감염 단핵구증(엡스타인-바 바이러스 감염병 /감염성 모노/모노 인두 편도염/키스 병/ 전염성 단핵구증) Infectious mononucleosis(Epstein-barr virus infection/Infectious mono/EBV infection)
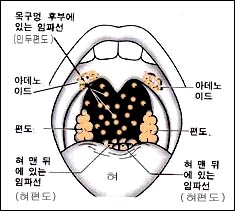
그림 35. 인두 강 주위에 있는 림프조직
입을 크게 벌렸을 때 아데노이드는 보이지 않지만 의료 기구를 이용해 볼 수 있다. X-선 사진이나 스캔 등으로 아데노이드의 크기를 알아 볼 수 있다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
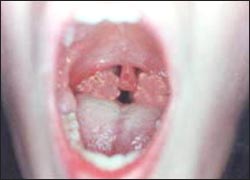
사진 36. 감염 성 단핵구증(모노)은 일종의 바이러스 인두 편도염이다. A군 베타 용혈성 연쇄상구균 인두 편도염으로 생긴 증상 징후와 모노로 생긴 인두 편도염으로 생긴 증상과 징후, 진찰 소견으로만 이 두 병을 확실히 감별 진단하기가 때로는 어렵다. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD.FAAP
감염단핵구증의 원인
- 엡스타인-바 바이러스(Epstein-Barr Virus) 감염으로 생기는 바이러스 감염병을 감염단핵구증(엡스타인-바 바이러스 감염병/ 엡스타인-바르 바이러스 감염성 모노/모노 인두 편도염/ 키스 병/모노/Infectious mononucleosis/Epstein-barr virus infection/EBV infection)이라 한다.
- EB 바이러스가 비강, 인두, 편도, 간, 비장, 림프절 등 신체 여러 계통에 동시 감염될 수 있다.
- 그래서 EB 바이러스 비염, EB 바이러스 인두염, EB 바이러스 편도염, EB 바이러스 간염 등이 동시 생길 수 있다.
- 그리고 신체 여러 계통의 여러 부위에 있는 림프절에 감염되어 림프절염과 림프증이 생길 수 있다.
- 또 이 병이 있을 때 간장, 비장 등이 크게 부을 수 있다.
- 2~10세 유아 학령기 아이들이 EB 바이러스에 감염되면 감기와 비슷한 증상 징후로 앓을 수 있고 아무 증상 징후 없이 지낼 수 있고 엡스타인-바 바이러스 감염병을 전형적으로 앓을 수 있다. EB 바이러스 항체가 신체 내에 생기는 경우가 많다.
- 일반적으로 5세 이전 대부분의 영유아들에게 EB 바이러스 항체가 이미 생겨 있을 수 있다.
- EB 바이러스 감염으로 생긴 인두 편도염의 초기의 증상 징후는 A군 베타 용혈성 연쇄상구균으로 생긴 인두 편도염의 초기 증상 징후와 비슷한 점이 많다.
- 그 때문에 EB 바이러스 감염으로 생긴 인두 편도염인지 A군 베타 용혈성 연쇄상구균 감염으로 생긴 인두 편도염인지 임상검사를 하지 않고 확실히 감별 진단하기 어려운 때가 많다.
- 키스를 할 때 EB 바이러스에 더 잘 감염될 수 있고 이 병에 잘 걸릴 수 있다고 해서 “키스 병”이란 별명도 있다.
- 기숙사 생활 하는 대학생들에게 이병이 더 잘 발생될 수 있다.
- 키스를 할 때 이 병에 잘 걸릴 수 있지만 대화나 숨 쉴 때, 또는 기침할 때 환자나 보균자에게서 나온 비말 속 EB 바이러스에 감염되면 엡스타인-바 바이러스에 감염 된다.
- 이 병을 앓는 사람의 피를 접촉해도 EB 바이러스에 감염 될 수 있고 이 병을 앓는 사람과 근접 생활을 하는 집안 식구에게도 EB 바이러스에 감염 될 수 있다.
- 엡스타인-바 바이러스에 감염 되었으나 아무 증상 징후가 없이 앓는(즉, 잠복형 감염이 있는) 소아 청소년들로부터 EB 바이러스에 감염될 수 있다.
- 잠복기는 10~50일 정도이다.
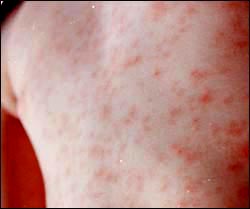
사진 43 감염성 단핵구증으로 생긴 피부 발진
Copyright ⓒ 2012 John Sangwon Lee, MD.FAAP
감염단핵구증의 증상 징후
- EB 바이러스 감염의 증상 징후는 다양하다.
