결핵(1), Tuberculosis(part 1)
(You may visit www.drleepediatrics.com – Volume 7,
Pediatric Adolescent Infectious Diseases or제 7권, 소아 청소년 감염병 질환 웹사이트)
결핵의 개요와 원인

사진 2-117.결핵균. 출처-CDC
- 마이코박테리움 투벨쿨로시스(Mycobcterium tuberculosis)균 감염으로 생기는 감염병을 결핵이라고 한다.
-
여기서는 마이코박테리움 투벨쿨로시스균을 편의상 “결핵균“이라 한다.
-
결핵균 감염으로 생긴 감염병은 결핵이라고 한다.
-
WHO 보고에 의하면 전 세계적으로 8백만 명이 결핵균에 감염되어 있고 3백만 명이 매년 결핵으로 죽는다고 한다.
-
미국에서는 년 약 1,000 명의 소아청소년들이 활동성 결핵(활동결핵)에 걸린다고 한다.
-
소아청소년 결핵은 5세 이전 영유아들에게 가장 흔히 생기고 그 다음은 사춘기 아이들에게 흔히 발생된다.
-
결핵균에는 사람 결핵균, 소 결핵균, 그 외 여러 종류의 결핵균이 있다.
-
사람 결핵균이 사람에게 감염되면 사람 결핵에 걸릴 수 있다.
-
때로는 사람이 소 결핵균에 감염되면 소결핵에 걸릴 수 있다. 그 외 다른 종류의 결핵균이 사람에게 감염되어 결핵을 앓을 수 있다.
-
그렇지만 대부분의 결핵은 사람 결핵균 감염으로 생긴다.
-
활동성 결핵이 폐에 있으면 활동성 폐결핵이라고 한다. 활동 폐결핵이 있는 사람이 기침을 할 때나 대화할 때 그 사람으로부터 나온 결핵균이 비말을 통해서 다른 사람들에게 감염될 수 있다.
-
또 결핵을 앓는 환자의 병소에 있는 결핵균이 가래 등을 통해 몸 밖으로 나와 다른 사람들에게 감염되면 결핵에 걸릴 수 있다.
-
폐 이외 신체 다른 부위에 있는 결핵 병소에 나온 피나 고름에 있는 결핵균을 코를 통해 기도로 흡인하거나 피나 고름에 직접 접촉될 때 결핵균에 감염될 수 있다.
-
신장 결핵이나 방광 결핵의 병소에 있는 결핵균이 소변을 통해 다른 사람에게 감염될 수도 있고 신체 다른 계통의 다른 기관이나 조직에 감염될 수 있다.
-
드물게, 결핵을 앓는 소에서 짠 생우유를 마셨을 때 소 결핵균에 감염되어 소결핵에 걸릴 수 있다.
-
활동성 결핵 병소에 있는 결핵균에 직접 접촉될 때 결핵균에 감염될 수 있다.
-
임신부가 활동성 결핵을 앓을 때 결핵균이 태아에게 감염될 때 선천성 결핵이 태아에게 생길 수 있다.
-
영유아들이나 영양실조 된 아이들, 어떤 원인으로든 쇠약한 아이들, 사춘기 아이들, 노약자들은 결핵에 더 잘 걸릴 수 있다.
-
결핵균이 신체의 어느 한 국소에 국한되어 감염된 후 그 국소에만 결핵이 생길 수 있고, 한정된 국소에 있던 결핵균이 신체의 여러 계통의 여러 기관, 조직으로 퍼져 그 부위에 결핵이 생길 수 있고 신체 내 한 국소에 있는 결핵 병소에 있는 결핵균의 수가 점점 더 증가된 후 전신으로 퍼져 결핵이 전신 여러 국소와 기관들에 생길 수 있다.
-
결핵균이 신체 어느 한 계통의 한 국소에 감염된 후 결핵균을 죽일 수 있는 결핵균 면역체가 몸에 자연적으로 생길 수 있다.
-
인체 내 생긴 자연 결핵균 면역체로 인해 인체 내로 감염됐던 결핵균이 항원항체반응으로 전부 죽기도 한다.
-
또 인체 내로 감염된 결핵 결핵균이 결핵 면역체로 인해 죽어서 결핵이 생기지 앓고 결핵병을 앓지 않게 될 수 있다.
-
그렇지만 결핵균이 체내에 감염됐을 때 결핵 면역체로 결핵균이 죽지 않을 때는 결핵 병이 발생되고 결핵을 앓게 된다.
-
이 때 인체의 한 국소에 국한되어 결핵이 생기든지 인체 여러 계통의 여러 부위에 결핵이 생길 수 있다. 이런 식으로 결핵이 폐에만 국한되어 생길 수도 있고 결핵이 폐 이외 다른 부위에도 생길 수 있다.
-
결핵균이 폐의 한 부위에 감염되어 한 부위에만 폐결핵이 생길 수도 있고 폐의 여러 부위에 감염될 수 있다.
-
일단 감염된 후 거기에 폐결핵이 생길 수 있다.
-
결핵균으로 폐가 처음으로 감염될 때는 폐문 림프절에 감염되는 경우가 가장 흔하다. 이렇게 생긴 폐결핵을 결핵성 폐문 림프절염이라 한다.
-
결핵성 폐문 림프절염을 일으켰던 결핵균이 폐의 다른 부위로 점점 더 퍼져 다른 부위의 폐에 폐결핵 병소가 또 생길 수 있다.
-
때로는 결핵균이 한쪽 폐의 일부분에만 국한되어 감염될 수 있고 그 결핵균이 폐 전체로 퍼질 수도 있다.
-
또 양쪽 폐 전체로 퍼질 수 있다. 이렇게 양쪽 폐 전체로 결핵균이 퍼져 생긴 폐결핵을 속립 결핵이라고 한다.
-
전술한바와 같이 폐결핵 병소에 있던 결핵균이 신체의 다른 부위로 퍼져 거기에 결핵이 생기기도 한다.
-
결핵균으로 인체의 어느 부위가 감염될 때 결핵균에 대한 인체의 저항력이 크면 클수록 결핵에 걸리지 않을 수 있고 결핵균이 더 이상 증식되지 않게 결핵균에 대항할 수 있는 결핵 면역체(결핵균 항체)가 생길 수 있다.
-
결국에는 인체에 침입한 결핵균이 결핵 면역체로 인해서 신체 내에서 다 죽게 된다. 이와 같이 결핵균이 인체 내에 감염되어도 결핵을 조금도 앓지 않고 결핵균의 감염이 있었는지 전혀 모르고 그냥 지낼 수 있다. 이런 경로로 결핵균에 감염되어 생긴 결핵을 불현성 결핵이라고 한다.
-
1960년대 한국에서 결핵을 앓았던 병력이 없는 20세 이상의 젊은이들에게 투베르쿨린 결핵 반응검사를 했을 때 투베르쿨린 결핵반응검사의 결과 거의가 양성으로 나타났었다는 연구결과도 있었다.
-
체내에 감염된 결핵균으로 불현성 결핵이 생기고 그 결핵균 감염으로 결핵이 더 이상 진행되지 않고 결핵균 면역체(항체)가 생겼던 사람들에게는 검사했던 투베르쿨린 결핵반응검사가 양성으로 나타나는 것이 보통이다.
-
1960년대 한국 젊은이들에게 투베르쿨린 결핵반응검사를 했을 때 양성으로 나타났던 이유는 아마도 그들이 불현성 결핵을 앓았기 때문일 것이다.
-
그 외로 다른 경우에도 투베르쿨린 결핵반응검사가 양성으로 나타날 수 있다. 더 자세한 것은 “투베르쿨린 검사, 결핵반응 검사, Tuberculin Test”를 참조한다.
-
결핵은 유전으로 생기는 병이 아니다.
-
그러나 결핵균에 감염된 태아가 태어난 후 선천성 결핵이 그 신생아에게 생길 수 있다.
-
어느 가족들에게는 결핵이 더 잘 생길 수 있다.
-
그 이유는 확실히 모른다. 그러나 그 가족들은 결핵균에 대한 저항력이 약해서 결핵에 더 잘 걸릴 수 있다고 추측한다.
-
결핵균이 신체 내 어느 부위에 침입해 현저한 결핵 병소가 생기기 전까지 결핵의 증상 징후가 나타나지 않을 수 있다.
-
다른 사람들에게 결핵균을 감염시키지도 않고 결핵의 증상 징후가 현저히 나타나지 않는 결핵을 비활동성 결핵 또는 잠복감염 결핵이라고 한다.
-
비활동성 결핵을 앓고 있던 아이에게 홍역이나 그 외 다른 종류의 급성 바이러스성 감염병이 생길 때, 또는 다른 병을 앓을 때 코르티코스테로이드제 등 어떤 종류의 약물로 치료받을 때 비활동성 결핵이 활동성 결핵으로 진전되어 결핵의 증상 징후가 갑자기 현저히 나타날 수 있다.
