급성 인두염 Acute pharyngitis
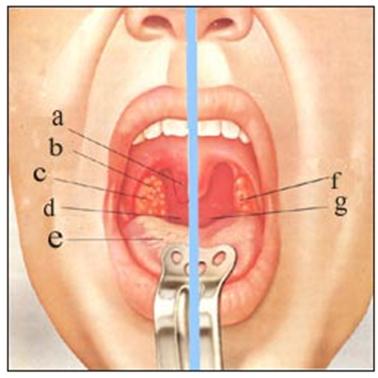
그림 28. 우–박테리아 급성 인두염(박테리아 급성 인두편도염), 좌–급성 바이러스 인두염 (바이러스 인두편도염),
a-분 목젖, b-작은 고름 주머니, c-붓고 빨간 편도, d-빨간 인두, e-백태가 낀 혀, f-약간 붓고 빨간 편도, g-약간 빨간 인두 출처: Used with permission from Schering Corporation Kenilworth, NJ 07033
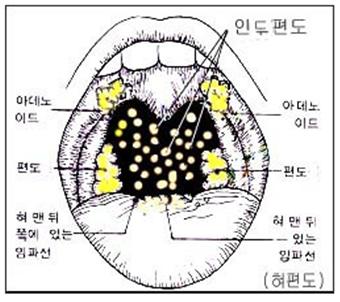
그림 29. 편도선(편도), 아데노이드, 설편도(혀 편도, 혀뿌리 맨 뒤에 있는 림프 조직), 인두 후부 벽에 있는 인두편도 등의 림프 조직들(노란색으로 표시된 점들)이 인두 강에 있다.
이 림프 조직들은 입과 코를 통과해서 하기도, 식도, 또는 신체 내로 들어오는 바이러스, 박테리아, 진균 등 병원체, 또는 해로운 항원 등을 잡아 인두강 이상 체내로 더 이상 들어오지 못하게 하는 역할을 한다.Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD.,FAAP
인두의 구조
-
후두의 최상 부분의 바로 위쪽, 후 비강의 맨 아래 쪽, 혀뿌리의 뒤쪽, 경부 척추의 전방 부위쪽에 있는 기도 부분을 인두또는 인두강이라고 한다.
-
인두의 상부는 후 비강으로 연결되고, 인두의 하부는 후두의 상부와 식도의 기시부로 연결된다.
-
인두의 좌우 양쪽에 편도가 각각 한 개 있다.
-
인두의 후부에는 인두 후부 벽 점막층이 있고, 인두의 앞 부위에는 혀뿌리가 있다.
-
인두는 호흡기에도 속하고 소화기에도 속한다.
-
임상적으로 인두강은 호흡기, 소화기, 그리고 이비인후 영역에도 속한다.
-
무슨 원인으로든 인두에 생긴 염증을 인두염, 또는 인후염이라고도 한다.
-
인두를 인두강이라고도 한다.
-
영어로 흔히들 “Pharyngitis(인두염)”라는 병명 대신 “Sore throat”라는 명명도 많이 쓴다.
급성 인두염을 일으키는 병원체
-
급성 인두염은 바이러스, 박테리아, 마이코플라스마, 곰팡이(진균), 또는 기생충 등 여러 종류의 병원체의 감염으로 생길 수 있다.
-
대부분의 급성 인두염의 원인은 바이러스이다. 급성 바이러스 감염으로 생긴 급성 인두염을 급성 바이러스 인두염이라고 한다.
-
그 다음으로 급성 인두염의 흔한 원인은 A군 베타 용혈성 연쇄상구균(A군 연쇄상구균 또는 A군 연구균)이다.
-
A군 베타 용혈성 연쇄상구균 감염으로 생긴 급성 인두염을 급성 스트렙토 인두염, 또는 급성 A군 베타 용혈성 연쇄상구균 인두염이라고 한다.
-
미국에서는 부모들이나 비 의료인들 중 일부는 급성 스트렙토 인두염을 “스트렙토“라고 한다.
