갑상선 기능 항진증과 그레이브스병 Hyperthyroidism and Graves’ disease
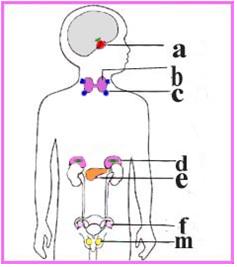
그림 1-34. 갑상선과 그 외 내분비선 해부도.
a-뇌하수체,
b- 갑상선,
c-부갑상선,
d-췌장,
e-부신,
f-난소,
m-고환 등은 내분비선들이다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
갑상선 기능 항진증의 원인
-
그레이브스병(비만성 중독성 갑상선종/Graves’ disease)-자가면역 질롼,
-
갑상선 양성 종양,
-
뇌하수체 양성 종양,
-
난소 종양
-
고환 종양,
-
바이러스성 갑상선염,
-
과량 갑상성 호르몬 섭취,
-
옥도 과잉 섭취 등으로 갑상선 호르몬이 정상 이상으로 더 많이 분비되어 생기는 병을 갑상선 기능 항진증이라고 한다.
-
다시 설명하면, 그레이브스 병 등 갑상선 항원 항체 이상 반응으로 갑상선 기능 항진증이 생길 수 있고,
-
갑상선 기능 항진성 악성 종양이나
-
그 외 갑상선 종양,
-
급성 화농성 갑상선염,
-
맥큔 알부라이트 증후군,
-
갑상선 자극 호르몬 과잉 등으로 갑상선 호르몬이 비정상적으로 더 많이 분비될 때도 갑상선 기능 항진증이 생길 수 있다.
-
그레이브스 병은 어느 연령층 아이들에게도 생길 수 있으나 11~15세 더 흔히 생길 수 있다.
-
갑상선 기능 저하증은 영유아들, 학령기 아이들에게도 생길 수 있지만 갑상선 기능 항진증은 사춘기 아이들에게 더 잘 생기고 사춘기 남아들보다 사춘기 여아들에게 더 잘 생긴다.
-
여기서는 주로 그레이브스 병에 관해서 설명한다.
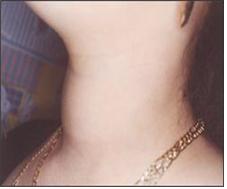
그림 1-38. 갑상선 비대.
갑상선 기능 항진증이 있고 갑상선이 비대해졌다. 15세 사춘기 여아의 목의 중앙 앞부분이 갑상선 비대로 두드러지게 나와 있다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
그레이브스 병(비만성 중독성 갑상선종)의 증상 징후
-
그레이브스 병은 일종의 갑상선 기능 항진증(Hyperthyroidism)이고 갑상선 기능이 정상 이상으로 항진되는 갑상선 병 중 하나이다.
-
원인과 중증도 등에 따라 증상 징후가 다르지만 전형적인 증상 징후는 다음과 같다.
- 아이들에게 생기는 그레이브스 병을 소아 그레이브스병이라고 한다.
- 그레이브스 병의 약 5%는 15세 이전 아이들에게 생기고 소아 그레이브스 병은 사춘기 아이들에게 가장 잘 생긴다.
- 특히 사춘기 여아들에게 더 잘 생긴다.
- 이 병의 증상 징후는 6~12개월 정도 걸려 서서히 나타나는 것이 보통이다.
- 이 병에 걸리면 그 동안 침착하고 공부를 잘 했던 아이가 정서적으로 불안해지고 학교 성적이 점점 떨어지며 운동신경이 전반적으로 항진될 수 있다.
- 가슴이 두근거릴 수 있고 깜짝깜짝 잘 놀랠 수 있다.
- 비정상적으로 땀이 많이 나고 신경이 예민해지고 하찮은 이유로 잘 흥분되고 화를 잘 내며 잘 울 수 있다.
- 이 병으로 식욕이 항진돼서 더 잘 먹지만 체중은 정상적으로 잘 늘지 않고 오히려 줄 수 있다.
- 갑상선이 두드러지게 비대 돼서 목 앞 부위에 있는 갑상선 부위가 육안으로 볼 수 있게 불룩 두드러지게 나올 수 있다.
- 그러나 때로는 육안으로 쉽게 볼 수 없을 정도 비대해 질 수 있다.
- 심할 때는 두 안구가 두드러지게 앞으로 튀어나와 안구 돌출증이 생길 수 있다. 이런 증상이 서서히 오는 것이 보통이다. 그리고 안구 후 압박감과 통증, 안검이 느러지거나 당겨올라가고, 안와 주위 부종, 결막 부종, 공막 충혈혈, 림프 조직 증식, 복시 등 눈 병이 생길 수 있다
- 빈맥, 숨 가쁨, 심장 비대, 부정맥, 고혈압, 체온 상승, 수면장애, 심신쇠약, 피부가 차고 피부 습기가 더 있고, 구토, 피부 소양증, 수전증, 탈모증, 설사, 고혈압, 얼굴이 화끈거림, 두통, 월경 불순, 간장비대 등의 증상 징후가 생길 수 있다.
