골수염 Osteomyelitis
세균(박테리아)이나 곰팡이(진균) 등 병원체가 골수에 감염되어 생긴 감염병을 골수염이라고 한다.
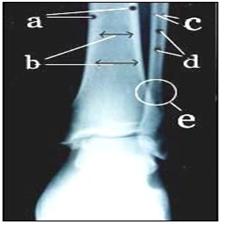
사진 135. 경골과 비골.
d-골수에 생긴 감염병을 골수염이라고 한다. a와 c-뼈의 바깥 부분(뼈의 피층) b와 d 부분에 골수가 있다, e◯내–비골 골절
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M., DFAAP
골수염의 원인
- 박테리아 등 병원체가 골수에 감염되어 생긴 감염병을 골수염이라고 한다.
- 이론적으로 세균성(박테리아성) 골수염, 바이러스성 골수염 또는 그 외 병원체 감염으로 골수에 감염병이 생길 수 있다.
- 그러나 여기에서는 박테리아 감염으로 생긴 골수염에 관해 주로 설명한다.
- 여러 종류의 세균(박테리아) 중 어떤 종류의 박테리아가 골수에 일차적으로 침입해 골수염만 일으킬 수 있고,
- 또 관절에 일차적으로 감염되어 관절염만 일으킬 수 있다.
- 박테리아가 골수와 관절 속에 동시에 침입해서 세균성(박테리아성) 골수염과 관절염을 동시에 일으킬 수 있다.
- 피부에 난 농가진 등 신체의 다른 계통의 어떤 부위에 감염병을 1차적으로 앓고 있는 중, 또는 다 나을 때쯤 1차적 감염병을 일으켰던 박테리아가 골수나 관절에 감염되어 골수염 및, 또는 관절염이 생길 수 있다.
- 수두 등 바이러스성 감염병을 앓을 때 황색 포도상구균이나 다른 종류의 박테리아가 골수 속이나 관절 속으로 감염되어 이차 세균 감염이 생겨 골수염 및, 또는 관절염이 생길 수 있다.
- 피부층이나 점막층에 생긴 외상이나 화상 또는 바이러스성 감염병이나 박테리아성 감염병으로 생긴 환부를 통해서 어떤 종류의 박테리아가 몸속으로 감염된 후 그 박테리아가 혈류를 따라 골수에 감염되어서 골수염이, 관절에 감염되어 관절염이 생길 수 있다.
- 예방접종 주사를 맞은 주사 바늘 상처, 또는 다른 병을 치료하기 위해서 준 주사 바늘 상처를 통해, 또는 못이나 예리한 물체로 찔린 피부 상처를 통해 어떤 종류의 박테리아가 감염되어 그 박테리아가 골수로 퍼져 골수염이 생길 수 있다.
- 거의 모든 박테리아가 골수나 관절에 감염되면 골수염 및, 또는 관절염이 생길 수 있다.
- 황색 포도상구균은 메티실린 내성 황색 포도상구균(MRSA)과 비 메티실린 내성 황색 포도상구균이 있다.
- 그 중 한 가지 황색포도상구균 감염에 의해서, A군 베타 용혈성 연쇄상구균, B군 연쇄상구균, 또는 폐렴 연쇄상구균 등 감염으로 골수염이 비교적 더 잘 생길 수 있다.
- 최근 그램 음성균 Kingella kingae 감염에 의해 소아 골수염이 생길 수 있고
- 소아 관절염이 생길 수 있다는 보고가 있다.
- Kingella kingae 세균 감염에 의해 생긴 소아 골수염과 소아 관절염은 증상 징후와 진찰, 종합검진, 박테리아 배양, PCR 검사로 진단할 수 있다.
골수염의 증상 징후
- 세균성 골수염이 급성으로도 생길 수 있고 만성으로도 생길 수 있다. 환자의 나이, 골수염을 일으킨 원인균, 정도, 골수염이 생긴 뼈의 종류, 급성 또는 만성, 합병증의 유무, 골수염 진행의 정도 등에 따라 증상 징후가 다르다.
- 골수염이나 관절염은 신생아를 비롯한 어느 연령층의 아이들에게 생길 수 있지만 특히 5~14세 후기 유아들, 학령기 아이들과 초기 사춘기 소아청소년들에게 더 잘 생긴다. 초기에는 갑자기 고열이 나고, 허탈상태에 빠질 정도로 전신이 몹시 아프다.
