기도 내 이물 (1), Foreign bodies in the airways
기도 내 이물의 개요
-
비강, 인두 강, 후두, 기관, 기관지 등을 통틀어 기도라 하고, 기도 속에 들어간 이물을 기도 속 이물 또는 기도 내 이물이라 한다.
-
기도는 후두를 중심으로 해 후두의 상 부분 기도를 상기도라고 하고 후두의 하 부분의 기도를 하기도라고 한다.
-
기도 속 이물(기도 내 이물)의 70∼80%는 4세 이전 영유아들에게 생긴다고 한다.
-
기도 속으로 들어간 이물로 기도의 일부분이 완전히 막히든지, 또는 기도의 일부가 불완전하게 막힐 수도 있다.
-
인두나 인두 이하에 있는 기도의 일부분이 기도 속 이물로 완전히 막히면 숨을 제대로 쉬지 못한다. 이때 이물을 곧 제거해주지 않으면 사망한다.
| 기도 내 이물로 질식 상태로 빠지는 장면을 목격했던 사람이 기도 내 이물을 제거할 수 있는 기도 내 이물 응급 처치 방법을 알고 또 필요에 따라 기본 심폐 소생술 처치법을 할 수 있었으면 기도 속 이물로 죽을 뻔했던 소아청소년들의 생명을 많이 구출 할 수 있었을 것이다. 이런저런 이유로 부모들은 물론 누구도 기도 속 이물 제거 처치법을 평소 배워야한다.. 특히 소아청소년과 의사들은 소아청소년들의 부모들에게 기도 내 이물 제거 처치법을 교육 시킬 의무를 갖도록 국가정책을 정했으면 좋겠다. 소아청소년이 기도 내 이물로 식물인간이 되지 않게 또 사망하지 않도록 기도 내 이물 제거 처치법을 정기 소아 건강 검진을 받을 때 단골 소아청소년과에서 부모들에게 교시키면 좋겠다. 아울러 자녀의 생명을 구할 수 있는 기도 속 이물 응급 제거 처치법과 기본 심폐 소생술 처치 법을 부모들에게 교육시키는 교육비는 국가에서 당연히 지불해야 한다고 생각 한다. |
출처 및 참조문헌
-
호흡곤란,
-
기본 심폐 소생술(기본 인공호흡과 심장 마사지) 참조.
기도 내 이물의 역학과 원인
-
기도의 크기는 나이에 따라 차이난다. 나이가 어릴수록 더 작다.
-
어린 영유아들의 기도는 이물로 쉽게 막힐 수 있다.
-
미국에서는 연간 1천명의 소아들이 질식, 교액, 또는 초킹(질식)으로 사망한다.
-
그 중 637명은 1세 이하 영아들이었고, 148명은 1~4세 유아들이었다.
-
견과류, 씨앗, 땅콩, 포도 알, 견고한 캔디, 핫도그, 요리하지 않은 당근 조각, 레이진, 팝콘 등의 음식물, 채소나 과일 등이 소아들의 기도 속으로 흡입되어 기도 속을 폐쇄시킬 수 있다.
-
그 외 플라스틱 장난감, 또는 쇠붙이로 만든 장난감 등을 입안에 물고 놀다가 그것이 기도 속으로 흡인될 수 있다.
-
음식물도 장난감도 아니지만, 플라스틱 백으로 질식될 수 있고,
-
차 트렁크 속, 장난감 장롱 속, 세탁기 속, 또는 협소한 장소에 들어가 놀다가 질식 사망할 수 있다.
-
영유아들의 기도 속 이물의 대부분의 직경은 32mm 보다 더 작고 둥글둥글하다.
-
기도 내 이물은 영아들이나 생후 48개월 이전 유아들에게 더 잘 생길 수 있지만 1~2세 유아들에게 가장 많이 생긴다.
-
영아들의 질식의 60%는 잠자리에서 생긴다.
