골반 내 염증성 질환(골반 내염/골반 염증 질환/골반염) Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
사진 2-15. 골반강(원내)
골반강 내 염증을 골반 내염이라고 한다.
Copyrightⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee,MD.FAAP
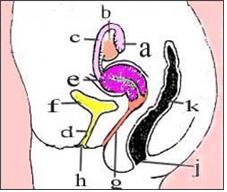
그림 2-16. 골반강 내 장기와 외요도구, 항문.
나팔관 (a), 난소(b), 난관(c), 요도(d), 자궁(e), 방광(f), 질강(g), 외요도구(h), 항문(j), 직장(k).
Copyrightⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee,MD.FAAP
-
임질균(N gonorrhoeae), 클라미디아균(C trachomatis), 가드렐라질균(Gardnerella vaginalis), 헤모필러스 인풀루엔자균(Hemophilus influenza), 마이코플라스마균(Mycoplasma), A군 연구균 또는 다른 종류의 연구균 등의 세균 감염으로 인해 자궁 내막염, 자궁 주위염, 난관염, 난소염, 난관–난소 농양, 골반강 내 복막염, 간 주위염 등이 생길 수 있다.
-
이런 종류의 골반강 내 염증을 통틀어 골반 내 염증성 질환, 골반 내염, 골반 염증성 질환이라 한다.
-
이 병은 복잡한 성관계를 하는 성인 여성들이나 사춘기 여아들에게 주로 생긴다.
-
골반 내염으로 외래 치료를 받은 사춘기 여아는 치료 후 48개월 이내에 성매개 감염병(Sexually transmitted infection/전염성 성병)에 걸리거나 골반 내염에 다시 걸릴 확률이 높다.
-
따라서 골반 내염을 최초로 치료하는 즉시 성 매개 감염과 골반 내염을 적극적으로 예방해야 한다(출처: Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine November 2008).
골반 내 염증성 질환의 증상 징후
-
원인, 세균의 종류, 급성 또는 만성, 병의 경과, 치료 여부 등에 따라 증상 징후가 다르다.
-
일률적 증상 징후가 없다.
-
열, 구토, 하복부 통증, 하복부 압통, 비정상적 질 분비, 불규칙 자궁 출혈, 열, 구토 등의 증상 징후가 생길 수 있다.
-
월경 후 이런 증상 징후가 시작되기도 한다.
-
증상 징후가 없을 때도 있고, 증상 징후가 경미할 수 있고, 비특이성 증상 징후가 주로 나타 나기 때문에 이 병에 결려 있는지 모르고 지낼 수 있다.
-
재발성 만성 골반 내염으로 변할 수 있고, 난관 임신이나 불임의 주원인이 될 수 있다.
골반 내 염증성 질환의 진단
-
병력, 성관계 유무, 증상 징후, 진찰, 여성 내진, 적혈구 침강 속도 검사(ESR), C-반응성 단백, 질 분비물로 임질균 및 클라미디아균 검사, 골반 강 초음파 검사 등의 결과를 종합해 진단한다.
-
때로는 자궁내막 생체 조직 검사, 골반 강 내 MRI 검사, 골반 강 내 초음파 검사 또는 골반 강 내시경 검사로 진단한다. Red book, 27th edition, 2006. p.495에 있는 진단 기준에 따라 진단한다.
골반 내 염증성 질환의 치료
-
골반 내염의 정도에 따라 다음 항생제 중 적절한 항생제를 선택해 병원 입원치료 또는 외래치료를 한다.
-
다음과 같이 여러 가지 방법으로 치료한다.
-
어디까지나 단골 소아청소년과 의사의 지시에 따라 치료 한다. 참고로 치료에 관한 정보를 여기에서 소개한다.
-
Cefotetan 2g, 12시간마다 혈관 주사 + Doxycycline, 100mg, 경구 또는 혈관 주사로 12시간 마다, 14일간 치료한다.
-
Cefoxitin 2g, 6시간마다 혈관 주사 + Doxycycline, 100mg, 경구 또는 12시간마다 혈관 주사로 14일간 치료한다.
-
Clindamycin 900mg 혈관 주사 + Gentamicin 2mg/kg, 혈관 주사 또는 근육 주사로 치료하고, 그 다음에 1.5mg/kg으로 유지 치료를 한다.
-
이상 제시한 주사로 치료하다가 치료 시작 후 24시간 내에 치료 효과가 상당히 있고 임상적으로 좋아지면, 항생제 주사 치료를 중지할 수도 있고, Doxycycline 100mg, 경구로 1일 2회 또는 Clindamycin 450mg을 1일 4회 경구로 14일간 치료한다.
-
Ofloxacin 400mg을 경구로 1일 2회 14일간 치료한다.
-
Ofloxacin 400mg을 경구로 1일 2회 및 Metronidazole 500mg 경구로 1일 1회 14일간 치료한다.
-
Levofloxacin 500mg을 1일 1회 경구로 14일간 치료한다.
-
Llevofloxacin 500mg을 1일 1회 경구로, Metronidazole 500mg을 경구로 1일 1회 14일간 치료한다.
-
Ceftriznone 250mg, 근육 주사, 1일 1회 치료한다.
-
Ceftriznone+ doxycycline+ metronidazole으로 치료한다.
-
Cefoxitin 2g, 근육 + probenecid 1g을 1회 + doxycycline으로 치료한다.
-
Cefoxitin + probenecid + doxycycline+metronidazole으로 치료한다.