그레이브스 병(비만성 중독성 갑상선종)의 진단
-
병력, 증상 징후와 진찰소견 등을 종합해서 이 병이 의심되면
-
혈 중 갑상선 호르몬 농도–티록신(T4)이 증가,
-
유리 티록신(T4),
-
트리요오드타리로닌(T3) 증가되고,
-
유리 트리요오드타리로닌(T3),
-
갑상선 자극 호르몬(TSH) 농도가 감소되고,
-
혈중 갑상선 글로불린(Tg) 농도,
-
혈중 티록신결합글로불린(TBG) 농도,
-
갑상선자극호르몬(TSH) 수용체 항체 농도 등을 검사해서 진단한다.
- 필요에 따라 갑상선 방사핵종 스캔 검사, 갑상선 초음파 검사, 신피그래피 검사, 방사능 옥도(옥소, 요오드) 섭취 검사 등으로 다른 병과 감별 진단할 수 있다.
-
■ 갑상선 기능 검사
|
갑상선 장애
|
TSH 갑상선 자극 호르몬 |
T4 티록신 |
유리 티록신 |
|
1차성 갑상선 기능 항진증 |
저하 |
증가 |
증가~낮은 치 정상 |
|
1차성 갑상선 기능 저하증 |
증가 |
저하 |
저하 |
|
시상 하부/ 뇌하수체 갑상선 기능 저하증 |
증가, 저하, 정상 |
저하 |
저하 |
|
TBG 결핍증 |
정상 |
저하 |
정상 |
|
정상 갑상선 병 증후군 |
증가, 저하, 정상 |
저하 |
저하~낮은 치 정상 |
|
갑상 선 자극 호르몬 분비 선정 또는 뇌하수체 정항 증 |
증가~정상 |
증가 |
증가 |
|
보상성 갑상선 기능 저하증 |
증가 |
정상 |
정상 |
참조 및 소스:HARVARD MEDICAL SCHOOL, Endocrine CONTROVERSIES IN ADULT PRIMARY CARE PRACTICE MAY15~16 2015
Nelson Pediatrics Textbook 19th Ed
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th ed
그레이브스 병(비만성 중독성 갑상선종)의 치료
-
소아 그레이브스 병은 갑상선 일부 적출 수술치료나 방사능 옥소 치료로 치료하는 것보다 프로필지오유라실(Propylthiouracil/PTU)과 Methimazole(Tapazole)로 주로 치료한다.
-
소아 그레이브스 병이 약물로 치료되지 않거나 다른 이유가 있을 때 갑상선의 일부 적출 수술이나 방사능 옥도 치료를 하기도 한다.
-
프로필지오유라실과 Methimazole(Tapazole)으로 치료 중 일시적 호중구 감소증, 두드러기, 간염, 간 기능부전증, 혈관염 등의 부작용이 생길 수 있다.
-
6년 이상 계속 약물 치료를 해야 할 때도 있다.
-
안구 돌출증이 심하게 생기거나 복시가 생기면 스테로이드제로 치료할 수 있다.
-
Propranolol 및, 또는 Methylprednisolone으로 대증치료를 할 때도 있다.
Hyperthyroidism and Graves’ disease 갑상선 기능 항진증과 그레이브스병

Figure 1-34. Anatomy of the thyroid gland and other endocrine glands. a-pituitary gland, b- thyroid gland, c-parathyroid gland, d-pancreas, e-adrenal, f-ovary, The m-testis and the like are endocrine glands. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP Causes of hyperthyroidism
• Graves’ disease (obesity addictive goiter)-autoimmune disease,
• benign thyroid tumors,
• benign pituitary tumor,
• ovarian tumor
• testicular tumors,
• viral thyroiditis,
• excessive thyroid hormone intake,
• Hyperthyroidism is a disease caused by the secretion of more thyroid hormone than normal due to excessive consumption of jade.
• In other words, hyperthyroidism may occur due to abnormal reactions to thyroid antigen antibodies such as Graves’ disease,
• Hyperthyroidism malignant tumor or • other thyroid tumors,
• acute purulent thyroiditis,
• McQueen Albulite syndrome,
• Hyperthyroidism can also occur when abnormally higher levels of thyroid hormones are secreted, such as due to an excess of thyroid-stimulating hormone.
• Graves’ disease can occur in children of any age, but it can be more common between the ages of 11 and 15.
• Hypothyroidism can also occur in infants and school-age children, but hyperthyroidism is more prevalent in adolescent children and is more prevalent in adolescent girls than in adolescent boys.
• This section mainly deals with Graves’ disease.

Figure 1-38. Hypertrophy of the thyroid gland. I have hyperthyroidism and my thyroid gland is enlarged. The central anterior part of the neck of a 15-year-old adolescent girl is prominent with an enlarged thyroid gland. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP Signs of symptoms of Graves’ disease (obesity addictive goiter)
• Graves’ disease is a type of hyperthyroidism and is one of the thyroid diseases in which thyroid function is more than normal.
