of infants and toddlers.
- In particular, some of the younger infants should put anything in their mouths to suck, eat, and not play.
- Anything that infants can put in their mouths to suck and play with is likely to be easily aspirated into the airways.
- Small toys that you can put in your mouth, clothespins, or metal toys should be kept in a safe place so that you do not play with them.
- Do not allow infants and toddlers to play with anything small enough to be easily aspirated into the airway, and supervise that peanuts and egg candy do not enter the airway.
- Be careful not to go inside the refrigerator and play.
- Small toys that infants play with are only bought large items that cannot be put in their mouths so that they do not go into the prayer.
- Do not buy toys smaller than 1½ inches in diameter.
- Install the cord out of reach of infants and toddlers as it can lead to suffocation due to the cord hanging on the window.
- The creep side slat spacing should be narrower than the 2⅜ inch spacing.
- Avoid bedding that is too soft for infants’ creeps as much as possible. Parents usually learn basic CPR for basic life support.
- Assuming that a 5-year-old child or 3-year child’s eating peanuts and witnessing the peanuts suck into the child’s airways and die from being blocked from breathing and her face spreading.
- How would her mom and dad do first aid in that emergency?
- Would you like to call a doctor?
- Would you take me to the hospital?
- Would you like to call a regular pediatrician?.
- If your child doesn’t take her breath to normal in 3 minutes, your child could become vegetative or die.
- Mom and Dad are at least the half-physicians who need to provide first aid to their children who are suffocating.
- You can save the lives of your loved ones with the usual methods of removing foreign objects in the airways, backstrokes, epigastric region push, Heimlik treatment, and basic CPR treatment.
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
-
심폐 소생술(CPR),-www.drleepediatrics.com –제1권. 소아청소년 응급의료
-
신생아 심폐 소생술-www.drleepediatrics.com –제1권. 소아청소년 응급의료,
-
호흡곤란, 콧구멍 속 이물-www.drleepediatrics.com –제1권. 소아청소년 응급의료,
-
비강 속 이물-www.drleepediatrics.com –제1권. 소아청소년 응급의료,
-
외비공의 이물-www.drleepediatrics.com –제1권. 소아청소년 응급의료
-
하임리크 처치법-www.drleepediatrics.com –제1권. 소아청소년 응급의료,
-
생선가시가 목구멍 속에 걸렸을 때-www.drleepediatrics.com –제1권. 소아청소년 응급의료,
- 소화기 속 이물-www.drleepediatrics.com –제1권. 소아청소년 응급의료,
- 소화관내 이물-www.drleepediatrics.com –제1권. 소아청소년 응급의료,
- 위장관 내 이물-www.drleepediatrics.com –제1권. 소아청소년 응급의료,
- 질식 참조-www.drleepediatrics.com –제1권. 소아청소년 응급의료
- Manual of emergency pediatrics 5th edition, Robert M. Reece, M.D., p.791-794, 22-23
- Quick Reference to Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., p.31
- Emergency care and transportation of the sick and injured, 3rd edition, American Academy of orthopedic surgeons. p.84-86, 93-94, 244-245, 273-274
- Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
Emergency care, Harvey grant, and Robert Murray
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
Manual of Emergency Care 응급환자관리 정담미디어
소아가정간호백과-부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원 저
The pregnancy Bible. By Joan stone, MD. Keith Eddleman, MD
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
임신에서 신생아 돌보기까지. 이상원
Breastfeeding. by Ruth Lawrence and Robert Lawrence
The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 18th edition
Red book 29th -31st edition 2021
Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th-21st Edition
Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
Growth and Development of Children, George H. Lowrey 8th edition
소아과학 대한교과서
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
Nelson textbook, 14 edition, p.225, 1069-1071. and 19th ed.
www.drleepediatrics.com –제1권. 소아청소년 응급의료
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”