급성 관절염과 패혈성 관절염(감염성 관절염) Acute arthritis and Septic arthritis
급성 관절염과 패혈성 관절염(감염성 관절염)의 원인
- 관절낭 속에 염증이 생기는 병을 관절염이라고 한다.
- 그 관절염이 세균(박테리아)감염으로 생기면 세균 감염성 관절염이라고 한다.
- 그 관절염이 패혈성 세균(패혈성 박테리아) 감염으로 생기면 패혈성 관절염(Septic arthritis)이라 한다.
- 인체의 관절을 비롯해 인체의 다른 어느 부위에 감염성 염증이 생기면 다음 1~5의 주 증상이 생길 수 있다.
다음 1~5의 주 증상징후가 있나 알아보고 그 정도가 어떤지 등을 알아보고 세균 감염성 염증인지 비 세균 감염성 염증인지 임상적 감별을 한다.
1. 동통(dolor)
2. 발열(calor)
3. 발적(rubor)
4. 종창(tumor)
5. 기능상실(functio laesa)이나 기능장애 등 1~5의 주 증상은 세균(박테리아) 감염성 염증이 있을 때 생기는 것이 보통이다.
- 관절에 이런 1~5의 주 증상이 있으면 세균 감염성 관절염이 있다고 진단하는 데 큰 도움이 된다.
사진 137. ◯내 왼쪽 고관절이 있다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
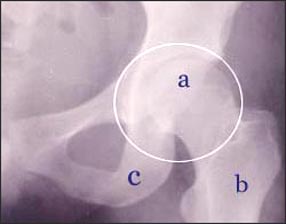
사진 138. 고관절
◯내에 고관절이다.
a-대퇴골 두부, b-대퇴골, c-좌골
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D. FAAP
관절염
1. 세균(박테리아) 감염이나
2. 바이러스 감염,
3. 그 외 다른 종류의 병원체 감염으로 생기는 것이 보통이며
4. 외상이나 내상으로도 생길 수 있고,
5. 류마티스 관절염(Rheumatic arthritis)이나 연소성 류마토이드 관절염(Rheumatoid arthritis) 등 으로도 생길 수 있다,
6. 알레르기 질환 등으로 인한 관절염이 생길 수 있다.
7. 통풍, 악성 종양 등으로도 생길 수 있다.
8. 그 외
- 여기서는 세균(박테리아) 감염으로 생긴 관절염에 대해서 주로 설명하기로 한다.
- 신체의 어떤 관절낭 속에 세균(박테리아)이 감염되어 그 관절이 곪는 것을 세균(박테리아)성 관절염 또는 패혈성 관절염(Septic arthritis)이라고 한다고 이미 언급했다.
- 여기서 편의상 세균(박테리아)성 관절염을 세균성 관절염 또는 그냥 관절염이라 한다.
- 신체의 어떤 종류의 관절낭 속에든지 박테리아가 감염되어 그 관절이 곪으면 관절염이 생길 수 있다.
- 신체의 모든 종류의 관절들 중 어깨관절(견관절), 무릎관절(슬관절), 또는 고관절에 관절염이 비교적 더 흔히 생길 수 있다.
거의 모든 종류의 세균(박테리아)이 소아 관절염을 일으킬 수 있으나 특히 더 잘 일으킬 수 있는 박테리아
1. 폐렴 연쇄상구균,
2. A군 베타 용혈성 연쇄상구균 ,
3. B군 용혈성 연쇄상구균,
4. 황색 포도상구균,
5. B형 헤모필러스 인플루엔자균(히브균) 등이 관절 낭 및, 또는 골수에 침입하여 관절염 및, 또는 골수염을 더 잘 일으킬 수 있다.
6. 최근에는, 킨겔라(Kingella kigae)(14 참조문헌) 란 세균에 의해 소아 관절염이나 소아 골수염이 소아들에게 더 잘 생긴다고 한다.
7. 그 외 결핵균, 라임 병 균 등으로도 관절염이 생길 수 있다.
선천성 고관절 탈구, 일과성 활막염, 탈구 참조.