-
Cephalosporin + doxycycline으로 치료한다.
-
Cephalosporin + doxycycline + metronidazole 등의 항생제로 치료한다.
-
이런 치료 방법은 아주 전문적인 감염병 학에 속한다. 그러나 비교적 흔한 성 매개 감염병(Sexually transmitted infection/전염성 성병)이기 때문에, 여기에 정보를 제공한다.
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) 골반 내 염증성 질환(골반 내염/골반 염증 질환/골반염)

Photo 2-15. Pelvic cavity (intra-hospital) Inflammation in the pelvic cavity is called pelvic endophthalmitis. Copyrightⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD.FAAP

Figure 2-16. Organs in the pelvic cavity, external ureters, and anus. Fallopian tubes (a), ovaries (b), fallopian tubes (c), urethra (d), uterus (e), bladder (f), vaginal cavity (g), external ureter (h), anus (j), rectum (k) . Copyrightⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD.FAAP
• N gonorrhoeae, Chlamydia bacteria (C trachomatis), Gardnerella vaginalis, Hemophilus influenza, Mycoplasma, group A research bacteria, or other types of research bacteria Bacterial infections such as endometritis, perimetritis, salpingitis, oophoritis, fallopian-ovarian abscess, peritonitis in the pelvic cavity, and perihepatic infection can occur.
• This type of inflammation in the pelvic cavity is called pelvic inflammatory disease, pelvic inflammatory disease, and pelvic inflammatory disease.
• This disease occurs mainly in adult women or girls in adolescence who have complex sexual intercourse. • Adolescent girls who have received outpatient treatment for pelvic endostitis are more likely to develop sexually transmitted infections or return to pelvic endoscopy within 48 months of treatment.
• Therefore, sexually transmitted infections and endopelvic inflammation should be actively prevented immediately upon initial treatment of endopelvicitis (Source: Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine November 2008).
Symptoms signs of inflammatory disease in the pelvis
• Symptoms and signs differ depending on the cause, type of bacteria, acute or chronic, disease course, and treatment.
• There are no signs of uniform symptoms.
• Symptoms may include fever, vomiting, lower abdominal pain, lower abdominal tenderness, abnormal vaginal discharge, irregular uterine bleeding, fever, and vomiting.
• Symptoms of these symptoms may begin after menstruation.
• Sometimes there are no signs of symptoms, symptoms can be mild, and symptoms of non-specific symptoms are usually present, so you may not know if you have the disease.
• It can turn into recurrent chronic pelvic pelvic inflammation and can be a major cause of fallopian tube pregnancy or infertility.
Diagnosis of inflammatory diseases in the pelvis
• Comprehensive diagnosis is made on the results of medical history, sexual intercourse, symptom signs, examination, female seismic examination, erythrocyte sedimentation rate test (ESR), C-reactive protein, gonorrhea and chlamydia test for vaginal secretions, and pelvic cavity ultrasound.
• Sometimes diagnosed by endometrial biopsy, MRI in the pelvic cavity, ultrasound in the pelvic cavity, or pelvic cavity endoscopy. Diagnosis is performed according to the diagnostic criteria in Red book, 27th edition, 2006. p.495.
Treatment of inflammatory diseases in the pelvis
• Depending on the degree of pelvic inflammatory disease, hospital inpatient or outpatient treatment is performed by selecting an appropriate antibiotic among the following antibiotics.
• Treated in several ways as follows.
• Treat according to the instructions of a regular pediatrician. For reference, information on treatment is introduced here.
• Cefotetan 2g, vascular injection every 12 hours + Doxycycline, 100mg, oral or vascular injection every 12 hours, 14 days.
• Cefoxitin 2g, intravenous every 6 hours + Doxycycline, 100mg, oral or intravenous every 12 hours for 14 days.
• Clindamycin 900mg vascular injection + Gentamicin 2mg/kg, vascular injection or intramuscular injection, followed by maintenance treatment with 1.5mg/kg.
• If the treatment with the above-mentioned injection is significantly effective and clinically improved within 24 hours after the start of treatment, the antibiotic injection treatment may be stopped, and Doxycycline 100mg, orally twice a day or Clindamycin 450mg 4 a day. It is treated for 14 days orally twice.
• Ofloxacin 400mg is treated orally twice a day for 14 days.
• Ofloxacin 400mg orally twice a day and Metronidazole 500mg once a day for 14 days. • Levofloxacin 500mg is treated orally once a day for 14 days.
• Treat Llevofloxacin 500mg once a day orally and Metronidazole 500mg once a day for 14 days.
• Ceftriznone 250mg, intramuscular injection, treated once a day. • Treated with Ceftriznone+ doxycycline+ metronidazole.
• Treat 2g of Cefoxitin, 1g of muscle + probenecid once + doxycycline.
• Treat with Cefoxitin + probenecid + doxycycline + metronidazole. • Treated with Cephalosporin + doxycycline.
• Treat with antibiotics such as cephalosporin + doxycycline + metronidazole.
• This treatment is a very specialized infectious disease. However, since it is a relatively common sexually transmitted infection, information is provided here.
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
www.drleepediatrics.com 제10권. 소아청소년 신장 비뇨 생식기 질환
www.drleepediatrics.com 제7권 소아청소년 감염병
Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th — 21st Edition
The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
Emergency care, Harvey grant and Robert Murray
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
Manual of Emergency Care
소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
소아과학 안효섭 외 대한교과서
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”