-
또 결핵균이 전신에 확 퍼질 수도 있고 또 신체의 한 기관이나 몇몇 기관에 퍼져 결핵 관절염, 결핵 뇌막염, 결핵 골수염, 결핵 신장염, 결핵 위장염, 결핵 림프절염, 결핵 늑막염 등 여러 종류의 결핵이 신체 여러 부위에 생길 수 있다. [부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다–소아가정간호백과]-제16권 소아청소년 정형외과 질환–결핵성 척추염, 결핵성 관절염 참조.
-
요즘, 외국에서 입양아로 들어오는 아이들에게 결핵발생률이 더 높다고 한다. 그 뿐만 아니라 외국에서 이민 온 사람들이나 여러 가지 목적으로 외국에 와서 장기간 체류하는 외국인들에게서 결핵 발생률이 더 높다고 한다.
-
따라서 각 나라에서 결핵관리에 신경을 더 많이 쓰고 있는 현 실정이다.
결핵의 증상 징후
-
결핵균이 신체의 어느 부위에 감염되어 어떤 종류의 결핵이 생겼는지
-
결핵 병소가 신체의 한 부위에만 있는지
-
또는 여러 부위에 있는지
-
결핵을 앓는 환아의 나이
-
활동성 결핵인지 비활동성 결핵인지
-
결핵균 감염력이 어느 정도 강력한지
-
결핵의 진행 정도에 따라 증상 징후가 다르다.
-
여기서는 폐결핵의 증상 징후에 대하여 주로 설명하기로 한다.
-
대부분의 경미한 폐결핵의 초기 얼마 동안 별다른 증상 징후가 없는 것이 보통이다.
-
폐결핵이 아주 경미할 때는 가슴 X-선 사진검사에 폐결핵 병소가 잘 나타나지 않을 수 있다.폐결핵의 초기의 증상 징후는 다양하다.
-
때로는 감기의 증상 징후와 비슷한 초기 결핵 증상 징후가 나타날 수 있다.
-
미열 내지 고열이 오랫동안 날 수 있고 때로는 원인불명의 열이 나기도 한다.
-
기침하면서 가래를 뱉고, 식욕이 떨어지고 체중이 감소될 수 있다.
-
이런 증상 징후가 몇 주 내지 몇 달 동안 계속될 수 있다.
-
폐결핵이 점점 더 진행되면서 폐결핵 병소가 폐의 상당한 부분을 차지할 때는 호흡곤란, 빈혈, 기침, 가래, 체중감소, 탈진, 미열 내지 고열, 각혈 등의 증상 징후가 생길 수 있다.
-
폐결핵 병소에 있는 결핵균이 신체 다른 부위로 퍼져 다른 부위에 여러 종류의 결핵이 생길 수 있다.
-
이 때 다른 계통의 다른 기관에 생긴 결핵으로 인한 결핵의 증상 징후가 따로 생기게 된다.
결핵의 잠복기
-
결핵균에 감염된 후 PPD 피부 반응 또는 타인 결핵 피부반응이 양성으로 나타나는 기간은 약 2~12주이고
-
결핵의 증상 징후가 나타나는 기간은 결핵에 따라 다르지만 약 6개월 내지 2년이다.
결핵의 진단
사진 2-118. 결핵을 진단하는데 쓰는 타인 테스트.
요즘 미 소아청소년과 학회에서는 타인 테스트 검사보다 PPD 피부 반응 검사를 더 권장한다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
사진 2-119. 결핵을 진단하기 위해 타인 테스트를 한다 .요즘은 PPD 검사를 주로 한다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
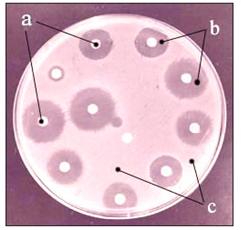
사진 2-120. 결핵을 가장 효과적으로 치료할 수 있는 항생제의 종류를 찾기 위해 결핵균 항균제 감수성 검사를 한다 a-각종 항생제 디스크, b-항생제 디스크 속에 있는 항생제로 인해 디스크의 바로 주위 세균 배양 배지에 결핵균이 자라지 않은 배지, c-결핵균이 자란 세균 배양 배지. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
-
병력, 증상 징후, 진찰소견, 결핵 피부반응 검사(PPD 피부 반응 검사나 타인 테스트), 가슴 X-선 사진검사, 결핵 병소가 있다고 의심되는 신체 부위 X-선 사진, 초음파 검사, CT 스캔 검사 또는 MRI 검사, 항산균(AFB)성 염색 현미경 검사, 결핵균 세균 배양 검사 등으로 진단할 수 있다.
-
한 집안 식구들 중 누군가가 결핵을 앓고 있는지 결핵 환자와 접촉했던 사실이 있는지 결핵을 앓고 있는 식구나 그 밖의 다른 사람과 접촉했으면 결핵을 진단하는 데 많은 도움이 된다.
-
결핵을 앓고 있는 환아에게 결핵 피부 반응검사를 하면 그 검사의 결과는 거의 양성으로 나타
-
난다.
-
그렇지만 결핵균이 신체에 감염된 후 결핵균 면역체가 형성되기 전 몇 주 동안은 결핵 피부 반응검사의 결과가 음성으로 나타날 수 있다.
-
잠복기에는 결핵 피부 반응검사가 음성으로 나타날 수 있다.
-
폐결핵이나 신체 다른 부위에 생긴 결핵병소가 아주 작을 때 검사한 가슴 X-선 사진이나 신체 다른 부위의 X-선 사진에 결핵 병소가 나타나지 않을 수 있다.
-
뇌척수액, 가래, 위액, 소변 등에서 피검 물을 채취해서 항산균성 염색 현미경 검사를 하고 결핵균 세균 배양 검사를 해서 확실히 진단할 수 있다.
-
영유아들이나 성인들 중 특히 여성들의 일부는 기침을 할 때 폐나 기관지 등 하기도 내에서 입안으로 나온 가래를 뱉어 내지 않고 위 속으로 삼키는 습관이 있다.
-
또 자는 동안 기침으로 나온 가래를 삼키는 소아들이 많다. 그들에게 폐결핵이 있다고 의심이 되면 아침에 잠자리에서 일어난 후 바로 작은 구위관을 입을 통해 위 속에 넣고 위액을 뽑아서 그 위액으로 결핵균 현미경 검사와 결핵균 세균 배양검사를 하여 진단할 수 있다.
-
결핵균 세균 배양검사를 하지 않고 결핵 치료를 시작할 수 있지만 결핵균 배양 검사로 어떤 종류의 결핵균에 의해서 폐결핵이 생겼는지 확실히 알고, 항균제 감수성 검사, 결핵균의 종류에 따라 가장 적절한 결핵 치료약을 선택해서 치료해야 치료 효과가 훨씬 좋다.
-
위액 이외, 늑막액, 뇌척수액, 침, 가래, 소변, 그 외 다른 결핵 병소에서 얻은 피고름, 생체 조직 검사 등으로 결핵균 현미경 검사와 결핵균 세균 배양 검사로 진단할 수 있다.
-
결핵성 림프절염이 의심되면 림프절염의 일부, 또는 전체 림프절을 피검물로 이용해 결핵균 현미경검사, 결핵균 세균 배양검사, 림프절 생체조직검사 등으로 림프절염이 결핵균 감염으로 생겼는지, 다른 원인으로 생겼는지 감별 진단할 수 있다.
-
그리고 결핵 피부 반응검사를 하면 거의가 양성으로 나타난다.
-
이 때 신체의 다른 부위에 결핵병소가 있는 것이 보통이다.
결핵 치료
-
결핵균의 종류, 결핵 병소, 중증도, 증상, 합병증의 유무, 나이 등에 따라 치료가 다르다.
-
결핵을 진단한 후 의사의 처방에 따라 결핵 치료약으로 적어도 6~12개월 동안 적극적으로 치료 받아야 한다.
-
어떤 종류의 결핵 치료약으로 결핵을 장기간 치료하면 결핵 치료약으로 부작용이 생길 수 있고 결핵균이 그 치료약에 내성이 생길 수 있다.
-
그러므로 가능한 한 결핵을 결핵약으로 치료를 시작하기 전에 정말로 결핵에 걸려 있는지 확실히 진단 받고 적절한 결핵약으로 치료를 시작하는 것이 대단히 중요하다.
-
결핵이 있다고 확실히 진단된 후 어떤 종류의 결핵 치료약이 그 결핵에 가장 치료 효력이 있는지 알기 위해 결핵균 항균제 감수성 검사를 하고 그 결과에 따라 결핵 치료약을 1~2 종류를 선택해서 치료하는 것이 이상적 결핵치료이다.