- 감염단핵구증에 걸려도 아무 증상 징후가 없이 EB 바이러스 면역체(항체)만 몸에 생기고 자연적으로 나을 수 있고 감기와 비슷한 증상 징후로 경미하게 앓을 수도 있다. 또 아주 심하게 앓을 수 있다.
- 특히 영유아들에게 생긴 EB 바이러스 감염은 증상 징후가 하나도 없을 때가 많다.
- EB 바이러스에 감염된 후 잠복기를 거쳐 4~6일간 전구증이 나타나고 4일 내지 2~3주 동안 급성 감염단핵구증의 증상 징후가 나타나고 2주 내지 1~2개월 간 시름시름 앓으면서 서서히 회복될 때도 있다.
- 심한 감염단핵구증을 앓을 때 생길 수 있는 증상 징후를 구체적으로 살펴본다.
-
- 미열 내지 고열(76%),
- 인두통(82%),
- 턱 바로 밑에 있는 목 림프절이나 신체 다른 부위에 있는 림프절이 붓고(84%),
- 구토(5%),
- 구기(12%),
- 두통(31%),
- 전신 권태감과 피로(57%),
- 구미상실(21%),
- 근육통(21%),
- 복통(9%),
- 기침(5%),
- 관절통(2%),
- 인두염과 편도염(84%),
- 림프증(94%),
- 비장비대(52%),
- 간 비대증(12%),
- 황달(5%),
- 홍반(10%) 등의 증상 징후가 급성기에 나타날 수 있다(가로에 있는 %는 각 증상의 발생%이다).
- 겨드랑이와 가랑이 등에 있는 림프절도 부을 수 있고 편도가 크게 붓고 붉고 거기에 하얀 곱이 낄 수 있다.
- 감염단핵구증을 박테리아 인두염으로 오진한 후 감염단핵구증을 페니실린이나 아목시실린 등으로 치료하면 홍반성 피부 발진이 거의 80~100% 경우 나타날 수 있다.
- 식욕이 감퇴되고 인두가 아프기 때문에 여러 날 동안 잘 먹지 못해 심하게 탈수될 수 있고 기운이 없어 축 늘어지고 잠을 비정상적으로 많이 자기도 한다.
- EB 바이러스 감염으로 아데노이드가 감염되면 아데노이드가 상당히 붓고 커져 후비강 기도부분이 막혀 입을 벌리고 입으로 숨을 쉬기도 한다.
EB 바이러스 감염으로
-
- 무균성 뇌막염과 뇌염,
- 귈랑-바레 증후군(Guillain-Barre syndrom),
- 폐렴,
- 심근염,
- 백혈구 감소증,
- 혈소판 감소증,
- 재생불량성 빈혈,
- 용혈성 빈혈,
- 상기도 폐쇄,
- 비장파열,
- 간염,
- 안검부종 등의 합병증이 생길 수 있다.
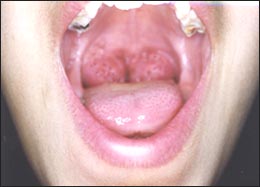
사진37.모노 인두 편도염(감염 성 단핵구증)으로 편도가 붓고 거기에 염증이 생겼다. A군 베타 용혈성 연구균 세균검사와 모노검사를 하지 않고 A군 베타 용혈성 연구균 인두 편도염과 감염 성 단핵구증을 확실히 감별 진단할 수 없는 때가 많다.
출처-Copyrightⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee,MD.FAAP
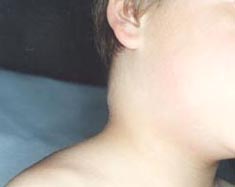
사진38.감염 성 모노 인두 편도염으로 목에 있는 림프절이 부었다. A군 베타 용혈성 연구균 편도염, 묘소병 또는 결핵 등으로 목의 림프절이 부을 수 있다. 출처-Copyrightⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee,MD., FAAP
감염단핵구증의 진단
- 병력, 증상 징후, 진찰소견 등을 종합해서 이 병을 의심하면 A군 베타 용혈성 연쇄상구균으로 생긴 인두 편도염과 다른 종류의 박테리아 감염성 인두편도염이나 바이러스 감염으로 생긴 인두편도염과 감별 진단해야 한다.
- PCR 검사, EBV RNA, IgA, IgM, EBNA 검사로 진단 하기도한다.
