갑상설관 낭 Thyroglossal duct cyst
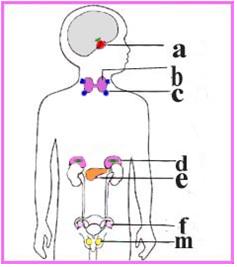
그림 1-34. 갑상선과 그 외 내분비선 해부도.
a-뇌하수체,
b- 갑상선,
c-부갑상선,
d-췌장,
e-부신,
f-난소,
m-고환 등은 내분비선들이다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
갑상설관 낭의 개요
- 혓바닥의 맨 뒤 부분을 혀뿌리라고 한다. 적어도 임신 6주 될 때까지 태아의 혀뿌리에 있던 태아기 갑상선은 갑상설 관(갑상혀 관)을 통과한 후 아래 턱 바로 밑에 있는 앞 목의 피부층 아래 부위로 이동되는 것이 정상적이다.
- 태아의 혀뿌리 부위 속에 있던 태아기 갑상선이 아래 턱 바로 밑 앞 목 부위의 피부층 아래로 이동된 후 갑상설관은 정상적으로 자연히 완전히 막힌다.
- 목의 앞부분으로 이동 된 후 갑상선은 평생 동안 그 부위에 자리 잡고 있는 것이 정상이다.
- 갑상선 설관이 막힌 이후에도, 때로는 갑상설관에 조그마한 주머니(낭)가 비정상적으로 생길 수 있다.
- 그 주머니를 갑상 설관 낭(甲狀舌管 囊/갑상 혀관 낭)이라고 한다.
- 태어날 때까지 정상적으로 막혀야 할 갑상선 설관이 태어난 후에도 비정상적으로 막히지 않고 열려 있을 수 있다.
- 그 막히지 않고 열려있는 갑상선 설관이 혀뿌리 속에서부터 앞 목에 있는 피부층 아래에 있는 갑상선까지 연결되어 있을 수 있다.
- 갑상선 설관 낭은 아래 턱 바로 밑 앞 목 중앙 부위에 있는 피하층 하에 가장 흔히 생겨 있다.
갑상설관 낭의 증상 징후
- 대부분의 갑상설관 낭은 육안으로 쉽게 볼 수 있을 정도로 크지 않다. 그렇지만 갑상설관 낭 속에 체액이 조금 괴면 눈에 띌 정도로 더 커진다.
- 세균이 갑상설관 낭 속에 감염되면 낭이 곪을 수 있다.
- 아래 턱 바로 밑 앞 목 중앙에 있는 갑상 설관 낭이 곪아 부을 수 있다.
- 이 때 육안으로 그것을 쉽게 볼 수도 있고 손으로 만져볼 수 있고 손으로 누르면 아플 수 있다.
- 갑상 설관 낭이 곪지 않고 그 속에 체액만 괴어 있을 수 있다.
- 갑상 설관 낭은 커졌다 작아졌다 할 수 있고 혓바닥을 입 밖으로 내밀거나 침을 삼킬 때마다 커진 갑상 설관 낭이 조금 움직이는 것을 볼 수 있다.
- 드물게는 갑상 설관 낭이 터져서 낭 속에 있던 고름이나 진물이 농루(膿瘻)를 통해 목 앞쪽 피부 층 밖으로 흘러나올 수 있다.
갑상 설관 낭의 진단 치료
- 병력, 증상 징후, 진찰소견 등을 종합해서 이 병을 진단한다.
- 드물게 갑상선이 정상 위치에 있지 않은 이소성 갑상선을 갑상 설관 낭으로 오진할 수 있다.
- 갑상설관 낭에 갑상선이 붙어 있을 수 있다.
- 이런 갑상 설관 낭과 갑상선을 수술로 전부 절제할 수 있다.
- 따라서 갑상 설관 낭 수술 제거 치료를 하기 전에 갑상선 방사선 요소 스캔 등으로 갑상선이 어디에 있는지 확인한 후 갑상설관 낭만 수술절제를 해야 한다.
