고환염 Orchitis
고환염의 원인과 개요
-
고환에 생긴 염증을 고환염이라고 한다.
-
박테리아나 바이러스 또는 다른 병원체 감염으로 인해 고환염이 생길 수 있다.
-
타박상으로 고환염이 생길 수 있다.
-
유행성 이하선염([부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다–소아가정간호백과]-제7권 소아청소년 감염병–볼거리 참조)을 앓을 때, 유행성 이하선염을 일으킨 이하선염 바이러스에 고환이 감염되어 이하선바이러스 고환염이 생길 수 있고,
-
이하선염 바이러스가 난소에 감염되어 이하선바이러스 난소염을 일으킬 수 있다.
-
유행성 이하선염 바이러스에 감염되어 이하선염은 생기지 않고 고환염에 만 감염되어 고환염만 생길 수도 있고,
-
유행성 이하선염 바이러스가 여아의 난소에만 감염되어 난소염만 생길 수 있다.
-
여기서는 유행성 이하선염 바이러스 감염으로 인한 고환염에 대해 주로 알아본다.
고환염의 증상 징후
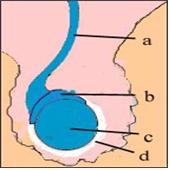
그림 2-23. 고환에 생긴 염증을 고환염이라 한다.
a-정관, b-부고환, c-고환, d-고환 초막.
Copyrightⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee,MD., FAAP
-
유행성 이하선염 바이러스 감염으로 생긴 고환염이 사춘기 남아에게 가끔 생길 수 있다. 그러나 사춘기 이전 남아들에게도 드물게 생길 수 있다.
-
유행성 이하선염 바이러스 감염으로 고환염과 부고환염이 동시에 생길 수 있다(그림 2-23).
-
고환염이 생긴 쪽의 음낭이 팽팽히 붓고 커질 수 있으며, 음낭의 피부가 빨갛게 발적될 수 있다.
-
고환염이 있는 고환을 만지면 매우 아플 수 있다.
-
고환염이 있는 쪽 정관과 요도에 통증이 생길 수 있으며, 그 쪽 아랫배가 아플 수 있다.
-
이런 증상 징후는 1~2주일 정도 지나면 자연히 없어진다.
-
고환염을 1차적으로 일으켰던 유행성 이하선염 바이러스가 신체의 다른 계통의 장기에 감염병을 일으킬 수 있고, 그 감염병으로 생긴 증상 징후가 함께 있을 수 있다.
-
열이 날 수 있고, 복통·관절통·두통 등의 증상 징후가 있을 수 있다.
-
그와 동시에 이하선염이 생기면, 이하선이 붓고 아플 수 있다.
고환염의 진단
-
병력·증상 징후·진찰소견을 종합해서 이 병을 진단할 수 있다.
-
드물게는 고환 염전으로 고환염이 생길 수 있고,
-
부고환 염전으로 고환이 심하게 아프고 붓는다. 고환염과 고환 염전 또는 부고환 염전 등을 서로 감별 진단하는 것이 중요하다.
-
고환 염전은 시간을 다투어 응급으로 수술 치료 해야 한다.
-
고환 염전을 의심되면, 의사에게 곧 문의하여 진단·치료를 응급으로 받아야 한다.
-
고환 초음파 검사는 진단에 큰 도움이 된다.
고환염의 치료
-
유행성 이하선염 바이러스 감염으로 생긴 고환염의 치료에는 특효약이 없다.
-
열이 나면서 고환이 아프면, 타이레놀 등 진통제로 해열 진통시킨다.
-
심하게 아플 때는 코데인이나 그보다 더 강력한 진통제로 치료할 수 있다.
-
서 있을 때 부은 고환과 음낭이 늘어지면, 고환염이 있는 고환이 더 아프다. 다 나을 때까지 누워 안정을 취한다.
-
붓고 아픈 고환을 탄력 붕대로 받치면 덜 아플 수 있다.
-
통증이 가시도록 찬물 찜질 치료도 할 수 있다.
-
양쪽 고환에 동시에 염증이 생길 수 있다.
-
그러나 한쪽 고환에 고환염이 더 잘 생긴다.
-
고환염이 다 나은 후에, 고환염이 생겼던 고환은 때로는 정상적으로 정자를 생산할 수 없다.