사진 139. ◯으로 표시된 부분에 무릎관절(슬관절)이 잇다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
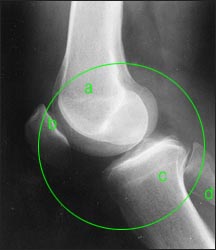
사진 140. ◯으로 표시한 부분이 무릎관절(슬관절)이다. 무릎관절이나 고관절 등 어떤 관절 속에 생긴 염증을 관절염이라 한다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
급성 관절염과 패혈성 관절염(감염성 관절염)의 증상 징후
- 관절염을 일으킨 세균의 종류, 원인, 정도, 관절의 종류, 급성, 만성, 나이, 합병증의 유무 등에 따라 세균성 관절염의 증상 징후가 다르다.
- 관절염은 어느 연령층 아이들에게도 생길 수 있으나 생후 6개월 이전 영아들에게 더 잘 생긴다. 감기나 수두를 앓는 중, 또는 그 밖에 다른 바이러스성 상기도염 등을 앓는 중 박테리아 감염이 관절 속에 생겨 갑자기 관절염이 발생될 수 있다.
- 외상 상처 등을 통해 세균이 감염된 후 그 세균이 혈류를 타고 관절 속에 감염되어 관절염이 생길 수 있고,
- 또는 신체의 어떤 부위의 1차성 박테리아 감염병의 병소에 있는 세균이 혈류를 따라 관절 속으로 전파되어 세균성 관절염이 생길 수 있다.
- 관절염의 초기의 증상 징후는 갑자기 고열이 나고 몹시 보채고 식욕이 없고 아무 것도 먹지 못한다.
- 관절염이 생긴 관절이 붓고 몹시 아프다.
- 관절염이 있는 관절과 그 관절에 연결된 신체의 부위를 잘 움직일 수 없다.
- 그 외 감염성 관절염으로 생긴 염증의 주증이 생길 수 있다
급성 관절염과 패혈성 관절염(감염성 관절염)의 진단
- 병력, 증상 징후와 진찰소견 등을 종합하여 이 병이 있다고 의심되면 CBC 피 검사, 적혈구 침강속도(ESR) 검사 등 피 검사, 혈액 세균 배양검사, 관절 X선 검사, 관절 초음파 검사, 관절 MRI 검사 등으로 진단한다.
- 관절염이 있는 관절낭 내에 있는 피고름을 주사 바늘로 빼 그 고름으로 그람 염색 현미경 세균 검사, 세균배양 검사 등을 한다.
- 연소성 류마토이드 관절염, 류마티스 관절염, 골수염, 골절, 탈골 등과 관절에 생길 수 있는 다른 질병과 세균성 관절염을 감별 진단한다.
급성 관절염과 패혈성 관절염(감염성 관절염)의 치료
- 세균성 급성 관절염을 응급으로 적절히 치료해주지 않으면 그 관절이 영구적으로 손상되어 일생동안 장애자가 될 수 있다.
- 때문에 관절염이 있다고 의심되면 급히 입원치료 해야 한다.
- 어떤 종류의 세균(박테리아)이 관절염을 일으켰는지 알아보기 위해 관절 속 피고름을 주사바늘로 빼서 그 피검물로 그람 염색 현미경 세균 검사, 세균배양 검사 등을 하고 항균제 감수성 검사를 한다.
- 관절염을 일으킨 박테리아의 종류, 나이 등에 따라 적절한 항생제 혈관주사로 약 1~3주 이상 치료한다.
- 경우에 따라 관절 속에 들어있는 피고름을 수술로 빼어주는 치료도 한다.
- 관절염과 골수염, 또는 관절염과 패혈증 등이 동시 있을 수 있다.
- 그에 따라 적절히 치료한다.