-
이물이 기도 속으로 흡인되어 인두 강 속, 후두 부분 기도 속으로 들어가는 찰나에 그 이물이 더 아래에 있는 기도 속으로 더 이상 들어가지 않게 자연 반사작용이 생긴다.
-
채기 하고, 기침 하고, 때로는 구토해 기도 내로 이물이 들어가지 않게 하는 자연반사가 생긴다.
-
모든 건강한 아이들, 성인들은 정상적으로 이런 이물 흡인 방어 자연반사–기침, 구토, 재채기 등을 가지고 있다.
-
음식물이나 장난감 등이 잘못해서 구강 속과 인두 강에서 후두 부분 기도 속으로 또는 그 아래속에 있는 후두 부분 기도 이하 기관 속으로 흡입되지 않게 기침, 재채기, 구토가 생겨 음식물 등 이물이 후두 부분 기도나 후두 부분 기도 이하에 있는 기관 속으로 더 이상 들어가지 않게 된다.
-
구슬, 안전핀, 못, 동전, 압핀, 귀걸이, 머리핀, 금속 장난감, 플라스틱 장난감, 고무풍선, 바늘, 사탕, 땅콩, 과자, 고기 덩어리, 떡, 빵 등이 잘못해서 영유아들의 입안에서 후두 부분 기도 또는 후두 부분 기도 이하 속에 있는 기관이나 기관지 속으로 흡인되면 기도의 일부가 완전히 막히거나 불완전하게 막힐 수 있다.
-
기도 내 이물의 크기, 모양, 기도 내 이물이 있는 기도의 부위에 따라 기도 내 이물이 구형판, 역행 방지판, 바이패스 판, 또는 정지판 역할을 한다.
-
그로 인해서 기도 내 이물의 증상 징후가 다르게 나타날 수 있다.
기도 내 이물의 증상 징후
-
기도 내 이물은 다음 항에 따라 증상 징후가 다르다.
-
기도 내 이물이 급성 또는 만성으로 생겼느냐에 따라.
-
인두, 후두, 기관, 기관지 등의 상하기도 중 어느 부분 기도 속에 이물이 있는지
-
기도 내 이물로 기도의 일부가 불완전하게 막혀 있는지 또는 완전하게 막혀 있는지
-
기도 내 이물로 기도가 자극될 수 있는지
-
기도 내 이물의 성분이 무엇인지
-
환아의 나이
-
기도 내 이물이 얼마나 오랫동안 기도 내 있었는지
-
기도 내 이물로 생긴 합병증의 유무와 합병증의 정도
-
기도 내 이물이 기도 내에서 구형판, 역행 방지판, 바이패스 판, 또는 정지판 역할 중 어떤 역할을 하느냐에 따라
-
작은 인두강 내 이물이 후두 부분 기도 속으로 흡인되어 그로 인해 후두 부분 기도가 완전히 막히지 않고 일부만 막혔을 때는 사례 들리고, 기침하고, 구토 등의 증상 징후가 생기는 것이 보통이다.
-
땅콩이나 장난감 등의 이물이 인두 강, 후두 또는 기관 속으로 흡입 될 때는 인두 강 부분 기도나 후두 부분 기도, 또는 기관 부분 기도 속이 완전하게 막히는 경우보다 불완전하게 막히는 경우가 흔하다.
-
인두강 부분 기도 속이나 후두 부분 기도 속, 또는 기관 부분 기도 속이 이물로 불완전하게 막힐 때 적절히 치료하면 질식 사망하는 경우는 드물다.
-
이물이 후두 부분 기도 속이나 기관 부분 기도 속으로 들어가 기도가 갑자기 완전히 막히면 갑자기 호흡곤란이 심하고 새파랗게 질리고 무호흡증이 생기고 천명이 나거나 협착음이 나고, 기침, 숨 가쁨 등의 증상 징후가 생긴다. 출혈 반점이 얼굴에 생길 수 있고 생명이 위험할 수 있다.
