급성 기관염과 급성 기관지염 Acute trachitis and Acute bronchitis
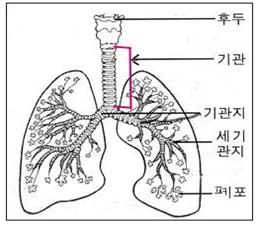
그림 95.기관지에 생긴 염증을 기관지염이라고 한다.
출처-Copyrightⓒ 2001 John Sangwon Lee,MD., FAAP
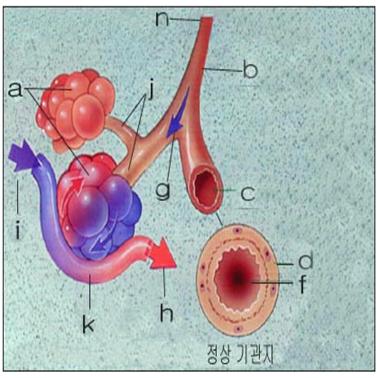
그림 96.정상 기관지, 세기관지, 폐포와 폐포 속에서 산소와 이산화탄소 교환이 되는 과정.
a-폐포, b-기관지, c-기관지 횡단면, d-기관지 벽, f-기관지 부분 기도, g-흡인되어 들어온 공기가 기관지를 통과해서 세기관지 속으로 들어간다. h-산소의 농도가 더 높은 피, i-산소의 농도가 더 낮은 피, 이산화탄소의 농도가 더 높은 피, j-세기관지(모세기관지), k-폐포 혈관, n-기관에 연결되는 기관지.
급성 기관염과 급성 기관지염의 원인
-
기관염도 없고, 세기관지염도 없고, 폐렴도 없고, 기관지에만 급성으로 생긴 염증을 급성 기관지염이라고 한다.
-
기관지에만 바이러스나 박테리아 등의 병원체가 감염되어 기관지염만 생기는 경우는 흔하지 않다.
-
기관지염에는 급성 기관지염과 만성 기관지염이 있다.
-
-
A형 인플루엔자바이러스,
-
B형 인플루엔자바이러스,
-
파라인플루엔자바이러스,
-
RS바이러스,
-
아데노바이러스,
-
코로나바이러스,
-
홍역바이러스,
-
라인노바이러스,
-
그 외 다른 여러 종류의 바이러스들 중 한 종류의 바이러스가 기관에 감염되면 급성 바이러스 기관지염이 생길 수 있다.
- 드물게, 백일해균,
- 장티푸스균,
- 디프테리아균,
- 황색 포도상구균,
- 또는 폐렴연쇄상구균 등 여러 종류의 박테리아 중 한 가지의 박테리아가 기관지에 감염되면 급성 박테리아 기관지염이 생길 수 있다.
- 그 외 마이코플라스마(미코플라스마)가 기관지에 감염되면 급성 마이코플라스마 기관지염이 생길 수 있다.
- 요즘 바이러스 감염이 후두에 생겨 그로 인해 생긴 바이러스 후두염, 크루프를 코르티코스테로이드제로 흔히 치료해서인지 박테리아 기관지염이 전보다 더 흔히 생긴다고 한다.
- 독성 화학 물질이나 독성가스, 또는 화염 등을 흡인할 때도, 또 담배 흡연으로 급성 기관지염이 생길 수 있다.
-
-
박테리아 기관지염은 소아들에게서 드물게 생기지만 급성 바이러스 기관지염은 비교적 흔히 생길 수 있다.
-
급성 바이러스 기관지염만 앓을 수 있지만 사실은 기관지염만 따로 생겨 앓는 경우는 아주 드물다.
-
바이러스 비염이나 바이러스 아데노이드염, 바이러스 부비동염, 바이러스 인두염, 바이러스 후두염 또는 바이러스 기관염 등을 앓을 때 급성 기관지염을 동시 앓을 때가 더 많다.
-
기관지 천식, 아토피성 피부염, 알레르기 비염, 또는 만성 부비동염을 앓고 있는 아이들이나 알레르기성 체질을 가진 아이들, 영양 상태가 좋지 않은 아이들에게는 급성 바이러스 기관지염이 더 잘 생길 수 있다.
급성 기관염과 급성 기관지염의 증상 징후
-
급성 기관지염을 일으킨 바이러스나 박테리아의 종류, 그 외 다른 원인, 나이 등에 따라 증상 징후가 다르다.
-
급성 기관지염만 앓을 때의 증상 징후와 급성 기관지염과 다른 병을 함께 앓을 때의 증상 징후가 다를 수 있다.