- 인두 편도염을 항생제로 치료를 시작하기 전에 가능한 한 인두 점액 면봉 채집 피검물로 A군 베타 용혈성 연쇄상구균 세균배양검사(“스트렙토 검사”-“스트렙토테스트 Strepto test”라고도 부른다.)나 A군 베타 용혈성 연쇄상구균 항원 항체 응집반응검사를 해서 감별 진단하는 것이 보통이다.
표 감염성 모노(전염성 모노) 환자들을 진찰할 때 발견되는 증상 징후
| 발견되는 증상 징후 | 발견되는 % |
| 림프절 비대 | 83% |
| 목 림프절 비대 | 46% |
| 전신에 있는 림프절 비대 | 34% |
| 열 | 86% |
| 인두염 | 57% |
| 하얀 곱이 낀 인두염 | 29% |
| 비장 비대 | 47% |
| 간 비대 | 28% |
| 눈꺼풀 부종 | 10% |
| 피부 발진 | 8% |
| 황달 | 5% |
| 신경 장애 | 1% |
- 인두 점액 면봉 채집 피검 물로 세균 배양 검사를 하거나 A군 베타 용혈성 연쇄상구균 항원 항체 응집 반응 검사를 하기 바로 며칠 전에 어떤 종류의 항생제로 A군 베타 용혈성 연쇄상구균 인두 편도염을 치료받았을 때는 A군 베타 용혈성 연쇄상구균 세균배양검사의 결과나 A군 베타 용혈성 연쇄상구균 항원 항체 응집반응검사의 결과가 허위성 음성으로 나타날 수 있다. 때문에 A군 용혈성 연쇄상구균 인두 편도염을 확진하기가 어려울 수 있다.
- A군 베타 용혈성 연쇄상구균 인두 편도염은 페니실린이나 그 외 다른 적절한 항생제 치료를 시작한 후 24~48시간 정도 지나면 증상과 징후가 아주 좋아지는 것이 보통이나 EB 바이러스 감염으로 생긴 감염 성 단핵구증은 항생제로 치료해도 증상 징후가 좋아지지 않는다.
- CBC 피검사에 나타난 비정형 림프구, 이종항체 반응, 모노 테스트, 간 기능검사 등으로 이 병은 비교적 쉽게 진단할 수 있다. EB 바이러스 감염으로 외생식기에 궤양이 생길 수도 있다(출처: Pediatrics News October 2008).
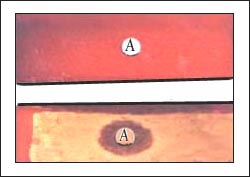
사진40.세균배양 인큐베이터 속에서 혈액 우무 세균 배양지에 자란 인두 상존 잡균(상),
A군 베타 용혈성 연쇄상구균이 자란 혈액 우무 세균 배양지(하)
EB 바이러스 감염으로 인두염을 않을 때 A군 베타 용혈성 연쇄상구균 배양검사의 결과가 음성으로 나타난다. 출처-Copyrightⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee,MD.FAAP
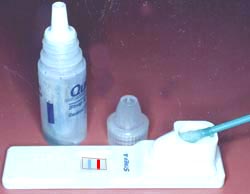
사진 41. 감염단핵구증을 앓을 때는 EB 바이러스 항원 항체 응집 반응검사가 양성으로 나타나는 것이 보통이다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee,MD., FAAP

사진 42. A군 베타 용혈성 연쇄상구균 편도염을 앓을 때는 A군 베타 용혈성 연쇄상구균 세균 배양검사의 결과가 양성으로 나타난다. A군 베타 용혈성 연쇄상구균 항원 항체 응집 반응검사도 양성으로 나타나는 것이 보통이다.
요즘 새로 나온 BioStar Strep A Ola Max rapid strep test로 A군 베타 용혈성 연쇄상구균 항원 항체 응집 반응검사를 하면 검사결과가 96% 신빙성이 있다. 항원 항체 응집 반응 검사가 음성으로 나타났어도 A군 연구균 세균배양 검사를 꼭 할 필요가 없다고 한다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD.FAAP
감염단핵구증 치료
- EB 바이러스로 생긴 감염단핵구증은 항생제로 치료되지 않기 때문에 대증치료를 한다.
- 앰피실린이나 아목사실린으로 의심 감염단핵증을 치료하면 피부발진이 생길 가능성이 많다.
- 증상이 급성으로 나타날 때는 육체적으로 정신적으로 7~21일 동안 휴식과 안정을 취한다.