활액 검사로 각종 관절염을 감별 진단을 할 수 있다. Differential diagnosis of arthritis by synovial fluid analysis
| 관절염의 종류 | 활액의 색 | 투명도 | 점착성 | 뮤신 응고성 | 백혈구 수/mm.3. 다형핵구 % |
연골 조각 | 크리스탈 | RA 세포 | 박테리아 |
| 정상 | 보리집색 | 투명 | 높다 | 좋다 | 200 백혈구 이하, 25% 이하 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 류마티스성 관절염 Rheumatic arthritis | 황 색 | 약간 혼탁 | 낮다 | 좋다 | 10.000-12,000 백혈구, 50% 이하 | 0 | 0 | 0 또는 + | 0 |
| 류마티스양 관절염(류마토이드 관절염 Rheumatoid arthritis) | 황 색, 프른색 | 불투명 | 낮다 | 낮다 | 15.000-20,000 백혈구, 75% 이하 | 0 | 가끔 콜레스테롤 | + | 0 |
| 박테리아감염성 관절염( 패혈성 관절염) Septic arthritis) | 재색 또는 혈색 | 혼탁, 고름 | 낮다 | 낮다 | 80.000-200,000 백혈구 75% 이하 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 박테리아 |
| 외상성 관절염 Traumatic arthritis) | 보리집색, 혈색, 황색 | 투명, 혼탁 | 높다 | 좋다 | 2000 백혈구 이하, 몇개정도내지 많은 적혈구, 25% 이하 | 0 또는 + | 0 | 0 | + |
| 결핵균성 관절염Tuberculous arthritis) | 황색 | 혼탁 | 낮다 | 낮다 | 25,000 백혈구, 50-60% | 0 | 0 | 0 | + |
출처: After holland and Joseph: Arthritis and aㅣㅣied conditon, Ed. 8, p.72
Acute arthritis and septic arthritis 급성 관절염과 패혈성 관절염(감염성 관절염)
Causes of Acute Arthritis and Septic Arthritis (Infectious Arthritis)
• A disease in which the joint capsule becomes inflamed is called arthritis.
• If the arthritis is caused by a bacterial (bacterial) infection, it is called bacterial infectious arthritis.
• If the arthritis is caused by a septic bacterial infection, it is called septic arthritis.
• The following 1-5 main symptoms may occur when infectious inflammation occurs in any other part of the body, including the joints of the body.
Find out if there are the following main symptoms of 1 to 5, find out what the level is, and clinically differentiate whether it is bacterial or non-bacterial infection.
1. pain
2. fever
3. Redness
4. Tumor
5. The main symptoms of 1 to 5, such as functional loss (functio laesa) or dysfunction, usually occur when there is bacterial (bacterial) infectious inflammation.
• The presence of these 1-5 major symptoms in the joints is a great help in diagnosing bacterial infection arthritis.

Picture 137. ◯I have my left hip joint. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP

Photo 138. Hip joint ◯In the hip joint. a – femoral head, b – femur, c – ischial bone Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D. FAAP
Arthritis
1. Bacterial (bacterial) infection or
2. viral infection;
3. It is usually caused by infection with other types of pathogens.
4. It can also be caused by trauma or internal trauma,
5. It can also occur with rheumatoid arthritis or juvenile rheumatoid arthritis,
6. Arthritis may occur due to allergic diseases, etc.
7. It can also be caused by gout, malignant tumors, etc.
8. Others
• Here, we will mainly discuss arthritis caused by bacterial (bacterial) infection.
• It has already been mentioned that bacterial (bacterial) infection in a certain joint capsule in the body and causing the joint to become sore is called bacterial (bacterial) arthritis or septic arthritis.
• For convenience, bacterial (bacterial) arthritis is referred to as bacterial arthritis or just arthritis.
• Bacterial infection in any type of joint capsule in the body can cause arthritis to occur.
• Of all types of joints in the body, arthritis is relatively more common in the shoulder (shoulder), knee (knee), or hip joints.
Almost all types of bacteria (bacteria) can cause arthritis in children, but are particularly prone to
1. Streptococcus pneumoniae, ‘
2. Group A beta-hemolytic streptococci ,
3. Group B hemolytic streptococci,
4. Staphylococcus aureus,
5. Haemophilus influenzae type B (H. pneumoniae), etc. may invade the joint capsule and/or bone marrow to more likely cause arthritis and/or osteomyelitis.
6. Recently, it is said that juvenile arthritis or juvenile osteomyelitis is more likely to be caused in children by a bacterium called Kingella kigae (14 refs).
7. In addition, Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Lyme disease can also cause arthritis. See congenital hip dislocation, transient synovitis, dislocation.

Picture 139. The part marked with
◯ has a knee joint (knee joint). Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP

Picture 140. The part marked with
◯ is the knee joint (knee joint). Inflammation of any joint, such as the knee or hip joint, is called arthritis. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
Symptoms, signs of Acute Arthritis and Septic Arthritis (Infectious Arthritis)
• Symptoms of bacterial arthritis differ depending on the type, cause, degree, type of joint, acute, chronic, age, and the presence or absence of complications of the bacteria that caused arthritis.
• Arthritis can affect children of any age, but it is more common in children younger than 6 months of age. During a cold, chickenpox, or other viral upper respiratory tract infection, a bacterial infection in the joint can cause sudden onset of arthritis.