-
이물이 후두 부분 기도 속을 지나 기관 부분 기도 속이나 기관지 부분 기도 속으로 들어갈 때 사례 들고, 기침 하는 등의 증상 징후가 갑자기 생겼다가 그 후 며칠 내지 몇 달 동안 아무런 증상 징후가 없다가 그 이물로 기도가 자극받거나 합병증이 생겨 그로 인해 증상 징후가 생겨 기도 내 이물이 있다는 것을 뒤 늦게 진단받을 수 있다.
-
후두 부분 기도 속 이물로 후두 부분 기도 속이 부분적으로 막히는 경우는 드물다. 그러나 후두 부분 기도 속이 부분적으로 막히면 숨이 몹시 가쁘고 목이 쉬고 말을 잘 못하고 기침하는 것이 보통이다.
-
후두 부분 이물로 후두 부분 기도 속이 완전히 막히면 숨을 쉬지 못하고 기침도 말도 전혀 못하고, 갑자기 질식되면서 손으로 턱을 받치는 등의 증상 징후가 갑자기 생길 수 있다.
-
이때 후두 부분 기도 속과 기관 부분 기도 내 있는 이물을 적절히 응급으로 제거해서 기관 내 이물이 구강을 통과해 입 밖으로 꺼내주지 않으면 불과 1∼3분 내에 질식되고 쇼크에 빠져 죽는다.
-
이물이 기관 부분 기도 속이나 기관지 부분 기도 속으로 흡인되어 기관 부분 기도 속이나 기관지 부분 기도 속 일부가 불완전하게 막힐 때는 쌕쌕거리는 호기성 천명, 또는 흡기성 협착음, 그렁그렁하는 호기성 천명, 흡기성 협착음이 날 수 있고 숨을 가쁘게 쉬는 것이 보통이다. 그리고 이물이 들어 있는 기관이나 기관지에 심한 염증이 생길 수 있다.
-
기관 부분 기도 속이나 기관지 부분 기도 속으로 흡인된 안전핀, 바늘, 못이나 머리핀 등의 이물로 기관 벽이나 기관지 벽이 뚫릴 수도 있고 이물이 들어있는 부분 기도에 염증이 생길 수 있다.
-
기관 내 이물이나 기관지 내 이물이 있는 위치에 따라, 또 이물이 구형판, 역행 방지판, 바이패스 판, 정지판 역할 중 어떤 역할을 하는 이물이냐에 따라 폐기종. 무기폐 등 합병증이 생길 수 있다. 때로는 폐렴도 생길 수 있다. 그에 따라 기도 내 이물의 증상 징후가 다르게 나타날 수 있다.
기도 내 이물의 진단
-
이물이 인두 부분 기도 속, 후두 부분 기도 속, 그 이하에 있는 기관 부분 기도 속, 기관지 부분 기도 속에 들어가서 기도 속이 완전히 폐쇄될 때는 불과 2~3분 이내에 질식 사망할 수 있다.
-
이물이 기도의 각 부분 중 어느 부분에 있는지, 기도 속을 완전히 차단했는지, 또는 불완전하게 차단했는지 등에 따라 기도 내 이물의 증상 징후, 진단 치료가 다르다.
-
기도 속으로 이물이 들어가 이물로 기도 속의 일부분이 불완전하게 차단되든지, 완전하게 차단되는 것을 목격할 때는 기도 속 이물이 있다는 것을 쉽게 진단할 수 있다.
-
이물로 기도 속의 일부가 불완전하게 막혔으나 이물이 기도 속을 흡입되는 것을 목격하지 안 했을 때는 병력, 증상 징후, 진찰소견 등을 종합해 기도 내 이물이 있다고 의심하면 목 X선 사진, 가슴 X선 사진, 후두 내시경, 기관 내시경 검사로 진단할 수 있다.