- 환아가 활동할 수 있을 정도에 따라 육체적 활동량을 서서히 조절한다.
- 음식물은 조금씩 자주 충분히 서서히 섭취하고 수분을 충분히 섭취해서 탈수를 예방한다. 병세가 좋아지고 환자가 잘 먹으면 전 유동식에서 반 유동식으로, 반 유동식에서 보통 때 먹는 음식으로 점차로 바꾼다.
- 두통, 근육통, 인두통, 열 등의 증상 징후는 타이레놀이나 모트린 등 해열 진통제로 대증 치료한다.
- 탈수가 심하면 입원하여 포도당 전해질용액 정맥주사로 수화 치료한다.
- 호흡곤란이 있고 그 감염 성 단핵구증의 증상이 심할 때는 경구용 프레드니손으로 4~7일 간 치료할 수 있다.
- Valacyclovir(Valtrex), acyclovir 또는 ganciclovir 등 항바이러스제로 치료할 수 있고 다른 사람들에게 감염시키는 감염률도 적다(출처-Ped. news Feb. 2006, Red book 29th edition 2012).
- 환아를 격리할 필요는 없다.
- 예방접종약과 백신은 아직 없다.
감염단핵구증(모노)환아는 언제 부터 육체 접촉성 운동을 시작 할 수 있나?
- 진찰, 증상 징후, 임상검사, 비장 CT 스캔 등 영상 검사의 결과에 기준으로 해 언제부터 육체 접촉성 운동을 할 수 있나 결정하기가 어렵다.
- 연구에 의하면, 감염단핵구증(모노)의 증상 징후가 생기기 시작한 날부터 1~14일 사이에 외상으로 비장 파열이 가장 잘 생길 수 있다.
- 언제부터 육체 접촉성 운동을 해도 좋은지는 임상적으로 판단하는 것이 가장 좋고 비장이 진찰할 때 만져지면 육체 접촉성 운동을 삼가는 것이 좋다고 권장한다.
|
다음은 “감염성 모노와 연구균 편도염”에 관한 인터넷 소아청소년 건강상담 질의응답의 예 입니다. |
Q&A. 감염성 모노와 연구균 편도염에 관해서
Q.
안녕하세요… 여기서 궁금한 많은 정보를 읽다가 궁금해서 문의 합니다..
제가 11월 24일부터 아프더니 25일은 열도 나고 기운도 편두통도 심하고 그래서 집에서 하루 쉬면 괜찮아지겠지 생각해서 26일날 쉬었는데도 괜찮아지지 않아서 27일 토요일날 우연히 편도를 보게 되었습니다..
굉장히 많이 부어있고 염증도 있는 거 같아 동네 병원에 갔습니다.. 가서 약을 먹고 주사도 맞고 약을 먹어서 괜찮아지는 듯싶더니.. 새벽에 다시 편두통이 심하게 와서 잠을 이룰 수가 없었습니다.. 여전히 목은 부어있고 염증도 있고요.. 다음날인 일요일날은 더욱 심해져서 한쪽 편도에만 있던 염증이 다른 한쪽까지 심하게 번져서 침도 삼키기가 힘듭니다..
11월 29일 월요일까지 조제한 약을 먹고 무슨 약을 조제해줬는지 병원에 물어보니 6가지였는데 목에 관한 건 오그멘틴이라는 약이었다고 합니다. 그래서 월요일날 다른 병원을 갔습니다.. 거기서 약을 하루 조제해 줬는데 오늘다시 와서 검사를 해보고 이약도 듣지 않을 경우 다른 약을 쓸 거라고. 균 검사도 2주 걸리기 때문에 2주 정도 지나면 거진 완치되기 때문에 구지 할 필요 없다고 말씀하시는데.. 좀 더 심해지면 입원해서 치료 받으라고 하는데.. 계속 여길 다녀야 할지 아님 다른 병원에 가야할지 문의합니다.. 그리고 여기서 조제해 준 약은 포비돈 요오드액 가글, 세파트리진, 마로나제정, 타스펜이알정, 미렌탈정 이렇게 조제해 주셨습니다..
여기 글을 읽어보면 이 병이 위험할 수도 있는데..
A.
숙희님
안녕하세요. 질문해 주셔 감사합니다.
자녀의 나이, 성별, 과거와 가족의 병력, 진찰소견, 임상검사 결과 등 많은 정보가 있으면 더 좋은 답변을 드릴 수 있습니다. 주신 정보를 참작해 답변을 드립니다.