-
급성 바이러스 기관지염을 앓을 때 다음과 같이 다양한 증상 징후가 나타날 수 있다.
-
급성 바이러스 상기도염과 급성 바이러스 기관이나 기관지염이 동시에 있을 때는 감기에 걸렸을 때 생길 수 있는 증상 징후와 비슷하게 콧물이 나고 코가 막히고 목안이 아프고 입맛이 떨어지고 미열 내지 고열이 나고 기침하고 근육통, 두통, 가슴이 아프고 노곤하고 수면 장애, 신경과민 등의 증상 징후가 있을 수 있다.
-
급성 기관지염으로 인해 기침할 때 구토할 수 있다.
-
기관지염을 일으킨 바이러스의 종류에 따라 이런 증상 징후가 5~10일 정도 계속 되다가 자연히 낫는 것이 보통이다.
-
급성 박테리아 기관지염의 증상 징후 역시 기관지염을 일으킨 박테리아의 종류에 따라 다양하다.
-
급성 바이러스 기관지염으로 기침할 때는 흰 점액 가래를 뱉는 것이 보통이지만 급성 박테리아 기관지염을 앓을 때는 누런 짙은 가래를 뱉는 것이 보통이다 .
-
기관지 천식을 과거에 앓았던 병력이 있는 아이들이 급성 바이러스 기관지염에 걸리면 기관지 천식 발작이 유발될 수 있다.
-
또 급성 기관지염이 시작되기 전에 기관지 천식을 앓고 있는 아이들이 급성 기관지염에 걸리면 기관지 천식의 증상 징후가 훨씬 더 심해지는 것이 보통이다.
-
급성 기관지염을 일으킨 바이러스에 의해서 급성 바이러스 기관염, 급성 바이러스 후두염이 함께 생길 수 있다. 즉 후두 기관, 기관지 감염이 생길 수 있고, 그 후두 기관, 기관지염으로 생긴 바이러스 크루프의 증상 징후가 생길 수 있다.
-
다시 설명하면, 바이러스 감염이 하기도에 생겨 후두염, 기관염과 기관지염이 동시에 생길 수 있다.
-
이런 때는 후두염, 기관염, 기관지염 등의 증상 징후가 동시 나타날 수 있고 크루프 증상 징후도 나타난다.
급성 기관염과 급성 기관지염의 진단
-
병력, 증상 징후, 진찰소견, 임상검사, 가슴 X-선 사진검사 등을 종합하여 비교적 쉽게 진단할 수 있다.
-
초기의 증상 징후는 폐렴, 기관지 천식, 또는 후두 기관 기관지염으로 생긴 크루프의 증상 징후와 비슷한 데가 많기 때문에 이런 병과 확실하게 감별 진단하기가 어려울 수 있다.
-
급성 박테리아 기관지염은 생명에 위험한 병이다. 또 그의 증상 징후가 급성 바이러스 기관지염의 증상 징후보다 훨씬 더 심한 것이 보통이다.
-
가래로 그람 염색 현미경 세균검사, 세균배양검사 등을 해서 진단 치료를 할 수 있다.
급성 기관염과 급성 기관지염의 치료
-
급성 기관지염의 대부분은 바이러스 감염으로 생기기 때문에 항생제치료에 효력 없다.
-
그러나 급성 박테리아 기관지염이나 급성 박테리아 기관염 등과 감별 진단을 쉽게 할 수 없으면 항생제로 우선 치료를 시작하기도 한다.
-
실내의 습도를 적절하게 조절하고 수분을 적절히 섭취한다.
-
기침할 때 가래를 쉽게 뱉을 수 있게 수분을 적절히 섭취한다.
-
급성 바이러스 기관지염으로 인한 기침을 치료하는 데 안전하고 치료효력이 좋고 이상적인 기침 치료약은 없다.
-
코데인이나 하이코민 등 강력한 기침 치료약으로 기침을 치료할 때는 그런 기침 치료약이 뇌 기침중추 기능을 둔화시켜 기침을 덜 나오게 하는 약리작용이 있다.
-
그러나 치료하는 동안 기관지 속에 가래가 생기지 않게 할 수 없고 가래를 쉽게 뱉을 수 있게 할 수 없다.
-
그런 기침 치료제로 치료 하는 동안 기관지 내 가래가 더 많이 차 있어도 기침을 잘 하지 않을 수 있다.
-
강력한 기침 치료제로 기침을 치료하면 기도 속이 막힐 정도로 가래가 많이 생겨도 정상적으로 기침을 할 수 없기 때문에 기관지 부분 기도 속이 가래로 막혀 호흡곤란이 더 심하게 생길 수 있다.