-
급성 인두염을 일으킨 바이러스의 종류에 따라서 급성 바이러스 인두염이 여러 종류로 나누어 질 수 있다.
-
예를 들면 엡스타인–바 바이러스(Epstein-Bar virus/EB 바이러스) 감염으로 급성 엡스타인–바 바이러스 인두염(감염단핵구증/모노/감염성 모노 인두 편도염) 생길 수 있다.
-
모든 연령층의 소아 청소년들에게 엡스타인–바 바이러스 감염성 인두염이 생길 수 있다.
-
엡스타인–바 바이러스 감염으로 신체의 여러 계통에 여러 종류의 EB 바이러스 감염병이 생길 수 있다.
-
엡스타인–바 바이러스 감염병은 사춘기 이전 학령기 아이들이나 사춘기 아이들에서 볼 수 있는 급성 엡스타인–바 바이러스 인두염이 생길 수 있다.[부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다–소아가정간호백과]-제7권 소아청소년 감염병–감염 성 단핵구증 참조.
-
드물게 디프테리아균 감염으로 급성 디프테리아균 인두염, 또는 임질균 감염으로 급성 임질균 인두염이 생길 수 있다.
-
요즘 디프테리아 백신을 모든 소아 청소년들에게 기본적으로 접종해주기 때문에 급성 디프테리아균성 인두염은 거의 볼 수 없다.
-
급성 임질균 인두염이 사춘기 이전 학령기 아이들과 사춘기 아이들에게 또는 성인들에게 가끔 생길 수 있다.
급성 인두염의 종류
의사들, 비 의료인들, 부모들은 급성 인두염을 다음과 같은 병명으로 부르기도 한다.
①감기,
②급성 비인두염,
③급성 상기도염,
④급성 편도염,
⑤급성 인두편도염,
⑥소어 스로트(Sore throat) 등.
그래서 의사들도 환자들도 이 병명에 관해 혼동할 때가 있다. 급성 편도염 참조.
원인에 따른 급성 인두염의 병명
1) 급성 박테리아 인두염
- 이론적으로, 모든 종류의 박테리아(세균)가 인두염을 일으킬 수 있다.
- 급성 박테리아 인두염 중 A군 베타 용혈성 연쇄상구균 인두염이 가장 흔히 생긴다. 특히 소아 청소년들에게는 더 그렇다.
- A군 베타 용혈성 연쇄상구균이 인두에 감염되어 생긴 박테리아 감염병을 급성 박테리아 인두염이라고 한다.
- 급성 박테리아 인두염의 주 원인은 A군 베타 용혈성 연쇄상구균이다.
- A군 베타 용혈성 연쇄상구균 감염으로 생긴 인두염을
- 영어로 스트렙토 파린자이티스(Strepto pharyngitis)라고도 하고,
- 급성 스트렙토 인두염,
- 스트렙토 인두편도염,
- 또는 스트렙토 편도염이라 한다.
A군 베타 용혈성 연쇄상구균을 여기서는 편의상 A군 연구균이라고도 한다.
급성 바이러스 인두염은 소아 청소년들에게서 흔히 볼 수 있는 인두염이다. 그리고 A군 베타 용혈성 연쇄상구균 인두염도 가끔 볼 수 있는 인두염이다. 다음 열거한 인두염은 소아청소년들에게서 드물게 볼 수 있다.
1) 급성 바이러스 인두염, 감기 참조
2) 급성 디프테리아 인두염
3) 급성 임질균 인두염
4) 급성 미코플라스마(마이코플라스마) 인두염
5) 급성 진균 인두염
6) 급성 기생충 감염으로 인한 인두염
-
-
급성 바이러스 인두염,
-
급성 바이러스 상기도염,
-
급성 바이러스 인두염,
-
또는 바이러스 인두 편도염이라고 한다.
-
때로는 바이러스 인두염이란 병명 대신 바이러스 편도염이라고도 한다.
-
때로는 감기라고도 한다.