-
일반적으로 한 가지의 결핵 치료약으로 결핵을 치료되는 경우는 아주 드물다.
-
결핵균 항균제 감수성 검사로 알아낸 항 결핵 치료 약물 두세 가지나 그 이상 여러 가지 항 결핵 치료약을 써서 치료하는 것이 보통이다.
-
영유아기에서 사춘기까지 소아 결핵의 종류에 따른 치료 방법 참조.
-
과거에 결핵을 앓은 병력도 없고
-
결핵을 진단받았던 병력도 없고
-
결핵을 치료했던 병력도 없고
-
BCG 예방접종을 받았던 병력도 없고
-
현재 결핵의 증상 징후가 없는
-
35세 이하 젊은이들이나 소아청소년들에게 검사한 결핵 피부 반응검사, 보통 많이 쓰는 PPD 피부 반응 검사가 양성으로 나타나면 비활동성 결핵을 앓고 있다고 간주할 수 있다.
-
이런 비활동성 결핵을 적절히 치료하지 않으면 비활동성 결핵이 활동성 결핵으로 진전될 수 있고 악화될 가능성이 있고, 또 비활동성 결핵 병소에 있는 결핵균이 전신으로 퍼져 신체 각 부위에 더 많은 결핵이 생길 수 있다.
-
따라서 비활동성 결핵이 활동성 결핵으로 진전되는 것을 예방하고 더 악화되지 않게 아이나 (Isonizid) 결핵 치료약 또는 그 밖의 결핵 치료약물로 적어도 6~12개월 동안 치료하는 것이 보통이다.
-
아이나 결핵 치료 약물이나 다른 종류의 결핵 치료약물로 치료를 시작하기 바로 전, 치료 중, 그리고 치료를 다 한 후에 가슴 X-선 사진 검사나 그 외 적절한 신체 부위의 X-선 사진검사로 결핵이 잘 치료되었는지 확인해야 한다.
-
또 폐결핵 이외 신체의 다른 부위에 결핵이 생겨 있는지 진찰 진단을 받아야 한다.
-
자세한 결핵 약물 치료 방법은 다음 표를 참조한다.
표 2-18. 영유아, 학령기 아이들, 사춘기 아이들의 결핵 치료
| 결핵의 종류 | 치료 방법 | 참고 사항 |
| 잠복 결핵(Latent tuberculosis infection) 결핵 피부 반응이 양성이지만 결핵이 없는 경우 | 결핵균이 Isoniazid에 감수성이 있는 결핵은 9개월 동안 1일 1회 치료한다. | 9개월 동안 1일 1회 치료할 수 없으면 주 2회 직접 관찰적 치료를 할 수 있다. |
| 잠복 결핵(Latent tuberculosis infection) 결핵 피부 반응이 양성이지만 결핵이 없는 경우 | 결핵균이 Isoniazid 치료에 내성이 있는 결핵-6개월 동안 Rifampin 1일 1회 치료한다. | 6개월 동안 1일 1회 치료할 수 없으면 주 2회 직접 관찰적 치료를 할 수 있다. |
| 폐결핵과 폐결핵 이외 결핵 (결핵성 뇌막염은 제외) | 결핵균이 결핵 치료약에 감수성이 있으면 1일 1회 Isoniazid, Rifampin, Pyrazinamide으로 2개월 동안 치료한 다음 Isoniazid, Rifampin으로 4개월 동안 치료한다. | 만일 Isoniazid, Rifampin, Pyrazinamide에 내성이 있다고 의심되면 Isoniazid, Rifampin, Pyrazinamide에 Ethambutol 또는 Aminoglycoside를 가해 치료시작하고 항생제 세균감수성 검사를 하고 그 결과에 따라 약을 선택해 치료한다. |
| 폐결핵과 폐결핵 이외 결핵(결핵성 뇌막염은 제외) | 결핵 치료약에 감수성이 있으면 1일 1회 Isoniazid, Rifampin, Pyrazinamide으로 9~12개월 동안 치료한다. | 결핵 치료제에 감수성이 있으면서 폐문 림프절만 부어있으면 Isoniazid와 Rifampin으로 치료해도 충분하다. 초기에 직접 관찰하면서 주 2~3회 투약 치료해도 된다. |
| 결핵성 뇌막염 | 결핵균에 감수성이 있는 Isoniazid, Rifampin, Pyrazinamide, Aminoglycoside 또는 Ethambutol로 2개월 동안 치료하고 Isoniazid, Rifampin을 1일 1회 7~10개월 동안 치료하든지 주 2회 9~12개월 동안 치료한다. 결핵균 감수성이 있으면 Pyrazinamide으로 적어도 12개월 동안 치료한다. | 결핵균 항생제 감수성 검사의 결과가 나올 때까지 Aminoglycoside 등 4번째 결핵약으로 조기 치료를 한다. Streptomycin에 내성이 생기는 지역에서 사는 사람의 결핵은 Streptomycin대신 Kanamycin, Amikacin, 또는 Capreomycin으로 치료한다. |
출처:Red book
표 미국 잠복 결핵 치료법
| 최근 미국 잠복 결핵 치료법 | |||
| 약명 | 약 용량, mg | 투약 빈도 | 복용 기간 |
| 선호 요법 선택 약 | |||
| Isoniazid | 300 | 매일 | 9개월 |
| Isoniazid | 900 | 주 2회 | 9개월 직접 관찰 치료 |
| Isoniazid+rifapentine | 900+900 | 매주 | 12개월 직접 관찰 치료 |
| 교대 요법 선택 약 | |||
| Isoniazid | 300 | 매일 | 6 개월 |
| Isoniazid | 900 | 주 2회 | 6개월 직접 관찰 치료 |
| Rifampin | 600 | 매일 | 4개월 |
| 최근 미국 약 감수성 폐결핵 치료법 (7/18/2012) |
| 선호 약물 요법 투약 빈도 |
| 초기(첫 2개월) |
| Isoniazid+Rifampin+Pirazinamide+ ethambutol 매일, 주 2회, 또는 주 3회 |
| 계속 치료(마지막 4개월) |
| Isoniazid+Rifampin 주 2회, 또는 주 3회 |
| Isoniazid+rifapentine 매주 |
소스:JAMA JULY 18,2012
| 과거 잠재 결핵을 isoniazid제로 9개월 간 치료했다. 그 대신 isoniazid +rifapentine으로 3 개월간 치료 한 결과가 동등하게 좋은 치료 결과가 나왔다. 소스:N Engl J Med, October 31, 2011 |
결핵을 앓는 임신부에게 태어난 신생아의 결핵치료
-
결핵을 앓고 있는 임신부에게 태어난 신생아에게 산후 엄마가 앓는 결핵병소에 있는 결핵균이감염될 가능성이 많다.
-
결핵을 앓는 엄마로부터 결핵균이 신생아에게 더 이상 감염되지 않을 때까지 신생아를 엄마로부터 격리시켜야 한다.
-
엄마로부터 신생아를 격리시키기 바로 전에 신생아에게 결핵 피부 반응검사를 하는 것이 보통이다.
-
엄마로부터 결핵균이 아기에게 더 이상 감염될 가능성이 없다고 판정되면 더 이상 격리시킬 필요가 없다.
-
그러나 아기가 엄마에게로 돌아오기 전에 결핵 피부 반응검사를 다시 해보는 것이 보통이다.
-
엄마가 결핵치료 약물로 계속 치료받고 있는 중 결핵균이 아기에게 감염되지 않게 아이나 결핵 치료약으로 아기를 예방적 치료할 때도 있다.
-
이런 복잡한 결핵 치료는 그때그때 상황에 따라 의사의 판단에 따라 조금씩 다르게 할 수 있다.
결핵 치료와 음식물
-
결핵을 앓는 소아청소년은 이것저것 가릴 것 없이 균형 잡힌 최고 영양분이 있는 음식물을 충분히 먹는다.
-
아이나 결핵 치료약으로 치료를 받을 때는 피리독신이나 피리독신이 든 종합비타민을 꼭 복용해야 한다.
-
결핵을 앓는 환자가 특별한 음식물을 먹을 필요는 없다.
결핵 치료와 휴식
-
결핵을 앓는 소아 청소년도 피로하지 않을 정도로 평소와 같이 육체적 운동을 적절히 해도 된다. 휴식을 특별히 많이 취할 필요도 없고 신선한 곳에서 특별히 휴양할 필요도 없다.
-
다른 사람에게 결핵균을 감염시킬 가능성이 있을 때는 결핵 환자를 격리시켜야 한다.
-
대부분의 결핵은 결핵약으로 적절히 치료하면 결핵이 잘 치료된다.
-
그러나 결핵이 완치되었다는 의사의 진단이 내릴 때까지 결핵 치료약으로 열심히 치료하고 필요한 혈액검사 등을 해야 한다.