-
이런 저런 이유로 기도가 이물로 완전히, 또는 불완전하게 막힐 때 생길 수 있는 기도 이물의 증상 징후, 진단과 기도 내 이물 제거 응급 처치법을 학교 보건 건강교육 시간이나 평소 건강 교육 과정, 또는 다른 프로그램 등을 통해 배우고, 그 후 기도 내 이물 제거 응급 처치법을
-
반복으로 연수해서 잘 익혔다가 필요할 때 이용한다.
- 참고로, 미 소아청소년과 학회는 부모들에게 기도 속 이물로 기도가 막힐 때 기도 내 이물 제거 응급 처치법과 기본 심폐 소생술을 교육시키기 위해 포스터를 만들어 팔고 있다.
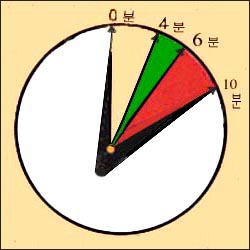
▴ 그림 59 두 강이나 후두, 또는 기관 등의 기도가 이물로 갑자기 완전히 막히면 숨을 전혀 쉴 수 없고 그로 인해 급성 산소 결핍증이 생겨 뇌 손상이 생길 수 있다. 불과 1∼3분 내 질식될 수 있고 쇼크에 빠져 죽을 수 있다. 이물로 막힌 기도를 열어 숨통이 통하게 해서 숨을 다시 쉬게 처치할 수 있는 시간은 극히 제한되어 있다. 기도가 막혀 숨을 쉬지 못하면 0~4분 이내에 뇌가 손상될 수 있고 4~6분이 지나면 뇌가 손상될 가능성이 많고 6~10분이 지나면 뇌가 아주 많이 손상되어 회복될 가능성이 거의 없다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
기도 내 이물 제거 응급처치
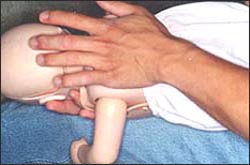
▴ 사진 1-218.
인두 부분 기도 내 이물이나 후두 부분 기도 내 이물, 또는 기관 부분 기도 내 이물로 숨통이 막혀 호흡이 정지되려고 할 때, 또는 호흡이 정지됐을 때 바로 다음과 같이 즉시 기도 내 이물 제거 응급처치를 시작 해야 한다.
1세 이전 영아들의 경우, 양쪽 견갑골 사이에 있는 등 부분을 손바닥으로 5번 정도 연달아 쳐서 기도 내 이물이 입안으로 나오게 하든지, 입 밖으로 나오게 응급처치를 한다. 그렇게 응급처치를 한 이후에도 인두 부분 기도나 후두 부분 기도 속에 있는 이물이 나오지 안 했을 때는 기도 내 이물 제거 앞가슴 밀기처치(사진120)를 5번 연달아 한다. 그래도 나오지 않으면 같은 처치 방법을 반복한다.
1세 이상 유아들이나 8세 이하의 학령기 소아들의 경우, 기도 내 이물 제거 심와부 손바닥 밀기 처치법(사진121)으로 5번 연달아 처치한다. 이 방법을 하임리크 처치법의 일종이다. 이 처치는 등을 바닥에 대고 누워 있는 자세에서도 할 수 있고 의식이 있으면 서 있는 자세에서 할 수 있다(그림122-4). 필요에 따라 이 처치법을 반복할 수 있다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
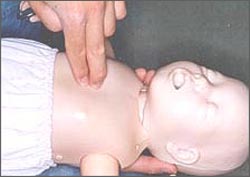
▴ 사진 1-219.
1 세 이전 영아의 기도 속에 있는 이물이 기도 내 이물 제거 등치기 처치법으로 처치해도 이물이 입 밖으로나 인두 강 속으로 나오지 않으면 사진과 같이 두 손가락으로 앞가슴을 미는 기도 내 이물 제거 응급처치를 한다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
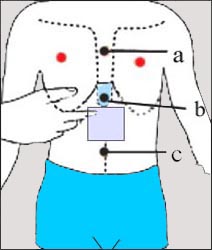
▴ 그림 1-220. 4. □ 으로 표시한 부분이 심와부(Epigastric region)다.