-
-
-
급성 라이노바이러스 인두염
-
급성 파라인플루엔자 바이러스 인두염
-
급성 알에스(RS)바이러스(호흡기세포융합바이러스) 인두염
-
급성 아데노바이러스 인두염([부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다–소아가정간호백과]-제7권 소아 청소년 감염병–아데노바이러스와 아데노바이러스 감염병)
-
급성 콕사키바이러스 인두염
-
급성 인플루엔자바이러스 인두염
-
급성 헤르판지나 인두염(급성 헤르팡기나 인두염)
-
급성 엡스타인–바 바이러스(EB 바이러스) 인두염(감염 성 단핵구증)
-
급성 사람 메타뉴모바이러스 인두염
-
그 외 다른 종류의 바이러스 인두염 등이 있다.
-
-
이 중에서 급성 RS 바이러스 인두염이 소아 청소년들에게 가장 흔하고 그 다음으로는 급성 사람 메타뉴모바이러스 인두염이라고 한다.
| 대부분의 소아들의 급성 인두염은 바이러스 감염으로 생기고 드물게는 A군 베타 용혈성 연쇄상구균으로 생긴다. |
급성 인두염의 경과에 따라 인두염을 다음과 같이 분류한다.
① 급성으로 생긴 인두염을 급성 인두염,
② 만성으로 생긴 인두염을 만성 인두염이라고 부른다.
③ 아급성으로 생긴 인두염을 아급성 인두염이라고 부른다.
정말로 복잡하고 혼동되는 인두염의 병명들이다.
참고로 알아두는 것도 좋을 것이다.
소아청소년 인두염의 일반적 치료
임상적으로, 인두염은 다음과 같이 6가지 방법으로 치료할 수 있다.
① 급성 바이러스 인두염이라고 추정 진단한 후, 아무 임상 검사도 하지 않고 약물로 치료하지 않고 관찰 치료 한다.
② 박테리아 인두염이 있다고 추정 진단을 하고 세균검사를 하지 않고 항생제로 치료한다.
③ 인두 점액면봉 채집 세균 배양 검사 결과가 양성으로 나온 인두염은 항생제로 치료한다.
④ A군 베타 용혈성 연쇄상구균 속성 항원 항체 응집검사(Rapid antigen test)의 결과가 양성으로 나오면 인두염을 항생제로 치료한다.
⑤ 베타 용혈성 연쇄상구균 속성 항원 항체 응집검사(Rapid antigen detection test)의 결과가 음성으로 나타나면 인두 점액 면봉 채집으로 A군 베타 용혈성 연쇄상구균 세균 배양 검사를 하고 그 결과가 양성으로 나오면 그 인두염을 항생제로 치료한다.26
⑥ 베타 용혈성 연쇄상구균 속성 항원 항체 응집검사 결과가 음성으로 나타나면 임상 경험적으로 판단 해 인두염을 항생제로 치료하든지 항생제로 치료를 하지 않고 관찰 치료를 한다.
⑦ 그 외 원인에 따라 치료한다
인두염의 이상적 치료
-
-
환자의 병력을 듣고 진찰하고,
-
인두 편도 점막층 점액을 면봉으로 채취해 그 피검 물로 세균 검사를 하고, 그 결과에 따라 치료하는 것이다.
-
그러나 A군 베타 용혈성 연쇄상구균 인두염은 바이러스 인두염의 발병률보다 흔하지 않고 세균 검사를 하는데 검사비가 많이 들고 보호자나 환자의 시간을 낭비하고 항생제 치료로 생기는 부작용 등을 고려하면 선택적으로 인두염을 관찰 치료하는 것도 좋다는 연구 결과도 있다.