결핵 환자의 격리
-
환아의 결핵 병소에서 결핵균이 신체 밖으로 나올 수 있는 결핵을 개방성 결핵이라고 한다.
-
개방성 결핵병소에 있는 결핵균이 체외로 더 이상 나오지 않을 때까지 결핵환자를 격리시켜야 한다.
-
개방성 결핵이 아닌 결핵을 결핵 치료약으로 치료 시작하면서 환자를 더 이상 격리시킬 필요가 없다.
-
결핵치료약물로 치료 시작한 후 결핵의 증상 징후가 없고 건강하면 의사의 지시에 따라 등교해도 된다.
-
환자가 할 수 있는 육체적 운동은 평소와 같이 해도 된다.
결핵환자에 접촉했을 경우
-
결핵의 증상 징후가 있고, 결핵 피부 반응검사가 양성으로 나타나는 결핵 환자와 접촉했거나 같이 살았을 경우에는 바로 결핵 피부 반응검사를 하고 가슴 X-선 사진검사를 한다.
-
최근까지 결핵 피부 반응검사가 음성으로 나타났던 아이의 최근 결핵 피부 반응검사의 결과가 양성으로 전향되면 결핵에 걸린 것으로 간주하는 것이 보통이다.
-
가슴 X-선 사진에 결핵 병소가 나타나지 않고 결핵의 증상 징후가 하나도 없어도 그 결핵이 활동성 결핵으로 진전되지 않게 하고, 결핵균이 신체 다른 부위로 더 퍼져 다른 부위에 결핵 병소가 새로 더 생기는 것을 예방하기 위해 아이나 Isoniazid 결핵약 등으로 적어도 6~12개월 동안 치료하는 것이 보통이다.
-
활동성 결핵 환자와 접촉했을 때 환자와 접촉한 사람에게 결핵균이 감염될 가능성이 많이 있다.
-
그러므로 활동성 결핵 환자에 근접했던 아이에게 결핵 피부 반응검사를 해서 그 결과가 음성으로 나타나도 아이나 결핵약으로 3개월 동안 치료한 다음 다시 결핵 피부 반응검사를 반복해 본다.
-
이 때 결핵 피부 반응검사의 결과가 또다시 음성으로 나타나면 그 아이는 결핵균에 감염되지 않았다고 판단할 수 있고 아이나 치료를 더 이상 할 필요가 없다. [부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다–소아가정간호백과]-제2권 소아청소년 질병, 안전사고 예방-BCG 예방접종 참조.
BCG 백신 부작용
-
BCG 백신으로 결핵예방접종을 받은 후 예방접종을 받은 국소의 피부에 상흔이 생기는 확률은 79% 정도였고
-
그런 상흔이 있는 아이들에게 결핵예방이 더 잘 된다고 한다.
-
BCG 백신 예방접종으로 결핵균 감염병이 더 효과적으로 예방된다는 연구가 있다.
-
BCG 백신 예방접종을 BCG 백신 접종 받은 후 피하 농양, 맞은 주위 림프절 비대 또는 림프절염 등의 부작용이 1~2%에서 나타날 수 있으나 일반적으로 위중한 부작용은 BCG 예방접종으로 나타나지 않는 것이 보통이다.
-
아주 드물게 BCG 백신에 든 생 결핵균 골수염 등이 생길 수 있다.
-
만성으로 생긴 피하 농양이나 림프절염의 대부분은 자연적으로 치유되기 때문에 특별히 치료하지 않아도 된다.
-
그러나 이 문제에 조예가 더 깊은 의사와 상담하는 것이 좋다.
|
다음은 “결핵 반응 검사, 폐결핵, 결핵 림프절염”에 관한 인터넷 소아청소년 건강상담 질의응답의 예 입니다. |
Q&A. 결핵 반응 검사, 폐결핵, 결핵 림프절염
Q.
얼마 전 집안에 어른이 폐결핵으로 입원을 하게 되었습니다. 그래서 저희 아이들을(2살,5살) 결핵반응 검사를 하였는데 양성 구진1.5cm 라고 하더군요. 큰아이는 부어오른 상태고 작은 아이는 36시간 경과 후 수포형성 및 피멍이 들었습니다.
그래서 가슴 사진을 찍어 보니 큰아이는 X선 사진 상으로는 별다른 흔적은 없으나 가족 중에 환자가 있으니 예방약을 3개월 먹이라고 처방을 받았습니다.
그리고 작은 아이는 폐렴 증세가 있는데 5일 경과 후에 다시 사진을 찍어 놓은 상태이고 목 부분에 임파선이 조금 부어 있는데 결핵에 의한 것인지는 아직 모른다고 합니다.
일주일 후에 다시 병원을 가서 사진 결과를 보고 판단하여야 한답니다. 우선 처방은 3개월 예방약을 먹이고 그 후로 6개월 결핵약을 먹여야 할지도 모른다고 합니다.
그래서 결핵에 대한 박사님의 자료를 읽어보고 그동안 궁금하던 부분이 해소가 되었으나 그래도 모르는 부분이 있어 여쭈어 봅니다.
1. 결핵반응검사는 결핵균이 있는지를 검사 하는 게 아니라 결핵균에 대한 항체가 있는지 검사하는 것이라고 하는데 현재 저희 아이들이 검사한 항목은 반응검사와 가슴 X선 사진 외에는 하지 않아서 실제로 결핵이 걸려 있는지 아니면 앓고 지나갔는지, BCG 접종에 의한 양성 반응인지 모르는 상황에서 예방약을 먹여야 하는 것 인가요?
작은 아이 같은 경우 폐렴이라고 하는데 기침도 전혀 안하고 너무나 건강해 보이거든요. 그리고 전에는 모르는 사이에 앓고 지나간다는 얘기도 있던데 모르고 넘어가도 되었을 수도 있는데 괜히 하는 짓인지 모르겠습니다.
2. 그리고 3개월 동안 먹는 예방약은 무엇이고 3개월 후에 6개월간 먹는 결핵약은 어떤 차이 인지?
3. 저희 부부는 보건소에 가서 가슴 사진을 찍어 보았는데 현재는 이상이 없다고 나왔는데 그냥 가만히 있으면 되는 건지 아니면 애들과 같이 약을 먹어야 하는 건지? 저희 부부는 보건소에 가서 가슴 사진을 찍어 보았는데 현재는 이상이 없다고 나왔는데 그냥 가만히 있으면 되는 건지 아니면 애들과 같이 약을 먹어야 하는 건지? 두서없이 여쭈어 보아서 죄송합니다.
A.
안녕하세요. 질문해 주셔서 감사합니다. 참 좋은 질문입니다.
자녀의 나이, 성별, 과거 병력, 가족 병력, 진찰소견, 임상검사 등의 정보를 많이 알수록 답변을 드리는데 도움이 됩니다. 주신 정보를 토대로 해서 답변을 드리겠습니다.
사실 이런 질문의 답변은 소아청소년과 전문의 자격시험에도 날 수 있는 질문들입니다.
Q.
“그래서 저희 아이들을(2살, 5살) 결핵반응검사를 하였는데 양성 구진 1.5cm 라고 하더군요. 큰아이는 부어오른 상태고 작은 아이는 36시간 경과 후 수포형성 및 피멍이 들었습니다.”
A.
결핵 피부 반응 검사에는 PPD(정제 단백질유도체)피부 반응 검사도 있고 TINE 피부검사 등이 있습니다.
아마 PPD 피부 반응 검사를 했을 줄 믿습니다. PPD 피부 반응 결과가 1.5cm 구진으로 나타났으면
과거에 결핵을 앓고 나은 경우
불현성 결핵을 앓고 나은 경우
BCG 예방접종 백신을 받은 경우
현재 결핵을 앓고 있는 경우
위 경우 중 하나 또는 둘의 경우에 속할 수 있습니다. 보통 BCG 예방접종 백신을 받은 후 결핵피부 반응검사의 결과는 직경 1cm 정도 이하이고 반응의 정도가 약한 것이 일반적입니다. 그러나 결핵피부반응 검사의 결과가 1.5cm 이상이고 수포가 생겼고 가족 중 결핵을 앓는 환자가 있으므로 현재 결핵을 앓고 있다고 진단하고 결핵치료약으로 치료받는 것이 옳은 것 같습니다.
Q.
“그래서 가슴 사진을 찍어 보니 큰아이는 X선 사진 상으로는 별다른 흔적은 없으나 가족 증에 환자가 있으니 예방약을 3개월 먹이라고 처방을 받았습니다.”
A.