기도 속으로 이물이 들어갔을 때 기도 내 이물 제거를 하기 위해 심와부를 5번 밀어(하임리크 처치법) 응급 치료할 수 있다.
붉은 ●점으로 표시한 부위는 젖꼭지이다.
a-흉골, b-흉골 돌기, c-배꼽.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
기도 내에 이물이 들어가 있지만
|
-
인두 부분 기도 내, 후두 부분 기도 내 이물이나 후두 부분 기도 이하에 있는 기도 내에 이물이 들어가서 기도가 거의 완전히, 또는 완전히 막혔을 때는 사고 현장에서 기도 내 이물 제거 응급처치를 즉시 시작하고 그와 동시, 가능하면 주위 사람의 도움을 받아 응급 치료를 해야 한다.
-
의료구급대, 병원 응급실, 또는 단골 소아청소년과 의사에게 긴급 전화로 연락해서 그들의 지시에 따라 응급처치를 사고 현장에서 바로 시작한다.
-
이물로 기도 속이 완전히 막혀 숨을 쉴 수 없고, 호흡이 정지되고 심장이 멈췄을 때는 바로 1∼3 분 내에 숨을 쉬게 처치하고 심장이 뛰게 하고 심장 혈관 혈액 순환이 되게 해, 즉 심폐 소생술을 해서 신체 각 계통의 각 기관과 조직에 산소를 적절히 공급하지 않으면 뇌가 손상될 수 있다.
-
따라서 단골 소아청소년과 의사나 다른 사람의 도움을 청하거나 병원 응급실로 이송하기 전에 가장 효과적이고 가장 빠르고 적절한 기본 생명유지를 위한 기본 심폐 소생술 처치를 사고 현장에서 시작해야 한다. 다음은
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
Foreign bodies in the airways (1) 기도 내 이물 (1)
Overview of foreign bodies in airways
- The nasal cavity, pharyngeal cavity, larynx, trachea, and bronchi are collectively referred to as airways, and a foreign body in the airway is called a foreign body in the airway.
- The airway parts on the larynx and the upper part of the larynx is called the upper airway, and the lower part of the larynx is called the lower airway.
- It is said that 70-80% of foreign bodies in the airway (foreign bodies in the airway) occur in infants and young children before the age of 4 years.
- Part of the airway may be completely blocked by a foreign object entering the airway, or part of the airway may be incompletely blocked.
- If the pharynx or part of the airway below the pharynx is completely blocked by a foreign body in the airway, your child cannot breathe properly.
- At this time, if you do not remove the foreign body soon, your child will die.
- A child who almost died from a foreign body in the airway if the person who witnessed the scene of falling into a state of suffocation with a foreign body in the airway knew the first aid method for the foreign body in the airway that could remove the foreign body in the airway and could perform basic CPR treatment as needed.
- It would have saved a lot of youth’s lives.
- For these and other reasons, parents as well as anyone should learn how to remove foreign objects in the airways.
- In particular, it would be nice if pediatricians and doctors set a national policy to have the duty to educate parents of children and adolescents on how to remove foreign objects in the airways.
- In order to prevent children and adolescents from becoming vegetative by foreign bodies in the airways and to die, it would be good to teach parents how to remove foreign bodies in the airways when they receive regular pediatric health checkups.
- In addition, I believe that the government should pay the education fee to educate parents about the emergency removal treatment method and basic CPR treatment method that can save their children’s lives. Sources and references
- Difficulty breathing,
- Refer to basic cardiopulmonary resuscitation (basic artificial respiration and heart massage).
The dynamics and causes of foreign bodies in the airways
- The size of the airways varies with age.
- The younger you are, the smaller it is.