-
기침을 더 이상 하지 않을 때까지 될 수 있는 한 강력한 기침 치료제로 기침을 치료하지 않는 것이 좋다.
-
심하게 앓으면서 구미가 떨어지고 탈수 될 때는 포도당 전해질용액 정맥주사로 탈수가 되지 않게 예방하고 치료한다.
-
필요에 따라 산소호흡 치료를 한다.
-
열이 나고 목안이 아프면 타이레놀로 해열 진통시킨다.
-
급성 바이러스 기관지염에 보통 이상으로 더 자주 걸릴 때는 그 원인이 무엇인지 알아보고 원인에 따라 적절히 치료한다.
-
급성 기관지염을 자주 앓는 아이들의 대부분은 기관지 천식을 앓고 있을 때가 많다.
-
드물게 선천성 기관지 기형, 기관지 내 이물, 기관지 확장증, 기관지 결핵, 또는 다른 알레르기성 질환이 있는 아이들은 급성 기관지염에 더 잘 걸릴 수 있다.
-
기관지염을 자주 앓으면 이런 병들과 감별 진단해야 한다.
-
급성 바이러스 기관지염을 앓는 동안 박테리아 부비동염(축농증)이나 박테리아 폐렴, 또는 박테리아 중이염 등 2차 박테리아 감염이 생길 수 있다.
-
이때는 적절한 항생제로 2차 박테리아 감염을 치료한다.
-
기관 지천식과 기관지염을 동시 앓을 때는 기관지 확장제 알부테롤제의 정이나 시럽, 분무, 또는 흡입용 HFA와 항 염증제 코르티코스테로이드제로 적절히 치료할 수 있다.
Acute trachitis and Acute bronchitis 급성 기관염과 급성 기관지염

Figure 95. Inflammation in the bronchi is called bronchitis. Source-Copyright© 2001 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Figure 96: The process of oxygen and carbon dioxide exchange in the normal bronchi, bronchioles, alveoli and alveoli.
a-alveoli
, b-bronchi,
c-bronchial cross section,
d-bronchial wall,
f-bronchial partial airway,
g-aspirated air passes through the bronchi and enters the bronchioles.
Blood with a higher concentration of h-oxygen, blood with a lower concentration of i-oxygen, a higher concentration of carbon dioxide, j-bronchioles (capillaries), k-alveolar vessels, bronchi that connect to the n-organs.
Causes of acute tracheitis and acute bronchitis
•There is no tracheitis, no bronchiolitis, no pneumonia, and acute inflammation of only the bronchi is called acute bronchitis.
• It is not common for only the bronchial tubes to be infected with pathogens such as viruses or bacteria, resulting in bronchitis alone.
• Bronchitis includes acute bronchitis and chronic bronchitis.
Acute bronchitis is usually caused by a viral infection of one of several types of viruses:
o Influenza A virus, o Influenza B virus,
o parainfluenza virus,
o RS virus, o adenovirus,
o Coronavirus,
o measles virus, o Linenovirus,
o Acute viral bronchitis can develop when an organ is infected with one of several other types of viruses.
o Rarely, pertussis,
o Typhoid bacteria,
o diphtheria,
o Staphylococcus aureus,
o Or, acute bacterial bronchitis can occur when the bronchi are infected with one of several types of bacteria, such as pneumonia and streptococci.
o Other mycoplasma (mycoplasma) infections in the bronchi can lead to acute mycoplasma bronchitis.
o These days, viral infections occur in the larynx and the resulting viral laryngitis and croup are often treated with corticosteroids, making bacterial bronchitis more common than before.
o When inhaling toxic chemicals, toxic gases, or flames, cigarette smoking can lead to acute bronchitis.
• Bacterial bronchitis is rare in children, but acute viral bronchitis is relatively common.
• You can only suffer from acute viral bronchitis, but in fact, only bronchitis is very rare.
• Acute bronchitis is more common with viral rhinitis, viral adenoiditis, viral sinusitis, viral pharyngitis, viral laryngitis, or viral tracheitis.
• Children with bronchial asthma, atopic dermatitis, allergic rhinitis, or chronic sinusitis, children with allergies, and children with poor nutrition are more likely to develop acute viral bronchitis.
Symptoms signs of acute tracheitis (trachitis)and acute bronchitis
• Symptoms differ depending on the type of virus or bacteria that caused acute bronchitis, other causes, and age.
• Symptoms of acute bronchitis alone may differ from those of acute bronchitis and other diseases.