결핵균감염이 폐 이외에 신장, 위장 등에도 생길 수 있고 거기에 결핵 병소가 생겨 있을 수 있습니다. 가슴 X-선 사진이 정상이라고 해서 꼭 결핵 감염병이 폐에 없다고 단정할 수도 없습니다. 현재 증상 징후가 없더라도 결핵 환자로 간주하고 치료하는 것이 옳은 것 같습니다. 이에 의견이 담당의사의 의견과 다를 수도 있으니 담당의사의 지시를 따르시기 바랍니다.
Q.
“그리고 작은 아이 경우는 폐렴 증세가 있는데 5일 경과 후에 다시 사진을 찍어 놓은 상태이고 목 부분에 임파선이 조금 부어 있는데 결핵에 의한 것인지는 아직 모른다고 합니다. 일주일 후에 다시 병원을 가서 사진 결과를 보고 판단하여야 한 답변입니다.
우선 처방은 3개월 예방약을 먹이고 그 후로 6개월 결핵약을 먹여야 할지도 모른다고 합니다.”
A.
림프절 결핵이 있다고 의심되면 주사바늘이나 다른 방법으로 림프절 생체 조직을 채취해 결핵성 림프절염인지 아닌지 알아볼 수도 있고 또 결핵균 배양을 해서 진단할 수 있습니다.
결핵 피부 반응 검사의 결과가 양성이고 + 집안에 결핵 환자가 있고+ 가슴 사진 결과가 비정상이고+ 림프절염이 있으므로 저는 기다리지 않고 림프절 결핵이 있다고 진단하고 바로 결핵치료를 시작하겠습니다.
그러나 아침에 일어나자마자 위액을 비위관이나 구위관으로 빼어 결핵균 항산성 염색 현미경 검사와 결핵균 배양검사를 하고 림프절 생체조직 검사와 결핵균 항산성 염색 현미경 검사와 결핵균 배양검사를 치료를 시작하기 전에 꼭 하겠습니다. 그러나 여기에도 전문의 간의 치료의견이 다를 수 있습니다.
Q.
3개월 동안 먹는 예방약은 무엇이고 3개월 후에 6개월간 먹는 결핵약은 어떤 차이 인지?
A.
그 말씀이 무슨 말인지 확실히 모르겠습니다. 여기서는 결핵으로 진단하고 치료하기 때문에 예방하는 것이 아닙니다. (결핵 치료표를 참조하시기 바랍니다.)
Q.
저희 부부는 보건소에 가서 가슴 사진을 찍어 보았는데 현재는 이상이 없다고 나왔는데 그냥 가만히 있으면 되는 건지 아니면 애들과 같이 약을 먹어야 하는 건지?
A.
가슴 X-선에 대해서만 말씀하셨고 결핵 피부 반응 검사에 관해 말씀을 하시지 않았는데요. 저의 의견으로는 PPD 피부 반응 검사가 양성이고 아무 증상 징후가 없으면 두 가지 중 한 가지를 택하는 것이 좋을 것 같습니다.
여기서는 바로 의술(Healing art)이 통합니다.
즉 Isoniazid로 6개월 동안 치료하든지 3개월 동안 치료하고 가슴 X-선 사진을 다시 찍어보고 아무 이상이 없으면 그 약을 중지하는 방법도 있습니다.
그렇지만 저는 소아청소년과 의사이므로 성인들의 질병을 전문으로 하시는 내과의사에게 상의하셔서 결정하시기 바랍니다.
Q.
아이들의 감염성 여부입니다. 현재 상태에서 외부 활동을 해도 되는 건지?
A.
학령기 아이들이나 사춘기 아이들 경우는, 치료를 받고 증상 징후가 하나도 없는 비개방성결핵을 앓고 있는 상태이기 때문에 외부 활동을 할 수 있습니다.
영유들의 경우는, 가래에서나 위액에서 결핵균이 나오는지 확인하고 나오지 않으면 결핵 치료 약물로 치료를 받고 외부 활동을 시작할 수 있습니다.
좋은 질문이신데 그들의 학교 당국에 자녀들이 결핵에 걸려 있을지도 모른다는 사실을 알려주고 그 결핵을 앓는 자녀들과 접촉한 친구, 가족에게 자녀가 결핵에 걸려 있다는 사실을 알려 주시는 것도 극히 중요합니다.
어디서 결핵균에 감염되었는지, 접촉한 친구들의 부모들에게 이 사실을 알려 그들도 진찰 진단 예방치료를 받도록 하시고
더 자세한 질문은 소아청소년 감염병 전문의나 아기 아빠의 의사, 아기들의 의사에게 문의하시기 바랍니다.
소아청소년과에서 이 문제에 관해서 상담하시고 그 분의 치료와 예방적 치료를 철저히 받으시기 바랍니다.
결핵을 참조하시기 바랍니다.
질문이 더 있으면 다시 연락해 주시기 바랍니다.
참고로 아주 좋은 질문을 하셨고 질문 내용이 감염병을 전문하신 의사 선생님들보다도 더 잘 하셨습니다. 감사합니다. 이상원 드림
Tuberculosis(1) 결핵 (1)
Overview and causes of tuberculosis

Photo 2-117. Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Source-CDC
• An infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection is called tuberculosis.
• Here, Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacteria are referred to as “Tuberculosis bacteria” for convenience.
• Infectious diseases caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection are called Tuberculosis.
• According to a WHO report, 8 million people worldwide are infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis, and 3 million people die of tuberculosis every year.
• In the United States, about 1,000 children and adolescents a year are said to develop active tuberculosis (active tuberculosis).
• Tuberculosis in children and adolescents is most common in infants and young children before 5 years of age, followed by adolescents.
• Mycobacterium tuberculosis includes human Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Bovine Mycobacterium tuberculosis, and many other types of Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
• Human TB germs infecting humans can lead to human TB.
• Sometimes people can get sintered nuclei when they are infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Other types of Mycobacterium tuberculosis can infect humans and cause tuberculosis.
• Nevertheless, most tuberculosis is caused by infection with human Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
• If active tuberculosis is in the lungs, it is called active pulmonary tuberculosis. Activity When a person with pulmonary tuberculosis coughs or talks, the tuberculosis bacteria from that person can infect others through droplets.
• You can also get tuberculosis if the tuberculosis bacteria in the lesion of a patient with tuberculosis come out of the body through phlegm and infect other people.
• You can become infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis when you aspirate the tuberculosis bacteria in the blood or pus from tuberculosis lesions other than the lungs into the airways through your nose or come into direct contact with blood or pus.
• Mycobacterium tuberculosis, which is in the lesions of kidney tuberculosis or bladder tuberculosis, can infect others through the urine, or it can infect other organs or tissues in other systems of the body.
• In rare cases, drinking raw milk from a cow with tuberculosis can lead to infection with bovine tuberculosis bacteria and sintering.
• You can become infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis through direct contact with Mycobacterium tuberculosis inactive tuberculosis lesions.
• When a pregnant woman has active tuberculosis Congenital tuberculosis can develop in the fetus when the Mycobacterium tuberculosis infects the fetus.
• Infants, children who are malnourished, children who are debilitating for any reason, adolescent children, and the elderly are more susceptible to tuberculosis.
• Tuberculosis may be localized in one area of the body, and after infection, tuberculosis may occur only in that area, and tuberculosis may spread to various organs and tissues in various systems of the body, and tuberculosis may occur in the body. The number of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in localized tuberculosis lesions increases and then spreads throughout the body, causing tuberculosis to occur in many areas and organs throughout the body.
• After the Mycobacterium tuberculosis is infected in a local area of any system in the body, the body may naturally develop a Mycobacterium tuberculosis immune system that can kill the Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
• Due to the natural Mycobacterium tuberculosis immune system in the human body, all Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacteria, which have been infected in the human body, are killed by the antigen-antibody reaction.
• In addition, the infected tuberculosis Mycobacterium tuberculosis in the body dies from the tuberculosis immune system, which can lead to tuberculosis and not suffering from tuberculosis.
• However, when the Mycobacterium tuberculosis is infected and the Mycobacterium tuberculosis is not killed by the tuberculosis immune system, the tuberculosis disease develops and tuberculosis suffers.
• At this time, tuberculosis may occur due to localization of the body, or tuberculosis may occur in various parts of the body. In this way, tuberculosis can occur only in the lungs, or tuberculosis can occur in areas other than the lungs.
• Mycobacterium tuberculosis can infect one area of the lung, causing pulmonary tuberculosis in only one area, or it can infect multiple areas of the lung.
• Once infected, pulmonary tuberculosis can develop there.
• The first time a lung is infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis, it is most often infected with the lymph nodes in the lungs. This pulmonary tuberculosis is called tuberculous pulmonary lymphadenitis.
• Mycobacterium tuberculosis, which caused tuberculous pulmonary lymphadenitis, can spread more and more to other parts of the lung, resulting in another lesion of pulmonary tuberculosis in the lungs in other parts of the lung.
