급성 췌장염 Acute pancreatitis
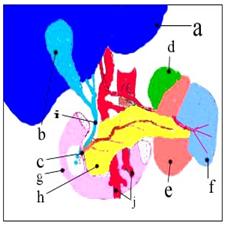
그림 263. 간과 그 부위의 해부도.
a-간, b-담낭, c-십이지장 유두(담즙과 췌장액이 분비되는 출구), d-좌 부신, e-좌 신장, f-지라, g-십이지장관, h-췌장, i-총수담관, j-혈관.
Copyright Ⓒ 2013 John Sangwon Lee,MD., FAAP
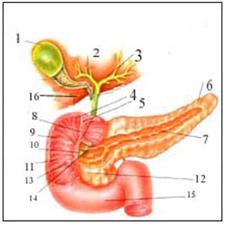
그림 264. 간, 담낭, 담도, 췌장, 십이지장.
1-담낭, 2-우 간 담도, 3-좌 간 담도, 4-십이지장, 5-유문괄약근, 6-췌장의 미부, 7-췌장 관, 8-유문, 9-십이지장, 10-총수 담관, 11-십이지장관, 12-췌장의 두부, 13-십이지장 유두, 14-췌장 관, 15-십이지장, 16-간 출처-소아가정간호백과와 Used with permission from Galaxo Wellcome
급성 췌장염의 원인
- 췌장에 급성으로 생긴 염증을 급성 췌장염이라 하고 만성으로 생긴 췌장염을 만성 췌장염이라고 한다.
- 유행성 이하선염 바이러스, A형 간염 바이러스, B형 콕삭키바이러스 또는 그 이외 바이러스 감염으로 생긴 췌장 감염병으로 급성 췌장염이 생길 수 있다.
- 아세토아미노펜(Acetaminophen), 코르티코스테로이드제, 에스트로겐 등의 약물에 의해서도 급성 췌장염이 생길 수 있다.
- 회충, 종양, 또는 크론스병 등에 의해서도 급성 췌장염이 생길 수 있다.
- 자가면역 질환, 가와사키 병, 또는 당뇨병 등에 의해서도 급성 췌장염이 생길 수 있다.
- 복부 외상, 소아 학대, 또는 복부수술 등에 의해서 급성 췌장염이 생길 수 있다.
급성 췌장염의 증상 징후
- 원인에 따라 증상 징후가 다양하다.
- 일반적으로 복통, 구기, 설사, 쇼크, 지속적인 구토, 열, 신경과민 등의 증상 징후가 생길 수 있다.
급성 췌장염의 진단
- 병력, 진찰소견 등을 참작해서 급성 췌장염이 의심되면 혈청과 소변에서 아밀레이스(아밀라제), 혈청 리파제(Lipase) 등 췌장 효소 혈중 농도를 측정해서 진단한다.
- 복부 X-선 검사, 초음파 검사, CT 스캔 검사 등으로 진단한다.
- 그레이 터너 징후(Grey Turner sign)나 쿨렌 징후(Cullen sign) 등이 있으면 진단 상 도움이 된다.
- 발사자 스코아 검사(Balthazar scoring)를 이용해서 진단하는 방법도 있다.
급성 췌장염의 치료
- 원인에 따라 치료하고 복통은 메페리딘(Meperidine )등 강력한 진통제로 치료하고 포도당 전해질용액 정맥주사로 치료하면서 비 위관을 통해서 위액을 빼준다.
- 원인에 따라 수술로 치료한다.
Acute pancreatitis 급성 췌장염

Figure 263. Anatomical view of the liver and its parts. a-liver, b-gallbladder, c-duodenal papilla (exit from which bile and pancreatic juice are secreted), d-left adrenal gland, e-left kidney, f-spinal, g-duodenal duct, h-pancreas, i-common bile duct, j-blood vessels. Copyright Ⓒ 2013 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Figure 264. Liver, gallbladder, biliary tract, pancreas, duodenum. 1-gallbladder, 2-right hepatic biliary tract, 3-left hepatic biliary tract, 4-duodenum, 5-pyloric sphincter, 6-pancreatic tail, 7-pancreatic duct, 8-pylorus, 9-duodenum, 10-common bile duct, 11 -Duodenal duct, 12-pancreatic head, 13-duodenal papilla, 14-pancreatic duct, 15-duodenum, 16-liver source-Used with permission from Galaxo Wellcome
Causes of acute pancreatitis
• Acute inflammation of the pancreas is called acute pancreatitis, and chronic pancreatitis is called chronic pancreatitis.
• Acute pancreatitis can result from pancreatic infections caused by mumps virus, hepatitis A virus, coxsackie B virus, or other viral infections.
• Acute pancreatitis can also be caused by drugs such as acetoaminophen, corticosteroids, and estrogen.
• Acute pancreatitis can also be caused by roundworms, tumors, or Crohn’s disease.
• Acute pancreatitis can also be caused by autoimmune diseases, Kawasaki disease, or diabetes.
• Acute pancreatitis may occur due to abdominal trauma, pediatric abuse, or abdominal surgery.
Symptoms signs of acute pancreatitis
• Symptoms and signs vary depending on the cause.
• Symptoms may include abdominal pain, goji, diarrhea, shock, persistent vomiting, fever, and nervousness.
Diagnosis of acute pancreatitis
• If acute pancreatitis is suspected, taking into account the medical history and medical findings, the blood levels of pancreatic enzymes such as amylase (amylase) and serum lipase are measured and diagnosed in serum and urine
• Diagnosis is performed by abdominal X-ray examination, ultrasound examination, and CT scan examination.
• A Gray Turner sign or Cullen sign is helpful in diagnosis.
• There is also a method of diagnosis using Balthazar scoring.
Treatment of acute pancreatitis
• Depending on the cause, stomach pain is treated with strong pain relievers such as Meperidine, and the gastric juice is drained through a nasal gastric tube while treating with a glucose electrolyte solution intravenously.
• Depending on the cause, it is treated with surgery.
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
-
Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, Harvey grant, and Robert Murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
-
The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
-
Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care
-
응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
-
Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
-
Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
-
Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
-
Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics 14th ed. Beherman,
-
The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 18th edition
-
Red book 29th edition 2012
-
Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th Edition
-
Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
-
소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”