급성 후두개염으로 생긴 크루프 Croup caused by acute epiglottitis
| 급성 후두개염으로 생긴 크루프의 원인 |
- B형 헤모필러스 인플루엔자균([부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다-소아가정간호백과]-제7권 소아 청소년 감염병-B형 헤모필러스 인플루엔자균(히비 균/Hib bacteria) 감염에 의한 질병 참조) 이란 박테리아가 이 병을 주로 일으킨다.
- 드물게 폐렴연쇄상구균이나 A군 베타 용혈성 연쇄상구균이 후두에 감염되어 급성 박테리아 감염성 후두개염이 생기고 그로 인해 크루프가 생길 수 있다.
- 편의상 여기서 B형 헤모필러스 인플루엔자균을 B형 인플루엔자균(히비균/Hib bacteria)이라 칭한다.
- B형 인플루엔자균이 후두개에 감염되어 생긴 급성 후두개염을 급성 히비 박테리아 후두개염이라고 한다. 또는 그냥 급성 박테리아 후두개염이라고도 한다.
- 급성 박테리아 후두개염으로 인해 급성 크루프가 생긴다.
- B형 인플루엔자균이 후두개에도 감염되고 후두개의 바로 위에 연결되어 있는 인두, 후두개가 붙어 있는 후두 전체, 후두의 아래에 연결되어 있는 기관에까지 감염될 수 있다.
- 후두와 후두 부분 상하에 있는 기도까지 감염병이 급성으로 퍼질 수 있다.
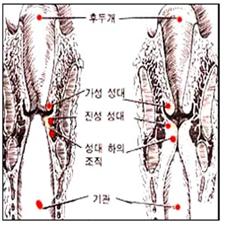
그림 89. 그림 좌-정상 후두.
그림 우-급성 박테리아 감염성 후두개염으로 후두가 부었다. 급성 박테리아 감염성 후두개염으로 호흡 곤란이 생기고 침을 흘리는 증상이 생길 수 있다. 출처: 부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다와 Used with permission from Infectious diseases of children,8th edition.The C.V Mosby Co. Saul Krugman, Samul L Katz and others
| 급성 후두개염으로 생긴 크루프의 증상 징후 |
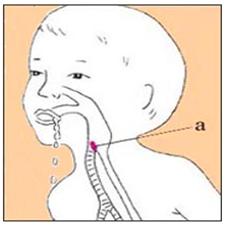
그림 90. 급성 박테리아 후두개염이 있을 때 호흡곤란.
빨간색으로 표시된 부분(a)은 후두개이고 거기에 생긴 박테리아 감염을 급성 박테리아 후두개염이라고 한다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
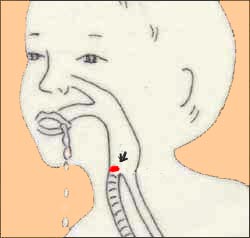
그림91.동반 질환이 없이 급성 박테리아 후두개염이 갑자기 생길 수도 있지만, 감기나 바이러스 인두염, 또는 다른 종류의 바이러스 상기도염을 3~4일 동안 앓다가 갑자기 급성 박테리아 후두개염이 발병될 때도 있다.
출처-Copyrightⓒ 2001 John Sangwon Lee,MD., FAAP
- B형 인플루엔자균 감염으로 생긴 급성 박테리아 후두개염에 의한 크루프의 증상 징후는 바이러스 감염으로 생긴 급성 후두염의 크루프의 증상 징후에 비해 훨씬 더 심하다.
- 이 병이 발병되면 환아는 독성 상태에 빠질 수 있다.
- 급성 박테리아 후두개염에 걸리면 생명이 위험하다.
- 삽시간에 호흡곤란이 아주 심하게 생기면서 침을 삼키지도 못해 흘린다.
- 금방 숨이 넘어갈 듯 호흡곤란이 생기면서 금방 죽을 것같이 심히 앓는 것이 보통이다.
- 그림 91에서 화살표로 표시된 부분이 후두개이다.
- 이 병이 시작된 후 불과 몇 분 내지 몇 시간 이내 갑자기 목안이 몹시 아프면서 심하게 목이 쉰다.
- 39~40℃ 정도 고열이 나고 심한 호흡곤란이 생긴다.