-
다행히 두 고환이 동시에 고환염이 걸리는 경우가 드물기 때문에 불임증이 생기는 경우는 드물다.
-
유행성 이하선염 백신이나 MMR 종합 백신 등으로 예방접종을 해서 이하선염 바이러스로 인한 볼거리와 고환염을 예방할 수 있다. 요즘 유행성 이하선염 바이러스로 인한 고환염은 드문 병이다.
-
유행성 이하선염 백신 예방접종에 관해서는 [부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다–제2권 소아청소년 질병 안전사고 예방 참조한다.
Orchitis고환염
Causes and overview of orchitis
• Inflammation of the testicles is called orchitis.
• Orchitis can be caused by bacterial, viral, or other pathogen infection.
• Bruises can lead to orchitis.
• When suffering from mumps (refer to [Parents should also be www.drleepediatrics.com-Volume 7 Child and Adolescent Infectious Diseases-Mumps), the testicles can be infected with the mumps virus that caused mumps, resulting in mumps virus orchitis.
• The mumps virus can infect the ovary and cause mumps virus ovary infection.
• Mumps infection may not occur due to mumps virus infection, but only orchitis may result.
• The mumps virus can only infect a girl’s ovaries, resulting in only ovariitis.
• Here, we mainly focus on orchitis caused by mumps virus infection.
Symptoms signs of orchitis

Figure 2-23. Inflammation in the testicles is called orchitis. a- vas deferens, b- epididymis, c-testis, d-testis hut. Copyrightⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
• Orchitis caused by mumps virus infection can occasionally develop in adolescent boys. However, it can be rare even in pre-adolescent boys.
• Mumps virus infection can cause orchitis and epididymitis at the same time (Figure 2-23).
• The scrotum on the side with orchitis may become swollen and enlarged, and the skin of the scrotum may become red and red.
• Touching testicles with orchitis can be very painful.
• Pain may occur in the vasectomy and urethra on the side of the orchitis, and the lower abdomen on that side may be painful.
• Symptoms of these symptoms disappear spontaneously after 1 to 2 weeks.
• The mumps virus, which primarily caused orchitis, can cause an infectious disease in other organs of the body, and there may be symptoms of the infectious disease.
• You may have a fever, and you may have symptoms such as abdominal pain, joint pain, and headache.
• If you develop mumps at the same time, the parotid glands can become swollen and painful.
Diagnosis of orchitis
• You can diagnose this disease by combining your medical history, symptoms, and examination findings.
• Rarely, testicular torsion can lead to orchitis,
• Epididymis torsion causes severe pain and swelling of the testicles. It is important to differentiate between orchitis and testicular torsion or epididymal torsion.
• Testicular torsion must be treated as an emergency surgery due to time consuming.
• If you suspect testicular torsion, you should contact your doctor right away for an emergency diagnosis and treatment.
• Testicular ultrasound is a great help in diagnosis.
Treatment of orchitis
• There is no specific drug for the treatment of orchitis caused by mumps virus infection.
• If the testicles hurt while having a fever, try to relieve fever with pain relievers such as Tylenol.
• When severely ill, it can be treated with codeine or a stronger pain reliever.
• If the swollen testicles and scrotum stretch while standing, the testicles with orchitis hurt more. Lie down and relax until you’re done.
• Swelling and sore testicles may be less painful if supported by an elastic bandage.
• Cold water treatment can also be done to relieve the pain.
• Both testicles may become inflamed at the same time.
• However, orchitis is more common on one testicle. • After orchitis has healed, the testicles that developed orchitis sometimes cannot produce sperm normally.
• Fortunately, it is rare for both testicles to develop orchitis at the same time, so infertility is rare.
• Mumps and orchitis caused by mumps virus can be prevented by vaccination with mumps vaccine or MMR comprehensive vaccine. These days, orchitis caused by the mumps virus is a rare disease.
• For mumps vaccination, refer to www.drleepediatrics.com-Volume 2 Prevention of Child and Adolescent Disease Safety Accidents.
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제10권. 소아청소년 신장 비뇨 생식기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제7권 소아청소년 감염병
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th — 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
- Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
- Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
- Emergency care, Harvey grant, and Robert Murray
- Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
- Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
- Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
- The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
- Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
- Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
- Manual of Emergency Care
- 응급환자관리 정담미디어
- 소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
- Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
- Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
- Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
- Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
- Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
- 소아과학 대한교과서
- 제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
- Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”