- 특히 골수염이 나 있는 뼈 부위가 몹시 아프고, 골수염이 생긴 뼈의 바로 위에 있는 피부가 빨갛게 발적되고 골수염이 생긴 부위에서 열이 나고 그 부위가 붓고 손으로 누르면 몹시 아프다. 팔이나 다리의 뼈에 골수염이 생길 때는 팔이나 다리를 움직이기 싫어하든지 조금도 움직일 수 없다.
골수염의 진단
- 병력, 증상 징후와 진찰 소견 등을 종합하여 이 병이 의심되면 입원 진단 치료를 받아야 한다. 피검사와 소변검사, 세균배양검사, 뼈나 관절의 X선 사진 검사, 초음파 검사, MRI 검사 등으로 골수염을 진단할 수 있다.
- 골수염이나 관절염이 생긴 뼈나 관절 속에 있는 고름을 바늘로 채취해서 그 피검물을 그람 염색 현미경 세균 검사, 세균 배양검사 등을 해서 어떤 종류의 박테리아 감염으로 골수염이나 관절염이 생겼는지 알아본다.
골수염의 치료
- 정도, 증상 징후, 박테리아의 종류, 급성 또는 만성이냐 등에 따라 1~4주간 항생제 주사로 치료한다.
- 골수염이 의심되면 병원에 입원 치료한다.
- 항균제 감수성 검사로 알아낸 적절한 항생제 정맥주사로 치료한다.
- 황색 포도상구균 감염으로 생긴 급성 골수염은 옥사실린, 토브라마이신, 또는 클라포란들 등의 항생제 중 적절한 항생제 혈관주사로 적어도 3주 이상 치료한다.
- 그리고 황색 포도상구균 감염으로 생긴 만성 골수염은 6~12개월 동안 치료할 때도 있다.
- 요즘 메티실린 내성 황색포도상구균(MRSA)에 감염되어 있느냐 또는 비 메티실린 내성 황색포도상구균에 감염되어 있느냐에 따라 치료 방법과 치료 효과가 다르다.
- 정형외과 전문의, 소아청소년과 전문의, 소아 감염병과 전문의 등이 한 치료 팀의 멤버가 되어 서로 협력하면서 치료할 때가 많다.
- 골수염이 있는 뼈는 쉽게 골절될 수 있기 때문에 골수염이 있는 뼈를 석고 붕대 고정 치료를 한다.
- 또 필요에 따라 골수염으로 생긴 고름을 빼 준다.
- 골수염을 일으킨 박테리아가 신체 다른 부위에 감염되어 패혈증, 뇌막염 등이 생길 수 있다.
Osteomyelitis 골수염
Osteomyelitis is an infection caused by pathogens such as bacteria (bacteria) or fungi (fungi) in the bone marrow.

Photo 135. Tibia and fibula. D-Bone marrow infection is called osteomyelitis. a and c – the outer part of the bone (cortex of the bone) b and d with the bone marrow, e◯intra-fibula fracture Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M., D FAAP
Causes of osteomyelitis
• An infectious disease caused by infection of the bone marrow with pathogens such as bacteria is called osteomyelitis.
• Theoretically, bacterial (bacterial) osteomyelitis, viral osteomyelitis or other pathogenic infection can cause an infection in the bone marrow.
• However, this article mainly discusses osteomyelitis caused by bacterial infection.
• Certain types of bacteria (bacteria) enter the bone marrow primarily and can only cause osteomyelitis;
• Also, the primary infection of the joint can cause only arthritis.
• Bacteria can simultaneously invade the bone marrow and joints, causing both bacterial (bacterial) osteomyelitis and arthritis.
• Bacteria that caused a primary infectious disease in any part of the body, such as impetigo, on the skin, or other parts of the body when the primary infectious disease is cured can infect the bone marrow or joints, resulting in osteomyelitis and/or arthritis.
• When you have a viral infection such as chickenpox, Staphylococcus aureus or other types of bacteria can infect the bone marrow or joints, resulting in secondary bacterial infection, resulting in osteomyelitis and/or arthritis.