- 의사나 간호사가 아닌 부모나 보통 사람들이 환아를 보아도 죽을병을 심히 앓고 있다는 것을 쉽게 짐작할 수 있을 정도로 심하게 앓는다.
- 초기에는 후두개에만 화농성 염증이 생길 수 있지만 삽시간에 인두, 후두, 기관, 후두개 주위에 있는 조직까지 화농성 감염병이 번지고 후두 전체와 후두개가 부어서 그 후두 부분의 기도 속이 점점 더 좁아지면서 호흡곤란도 점점 더 심해진다.
- 이 때 숨을 제대로 쉴 수 없기 때문에 안절부절못하면서 목을 앞으로 쑥 빼고 혀를 입 밖으로 내밀고 침을 질질 흘릴 수 있다.
- 이런 상태가 짧은 시간동안 점점 더 해지면서 얼굴이 창백해지고 피부가 파랗게 질릴 수 있다.
- 이 때 목안 어디가 아픈가를 알아보기 위해 입을 벌리고 목안을 살펴 볼때 부었던 후두개가 갑자기 후두 부분 기도를 꼭 막아 질식 사망할 수 있다.
- 숨을 들이 마시고 쉴 때 흡기 협착음이 생기고, 앞가슴의 늑골 사이에 있는 늑골 근육들이 흉강 속으로 빨려들어 갔다 나왔다 할 수 있다.
- 급성 후두개염을 일으킨 B형 헤모필러스 인푸루엔자균이 후두개염과 패혈증을 동시 함께 일으킬 수도 있다.
급성 후두개염으로 생긴 크루프의 진단 치료
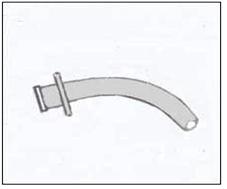
그림 92. 기관 절개 개구 삽입관(Cannula 캐뉼라).
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
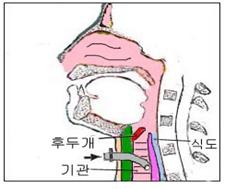
그림93.기관 절개 개구 삽입관이 기관 속에 삽입되어 있다
a-식도, b-기관, c-후두개
화살표로 가리킨 삽입관을 통해 숨 쉬는 대로 산소나 공기가 기도 속으로 들어가고 나온다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
- 앞서 설명한 증상 징후가 나타나면서 급성 크루프가 시작되면 바로 119 의료구급대나 병원 응급실이나 단골 소아청소년과 의사의 지시에 따라 구급차나 다른 적절한 교통수단을 이용해 가까운 종합 병원 응급실로 급히 데리고 가야 한다.
- [부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다-소아가정간호백과]-제1권 소아청소년 응급의료-호흡 곤란 참조
- 병력, 증상 징후, 진찰소견 등을 종합해서 이 병이 있다고 의심되면 목과 가슴 X-선 사진·목과 인두 후두 기관 초음파 검사, 피검사, 세균배양검사 등으로 비교적 쉽게 진단할 수 있다.
- 심할 때는 목과 가슴 X-선 사진을 찍어 확진 할 여유도 없다.
- 또 이 병에 걸린 환아를 병원으로 데리고 가는 도중에 목안을 들여다보고 진찰 하는 중 곪고 부은 후두개가 후두 부분 기도를 갑자기 꼭 막아서 질식 사망할 수 있다.
- 따라서 이 병이 있다고 의심되면 언제든지 기관내관 삽입치료를 즉시 응급으로 할 수 있고, 기관 절개수술 응급치료를 응급으로 즉시 할 수 있는 종합 병원 수술실의 수술대 위에서 진찰 진단 치료를 하는 것이 이 병의 진단 치료의 원칙이다.
- 수술실에서 후두경을 통해 육안으로 후두를 직접 들여다보고 진단하면서 필요에 따라 기관 절개 개구 수술로 만든 인공 기도를 통해 숨을 쉬게 치료해 주든지,
- 기관 내 삽입 관을 통해 숨을 쉬게 해서 치료한다.
- 나이, 중증도, 합병증의 유무에 따라 이 병을 달리 치료할 수 있다.
- 포도당 전해질용액 정맥주사로 탈수를 예방 치료한다.