- The airway of young infants and young children can be easily blocked by foreign objects. In the United States, 1,000 children die annually from suffocation, grafting, or choking (suffocation).
- Among them, 637 were infants under the age of 1, and 148 were infants aged 1 to 4.
- Nuts, seeds, peanuts, grape eggs, hard candy, hot dogs, uncooked carrot slices, foods such as resin, popcorn, etc., and vegetables or fruits can be inhaled into children’s airways and block the airways.
- Other plastic toys, metal toys, etc., can be sucked into the airways while playing with them in their mouths.
- It is either food or toys, but it can be suffocated with plastic bags, In the trunk of a car, in a toy wardrobe, in a washing machine, or in a confined place, you may die from suffocation while playing.
- Most of the foreign bodies in the airways of infants and toddlers are smaller and rounder than 32mm.
- Foreign bodies in the airways may be more common in infants and infants before 48 months of age, but most often occur in children aged 1-2 years. 60% of infants’ suffocation occurs in bed.
- At the moment a foreign body is sucked into the airways and enters the pharyngeal cavity and the laryngeal part of the airways, a natural reflex occurs so that the foreign body no longer enters the lower airways.
- There is a natural reflex that prevents foreign objects from entering the airways by sneezing, coughing, and sometimes vomiting.
- All healthy children and adults normally have these foreign body aspiration defense natural reflexes-coughing, vomiting, sneezing, etc.
- Coughing, sneezing, vomiting, etc., so that food or toys are not inhaled from the oral cavity and pharyngeal cavity into the larynx portion of the airways or into the trachea below the trachea. It no longer enters the organs below the airways.
- Beads, safety pins, nails, coins, thumbtack pins, earrings, hairpins, metal toys, plastic toys, rubber balloons, needles, candy, peanuts, sweets, chunks of meat, rice cakes, bread, etc.
- When aspirated into the trachea or bronchi that lies below the partial airway, a portion of the airway may be completely or incompletely blocked.
- Depending on the size and shape of the foreign body in the airway, and the part of the airway where the foreign body is in the airway serves as a spherical plate, a retrograde prevention plate, a bypass plate, or a stop plate.
- As a result, symptoms of a foreign body in the airways may appear differently.
Symptoms, signs of a foreign body in the airways
- Foreign bodies in the airways have different symptoms according to the following clauses.
- Depending on whether a foreign body in the airway is acute or chronic.
- Which part of the upper respiratory tract of the pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, etc. is there a foreign body in the airway?
- Whether a part of the airway is incompletely blocked or completely blocked by a foreign object in the airway If a foreign body in the airway can stimulate the airway
- What is the composition of the foreign body in the airways?
- The age of the patient airway,
- How long my foreign body has been praying
- Presence of complications caused by foreign bodies in the airways and degree of complications
- Depending on whether the foreign object in the airway plays the role of a spherical plate, a retrograde plate, a bypass plate, or a stop plate in the airway
- When a foreign body in the small pharyngeal cavity is aspirated into the laryngeal part of the airway,
- it is common for symptoms such as coughing, vomiting, etc.
- when the laryngeal part of the airway is not completely blocked but only part of it is blocked.
- When foreign objects such as peanuts or toys are inhaled into the pharyngeal cavity, larynx, or trachea, it is more common to block the pharyngeal cavity, larynx, or trachea incompletely than when the inside of the trachea is completely blocked.
- When the pharyngeal cavity, laryngeal, or tracheal are incompletely blocked with a foreign body, it is rare to die asphyxia if appropriately treated.
- If a foreign body enters the laryngeal airway or the trachea part of the airway and the airway is suddenly completely blocked, symptoms such as severe breathing difficulties, apnea, wheezing or narrowing sound, coughing, shortness of breath, etc. may occur suddenly. Bleeding spots can occur on the face and can be life-threatening.