• After a certain type of bacteria enters the body through trauma or burns on the skin or mucous membranes, or through a wound caused by a viral or bacterial infection, the bacteria travels through the bloodstream and infects the bone marrow, causing osteomyelitis, joint infection and arthritis. can happen
• Through a needle wound from an immunization shot, a needle wound given to treat another disease, or through a skin wound punctured with a nail or sharp object, bacteria of some kind can become infected and spread to the bone marrow, causing osteomyelitis. can happen • Almost all bacteria in the bone marrow or joints can cause osteomyelitis and/or arthritis.
• Staphylococcus aureus includes methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and non-methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.
• One of them is Staphylococcus aureus infection, which is more likely to cause osteomyelitis, such as group A beta-hemolytic streptococci, group B streptococci, or pneumococcus pneumoniae.
• Recent infection with the gram-negative bacteria Kingella kingae can cause osteomyelitis in children.
• There are reports that juvenile arthritis can develop.
• Pediatric osteomyelitis and juvenile arthritis caused by bacterial infection of Kingella kingae can be diagnosed by symptom signs and examination, comprehensive examination, bacterial culture, and PCR test.
Symptoms, Signs of osteomyelitis
• Bacterial osteomyelitis can be acute or chronic. Symptoms vary depending on the patient’s age, the causative agent of osteomyelitis, the degree of osteomyelitis, the type of bone that has osteomyelitis, acute or chronic, the presence or absence of complications, and the degree of osteomyelitis progression.
• Osteomyelitis and arthritis can occur in children of any age, including newborns, but are more common in late-five to 14-year-olds, school-age children, and early puberty children. In the early stages, you suddenly have a high fever, and your whole body hurts so much that you fall into a collapsed state.
• The bone area with osteomyelitis is particularly painful, the skin immediately above the bone with osteomyelitis is red and red, the area with osteomyelitis has a fever, the area is swollen, and it hurts when you press it with your hands. When osteomyelitis develops in the bones of an arm or leg, the arm or leg may or may not be able to move at all.
Diagnosis of osteomyelitis
• If this disease is suspected based on the medical history, symptom signs, and examination findings, hospitalized diagnosis and treatment should be sought. Osteomyelitis can be diagnosed with blood tests, urine tests, bacterial culture tests, X-ray tests of bones or joints, ultrasound tests, and MRI tests.
• Pus from bones or joints with osteomyelitis or arthritis is collected with a needle, and the specimen is subjected to Gram-stained microscopic bacteriological examination and bacterial culture to find out what kind of bacterial infection caused osteomyelitis or arthritis.
Treatment of osteomyelitis
• Treatment with antibiotic injections for 1 to 4 weeks, depending on the severity, symptom signs, the type of bacteria, and whether it is acute or chronic.
• If osteomyelitis is suspected, be hospitalized.
• Treat with an appropriate antibiotic, intravenous, as determined by an antimicrobial susceptibility test.
• Acute osteomyelitis caused by Staphylococcus aureus infection should be treated for at least 3 weeks with appropriate antibiotic injections such as oxacillin, tobramycin, or claporans.
• And chronic osteomyelitis caused by Staphylococcus aureus infection is sometimes treated for 6 to 12 months. • Nowadays, treatment methods and treatment effects differ depending on whether you are infected with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) or non-methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.
• Orthopedic surgeons, pediatricians, and pediatric infectious diseases specialists often work together as members of a treatment team to treat each other.
• Bone with osteomyelitis can be fractured easily, so bone with osteomyelitis is treated with plaster and bandage fixation.
• Also, if necessary, drain the pus caused by osteomyelitis.
• Bacteria that cause osteomyelitis can infect other parts of the body, leading to sepsis and meningitis.
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제16권 소아청소년 정형외과 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제9권 소아청소년 소화기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제10권. 소아청소년 신장 비뇨 생식기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제11권. 소아청소년 심장 혈관계 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제12권. 소아청소년 신경 정신 질환, 행동 수면 문제
- www.drleepediatrics.com제13권. 소아청소년 혈액, 림프, 종양 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제14권. 소아청소년 내분비, 유전, 염색체, 대사, 희귀병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제15권. 소아청소년 알레르기, 자가 면역질환
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th — 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
-
Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, Harvey grant, and Robert Murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
-
The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
-
Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care
-
응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
-
Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
-
Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
-
Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
-
소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”