결핵균성 척추염 Tuberculous spondylitis
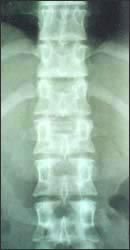
사진 147. 전 후면 흉부 척추 X선 사진.
척추 관절에 생긴 결핵균성 감염병을 결핵성 척추 관절염이라 한다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
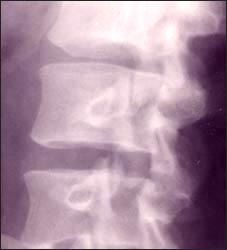
사진 148. 측면 요부 척추 X선 사진
요부 척추에 생긴 결핵균성 감염병을 결핵균성 요부 척추염이라 한다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
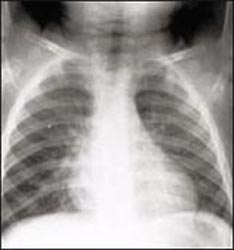
사진 149. 전 후면 가슴 X선 사진
결핵균성 척추염이 있으면 폐결핵 등 다른 결핵이 신체의 다른 부위에 있나 알아보기 위해 가슴 X선 사진 검사 등을 한다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
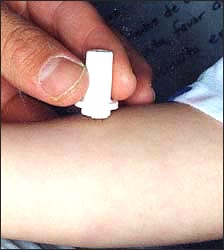
사진 150. 결핵균성 척추염을 진단하기 위해 투베르쿨린 결핵 피부반응 검사나 PPD결핵 피부반응 검사 등을 한다. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
결핵균성 척추염의 원인
- 척추 체에 결핵균이 감염되어 생긴 척추감염을 결핵균성 척추염이라 한다.
- 결핵균성 척추염을 결핵균성 척추골염, 또는 척추 결핵이라 한다.
- 신체의 다른 부위에 있는 1차성 결핵병 병소에 있던 결핵균이 척추로 감염되어 척추에 2차성 결핵 감염이 생기거나,
- 신체의 다른 부위에 결핵균성 감염병의 병소가 없는데도 결핵균이 척추에 1차적으로 직접 감염되어 1차성 결핵균성 척추염이 생길 수 있다.
- 결핵병을 앓는 가족이나 친구 등으로부터 결핵균이 감염될 수 있다.
- 또 본인이 결핵균성 척추염을 않을 때 그 척추염 병소에 있는 결핵균이 환아 자신의 폐, 신장, 또는 그 외의 다른 계통의 다른 기관으로 2차 감염성 폐결핵이나 2차 감염 결핵균성 신장염 등을 일으킬 수 있다.
결핵균성 척추염의 증상 징후
- 결핵균성 척추염의 중증도·합병증의 유무·나이·어느 부위의 척추에 결핵균성 감염이 생겼느냐에 따라 증상 징후가 다르다.
- 결핵균성 척추염은 비교적 서서히 진행된다.
- 말로 증상 징후를 잘 표현할 능력이 없는 어린 영유아가 이 병에 걸리면 보채고 기운이 없이 시름시름 앓을 수 있다.
- 결핵균성 척추염의 병소에 있던 결핵균이 척추염의 병소의 바로 주위에 있는 근육, 척추, 또는 그 외 다른 계통의 신체 부위로 감염되어 다른 종류의 결핵균성 감염병이 생길 수 있다.
- 결핵균성 척추염이 생긴 등뼈에 통증이 생길 수 있다.
- 척추염 부위에 있는 척수 신경근에서 나온 말초신경이 마비될 수 있고
- 그 말초신경이 분포되어 있는 근육도 마비되고 근육기능이 상실될 수 있고 감각 장애가 피부에 생길 수 있고 피부의 모든 감각이 상실될 수 있다.
- 결핵균성 척추염이 생긴 척추의 종류에 따라 등이나 허리가 뻣뻣해지고, 구부렸다 폈다 하기가 어려워진다.
- 결핵균성 척추염은 전체 척추 중 어느 척추에도 생길 수 있지만 흉부 척주의 척추에 가장 많이 생긴다.
- 그 다음으로 허리에 있는 요부 척주의 척추에도 생긴다.
- 결핵균이 척추에 감염되어 그 척추가 파괴될 때 등이나 허리가 앞으로 구부러져 척주 전만증이 생기거나 뒤로 구부러져 척주 후만증 또는 등뼈가 옆으로 구부러져 척주 측만증이 생길 수 있다.