자세한 정보를 주셔 감사합니다. 그러나 주신 약 이름에 관해서는 무슨 약인지 잘 몰라 답변을 드리는 데 많은 도움을 드릴 수가 없습니다.
연령을 몰라 답변드리는 데 많은 지장이 있습니다. 왜냐하면 연령에 따라 생기는 병이 다르기 때문입니다.
질문하신 분의 나이가 15~25세 정도로 추정하고 그런 증상 징후으로 저의 의원에 오신다면 병력을 더 듣고 진찰하고 편도가 붓고 열이 나고 아프면 바이러스 편도염이 있는지 박테리아 편도염이 있는지 알아보기 위해서 “스트렙토 테스트“를 하겠습니다.
아시겠지만 바이러스 편도염은 항생제로 치료 되지 않습니다. 그러나 박테리아 편도염은 항생제로 치료를 시작한 후 2~3일 내에 증상이 많이 호전되는 것이 보통입니다.
그러나 박테리아 편도 농양이나 편도 주위농양은 항생제로 치료하여도 완치가 잘 되지 않는 경우가 간혹 생깁니다.
또 과거에는 연쇄상 구균성 박테리아 편도염은 페니실린으로 잘 치료됐었지만 요즘은 페니실린으로 잘 치료되지 않습니다.
그러나 A군 베타 용혈성 연쇄상구균 편도염이나 편도농양 또는 편도주위 농양을 일반적으로 페니실린 치료를 시작한 후 2~3일 내에 치료효과가 아주 좋게 나타나는 것이 일반적입니다.
박테리아 편도염의 원인균의 거의가 A군 베타 용혈성 연쇄상구균입니다.
항생제로 치료가 되지 않고 스트렙토 테스트가 음성으로 나타나고 귀하가 가진 증상과 징후가 있을 때는 감염성 모노(감염 성 단핵구증)를 의심해 봐야 합니다.
감염단핵구증의 원인은 EB 바이러스 감염이고 그 병의 특효 치료약은 없으며 자연히 나을 때까지 기다리는 것이 일반적 치료입니다.
요즘 항바이러스제 Valacyclovir로 치료한 결과 치료효과도 좋고 다른 사람들에게 감염시키는 감염률도 적다고 합니다.
좀 복잡하고 전문적 의학 정보를 드리지만 저의 경험으로 이곳 미국에 많은 사람들은 이 병에 관해 많이 알고 있습니다.
아프면 타이레놀로 진통시키고 열이 나면 타이레놀로 해열시키면서 치료하는 것도 중요합니다.
소아청소년과나 내과에서 진찰 진단 치료를 또 받으시고 문제가 있으면 상담하시기 바랍니다. [부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다–소아가정간호 백과]-제7권 소아청소년 감염병-A군 연구균 감염. 급성 편도염 등을 참조하시기 바랍니다. 질문이 더 있으면 또 방문하세요. 감사합니다. 이상원 드림
Infectious mononucleosis (Epstein-barr virus infection/Infectious mono/EBV infection)
감염 단핵구증(엡스타인-바 바이러스 감염병 /감염성 모노/모노 인두 편도염/키스 병/ 전염성 단핵구증)

Figure 35. Lymphatic tissue around the pharyngeal cavity Adenoids are not visible when you open your mouth wide, but you can use medical devices. You can check the size of adenoids by using an X-ray photo or a scan. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Picture 36. Infectious mononucleosis (mono) is a type of viral pharyngeal tonsillitis. Group A beta hemolytic streptococcal pharyngeal tonsillitis symptoms and symptoms, symptoms and symptoms caused by mono-induced pharyngeal tonsillitis, it is sometimes difficult to reliably diagnose these two diseases only by examination findings. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD.FAAP
Causes of infectious mononucleosis
• Infectious mononucleosis (Epstein-Barr virus infectious disease/ Epstein-Barr virus infectious mono/monopharyngeal tonsillitis/ Kiss disease/ Mono/Infectious mononucleosis/Epstein-barr virus infection) /EBV infection).
• The EB virus can simultaneously infect multiple systems of the body, including the nasal cavity, pharynx, tonsils, liver, spleen, and lymph nodes.
• So, EB viral rhinitis, EB viral pharyngitis, EB viral tonsillitis, EB viral hepatitis, etc. can occur simultaneously.
• In addition, lymph nodes in many parts of the body can become infected, resulting in lymphadenitis and lymphosis.
• Also, when you have this disease, the soy sauce and spleen can be swollen.