• Symptoms and signs vary depending on the cause and severity, but typical symptoms are as follows. o Graves disease in children is called childhood Graves disease.
o About 5% of Graves’ disease occurs in children before the age of 15, and childhood Graves disease is most prevalent in adolescent children.
o It looks especially good for girls in adolescence.
o Symptoms of this disease usually take 6 to 12 months and appear gradually.
o If you get this disease, the child who has been calm and studied well during that time may become emotionally anxious, school grades gradually decline, and overall motor nerves may be enhanced.
o Your heart may be pounding and you may be surprised and startled.
o Abnormally sweaty, nervous, well-excited, angry, and able to cry well for insignificant reasons.
o I eat better because I have an increased appetite from this disease, but I can’t gain weight normally, but rather give it.
o The thyroid gland is markedly enlarged and the area of the thyroid gland in the front of the neck can be seen as a prominent bulge to the naked eye.
o However, it can sometimes become so enlarged that it cannot be easily seen with the naked eye.
o In severe cases, both eyes protrude prominently, causing bulging eyes. It is common for these symptoms to come slowly. In addition, eye diseases such as pressure and pain after the eyeball, the eyelids are loose or pulled, swelling around the orbit, conjunctival edema, scleral congestion, lymphatic tissue proliferation, and diplopia can occur
o Tachycardia, shortness of breath, heart enlargement, arrhythmia, high blood pressure, body temperature rise, sleep disturbance, mental and physical weakness, cold skin and more moisture, vomiting, skin itching, tremors, alopecia, diarrhea, high blood pressure, burning face, headache , Menstrual irregularities, liver disease, etc. Symptoms may occur.
Diagnosis of Graves’ disease
• If you suspect this disease by combining your medical history, symptoms, and examination findings,
o Thyroid hormone concentration in blood-thyroxine (T4) increases, o free thyroxine (T4),
Triiodotarironin (T3) is increased,
o Free triiodotarironine (T3),
o Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) concentration is reduced,
o Thyroid globulin (Tg) concentration in the blood,
o Thyroxine-binding globulin (TBG) concentration in blood,
o It is diagnosed by testing the concentration of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) receptor antibody.
o If necessary, a thyroid radionuclide scan, a thyroid ultrasound, a neophyte, and a radioactive oxo (oxo, iodine) intake test can be used to differentiate and diagnose other diseases.
Thyroid function test 갑상선 기능 검사
|
Thyroid disorder |
TSH thyroid-stimulating hormone |
T4 thyroxine |
Free thyroxine |
|
Primary hyperthyroidism |
decreased |
increase |
Increase or low level Normal |
|
Primary hypothyroidism |
increase |
decreased |
decreased |
|
Hypothalamic/pituitary hypothyroidism |
Increase, decrease, normal |
decreased |
decreased |
|
TBG deficiency syndrome |
normal
|
decreased |
normal |
|
Normal thyroid disease syndrome |
Increase, decrease, normal
|
decreased |
Increase or low level Normal |
|
thyroid-stimulating hormone secretion or hypopituitary gland |
Increase or normal |
increase |
increase |
|
Compensatory hypothyroidism |
increase |
normal |
normal |
References and Sources: HARVARD MEDICAL SCHOOL, Endocrine CONTROVERSIES IN ADULT PRIMARY CARE PRACTICE MAY15~16 2015 Nelson Pediatrics Textbook 19th Ed The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th ed
Treatment of Graves’ disease
• Children’s Graves’ disease is mainly treated with Propylthiouracil (PTU) and Methimazole (Tapazole), rather than with partial thyroid surgery or radioactive iodine treatment.
• When children’s Graves’ disease is not treated with drugs or for other reasons, surgery to remove some of the thyroid gland or treatment with radioactive jade is sometimes performed.
• During treatment with propylthiouracil and Methimazole (Tapazole), side effects such as temporary neutropenia, urticaria, hepatitis, liver failure, and vasculitis may occur.
• Sometimes you need to continue on medication for more than 6 years.
• Severe bulging eyes or double vision can be treated with steroids.
• Sometimes symptomatic treatment is given with Propranolol and or Methylprednisolone.
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- www.drle epediatrics.com제14권. 소아청소년 내분비, 유전, 염색체, 대사, 희귀병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제6권 신생아 성장 발육 육아 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제9권 소아청소년 소화기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제10권. 소아청소년 신장 비뇨 생식기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제11권. 소아청소년 심장 혈관계 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제12권. 소아청소년 신경 정신 질환, 행동 수면 문제
- www.drleepediatrics.com제13권. 소아청소년 혈액, 림프, 종양 질환
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th — 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
-
Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, Harvey grant, and Robert Murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
-
The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
-
Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care
-
응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
-
Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
-
Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
-
Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Berverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gerhon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
-
소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”