- 이 때 척추염이 생긴 척추가 쪼그라들거나 파괴되고 척추염이 생긴 척추 부위에 있는 척수 신경근에서 나오는 말초신경이 손상될 수 있다.
- 그렇게 되면 손상된 말초신경이 분포된 근육이 완전히 마비될 수 있다.
- 다행히도 요즘 이 정도 진행된 결핵성 척추염은 보기가 드물다.
결핵균성 척추염의 진단
- 병력·증상 징후와 진찰소견 등을 종합해 이 병이 의심되면 가슴 X선, 척추 X선, 척추 CT 스캔, 척추 MRI 사진 등의 검사로 진단할 수 있다.
- 피·가래·소변검사, 항산성 염색 현미경 결핵균 세균검사, 결핵균 세균 배양검사 등으로 진단한다.
- PPD 결핵 피부반응 검사나 투베르쿨린 결핵 피부반응 검사를 하면 반응이 양성으로 나타난다. 이런 검사를 총 종합해 진단할 수 있다.
결핵균성 척추염의 치료
- 결핵균성 척추염이 진단되면 소아청소년과 전문의와 정형외과 전문의·소아 신경외과 전문의·소아 신경내과 전문의, 소아 감염병과 전문의 등이 한 치료 팀의 멤버가 되어 이 병을 치료하는 것이 이상적이다.
- 결핵균성 척추염을 앓을 때 그 환아의 신체의 다른 계통에도 결핵균성 감염병 병소가 더 있을 가능성이 있다.
- 따라서 신체의 다른 계통도 진찰받아 결핵 감염병이 있으면 그것도 함께 치료해야 한다.
- 결핵균이 누구로부터 감염되었나 그 감염원을 알아본다.
- 결핵균을 전염시킨 사람도 함께 치료받아야 한다.
- 결핵균성 척추염은 아이나, 에탐부톨 등의 결핵약으로 치료한다.
- 결핵균 항균제 감수성검사에서 얻은 결과에 따라 적절한 항 결핵약으로 치료할 수 있다.
- 상당히 진행된 결핵균성 척추염은 척추 수술 치료를 받아야 할 때도 있다.
- 브래드포드 플레임 장치 치료나 척추 석고 붕대 고정 치료로 척추를 고정시켜 치료해주기도 한다. [부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다-소아가정간호백과]-제7권 소아청소년 감염병-폐결핵 참조)
결핵균성 척추염의 감별진단
- 골수염 (Osteomyelitis)
- 급성 관절염과 패혈성 관절염(감염성 관절염) (Acute arthritis and septic arthritis)
- 연소성 류마토이드 관절염 (Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis)
- 박테리아 고관절염 (Bacterial arthritis of hip/Septic hip arthritis)
- 결핵균성 관절염 (Tuberculosis arthritis)
- 일과성 활막염 (Transient synovitis/Toxic synovitis)
Tuberculous spondylitis 결핵균성 척추염

Picture 147. Anterior and posterior thoracic spine X-ray. Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection of the vertebral joints is called tuberculous spondyloarthritis. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP

Picture 148. Lateral lumbar spine X-ray Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection of the lumbar spine is called Mycobacterium tuberculosis lumbar spondylitis. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP

Picture 149. Anterior and posterior chest X-ray If you have Mycobacterium tuberculosis spondylitis, a chest X-ray is done to check for other tuberculosis, such as pulmonary tuberculosis, in other parts of the body. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP

Picture 150. To diagnose Mycobacterium tuberculosis spondylitis, a tuberculin tuberculosis skin test or PPD tuberculosis skin test is performed. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
Causes of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Spondylitis
• Spinal infection caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection in the vertebral body is called Mycobacterium tuberculosis spondylitis.
• Mycobacterium tuberculosis spondylitis is called Mycobacterium tuberculosis spondylitis, or tuberculosis of the spine.
• Infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis from primary tuberculosis lesions in other parts of the body, resulting in secondary tuberculosis infection of the spine;
• Even though there are no lesions of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in other parts of the body, Mycobacterium tuberculosis may directly infect the spine and cause primary Mycobacterium tuberculosis spondylitis.
• Mycobacterium tuberculosis can be transmitted from family members or friends with tuberculosis disease. • Also, when the person does not have Mycobacterium tuberculosis spondylitis, the Mycobacterium tuberculosis in the spondylitis lesion can cause secondary infectious pulmonary tuberculosis or secondary infection Mycobacterium tuberculosis nephritis to the patient’s own lungs, kidneys, or other organs.