• Sometimes the Mycobacterium tuberculosis can be confined to one part of the lung and can become infected, and the Mycobacterium tuberculosis can spread throughout the lung.
• It can also spread to both lungs. Pulmonary tuberculosis caused by spreading the tuberculosis bacteria throughout both lungs is called sequela tuberculosis.
• As mentioned above, the tuberculosis bacteria in the pulmonary tuberculosis lesions spread to other parts of the body, causing tuberculosis there.
• When a part of the body is infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the greater the body’s resistance to Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the more likely it is that the person will not get tuberculosis, and the tuberculosis immune body (Mycobacterium tuberculosis antibody) that can fight the Mycobacterium tuberculosis so that the Mycobacterium tuberculosis does not proliferate anymore can develop.
• Eventually, the tuberculosis bacteria invading the human body die in the body due to the tuberculosis immune system. In this way, even if the tuberculosis bacteria are infected in the human body, they do not suffer from tuberculosis at all, and they can stay without knowing whether there was an infection with the tuberculosis bacteria. Tuberculosis caused by infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis through this pathway is called invisible tuberculosis.
• In the 1960s, when a tuberculin tuberculosis test was performed on young people 20 years of age or older without a history of tuberculosis in Korea, there was also a study showing that most of the tuberculin tuberculosis test results were positive.
• The tuberculosis test, which was tested, is usually positive for those who develop unexplained tuberculosis due to infected Mycobacterium tuberculosis, and tuberculosis is no longer progressing due to the Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection and the tuberculosis immunity (antibody) has been developed.
• The reason that the tuberculin tuberculosis test was positive for young Koreans in the 1960s is probably that they suffered from unexplained tuberculosis.
• In other cases, the tuberculin tuberculosis test may be positive. For more information, refer to “Tuberculin Test, Tuberculin Test,” Tuberculin Test.
• Tuberculosis is not a genetic disease.
• However, congenital tuberculosis can develop in the newborn after a fetus infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis is born.
• Some families are more likely to develop tuberculosis.
• I don’t know for sure why. However, their families speculate that they are more susceptible to tuberculosis due to their weak resistance to the tuberculosis bacteria.
• Symptoms of tuberculosis may not appear until the tuberculosis bacteria invade any part of the body and cause significant tuberculosis lesions.
• Tuberculosis is called inactive tuberculosis or latent tuberculosis that does not infect other people with the tuberculosis bacteria and does not show significant signs of tuberculosis.
• When a child with inactive tuberculosis develops measles or other types of acute viral infections, or when he or she is treated with some type of drug, such as corticosteroids, the progression of inactive tuberculosis to active tuberculosis. As a result, symptoms of tuberculosis can appear suddenly and noticeably.
• In addition, the Mycobacterium tuberculosis may spread throughout the body, and various types of tuberculosis, such as tuberculosis arthritis, tuberculosis meningitis, tuberculosis osteomyelitis, tuberculosis nephritis, tuberculosis gastroenteritis, tuberculosis lymphadenitis, tuberculosis pleurisy, etc., spread to various parts of the body. Can occur.
www.drleepediatrics.com-Vol. 16 Children and Adolescents Orthopedic Diseases-Tuberculous spondylitis, tuberculous arthritis.
• These days, it is said that the incidence of tuberculosis is higher among children entering adopted children from abroad. In addition, it is said that the incidence of tuberculosis is higher among immigrants from foreign countries and foreigners who come to foreign countries for various purposes and stay for a long time.
• Therefore, each country is paying more attention to tuberculosis management.
Symptoms, signs of tuberculosis
• What type of tuberculosis is caused by the infection of the tuberculosis bacteria in which part of the body
• whether tuberculosis lesions are in only one area of the body
• or in multiple areas
• The age of the child with tuberculosis
• Whether active tuberculosis or inactive tuberculosis
• How strong is mycobacterium tuberculosis infection?
• Symptoms and signs differ depending on the progression of tuberculosis.
• Here, we will mainly explain the symptoms and signs of pulmonary tuberculosis.
• Most mild pulmonary tuberculosis usually has no signs of symptoms during the initial period.
• When pulmonary tuberculosis is very mild, chest X-rays may not show pulmonary tuberculosis lesions well. The initial symptoms of pulmonary tuberculosis vary.
• Sometimes, early signs of tuberculosis symptoms similar to those of a cold may appear.
• Mild or high fever can last for a long time, sometimes with an unexplained fever.
• Spitting phlegm while coughing, loss of appetite and weight loss can occur.
• Signs of these symptoms can last for weeks to months.
• As pulmonary tuberculosis progresses more and more, symptoms such as dyspnea, anemia, cough, phlegm, weight loss, exhaustion, mild to high fever, and hemoptysis may occur when pulmonary tuberculosis lesions occupy a significant part of the lungs.
• Mycobacterium tuberculosis in pulmonary tuberculosis lesions can spread to other parts of the body, resulting in several types of tuberculosis in other areas.
• At this time, symptoms of tuberculosis due to tuberculosis in different organs of different strains will be produced separately.
The incubation period of tuberculosis
• After infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the PPD skin reaction or the other person’s tuberculosis skin reaction is positive for about 2 to 12 weeks.
• The duration of symptoms and signs of tuberculosis depends on tuberculosis, but is about 6 months to 2 years.
Diagnosis of tuberculosis

Photo 2-118. Other tests are used to diagnose tuberculosis. These days, the American Academy of Pediatrics and Adolescents recommends the PPD skin test more than other tests. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Photo 2-119. Other tests are done to diagnose tuberculosis. These days, the PPD test is mainly done. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Photo 2-120. In order to find the type of antibiotic that can most effectively treat tuberculosis, a susceptibility test for Mycobacterium tuberculosis is performed. a-Antibiotic discs, b-Antibiotics A medium in which the bacteria in the disc does not grow in the bacterial culture medium immediately surrounding the disc, c- Bacterial culture medium overgrown with Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
• Medical history, signs of symptoms, examination findings, tuberculosis skin test (PPD skin test or other test), chest X-ray, X-ray of the body part suspected of having a tuberculosis lesion, ultrasound, CT scan, or It can be diagnosed with MRI, anti-acid bacteria (AFB) staining microscopy, and Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacteria culture test.
• Whether someone in your household has tuberculosis or has been in contact with a tuberculosis patient, contact with a family member or other person with tuberculosis can be very helpful in diagnosing tuberculosis.
• When a tuberculosis skin test is performed on a patient with tuberculosis, the test results are almost positive.
• Flies.
• However, the results of the tuberculosis skin test may be negative for several weeks after the tuberculosis bacteria infect the body and before the tuberculosis immune system is formed.
• During the incubation period, the tuberculosis skin test may be negative. • When pulmonary tuberculosis or tuberculosis lesions in other parts of the body are very small, no tuberculosis lesions may appear on the chest x-rays or x-rays of other parts of the body.
• It is possible to reliably diagnose by collecting specimens from cerebrospinal fluid, sputum, gastric juice, urine, etc., performing a microscopic examination for mycobacterial staining, and performing culture of Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
• Some infants and adults, especially women, have a habit of swallowing phlegm into the stomach when coughing, without spitting out phlegm from the lower respiratory tract, such as the lungs or bronchi.
• Many children also swallow phlegm from coughing while sleeping. If they are suspected of having pulmonary tuberculosis, they can be diagnosed with a tuberculosis microscopic examination and a culture of Mycobacterium tuberculosis using the gastric juice by inserting a small gut tube into the stomach through their mouth immediately after waking up in the morning.
• Although tuberculosis treatment can be started without performing the tuberculosis bacteria culture test, it is necessary to know clearly what type of tuberculosis was caused by the tuberculosis bacteria culture test and to select and treat the most appropriate tuberculosis drug according to the antimicrobial susceptibility test and the type of tuberculosis bacteria. Is much better.
• In addition to gastric juice, pleural fluid, cerebrospinal fluid, saliva, sputum, urine, and blood pus obtained from other tuberculosis lesions, biopsy, etc., can be diagnosed through a microscopic examination of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and a culture of Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
• If tuberculosis lymphadenitis is suspected, a part of or all lymph nodes of lymphadenitis can be used as a specimen to differentiate whether lymphadenitis is caused by a Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection or other causes by microscopic examination of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, bacterial culture of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, and biopsy of lymph nodes.
• And most of them are positive when tested for tuberculosis skin.
• At this time, it is common to have tuberculosis lesions in other parts of the body.
Tuberculosis treatment
• Treatment differs depending on the type of tuberculosis bacteria, tuberculosis lesion, severity, symptoms, presence of complications, and age.
• After diagnosis of tuberculosis, you should be actively treated with tuberculosis drugs for at least 6-12 months as prescribed by your doctor.