- 세포택심(Cefotaxime), 세프트리액손(Ceftriaxone), 또는 클로램페니콜과 앰피실린이나 그밖에 다른 적절한 항생제 중 한두 가지 항생제를 선택해 정맥주사로 치료 한다.
- 기관 내 삽입 관 튜브 치료를 할 때는 치료 결과에 따라 적절한 시기에 기관 내 삽입 관을 빼내고 정상 상하 기도를 통해 호흡하게 한다.
- 기관 절개수술과 기관 내 삽입 관을 통해서 임시로 숨을 쉬게 하면서 치료할 때는 그 기관 내 삽입 관 숨구멍을 통해서 수증기와 산소를 공급한다.
- 이렇게 3~4일 정도 적극적으로 치료하면 급성 후두개염의 대부분은 잘 낫는다.
- 후두개염이 다 나은 후에는 기관 절개수술과 기관 내 삽입 관 숨구멍을 다시 수술로 막아준다. 적어도 10일 정도는 적절한 항생제로 치료한다.
- 요즘 디프테리아로 인한 크루프는 거의 볼 수 없는 감염병이 됐고, B형 인플루엔자균 감염에 의한 후두개염으로 인한 크루프도 보기 드문 감염병이다.
- B형 인플루엔자균 감염에 의한 감염병을 예방할 수 있는 예방접종 백신으로 접종을 적절히 잘 하면 이 병에 거의 걸리지 않는다. [부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다-소아가정간호백과]-제7권 소아청소년 감염병-B형 헤모필러스 인플루엔자균에 의한 감염병의 예방 참조
Croup caused by acute epiglottitis급성 후두개염으로 생긴 크루프
Causes of croup from acute epiglottis
• Haemophilus influenzae type B www.drleepediatrics.com-Volume 7 Child and Adolescent Infectious Diseases-Refer to Diseases caused by Haemophilus influenzae type B (Hib bacteria) infection) mainly cause this disease.
• Rarely, streptococci pneumonia or group A beta hemolytic streptococcus can infect the larynx, resulting in acute bacterial infectious epiglottis, resulting in croup.
• For convenience, Haemophilus influenzae type B is referred to as influenzae type B (Hib bacteria).
• Acute epiglottis caused by infection of the epiglottis with influenza B bacteria is called acute Hibibacterial epiglottis. Or just called acute bacterial epiglottis. • Acute bacterial epiglottis causes acute croup.
• Influenza B can also infect the epiglottis and can infect the pharynx directly above the epiglottis, the entire larynx where the epiglottis is attached, and even the organs connected below the larynx.
• Infectious diseases can spread acutely to the larynx and airways above and below the larynx.

Fig. 89. Fig. Left-normal larynx. Figure U-acute bacterial infectious epiglottis swollen larynx. Acute bacterial infectious epiglottis infection can cause shortness of breath and drool. Source: Parents should also be anti-doctors and Used with permission from Infectious diseases of children, 8th edition.The C.V Mosby Co. Saul Krugman, Samul L Katz and others
Symptoms of Croup from Acute Epiglottis

Figure 90. Difficulty breathing with acute bacterial epiglottis.
The area marked in red (a) is the epiglottis, and the bacterial infection in it is called acute bacterial epiglottis. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Figure 91: Acute bacterial epiglottis may develop suddenly without comorbid disease, but sometimes acute bacterial epiglottis develops suddenly after a cold, viral pharyngitis, or other type of viral upper respiratory tract infection for 3 to 4 days. Source-Copyright© 2001 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
• Symptoms of Croup caused by acute bacterial epiglottis caused by influenza B infection are much more severe than those of Croup in acute laryngitis caused by viral infection.
• When the disease develops, the child may become toxic.
• Acute bacterial epiglottis infection is life-threatening. • Difficulty breathing occurs very quickly, and she can’t swallow and shed.
• It is common for people to suffer severely as if they are going to be out of breath and have difficulty breathing and will die soon.
• In Figure 91, the area indicated by the arrow is the epiglottis.
• Within just a few minutes to a few hours after the onset of the disease, my throat suddenly hurts and sore throat.
• I have a high fever about 39~40℃ and have severe breathing difficulties.