- When a foreign body passes through the laryngeal part of the airway and enters the trachea part of the airway or the broncho part of the airway, symptoms such as coughing, etc. suddenly appear, and there are no symptoms for several days to several months thereafter, and the airway with the foreign body.
- It may be irritated or complications, which can lead to symptoms. signs, which can lead to a late diagnosis of a foreign body in the airways.
- It is rare that the laryngeal part of the airway is partially blocked by a foreign body in the laryngeal part of the airway.
- However, when the airway in the laryngeal region is partially blocked, it is common to have shortness of breath, have a sore throat, cannot speak well, and a cough.
- If the laryngeal part of the airway is completely blocked by a foreign body in the larynx, you may not be able to breathe, cough, or speak at all, and symptoms such as sudden suffocation and chin support may occur suddenly.
- At this time, if the foreign body in the larynx and tracheal airways is properly removed in an emergency and the foreign body in the trachea passes through the oral cavity and is not taken out of the mouth, it will suffocate within 1 to 3 minutes and die in shock.
- When a foreign body is aspirated into the tracheal part of the airway or the tracheal part of the airway and the part of the tracheal part of the airway or the part of the bronchial part of the airway is incompletely blocked, wheezing aerobic wheezing, or inspiratory stenosis, sloppy aerobic wheezing, or respiratory tr narrowing.
- It is common to be able to see flaring alar nase and to take a short breath. In addition, severe inflammation may occur in the organs or bronchi containing foreign bodies.
- The tracheal wall or bronchial wall may be pierced with foreign objects such as safety pins, needles, nails or hairpins sucked into the trachea part airway or the trachea part airway, and the partial airway containing the foreign body may become inflamed.
- Emphysema depends on the location of the foreign body in the trachea or the foreign body in the bronchi and depending on whether the foreign body is a foreign body that plays the role of an old plate, a retrograde plate, a bypass plate, or a stop plate.
- Complications such as atelectasis may occur.
- Sometimes pneumonia can develop. As a result, symptoms of a foreign body in the airways may appear differently.
Diagnosis of foreign bodies in the airways
- When a foreign body enters the pharyngeal part of the airway, the larynx part of the airway, or the lower part of the trachea part of the airway, or the part of the bronchi part of the airway, and the airway is completely closed, suffocation may occur within only 2-3 minutes.
- Symptoms of a foreign body in the airway and diagnostic treatment differ depending on which part of each part of the airway is in the airway, whether the airway is completely blocked or incompletely blocked.
- When a foreign body enters the airway and a part of the airway is incompletely blocked with a foreign body, it is easy to diagnose that there is a foreign body in the airway.
- If a foreign body in the airway is partially blocked by a foreign body, but you have not observed that the foreign body is inhaled into the airway, combine your medical history, symptoms, and medical findings, and if you suspect that there is a foreign body in the airway, an X-ray picture of the neck and an X-ray of the chest ,
- Can be diagnosed with laryngeal endoscopy or institutional endoscopy.
- For these and other reasons, when the airway is completely or incompletely blocked with a foreign body, the symptoms and signs of the airway foreign body, diagnosis and first aid for removing foreign bodies in the airway are learned through school health and health education classes, regular health education courses, or other programs.,
- After that, take the first aid method to remove foreign objects in the airway. After training it repeatedly, cook it well, and use it when necessary.
- For reference, the American Academy of Pediatrics and Adolescents makes and sells posters to educate parents on how to remove foreign bodies in the airways and basic cardiopulmonary resuscitation when airways are blocked by foreign bodies in the airways.

▴ Figure 59. If the airways such as the pharyngeal cavity, larynx, or trachea are suddenly completely blocked with a foreign object, your child cannot breathe at all, resulting in acute oxygen deficiency, which can lead to brain damage.
You can suffocate in just 1-3 minutes and die in shock. The amount of time that a foreign body can open an airway clogged with a foreign body to breathe and breathe again is extremely limited.