• Long-term treatment of tuberculosis with some type of tuberculosis medication can cause side effects from tuberculosis medications, and tuberculosis bacteria can become resistant to the medication.
• Therefore, it is very important to ensure that you are diagnosed with tuberculosis and start treatment with appropriate tuberculosis medications before starting treatment for tuberculosis with tuberculosis drugs whenever possible.
• After being clearly diagnosed with tuberculosis, it is ideal to perform a tuberculosis antibacterial susceptibility test to find out which type of tuberculosis drug is the most effective treatment for the tuberculosis, and select one or two tuberculosis drugs according to the results. to be.
• In general, it is very rare to treat tuberculosis with a single tuberculosis drug.
• It is common to treat two or three or more anti-tuberculosis medications identified by a susceptibility test for Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
• From infancy to puberty, see how to treat tuberculosis by type in children.
• No history of tuberculosis in the past
• No history of being diagnosed with tuberculosis • No history of treating tuberculosis
• You have no history of getting vaccinated with BCG
• Currently no signs of tuberculosis
• If the tuberculosis skin test, which is tested on young people under the age of 35 or children and adolescents, is positive for the commonly used PPD skin test, it can be considered as having inactive tuberculosis.
• If this inactive tuberculosis is not properly treated, inactive tuberculosis can develop and worsen, and the tuberculosis bacteria in inactive tuberculosis lesions can spread throughout the body and cause more tuberculosis in each part of the body.
• Therefore, it is common to treat inactive tuberculosis with an Isoniazid tuberculosis medication or other tuberculosis medication for at least 6 to 12 months to prevent the progression to active tuberculosis and to prevent it from getting worse.
• Tuberculosis can be diagnosed with a chest x-ray or other appropriate body part immediately before, during, and after starting treatment with a child or tuberculosis medication or other tuberculosis medication. Make sure that it has been treated well.
• You should also get a medical examination to see if you have tuberculosis in other parts of the body other than pulmonary tuberculosis. • Refer to the following table for detailed tuberculosis drug treatment methods.
Table 2-18. Tuberculosis treatment for infants, school-age children, and adolescent children
표 2-18. 영유아, 학령기 아이들, 사춘기 아이들의 결핵 치료
Types of tuberculosis
| Types of tuberculosis | Treatment method | Note |
| Latent tuberculosis infection A positive skin reaction to tuberculosis but no tuberculosis | Tuberculosis, which is susceptible to Isoniazid by Mycobacterium tuberculosis, is treated once a day for 9 months. | If the treatment cannot be performed once a day for 9 months, direct observational treatment can be performed twice a week. |
| Latent tuberculosis infection A positive skin reaction to tuberculosis but no tuberculosis | When tuberculosis bacteria are resistant to Isoniazid treatment, Rifampin is treated once a day for 6 months. | If the treatment cannot be performed once a day for 6 months, direct observational treatment can be performed twice a week. |
| Pulmonary tuberculosis and tuberculosis other than pulmonary tuberculosis (excluding tuberculous meningitis) | If the Mycobacterium tuberculosis is susceptible to tuberculosis drugs, it is treated with Isoniazid, Rifampin, and Pyrazinamide once a day for 2 months, and then treated with Isoniazid and Rifampin for 4 months. | If it is suspected that there is resistance to Isoniazid, Rifampin, or Pyrazinamide, start treatment by adding Ethambutol or Aminoglycoside to Isoniazid, Rifampin, or Pyrazinamide, and perform an antibiotic bacteriological susceptibility test, and select a drug according to the result. |
| Pulmonary tuberculosis and tuberculosis other than pulmonary tuberculosis (excluding tuberculous meningitis) | If you are susceptible to tuberculosis drugs, treat with Isoniazid, Rifampin, and Pyrazinamide once a day for 9 to 12 months. | If there is susceptibility to tuberculosis treatment and only the lung lymph nodes are swollen, treatment with Isoniazid and Rifampin is sufficient. Dosing 2 or 3 times a week may be administered during direct observation at the beginning. |
| Tuberculous meningitis | Treatment with Isoniazid, Rifampin, Pyrazinamide, Aminoglycoside, or Ethambutol, which are susceptible to Mycobacterium tuberculosis, for 2 months, and Isoniazid and Rifampin once a day for 7 to 10 months or twice a week for 9 to 12 months. If you are susceptible to Mycobacterium tuberculosis, treat with Pyrazinamide for at least 12 months. | Treat early with a fourth tuberculosis drug such as aminoglycoside until the tuberculosis antibiotic susceptibility test results are obtained. Tuberculosis in people living in areas that are resistant to streptomycin should be treated with Kanamycin, Amikacin, or Capreomycin instead of Streptomycin. |
출처:Red book
Table US latent tuberculosis treatment 표 미국 잠복 결핵 치료법
| Recent U.S. latent tuberculosis treatment | |||
| Drugs | drug dose, mg | Dosing frequency | Dosing period |
| Preferred Therapy Choice Medicines | |||
| Isoniazid | 300 | everyday | 9 month |
| Isoniazid | 900 | Twice a week | Months direct observation treatment |
| Isoniazid+rifapentine | 900+900 | every week | 12 months direct observation treatment |
| Shift Therapy Choice Medicine | |||
| Isoniazid | 300 | everyday | 6 month |
| Isoniazid | 900 | Twice a week | 6 months direct observation treatment |
| Rifampin | 600 | everyday | 4month |
| Recent US drug-sensitive pulmonary tuberculosis treatment (7/18/2012) |
| Preferred medication regimen dosing frequency |
| Initial (first 2 months) |
| Isoniazid+Rifampin+Pirazinamide+ ethambutol 매일, 주 2회, 또는 주 3회 |
| Continue treatment (last 4 months) |
| Isoniazid+Rifampin 주 2회, 또는 주 3회 |
| Isoniazid+rifapentine every
Source: JAMA JULY 18,2012 In the past, latent tuberculosis was treated with isoniazid for 9 months. Instead, treatment with isoniazid +rifapentine for 3 months yielded equally good results. Source: N Engl J Med, October 31, 2011 소스:JAMA JULY 18,2012 |
Tuberculosis Treatment for Newborns Born to Pregnant Women with Tuberculosis
• Newborns born to pregnant women with tuberculosis are more likely to be infected with the tuberculosis bacteria found in the tuberculosis lesions of postpartum mothers.
• From mothers with tuberculosis, newborns should be isolated from mothers until the tuberculosis bacteria are no longer infecting the newborns.
• It is common for the newborn to have a tuberculosis skin test immediately before isolating the newborn from the mother.
• If the mother determines that the tuberculosis bacteria are no longer likely to infect the baby, she no longer needs to be quarantined.
• However, it is common for the baby to do her TB skin test again before returning to the mother.
• While the mother is still being treated with tuberculosis drugs, there are times when the baby is treated prophylactically with the child or tuberculosis drug to prevent the infection of the baby.
• Such complex tuberculosis treatment can be done slightly differently according to the judgment of the doctor depending on the situation at that time.
Tuberculosis Treatment and Food
• Children and adolescents with tuberculosis eat plenty of foods with the highest nutritional value in a balanced manner.
• When receiving treatment with a child or tuberculosis drug, you must take pyridoxine or a multivitamin containing pyridoxine.
• Patients with tuberculosis do not need to eat special foods. Tuberculosis Treatment and Rest
• Children and adolescents with tuberculosis may also exercise adequately as usual to avoid fatigue. You don’t have to take a lot of rest, and you don’t need to take a special rest in a fresh place.
• Patients with tuberculosis should be quarantined when there is a possibility of infecting other people with Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
• Most of the tuberculosis is treated well with tuberculosis drugs.
• However, until the doctor makes a diagnosis that tuberculosis is cured, you should treat it hard with tuberculosis drugs and do necessary blood tests.
Isolation of patients with tuberculosis
• Tuberculosis, in which tuberculosis bacteria can come out of the body in a patient’s tuberculosis lesion, is called open tuberculosis.
• Patients with tuberculosis should be quarantined until tuberculosis bacteria in open tuberculosis lesions no longer come out of the body.
• There is no longer a need to quarantine patients with TB treatment, which is not open TB, with TB drugs.
• After starting treatment with tuberculosis drugs, if there are no signs of tuberculosis and are healthy, you can go to school according to your doctor’s instructions.
• Physical exercises that the patient can do can be done as usual.
In case of contact with a tuberculosis patient
• If you have any symptoms of tuberculosis and have been in contact with or lived with a tuberculosis patient who has a positive tuberculosis skin test, you should immediately have a tuberculosis skin test and a chest x-ray.
• If the result of the recent TB skin test for a child whose skin test for tuberculosis was negative until recently turned positive, it is common to be considered as having tuberculosis.