-
Acute pharyngitis 급성 인두염

Figure 28. Right-bacterial acute pharyngitis (bacterial acute pharyngeal tonsillitis), left-acute viral pharyngitis (viral pharyngeal tonsillitis), a-uvula, b-small pus sacs, c-swollen red tonsils, d-red pharynx, e-electrified tongue, f-slightly swollen red tonsils, g-slightly red pharynx Source: Used with permission from Schering Corporation Kenilworth , NJ 07033

Figure 29. Lymphoid tissues (dots marked in yellow) in the pharyngeal cavity: tonsils , adenoids, lingual tonsils, lymphatic tissue at the back of the tongue root), and pharyngeal tonsils in the posterior wall of the pharynx. These lymphoid tissues catch pathogens such as viruses, bacteria, fungi, or harmful antigens that pass through the mouth and nose and enter the lower respiratory tract, esophagus, or body. Copyright © 2011 John John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
Structure of the pharynx
• The part of the airway located just above the top of the larynx, at the bottom of the posterior nasal cavity, behind the tongue root, and at the anterior portion of the cervical spine is called the pharynx or pharyngeal cavity.
• The upper part of the pharynx connects to the posterior nasal cavity, and the lower part of the pharynx connects to the upper part of the larynx and the origin of the esophagus.
• There is one tonsil on both sides of the pharynx.
• The posterior part of the pharynx has a mucous layer of the posterior pharyngeal wall, and the anterior part of the pharynx has a tongue root.
• The pharynx belongs to the respiratory system and also the digestive system.
• Clinically, the pharyngeal cavity also belongs to the respiratory, digestive, and otorhinolaryngeal areas.
• Inflammation of the pharynx from any cause is also called pharyngitis or sore throat.
• The pharynx is also called the pharyngeal cavity.
• In English, the name “Sore throat” is often used instead of “Pharyngitis”.
Pathogens that cause acute pharyngitis
• Acute pharyngitis can result from infection with several types of pathogens, including viruses, bacteria, mycoplasma, fungi, or parasites.
• The cause of most acute pharyngitis is a virus. Acute pharyngitis resulting from an acute viral infection is called acute viral pharyngitis.
• The next most common cause of acute pharyngitis is group A beta hemolytic streptococcus (group A streptococci or group A streptococcal bacteria).
• Acute pharyngitis resulting from group A beta hemolytic streptococcal infection is called acute streptopharyngitis, or acute group A beta hemolytic streptococcal pharyngitis.
• In the United States, some parents and non-medical practitioners refer to acute streptopharyngitis as “strepto”.
• Depending on the type of virus that caused acute pharyngitis, acute viral pharyngitis can be divided into several types.
• Acute Epstein-Bar virus pharyngitis (infectious mononucleosis/mono/infectious monopharyngeal tonsillitis), for example, can result from an Epstein-Bar virus/EB virus infection.
• Epstein-Barr virus infectious pharyngitis can develop in children and adolescents of all ages.
• Epstein-Barr virus infection can lead to several types of EB virus infections in different systems of the body.
• Epstein-Barr virus infectious disease can lead to acute Epstein-Barr virus pharyngitis, which can be seen in pre-adolescent school-age children or adolescent children. See infectious mononucleosis.
• Rarely, a diphtheria infection can lead to acute diphtheria pharyngitis, or a gonorrhea infection can lead to acute gonorrhea pharyngitis.
• Acute diphtheria pharyngitis is rarely seen because the diphtheria vaccine is given by default to all children and adolescents these days.
• Acute gonococcal pharyngitis can occasionally develop in pre-pubertal school-age children and adolescent children, or in adults.
Types of acute pharyngitis
Doctors, non-medical practitioners, and parents sometimes refer to acute pharyngitis by the name:
① Cold,
② acute nasopharyngitis,
③ acute upper respiratory tract infection,
④ acute tonsillitis,
⑤ acute pharyngeal tonsillitis,
⑥ Sore throat, etc. So doctors and patients sometimes get confused about the disease. See acute tonsillitis.
Disease names of acute pharyngitis depending on the cause
1) acute bacterial pharyngitis
• In theory, all kinds of bacteria (germs) can cause pharyngitis.
• Among acute bacterial pharyngitis, group A beta hemolytic streptococcal pharyngitis is the most common. Especially for children and adolescents.
• A bacterial infection caused by a group A beta hemolytic streptococcus infection in the pharynx is called acute bacterial pharyngitis.
• The main cause of acute bacterial pharyngitis is group A beta hemolytic streptococcus.