• After bacterial infection through traumatic wounds, etc., the bacteria can enter the joint through the bloodstream and cause arthritis.
• Alternatively, bacteria from the lesion of a primary bacterial infection in any part of the body can spread through the bloodstream into the joint, resulting in bacterial arthritis.
• The earliest symptomatic signs of arthritis are sudden high fever, irritability, loss of appetite, and inability to eat.
• Arthritic joints are swollen and very painful.
• Inability to move joints with arthritis and parts of the body connected to those joints.
• Other symptoms of inflammation caused by infectious arthritis may occur. Diagnosis of acute arthritis and septic arthritis (infectious arthritis)
• If you suspect that you have this disease based on your medical history, symptom signs, and examination findings, blood tests such as CBC blood test, ESR test, blood bacterial culture test, joint X-ray test, joint ultrasound test, joint MRI test Diagnose, etc.
• The blood pus in the joint capsule with arthritis is removed with an injection needle and the pus is used for Gram-stained microscopic bacterial examination and bacterial culture examination.
• Differential diagnosis of bacterial arthritis from other diseases that can occur in joints such as juvenile rheumatoid arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, osteomyelitis, fractures, and dislocations.
Treatment of acute arthritis and septic arthritis (infectious arthritis)
• If acute bacterial arthritis is not treated promptly and properly, the joint can be permanently damaged and become disabled for life.
• If you suspect that you have arthritis because of this, you must be hospitalized immediately.
• To find out what kind of bacteria (bacteria) caused arthritis, the blood pus in the joint is withdrawn with a needle, and the specimen is subjected to a Gram-stained microscopic bacterial test, bacterial culture test, etc., and antimicrobial susceptibility test.
• Depending on the type of bacteria causing arthritis, age, etc., it is treated with an appropriate antibiotic vascular injection for about 1-3 weeks.
• In some cases, there is also a treatment to remove the blood pus in the joint with surgery.
• Arthritis and osteomyelitis, or arthritis and sepsis may coexist.
• Treat accordingly. A synovial fluid test can be used to differentially diagnose various types of arthritis.
Differential diagnosis of arthritis by synovial fluid analysis
활액 검사로 각종 관절염을 감별 진단을 할 수 있다. Differential diagnosis of arthritis by synovial fluid analysis
| Types of Arthritis | color of synovial fluid | transparency | adhesive | Mucin coagulability | White blood cell count/mm.3. Polymorphonuclear % | piece of cartilage | crystal | RA cells | bacteria |
| Normal | Straw barley color | Transparency | high | good | 200 leukocytes or less, 25% or less | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 류마티스성 관절염 Rheumatic arthritis | yellow | slightly cloudy | low | good | 10.000-12,000 white blood cells, less than 50% | 0 | 0 | 0 or + | 0 |
| Rheumatoid arthritis) | yellow, green | opacity | low | low | 15.000-20,000 white blood cells, less than 75% | 0 | sometimes cholesterol | + | 0 |
| Bacterial Infectious Arthritis (Septic Arthritis) | Gray color or blood color | cloudiness, pus | low | low | 80.000-200,000 leukocytes 75% or less 0 0 | 0 | bacteria | ||
| Traumatic arthritis) | barley color, bloody, yellow | transparent, turbid | high | good | Less than 2000 white blood cells, few to many red blood cells, less than 25% | 0 or + | 0 | 0 | + |
| Tuberculous arthritis) | yellow | cloudy | low | low | 25,000 white blood cells, 50-60% | 0 | 0 | 0 | + |
Source: After holland and Joseph: Arthritis and aㅣied conditon, Ed. 8, p.72
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제16권 소아청소년 정형외과 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제9권 소아청소년 소화기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제10권. 소아청소년 신장 비뇨 생식기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제11권. 소아청소년 심장 혈관계 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제12권. 소아청소년 신경 정신 질환, 행동 수면 문제
- www.drleepediatrics.com제13권. 소아청소년 혈액, 림프, 종양 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제14권. 소아청소년 내분비, 유전, 염색체, 대사, 희귀병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제15권. 소아청소년 알레르기, 자가 면역질환
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th — 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
-
Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, Harvey grant, and Robert Murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
-
The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
-
Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care
-
응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
-
Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
-
Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
-
Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
-
소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”