• Infants 2-10 Years Old School-aged children who are infected with the EB virus can get sick with symptoms similar to a cold, have no signs of symptoms, and typically suffer from Epstein-Barr virus infection. EB virus antibodies are often produced in the body.
• In general, most infants and toddlers before age 5 may already have EB virus antibodies.
• Early symptomatic signs of pharyngeal tonsillitis caused by EB virus infection are similar to those of pharyngeal tonsillitis caused by group A beta hemolytic streptococcus.
• Because of that, it is often difficult to reliably diagnose whether it is pharyngeal tonsillitis caused by EB virus infection or pharyngeal tonsillitis caused by group A beta hemolytic streptococcal infection without clinical testing.
• There is also a nickname for “kissing disease” because kissing can be more susceptible to the EB virus and prone to this disease. • College students living in dormitories may be more susceptible to disease.
• You can get the disease when kissing, but you can get EBstein-Barr virus when you are infected with the EB virus in droplets from the patient or carrier when talking, breathing, or coughing.
• Contact with the blood of a person suffering from the disease can lead to infection with the EB virus, and family members living in close proximity to a person with the disease can also become infected with the EB virus.
• Children and adolescents who have been infected with the Epstein-Barr virus but have no symptoms (ie, have a latent infection) can get the EB virus.
• The incubation period is about 10 to 50 days.

Picture 43 Skin rash caused by infectious mononucleosis Copyright ⓒ 2012 John Sangwon Lee, MD.FAAP
Symptoms, signs of infectious mononucleosis
• Symptoms and signs of EB virus infection vary.
• Even with infectious mononucleosis, there are no symptoms, only the EB virus immunity (antibody) occurs in the body, and you can heal naturally, and you may get mildly ill with symptoms similar to a cold. It can also be very sick.
• EB virus infections, especially in infants and young children, often have no symptoms. • After infection with EB virus, prognosis develops for 4-6 days after incubation period, symptoms of acute infectious mononucleosis appear for 4 to 2 to 3 weeks, and sometimes recovers gradually after suffering from irritation for 2 to 1 to 2 months.
• Look for specific signs of symptoms that may occur when you have severe infectious mononucleosis.
o Mild to high fever (76%),
o Pharyngeal pain (82%),
o Swollen lymph nodes in the neck or other parts of the body just under the chin (84%),
o vomiting (5%),
o nausea (12%),
o Headache (31%),
o Systemic boredom and fatigue (57%),
o loss appetite (21%),
o Myalgia (21%),
o Abdominal pain (9%),
o cough (5%),
o Joint pain (2%),
o Pharyngitis and tonsillitis (84%),
o Lymphosis (94%),
o Non-equipment zone (52%),
o Enlarged liver (12%),
o Jaundice (5%),
o Symptoms such as erythema (10%) may appear in the acute phase (% on the horizontal is the percent occurrence of each symptom).
• Lymph nodes in the armpits and crotch may also be swollen, and the tonsils may be swollen and red, and white mud may stick there.
• If infectious mononucleosis is misdiagnosed as bacterial pharyngitis and then infectious mononucleosis is treated with penicillin or amoxicillin, erythematous skin rash can occur in almost 80-100% of cases.
• Due to decreased appetite and sore pharynx, you may not be able to eat well for many days, so you may be severely dehydrated. You may be drooping due to lack of energy, and you may sleep abnormally a lot.
• When adenoids are infected by EB virus infection, the adenoids become quite swollen and enlarged, causing the posterior nasal airway to be blocked, causing the mouth to open and breathe through the mouth.
With EB virus infection
• o Aseptic meningitis and encephalitis,
o Guillain-Barre syndrom,
o pneumonia,
o myocarditis,
o leukopenia,
o thrombocytopenia,
o aplastic anemia,
o hemolytic anemia,
o upper respiratory tract obstruction,
o Spleen rupture,
o hepatitis,
o Complications such as eyelid edema may occur.

Picture 37: Monopharyngeal tonsillitis (infectious mononucleosis) swollen tonsils and inflamed there. In many cases, it is not possible to reliably diagnose pharyngeal tonsillitis and infectious mononucleosis from group A beta-hemolytic bacteria without bacteriological and mono-tests. Source-Copyrightⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD.FAAP

Picture 38: Infectious monopharyngeal tonsillitis swollen lymph nodes in the neck. Group A beta-hemolytic research bacteria can cause swollen lymph nodes in the neck due to tonsillitis, catarrhal disease, or tuberculosis. Source-Copyright© 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
Diagnosis of infectious mononucleosis
• If you suspect this disease based on your medical history, symptoms, and medical findings, you should differentiate between pharyngeal tonsillitis caused by group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus and pharyngeal tonsillitis caused by other types of bacterial infectious pharyngeal tonsillitis or viral infection.