Symptoms, signs of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Spondylitis
• Symptoms and signs of Mycobacterium tuberculosis spondylitis vary depending on the severity, presence of complications, age, and where the Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection occurred in the spine.
• Mycobacterium tuberculosis spondylitis progresses relatively slowly.
• Young infants who are not able to verbally express symptoms and symptoms may suffer from irritability and lack of energy when ill with this disease.
• Mycobacterium tuberculosis in the lesion of Mycobacterium tuberculosis spondylitis can infect the muscles, spine, or other parts of the body immediately adjacent to the lesion of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, resulting in other types of Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection.
• Pain in the spine with Mycobacterium tuberculosis spondylitis may occur.
• Peripheral nerves from the spinal nerve roots at the site of spondylitis may be paralyzed and
• The muscles to which the peripheral nerves are distributed may also be paralyzed and lose muscle function, sensory disturbance may occur in the skin, and all sensations in the skin may be lost.
• Depending on the type of spine in which Mycobacterium tuberculosis spondylitis occurs, the back or lower back becomes stiff, making it difficult to bend and straighten.
• Mycobacterium tuberculosis spondylitis can occur in any vertebra of the entire spine, but it occurs most often in the thoracic spine.
• Next, it occurs in the lumbar spine in the lower back.
• When Mycobacterium tuberculosis infects the spine and destroys the spine, it can cause lordosis by bending the back or lower back, or kyphosis by bending backwards or scoliosis by bending the spine to the side.
• In this case, the spondylolisthesis vertebrae may shrink or be destroyed, and the peripheral nerves from the spinal nerve roots in the spondylolisthesis area may be damaged.
• Doing so can result in complete paralysis of the muscles to which the damaged peripheral nerves are distributed.
• Fortunately, tuberculous spondylitis of this degree is rare these days.
Diagnosis of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Spondylitis
• If the disease is suspected by combining the medical history, symptoms, and examination findings, it can be diagnosed with chest X-rays, spine X-rays, spine CT scans, and spine MRI images.
• Diagnosis is made by blood, sputum, and urine tests, acid-staining microscopic examination of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, and culture of Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
• PPD tuberculosis skin test or tuberculin tuberculosis skin test results in a positive reaction. These tests can be combined to make a diagnosis.
Treatment of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Spondylitis
• When Mycobacterium tuberculosis spondylitis is diagnosed, it is ideal for a pediatrician, an orthopedic surgeon, a pediatric neurosurgeon, a pediatric neurosurgeon, and a pediatric infectious disease specialist to become members of a treatment team to treat the disease. to be.
• If you have Mycobacterium tuberculosis spondylitis, there may be more lesions of Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection in other systems of the child’s body.
• Therefore, other systems of the body should also be examined, and if there is a tuberculosis infection, it should be treated as well.
• Find out who was infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis and the source of the infection.
• People who have transmitted tuberculosis must also be treated.
• Mycobacterium tuberculosis spondylitis is treated with tuberculosis drugs such as Aina or ethambutol.
• Depending on the results obtained from the Mycobacterium tuberculosis antibacterial drug susceptibility test, it can be treated with an appropriate anti-tuberculosis drug.
• Highly advanced Mycobacterium tuberculosis spondylitis may require spinal surgery.
• Bradford flame device treatment or spinal plaster fixation treatment may be used to fix the spine. www.drleepediatrics.com – Volume 7 Infectious Diseases in Children and Adolescents – See Pulmonary Tuberculosis)
Differential diagnosis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis spondylitis
• Osteomyelitis
• Acute arthritis and septic arthritis
• Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis
• Bacterial arthritis of hip/Septic hip arthritis
• Tuberculosis arthritis
• Transient synovitis/Toxic synovitis
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제16권 소아청소년 정형외과 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제9권 소아청소년 소화기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제10권. 소아청소년 신장 비뇨 생식기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제11권. 소아청소년 심장 혈관계 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제12권. 소아청소년 신경 정신 질환, 행동 수면 문제
- www.drleepediatrics.com제13권. 소아청소년 혈액, 림프, 종양 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제14권. 소아청소년 내분비, 유전, 염색체, 대사, 희귀병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제15권. 소아청소년 알레르기, 자가 면역질환
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th — 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
-
Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, harvey grant and robert murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
-
The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
-
Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies , Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care
-
응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
-
Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
-
Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
-
Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Berverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gerhon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
-
소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”