• Parents and ordinary people who are not doctors or nurses are so sick that it is easy to guess that they are seriously ill even when they see a child.
• Initially, purulent inflammation may only develop in the epiglottis, but in a short time, purulent infections spread to the pharynx, larynx, trachea, and tissues around the epiglottis. It gets worse.
• Since you cannot breathe properly at this time, you may feel restless, pull your throat forward, stick your tongue out of your mouth, and drool.
• As this condition worsens over a short period of time, the face may become pale and the skin may become blue.
• At this time, the swollen epiglottis may suddenly block the airways of the occipital region when opening his mouth to find out where the pain is in the throat, and suffocating death may occur.
• When inhaling and breathing, an inspiratory stricture is produced, and the rib muscles between the ribs of the anterior chest may be sucked into and out of the chest cavity. • Haemophilus influenzae type B, which causes acute epiglottis, may cause epiglottis and sepsis at the same time.
Diagnosis and treatment of croup caused by acute epiglottis

Figure 92. Tracheostomy opening cannula (Cannula cannula). Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Figure 93: Tracheostomy Aperture Insertion tube inserted into the trachea a-esophagus, b-trachea, c-epiglottis As you breathe through the cannula indicated by the arrow, oxygen or air enters and exits the airways. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
• If an acute croup begins with the symptoms of the above-described symptoms, you should immediately take it to the nearest general hospital emergency room using an ambulance or other appropriate means of transportation, as directed by 119 medical paramedics or hospital emergency departments or as directed by your regular pediatrician. • www./drleepediatrics.com-Volume 1 Children and Adolescent Emergency Medical Services-Refer to Difficulty Breathing
• If you suspect that you have this disease by combining your medical history, symptoms, symptoms, and examination findings, you can diagnose it relatively easily by using neck and chest X-rays, ultrasound of the neck and pharyngeal and laryngeal organs, blood tests, and bacterial culture tests.
• In severe cases, there is no room for confirmation by taking an X-ray of the neck and chest.
• In addition, while taking a patient with this disease to the hospital, a festering and swollen epiglottis may suddenly block the airway in the larynx, which may cause suffocation and death during the examination.
• Therefore, if you suspect that you have this disease, endotracheal tube implantation treatment can be performed immediately as an emergency at any time, and diagnosis treatment of this disease is performed on the operating table of the operating room of a general hospital where emergency treatment for tracheostomy can be performed immediately. Is the principle of.
• In the operating room, through a laryngoscope, visually inspect the larynx with the naked eye and diagnose it, and if necessary, treat it to breathe through an artificial airway made by tracheostomy opening surgery,
• Treat by breathing through an endotracheal tube.
• The disease can be treated differently depending on the age, severity, and the presence or absence of complications.
• Prevent and treat dehydration by intravenous injection of glucose electrolyte solution.
• Treat intravenously with one or two antibiotics from Cefotaxime, Ceftriaxone, or chloramphenicol and ampicillin or other appropriate antibiotics.
• When performing endotracheal tube treatment, the endotracheal tube is removed at an appropriate time according to the treatment result and breathed through the normal upper and lower airways.
• When treating with tracheostomy and temporary breathing through an endotracheal tube, water vapor and oxygen are supplied through the pores of the endotracheal tube.
• Most of the acute epiglottis is well healed by aggressive treatment for 3 to 4 days.
• After the epiglottis is cleared, the tracheostomy and the endotracheal tube pore are closed again with surgery. Treat with appropriate antibiotics for at least 10 days.
• Nowadays, croup caused by diphtheria has become an infectious disease that is rarely seen, and croup caused by epiglottis caused by influenza B infection is also a rare infectious disease.
• It is a vaccination vaccine that can prevent infectious diseases caused by influenza B infection.
If the vaccine is properly administered, the disease rarely occurs.www.drleepediatrics.com-Volume 7 Child and Adolescent Infectious Diseases-See Prevention of Infectious Diseases Caused by Haemophilus Influenza B
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
-
www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
-
www.drleepediatrics.com제8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환
-
Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th — 21st Edition
-
The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
-
Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, Harvey grant and Robert Murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
-
The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
-
Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care
-
응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
-
Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
-
Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
-
Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
-
소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”