• It is also diagnosed by PCR test, EBV RNA, IgA, IgM, EBNA test.
• Before starting treatment with antibiotics for pharyngeal tonsillitis, use a group A beta hemolytic streptococcus bacterial culture test (also called a “Strepto test”-“Strepto test”) or a group A beta hemolytic swab with a pharyngeal mucosa swab as much as possible. It is common to perform differential diagnosis by performing a streptococcal antigen-antibody agglutination test.
Table Symptoms Signs Found When Examining Patients with Infectious Mono (Infectious Mono)
표 감염성 모노(전염성 모노) 환자들을 진찰할 때 발견되는 증상 징후
| Symptom Signs Found | Found % |
| Enlarged lymph nodes | 83% |
| Enlarged lymph nodes in the neck | 46% |
| Enlarged lymph nodes throughout the body | 34% |
| Fever | 86% |
| pharyngitis | 57% |
| Pharyngitis with white mucus | 29% |
| Splenomegaly | 47% |
| Hepatomegaly | 28% |
| eyeli edema | 10% |
| Skin Rashes | 8% |
| Jaundice | 5% |
| Neurological disorder | 1% |
• Group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus pharyngeal tonsillitis was treated with some kind of antibiotic a few days before the bacterial culture test with a pharyngeal mucus swab or group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus antigen-antibody aggregation test. Aureus bacterial culture test results or group A beta-hemolytic streptococcal antigen-antibody agglutination test results may be falsely negative. Therefore, it may be difficult to confirm group A hemolytic streptococcal pharyngeal tonsillitis.
• Group A beta-hemolytic streptococcal pharyngeal tonsillitis usually improves 24 to 48 hours after starting penicillin or other appropriate antibiotic treatment, but infectious mononucleosis caused by EB virus infection is usually treated with antibiotics. Symptoms do not improve.
• CBC blood test shows atypical lymphocytes, mono-antibody reaction, mono test, liver function test, etc. This disease can be diagnosed relatively easily. EB virus infection can lead to exogenous ulcers (Source: Pediatrics News October 2008).

Photo 40. Pharyngeal supernatant bacteria (top), grown on blood-dried bacterium culture in a bacterial culture incubator, Group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus-grown blood mucus culture medium (bottom) When not suffering from pharyngitis due to EB virus infection, the result of group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus culture test is negative. Source-Copyrightⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD.FAAP

Picture 41. When suffering from infectious mononucleosis, it is common for the EB virus antigen-antibody aggregation test to be positive. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Picture 42. When suffering from group A beta-hemolytic streptococcal tonsillitis, the result of the group A beta-hemolytic streptococcal bacterial culture test is positive.
A group A beta-hemolytic streptococcal antigen-antibody aggregation test is also usually positive. When a group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus antigen-antibody agglutination test is performed with the new BioStar Strep A Ola Max rapid strep test, the test result is 96% reliable.
Even if the antigen-antibody agglutination test is negative, it is not necessary to perform a bacterial culture test for group A research bacteria.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD.FAAP
Infectious mononucleosis treatment
• Infectious mononucleosis caused by EB virus is not treated with antibiotics, so symptomatic treatment is given.
• Treatment of suspected infectious mononucleosis with ampicillin or Amoxycillin is more likely to result in a skin rash.
• When symptoms appear acute, take a break and rest for 7 to 21 days, physically and mentally.
• Adjust the amount of physical activity gradually according to the extent to which the child can be active.
• Eat food little by little, often enough, slowly, and drink plenty of fluids to prevent dehydration. When the condition improves and the patient eats well, the whole formula is gradually changed to semi-liquid, and semi-liquid to the usual food.
• Symptoms such as headache, muscle pain, sore throat, and fever are usually treated with antipyretic analgesics such as Tylenol or Motrin.
• If dehydration is severe, hospitalize and receive hydration treatment with intravenous glucose electrolyte solution.
• If you have difficulty breathing and the symptoms of infectious mononucleosis are severe, oral prednisone can be treated for 4 to 7 days.
• Can be treated with antiviral drugs such as valacyclovir (Valtrex), acyclovir, or ganciclovir, and the infection rate that infects others is low (Source-Ped. news Feb. 2006, Red book 29th edition 2012).
• There is no need to isolate the child.