• Preventing tuberculosis from progressing to active tuberculosis even if no tuberculosis lesions appear on the chest X-ray and no signs of tuberculosis are present, and prevents the spread of tuberculosis bacteria to other areas of the body and further tuberculosis lesions appear in other areas. It is usually treated with children or Isoniazid tuberculosis drugs for at least 6 to 12 months.
• When you come into contact with a patient with active TB, there is a high possibility that people who have come into contact with the patient will be infected with the TB bacteria.
• Therefore, if the child who was close to the active tuberculosis patient is tested for tuberculosis skin and the result is negative, the child or tuberculosis drug should be treated for 3 months, and then the tuberculosis skin test should be repeated.
• If the tuberculosis skin test result is negative again at this time, the child can be judged not to be infected with the tuberculosis bacillus, and the child or treatment is no longer required. [Parents should also be anti-doctors-Child and Family Nursing Encyclopedia]-Volume 2 Prevention of pediatric and adolescent diseases and safety accidents-Refer to BCG vaccination.
BCG vaccine side effects
• After receiving tuberculosis vaccination with BCG vaccine, the probability of developing a scar on the vaccinated topical skin was about 79%.
• Children with such scars are said to be better at preventing tuberculosis.
• There are studies showing that the BCG vaccination prevents Mycobacterium tuberculosis more effectively.
• BCG vaccination After receiving the BCG vaccination, side effects such as subcutaneous abscess, enlarged lymph nodes around the affected area, or lymphadenitis may occur in 1 to 2%, but in general, serious side effects do not appear with BCG vaccination.
• Very rarely, such as live tuberculosis osteomyelitis from the BCG vaccine can occur.
• Most of chronic subcutaneous abscesses or lymphadenitis heal naturally and do not require special treatment. • However, it is advisable to consult a doctor who is more versed in this matter.
The following is an example of the online pediatric and adolescent health counseling question and answer on “Tuberculosis Test, Pulmonary Tuberculosis, Tuberculosis Lymphadenitis”
Q&A.
Tuberculosis reaction test, pulmonary tuberculosis, tuberculosis lymphadenitis
Q.
Not long ago, an adult in the house was hospitalized for pulmonary tuberculosis. So, my children (2 years old, 5 years old) were tested for tuberculosis, and they said that they had a positive papule of 1.5cm.
The oldest child is swollen, and the smallest child has blistering and bruising after 36 hours. So when I took a picture of her breasts, there was no sign of the oldest child on the X-ray, but there was a patient in her family, so she was prescribed a preventive medication for 3 months. And she said that a small child has symptoms of pneumonia, and she has taken a picture again after 5 days, and she has a little swollen lymph gland in her neck, but she does not know yet whether it is caused by tuberculosis. She has to go back to the hospital a week later and look at the photo results to judge. First of all, the prescription is to give 3 months preventive medicine and then 6 months tuberculosis medicine. So, after reading your data on tuberculosis, my questions about tuberculosis have been resolved, but there are still areas I do not know, so I ask.
1. The tuberculosis reaction test is not to test for the presence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, but to test if there is an antibody against Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Should I be given a preventive drug when I don’t know if I have gone or if I have a positive response from the BCG vaccination? Small children are called pneumonia, but they don’t cough at all and they look very healthy. And before, there was a story that I was suffering without knowing, but it may have been okay to pass without knowing, but I do not know if it is for nothing.
2. And what are the preventive drugs taken for 3 months and what is the difference between the tuberculosis drugs taken for 6 months after 3 months?
3. My husband and I went to the public health center and took pictures of their breasts, and it turned out that there is nothing wrong now. Is it okay to just stay still or take medicine with the kids? My husband and I went to the public health center and took pictures of their breasts, and it turned out that there is nothing wrong now. Is it okay to just stay still or take medicine with the kids? Sorry for asking without question.
A.
Good morning. Thanks for asking. That’s a great question. The more information you know about your child’s age, gender, past medical history, family medical history, medical examination findings, and clinical examination, the more helpful it is to give you an answer. We will respond based on the information you provided. In fact, the answers to these questions are questions that may be asked on the pediatric and adolescent professional qualification exam.
Q.
“So, my children (2 years old, 5 years old) were tested for tuberculosis, and they said that they had a positive papule of 1.5cm. The old one was swollen and the small one had blisters and bruising after 36 hours.”
A.
There are also PPD (purified protein derivative) skin tests and TINE skin tests for a tuberculosis skin test. I’m sure you’ve done a PPD skin test. If the PPD skin reaction result is 1.5cm papules If you have had tuberculosis in the past and get better If you suffer from atypical tuberculosis and get better If you have been vaccinated against the BCG vaccine If you currently have tuberculosis You may fall into one or both of the above cases. Usually, after receiving the BCG vaccination, the results of the tuberculosis skin reaction test are less than 1cm in diameter and the degree of reaction is generally weak. However, as the result of the tuberculosis skin reaction test is more than 1.5cm, blisters have occurred, and there is a patient with tuberculosis in the family, it seems that it is correct to diagnose that you are currently suffering from tuberculosis and be treated with tuberculosis drugs.
Q.
“So, when I took a picture of her breasts, the oldest child showed no sign on the X-ray, but she had a patient with family ailments, so she was prescribed a preventive medication for three months.”
A.
In addition to the lungs, tuberculosis infection can occur in the kidneys and stomach, and tuberculosis lesions may develop there. Just because a chest X-ray is normal doesn’t necessarily mean that you don’t have a tuberculosis infection in your lungs. Even if there are currently no signs of symptoms, it seems to be the right thing to consider and treat as a tuberculosis patient. Therefore, your opinion may differ from that of your doctor, so please follow the instructions of your doctor.
Q.
“And in the case of a small child, he has symptoms of pneumonia, and he has taken pictures again after 5 days, and there is a little swollen lymph gland on his neck, and he does not know if it is caused by tuberculosis. That’s the answer. First of all, the prescription is to give 3 months preventive medicine and then 6 months tuberculosis medicine.”
A.
If you suspect that you have tuberculosis in the lymph nodes, you can use a needle or other method to collect living tissue from the lymph nodes to see if you have tuberculosis lymphadenitis, or you can culture the tuberculosis bacteria to diagnose. The result of the tuberculosis skin test is positive + there is a tuberculosis patient in the house + the chest photo result is abnormal + I have lymphadenitis. However, as soon as I wake up in the morning, I will drain the gastric juice through a nasogastric tube or an oral gastrointestinal tube to perform a Mycobacterium tuberculosis staining microscopic examination and a Mycobacterium tuberculosis culture test. However, treatment opinions among specialists may differ.
Q
. What is the preventive drug taken for 3 months and what is the difference between the tuberculosis drug taken for 6 months after 3 months?
A.
I’m not sure what that means. It is not prevented because it is diagnosed and treated as tuberculosis here. (Please refer to the tuberculosis treatment table.)
Q.
My husband and I went to the public health center and took pictures of their breasts, and it turned out that there is nothing wrong now. Is it okay to just stay still or take medicine with the kids?
A.
You only talked about chest x-rays, you didn’t talk about a tuberculosis skin test. In my opinion, if the PPD skin test is positive and there are no signs of symptoms, it would be a good idea to take one of two options. Here, healing artworks.
That is, treatment with Isoniazid for 6 months or for 3 months, taking a chest x-ray again, and stopping the drug if nothing is wrong.
However, since I am a pediatrician, please consult with a physician who specializes in adult diseases to make a decision.
Q.
Whether children are infectious. Can I do outside activities in my current state?
A.
In the case of school-age children or adolescent children, they can do outside activities because they have unopened tuberculosis with no signs of symptoms after being treated. In the case of infants and children, they can be checked for tuberculosis bacteria coming out of the sputum or gastric juice, and if they do not, they can be treated with tuberculosis drugs and begin outside activities.
That’s a good question, but it’s also extremely important to let their school authorities know that your children may have TB, and to let friends and family members who have come into contact with your children with TB know that your child has TB. Let them know where they were infected with the tuberculosis bacteria and the parents of friends they had contacted so that they can also receive medical checkups, diagnosis, and preventive treatment. For more detailed questions, please contact your pediatric and adolescent infectious disease specialist, your baby’s father’s doctor, or your baby’s doctor. Please consult with the Department of Pediatrics and Adolescents about this problem and receive thorough treatment and preventive treatment from him. See tuberculosis. If you have more questions, please contact us again. For reference, you asked a very good question, and the content of the question was better than the doctors who specialized in infectious diseases. Thank you. Lee Sang-won. MD
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
-
www.drleepediatrics.com제7권. 소아청소년 감염병
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th- 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
- Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
- Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
- Emergency care, harvey grant and robert murray
- Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
- Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
- Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
- The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
- Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
- Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies , Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
- Manual of Emergency Care
- 응급환자관리 정담미디어
- 소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
- Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
- Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
- Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
- Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
- Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
- 소아과학 대한교과서
- 제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
- Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”