- 갑상설관 낭이 곪았을 때는 우선 적절한 항생제로 치료해 준 후 다 나은 후에 수술로 치료해 준다.
Thyroglossal duct cyst 갑상설관 낭

Figure 1-34. Anatomy of the thyroid gland and other endocrine glands. a-pituitary gland, b- thyroid gland, c-parathyroid gland, d-pancreas, e-adrenal, f-ovary, The m-testis and the like are endocrine glands. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
Overview of the thyroid duct cyst
• The back part of the tongue is called the tongue root. It is normal for the prenatal thyroid gland, which was at the root of the fetus’ tongue until at least 6 weeks of pregnancy, to pass through the thyroid duct (thyroid duct) and then move to the area under the skin layer of the anterior neck, just under the lower jaw.
• After the prenatal thyroid gland, which was in the fetal tongue, has moved under the skin layer in the front neck area just under the lower jaw, the thyroid duct is normally and completely blocked.
• After moving to the front of the neck, it is normal for the thyroid gland to remain in that area for life. • Even after an obstruction of the thyroid glandular duct, sometimes a small sac (sac) in the thyroid gland may develop abnormally. • The pouch is called the thyroid glandular sac (甲狀舌管囊/thyroid glandular sac).
• The thyroid gland duct, which must be blocked normally until birth, may remain abnormally unblocked and open after birth.
• The unobstructed open thyroid gland duct may extend from the root of the tongue to the thyroid gland beneath the layer of skin in the anterior neck.
• The thyroid glandular sac is most commonly formed under the subcutaneous layer in the middle of the anterior neck just below the lower jaw.
Symptoms, signs of a thyroid duct cyst
• Most thyroid cysts are not large enough to be easily seen with the naked eye. However, a little bit of fluid in the sac of the thyroid duct makes it noticeably larger.
• If the bacteria infect the cyst in the thyroid duct, the cyst can fester.
• The sac of the thyroid gland, located in the middle of the anterior neck just under the lower jaw, may fester and swell.
• At this point, you can easily see it with the naked eye, you can touch it with your hand, or it can hurt when you press it with your hand.
• The thyroid glandular sac may not fester and contain only body fluids in it.
• The thyroid glandular sac may become large or small, and the enlarged glandular sac may move slightly whenever the tongue is pushed out of the mouth or when saliva is swallowed.
• In rare cases, the cyst of the thyroid duct may burst, causing pus or ooze in the sac to flow out of the layer of skin in front of the neck through the fistula.
Diagnosis, treatment of thyroid glandular cyst
• Diagnose this disease by synthesizing medical history, symptoms, and examination findings.
• Rarely, an ectopic thyroid gland in which the thyroid gland is not in its normal position can be misdiagnosed as a thyroid glandular sac.
• The thyroid gland may be attached to the sac of the thyroid duct.
• All of these cysts and thyroid glands can be surgically removed.
• Therefore, before performing the surgical removal of the thyroid ductal sac, the thyroid gland should be checked where the thyroid gland is located, such as by a thyroid radiation element scan, and then a romantic surgical resection of the thyroid duct is required.
• When the thyroid duct cyst is festered, first treat it with an appropriate antibiotic and then treat it with surgery after it is healed.
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com제14권. 소아청소년 내분비, 유전, 염색체, 대사, 희귀병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제6권 신생아 성장 발육 육아 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제9권 소아청소년 소화기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제10권. 소아청소년 신장 비뇨 생식기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제11권. 소아청소년 심장 혈관계 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제12권. 소아청소년 신경 정신 질환, 행동 수면 문제
- www.drleepediatrics.com제13권. 소아청소년 혈액, 림프, 종양 질환
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th — 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
-
Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, Harvey grant, and Robert Murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
-
The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
-
Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care
-
응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
-
Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
-
Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
-
Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
-
소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”