• There are no vaccines and vaccines yet.
When can a child with mononucleosis (mono) infection start physical contact exercise?
1. It is difficult to determine when physical contact exercises can be performed based on the results of imaging tests such as examination, symptom signs, clinical examination, and spleen CT scan.
2. According to research, the spleen rupture is most likely caused by trauma between 1 and 14 days from the beginning of the onset of symptoms of infectious mononucleosis (mono).
3. It is best to clinically judge when it is okay to do physical contact exercise, and it is recommended to refrain from physical contact exercise if it is touched when examining the spleen.
The following is an example of questions and answers for online pediatric and adolescent health counseling on “infectious mono and research tonsillitis”.
Q&A.
About infectious mono and study bacterial tonsillitis
Q.
Good morning… I have read a lot of information that I am curious about here, and I am curious to inquire.
I got sick from November 24th, and on the 25th I had a fever, my energy, and a migraine, so I thought that it would be okay if I took a day off at home. It was very swollen and inflamed, so I went to the local hospital.
I went to the local hospital, took medicine, got an injection, and took medicine, so I felt okay..
I had a migraine again at dawn, so I couldn’t sleep. My throat was still swollen. There is also inflammation..
The next day, Sunday, it gets worse, so the inflammation that was only on one side of the tonsils spreads to the other, making it difficult to swallow saliva. By Monday, November 29th, I took the medicine and asked the hospital what kind of medicine it was given.
So I went to another hospital on Monday..
I gave me medicine for a day there, but I came back to do the tests today and if I don’t take this medicine, I’ll use another medicine. Because the fungal test takes 2 weeks, he says that there is no need to go to the hospital because it will be cured after about 2 weeks..
If it gets worse, he asks you to be hospitalized and treated..
I ask if I should go to another hospital or not..
And here The medicines I prepared were povidone-iodine gargle, cefatrigin, marona formulation, tasfenyl tablet, mirental tablet, and so on. If you read the text here, this disease can be dangerous…
A.
Sook-hee Good morning.
Thank you for asking. If you have a lot of information, such as your child’s age, gender, past and family history, medical examination findings, and clinical test results, we can give you a better answer.
We will respond by taking the information you provided into consideration. Thank you for the detailed information.
However, regarding the name of the drug you have given, I am not sure what drug it is, so I cannot help you much to answer. I don’t know the age, so there are many difficulties in responding.
This is because the diseases that occur according to age are different. If the person who asked the question is estimated to be between 15 and 25 years old, and if you come to my clinic with such symptoms, the “Strepto Test” is used to check if you have viral tonsillitis or bacterial tonsillitis if you have more medical history and have a medical history.
I’ll do it. As you may know, viral tonsillitis is not treated with antibiotics. However, bacterial tonsillitis usually improves significantly within 2 to 3 days after starting treatment with antibiotics.
However, bacterial tonsil abscesses or peritonsillar abscesses are sometimes not cured well even when treated with antibiotics.
Also, in the past, streptococcal bacterial tonsillitis was treated well with penicillin, but these days it is not well treated with penicillin.
However, it is common to treat group A beta hemolytic streptococcal tonsillitis, tonsil abscess or peritonsillar abscess in general within 2-3 days after starting penicillin treatment. Most of the causative agents of bacterial tonsillitis are group A beta hemolytic streptococcus.
If you are not treated with antibiotics and your strepto test is negative and you have symptoms and signs, you should suspect infectious mono (infectious mononucleosis).
The cause of infectious mononucleosis is EB virus infection, and there is no specific cure for the disease, and waiting for it to heal naturally is a general treatment.
These days, treatment with the antiviral drug Valacyclovir is said to have a good therapeutic effect and a low rate of infection that infects other people. I’ll give you some complex and specialized medical information, but from my experience, many people here in America know a lot about this disease. It is also important to treat pain with Tylenol if you are sick, and treat it with Tylenol to relieve fever if you have a fever.
If you have any problems, please consult with the Department of Pediatrics or Internal Medicine.www.drleepediatrics.com-Volume 7 Infectious Diseases for Children and Adolescents- Infection with group A research bacteria. See acute tonsillitis, etc. If you have more questions, please visit again. Thank you. Lee Sang-won.MD
Copyright ⓒ 2011 Joh
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
-
www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
-
www.drleepediatrics.com제8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환
-
Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th — 21st Edition
-
The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd editio
-
Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, harvey grant and robert murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
-
The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
-
Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies , Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care
-
응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
-
Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
-
Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
-
Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
-
소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”