If the airway is blocked and you cannot breathe, the brain may be damaged within 0 to 4 minutes, the brain is likely to be damaged after 4 to 6 minutes, and after 6 to 10 minutes, the brain is very damaged and there is little possibility of recovery. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
First aid to remove foreign objects in the airways

▴ Photo 1-218. When breathing is about to stop due to clogged breath due to a foreign body in the pharyngeal part of the airway, a foreign body in the larynx part, or a foreign body in the trachea part, or when breathing is stopped,
- you must immediately start removing the foreign body in the airways as follows.
- In the case of infants before the age of 1, first, strike the back part between the shoulder blades on both sides with the palm of the hand 5 times in a row so that foreign objects in the airways can come out of the mouth or out of the mouth.
- If the foreign body in the pharyngeal or laryngeal airway does not come out even after the first aid treatment, remove the foreign body in the airway, and carry out the chest push treatment (photo 120) five times in a row.
- If it still doesn’t come out, repeat the same treatment. Infants over the age of 1 or under the age of 8 are treated 5 times in a row with the method of pushing the palms of the proximal part of the airways to remove foreign objects in the airways (photo 121).
- This method is a kind of Heimlik treatment.
- This treatment can be done in a lying position with your back on the floor, or in a standing position if you are conscious (Fig. 122-4). If necessary, this treatment can be repeated. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

▴ Photo 1-219. If a foreign body in the airway of an infant before the age of 1 is treated with the method of removing foreign body in the airway if the foreign body does not come out of the mouth or into the pharyngeal cavity, take first aid to remove the foreign body in the airway by pushing the front chest with two fingers as shown in the picture. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

▴ Figure 1-220. The part marked with 4. □ is the Epigastric region.
- When a foreign body enters the airway, it can be pushed 5 times Epigastric region to remove the foreign body inside the airway (Heimlik treatment method).
- Emergency treatment can be performed.
- The area marked with a red dot is the nipple. a-sternum, b-sternal process, c-navel. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
- There is a foreign object in the airway and he can breathe almost normally,
- First-aid measures for foreign objects in the airways of a fully conscious child Breathing stops due to a foreign body in the airway
- First aid measures for foreign bodies in the airways of a child just before suffocation and death are completely different
- When a foreign body in the pharyngeal airway or in the laryngeal airway or in the airway below the laryngeal airway is almost completely or completely blocked, immediately start removing the foreign body in the airway at the site of the accident, and at the same time, if possible.
- Emergency treatment is required with the help of people around you.
- Call a medical paramedic, hospital emergency room, or regular pediatrician by emergency phone and follow their instructions to begin first aid at the accident site.
- When the airway is completely blocked with a foreign body and your child cannot breathe, and when breathing is stopped and the heart stops, treat it to breathe within 1 to 3 minutes, make the heartbeat, and cause cardiovascular blood circulation, i.e., perform cardiopulmonary resuscitation to prevent the body from breathing.
- The brain can be damaged if oxygen is not properly supplied to each organ and tissue in each system.
- Therefore, the most effective, fastest, and most appropriate basic CPR treatment for basic life maintenance should be initiated at the accident site before asking for help from a regular pediatrician or other person or transferring to a hospital emergency room.
Next
- The following will lead to the foreign object in the airway (2).
- Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- Emergency Pediatrics, A guide to ambulatory care, 5th ed Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen, p.548
- Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
- Emergency care, Harvey grant, and Robert Murray
- Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
- Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
- Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
- Manual of Emergency Care
- 소아가정간호백과-부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원 저
- The pregnancy Bible. By Joan stone, MD. Keith Eddleman, MD
- Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- 임신에서 신생아 돌보기까지. 이상원
- Breastfeeding. by Ruth Lawrence and Robert Lawrence
- Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics 14th ed. Beherman,
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 18th edition
- Red book 29th-31st Ed 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th-21st Edition
- Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
- Growth and Development of Children, George H. Lowrey 8th edition
- 소아과학 대한교과서
- 제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
- Other
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”