• Group A beta hemolytic streptococcal infection with pharyngitis
o Also known as Strepto pharyngitis in English,
o acute streptopharyngitis,
o streptopharyngeal tonsillitis,
o Also called strepto tonsillitis. Group A beta hemolytic streptococcus is also referred to herein as group A research bacteria for convenience.
Acute viral pharyngitis is a common pharyngitis in children and adolescents. In addition, group A beta hemolytic streptococcal pharyngitis is also occasionally seen. The pharyngitis listed below is rare in children and adolescents.
1) See acute viral pharyngitis, cold
2) acute diphtheria pharyngitis
3) Acute gonorrhea pharyngitis
4) Acute mycoplasma pharyngitis
5) acute fungal pharyngitis
6) Pharyngitis due to acute parasitic infection
Acute pharyngitis is caused by a viral infection
Acute viral pharyngitis,
o acute viral upper respiratory tract infection,
o acute viral pharyngitis,
o or viral pharyngeal tonsillitis.
o Sometimes it is called viral tonsillitis instead of the name of viral pharyngitis.
o Sometimes it is called a cold.
Depending on the type of virus that caused the acute viral pharyngitis, viral pharyngitis is as follows:
They can be classified together.
o Acute rhinovirus pharyngitis
o Acute parainfluenza virus pharyngitis
o Acute RS (RS) virus (respiratory syncytial virus) pharyngitis
o Acute adenovirus pharyngitis
www.drleepediatrics.com-Vol. 7 Child and Adolescent Infectious Diseases-Adenovirus and Adenovirus Infectious Diseases) o Acute coxsackie virus pharyngitis
o Acute influenza virus pharyngitis
o Acute herpanic or pharyngitis
o Acute Epstein-Barr virus (EB virus) pharyngitis (infectious mononucleosis)
o Acute human metapneumovirus pharyngitis
o There are other types of viral pharyngitis.
• Among these, acute RS viral pharyngitis is the most common among children and adolescents, followed by acute human metapneumovirus pharyngitis
Acute pharyngitis in most children is caused by viral infection and rarely by group A beta hemolytic streptococci.
Pharyngitis is classified as follows according to the course of acute pharyngitis.
① Acute pharyngitis,
② Chronic pharyngitis.
③ Subacute pharyngitis is called subacute pharyngitis. These are really complex and confusing pathologies of pharyngitis. It would be good to know for your reference.
General treatment of pharyngitis in children and adolescents
Clinically, pharyngitis can be treated in six ways:
① After presumptive diagnosis of acute viral pharyngitis, no clinical tests are performed and observational treatment is performed without treatment with drugs.
② Presumed diagnosis of bacterial pharyngitis and treatment with antibiotics without bacteriological examination.
③ Pharyngitis Mucus Swab Collection Treat pharyngitis with positive bacterial culture results with antibiotics.
④ If the result of group A beta hemolytic streptococcal rapid antigen antibody aggregation test is positive, treat pharyngitis with antibiotics.
⑤ If the result of the beta hemolytic streptococcal rapid antigen detection test is negative, a group A beta hemolytic streptococcus bacterial culture is tested by collecting a pharyngeal mucus swab. Do. 26
⑥ If the result of the beta-hemolytic streptococcal attribute antigen antibody aggregation test is negative, judge pharyngitis by clinical experience and treat pharyngitis with antibiotics or observational treatment without antibiotics.
⑦ Treat according to other causes
Ideal treatment for pharyngitis
Listen to and examine the patient’s medical history,
o Pharyngeal tonsil mucosa is collected with a cotton swab, tested for bacteria with the specimen, and treated according to the result.
o However, group A beta hemolytic streptococcal pharyngitis is less common than viral pharyngitis. Some research shows that it is good.
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
-
www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
-
www.drleepediatrics.com제8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환
-
Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th — 21st Edition
-
The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd editio
-
Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, harvey grant and robert murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
-
The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
-
Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies , Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care
-
응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
-
Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
-
Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
-
Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Berverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gerhon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
-
소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”