• When you have acute viral bronchitis, you may have a variety of symptoms, including:
• If you have acute viral upper respiratory tract and acute viral trachea or bronchitis at the same time, you may have a runny nose, stuffy nose, sore throat, loss of taste, mild to high fever, coughing, muscle pain, headache, chest similar to symptoms that may occur when you have a cold. There may be symptoms such as sick, tired, sleep disturbances, and nervousness.
• Acute bronchitis can cause vomiting when coughing.
• Depending on the type of virus that caused bronchitis, these symptoms usually last 5 to 10 days and then heal naturally.
• Symptoms of acute bacterial bronchitis also vary depending on the type of bacteria that caused the bronchitis.
• When coughing with acute viral bronchitis, it is common to spit out white mucous sputum, but when you have acute bacterial bronchitis, it is common to spit out dark yellow sputum.
• Acute viral bronchitis in children with a history of bronchial asthma can lead to a bronchial asthma attack.
• Also, if children with bronchial asthma develop acute bronchitis before the onset of acute bronchitis, symptoms of bronchial asthma are usually much more severe.
• Acute viral tracheitis and acute viral laryngitis may be caused by the virus that caused acute bronchitis. In other words, infection of the laryngeal organ and bronchial tubes may occur, and symptoms of virus croup caused by bronchitis may occur.
• In other words, a viral infection can occur in the lower respiratory tract, causing laryngitis, tracheitis and bronchitis at the same time.
• In this case, symptoms such as laryngitis, tracheitis, and bronchitis may appear simultaneously, and symptoms of Croup may also appear.
Diagnosis of acute tracheitis and acute bronchitis
• Comprehensive medical history, symptom signs, examination findings, clinical examination, chest X-ray examination, etc. can be diagnosed relatively easily.
• Early symptomatic signs are often similar to those of Croup resulting from pneumonia, bronchial asthma, or laryngeal bronchitis, so it can be difficult to reliably diagnose these diseases.
• Acute bacterial bronchitis is a life-threatening disease. Also, his symptoms are usually much worse than those of acute viral bronchitis.
• Diagnosis treatment can be performed by performing gram-staining microscopic bacterial tests and bacterial culture tests with sputum.
Treatment of acute tracheitis and acute bronchitis
• Most of the acute bronchitis is caused by viral infections, so antibiotic therapy is ineffective.
• However, if differential diagnosis such as acute bacterial bronchitis or acute bacterial tracheitis cannot be easily diagnosed, antibiotics may be used first.
• Adjust indoor humidity appropriately and drink adequate water.
• Drink adequate fluids to make it easier to spit out phlegm when coughing.
• There is no safe, effective, and ideal cough remedy for treating cough caused by acute viral bronchitis.
• When treating cough with powerful cough medicines such as codeine or haicomin, such cough medicine has a pharmacological effect that slows the function of the brain cough center and makes cough less likely.
• However, during treatment, sputum cannot be prevented from forming in the bronchi, and sputum cannot be easily spit out.
• During treatment with such a cough remedy, you may not cough well, even if there is more sputum in the bronchi.
• If you treat cough with a powerful cough medicine, you cannot cough normally even if there are enough phlegm to block the airways, so the inside of the airway in the bronchial section may be blocked with phlegm, which may cause more severe breathing difficulties. • It is best not to treat your cough with a strong cough remedy as much as possible until you are no longer coughing.
• In case of dehydration and dehydration due to severe illness, prevent and treat dehydration by intravenous injection of glucose electrolyte solution.
• Take oxygen breathing treatment as needed.
• If you have a fever and sore throat, use Tylenol to relieve fever.
• If you get acute viral bronchitis more often than usual, find out what the cause is and treat it accordingly.
• Most children with frequent acute bronchitis often have bronchial asthma.
• Rarely, children with congenital bronchial anomalies, bronchial foreign bodies, bronchiectasis, bronchial tuberculosis, or other allergic conditions are more likely to develop acute bronchitis.
• If you suffer from bronchitis frequently, you should be diagnosed differently from these diseases.
• During acute viral bronchitis, you may develop a secondary bacterial infection, such as bacterial sinusitis (sinusitis), bacterial pneumonia, or bacterial otitis media.
• In this case, treat the secondary bacterial infection with appropriate antibiotics.
• If you have both bronchial asthma and bronchitis, it can be treated appropriately with a bronchodilator albuterol tablet or syrup, spray, or inhaled HFA and anti-inflammatory corticosteroids.
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
-
www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
-
www.drleepediatrics.com제8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환
-
Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th — 21st Edition
-
The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
-
Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, Harvey grant, and Robert Murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
-
The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
-
Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care
-
응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
-
Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
-
Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
-
Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
-
소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”