고환 종양 Testicular tumors
- 여러 종류의 양성 종양과 악성 종양이 고환에 생길 수 있다.
- 고환 종양은 남성에게 생기는 전체 종양의 2%를 차지한다.
-
고환 종양은 영아기부터, 80세까지 모든 연령층의 남성들에게 생길 수 있고, 왼쪽 고환보다 오른쪽 고환에 더 잘 생길 수 있다.
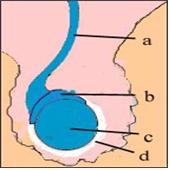
그림 2-23. 고환에 생긴 염증을 고환염이라 한다.
a-정관, b-부고환, c-고환, d-고환 초막.
Copyrightⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee,MD., FAAP
고환 종양의 원인
-
원인은 확실히 모른다. 외상을 입었던 고환, 쇠퇴 고환 또는 잠복 고환에 고환 종양이 더 잘 생길 수 있다.
-
특히 고환 종양은 절제 치료를 받지 않은 잠복 고환이나 고환 고정 수술 치료를 받은 고환에 더 잘 생길 수 있다.
-
또 한쪽에 잠복 고환이 있고 다른 쪽에 정상적인 고환이 있을 때 잠복 고환에 고환 종양이 날 가능성이 더 많다., 정상적인 고환에도 고환 종양이 생길 가능성이 있다.
고환 종양의 증상 징후
-
종양의 종류, 진행 정도와 전이 유무에 따라 증상 징후가 다르다.
-
종양이 있는 고환의 음낭은 무거운 감이 있고 아플 수 있다.
-
하찮은 고환 외상을 입고 보통 이상으로 고환 통증을 호소하면서 병원을 찾을 수 있다.
-
또 아프지도 않은데 응어리가 고환에서 만져질 수 있다.
고환 종양의 진단
-
병력·증상 징후·진찰소견 등을 종합해 고환 종양이 의심되면 혈중 β-hCG와 AFP 등을 검사하고, 고환 초음파 검사, 전신 CT 스캔 검사, 진단 고환 수술 등으로 진단한다.
고환 종양의 치료
-
조기에 진단해서 치료하면 100% 완치될 수 있으나, 신체의 다른 장기로 전이된 고환 종양은 생명에 위험할 수 있다.
-
고환 종양의 종류와 진행 정도에 따라 고환 절제 수술 치료, 방사능 치료, 악성 종양 화학 요법 등으로 치료할 수 있다.
고환 종양의 자가 조기 진단 법
-
모든 여성들이 유방암이 유방에 생겼는지 자가 조기 유방암 검진을 하는 것과 같이, 모든 남성들은 사춘기 때부터 일생동안 자가 고환 종양 검진을 해서 고환에 어떤 응어리가 있는지 알아보고, 어떤 응어리가 만져지거나 고환에 어떤 이상이 생기면 의사에게 곧 문의하여 진단 받아야 한다.
-
특히 고환 고정 수술을 받은 병력이 있는 사춘기 아이나 잠재고환이 있는 사춘기 아이는, 고환 종양이 생기는지 주기적으로 의사의 검진을 받아야 한다.
Testicular tumors 고환 종양
• Several types of benign and malignant tumors can develop in the testicles.
• Testicular tumors account for 2% of all tumors in men.
• Testicular tumors can occur in men of all ages, from infancy through the age of 80, and are more likely to develop in the right testicle than in the left testis.

Figure 2-23. Inflammation in the testicles is called orchitis. a- vas deferens, b- epididymis, c-testis, d-testis hut. Copyrightⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
Causes of testicular tumors
• The cause is not clear. Testicular tumors are more likely to develop in the injured, decaying, or latent testes.
• Testicular tumors in particular are more likely to develop in latent testicles that have not been resected or that have been treated with testicular fixation surgery.
• Testicular tumors are more likely to develop on the latent testis when there is a latent testicle on the other and a normal testicle on the other.
Symptoms signs of a testicular tumor
• Symptoms differ depending on the type of tumor, the degree of progression, and the presence or absence of metastasis.
• The scrotum of the tumorous testicle is heavy and can be sore.
• You may see a hospital with minor testicular trauma and unusual testicular pain.
• It is also not painful, but the core can be touched in the testicles.
Diagnosis of testicular tumor
• If a testicular tumor is suspected by combining medical history, symptoms, and examination findings, blood β-hCG and AFP are examined, and testicular ultrasound, whole body CT scan, diagnostic testicular surgery, etc. are used to diagnose.
Treatment of testicular tumors
• Early diagnosis and treatment can lead to 100% cure, but testicular tumors that have spread to other organs in the body can be life-threatening.
• Depending on the type and progression of the testicular tumor, it can be treated with testicular resection surgery, radiation therapy, and malignant tumor chemotherapy.
Early self-diagnosis of testicular tumors
• Just as all women have their own early breast cancer screening for breast cancer, all men have their own testicular tumor screening for life from puberty to find out what clumps are in the testicles, and what clumps are touched or what abnormalities in the testes are. If it occurs, you should contact your doctor immediately for a diagnosis.
• In particular, adolescent children with a history of testicular fixation surgery or adolescent children with latent testicles should see a doctor regularly for testicular tumors.
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
-
Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, Harvey grant, and Robert Murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
-
The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
-
Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care
-
응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
-
Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
-
Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
-
Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
-
Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics 14th ed. Beherman,
-
The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 18th edition
-
Red book 29th edition 2012
-
Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th Edition
-
Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
-
소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”