간 비대(간이 커졌을 때) Hepatomegaly
간 비대의 개요와 원인
- 간의 크기가 정상 이상으로 더 커져 있는 것을 간 비대라고 한다.
- 간 비대란 말 대신 간이 커졌다 또는 간이 부었다는 말도 많이 쓴다.
- 간이 경미하게 정상보다 더 커져있을 수도 있고 때로는 오른쪽 상 복부가 현저하게 불러져 있을 정도로 간 전체가 심하게 부어 있을 수 있다.
- 간 비대는 어떤 병으로 생기는 증상 징후이지 병명은 아니다.
- 간이 비정상으로 클 때는 어떤 원인으로 간이 커져 있나 확실히 알아본다.
- 원인에 따라 치료해야 한다.
- 신체 검진으로 간이 비정상적으로 커져있는지 확실히 알 수 없는 때도 많이 있다.
- 간 비대는 때로는 비장 비대와 함께 있을 수 있다.
- 소아청소년들의 간 비대의 원인은 아주 많다.
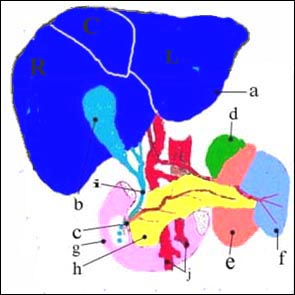
그림 249. 간, 담관과 그 주위의 장기.
간이 커지는(간 비대) 원인은 많이 있다.
a-간, b-담낭, c-십이지장관 유두(담즙과 췌장액이 분비되는 출구), d-좌 부신, e-좌 신장, f-지라, g-십이지장관, h-췌장, i-총수담관, j-혈관, 대문자의 R-우엽의 간, L은 좌엽의 간, C는 유미 엽의 간.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
신생아의 간 비대의 원인
- 선천성 풍진증후군, 선천성 톡소플라스마증, 선천성 매독, 선천성 수두, 선천성 단순포진 감염병, 선천성 감염성 간염병, 선천성 콕삭키바이러스 감염병, 선천성 사이토메갈로바이러스 감염병, 또는 용혈성 빈혈, Rh 부적합증이나 ABO 혈액형 부적합증, 심부전증, 담관 폐쇄증 등으로 신생아들의 간이 커질 수 있다.
- 후천성 감염병에 의해서 신생아의 간이 커질 수 있다.
신생아기 이후 영유아들, 학령기 아이들, 사춘기 아이들의 간 비대의 원인
- 신생아기 이후 소아청소년들(생후 28일~말기 사춘기)의 간은 간 종양, 간농양, A형 간염, B형 간염, C형 간염, D형 간염, E형 간염, 담관 폐쇄증, 심장 부전증, 신진대사 이상, 윌슨병, 갈랙토스혈증, 백혈병, 말라리아, 감염단핵구증(감염성 모노), 패혈증, 연소성 류마토이드 관절염, 약물, 그 외 다른 여러 종류의 박테리아 감염병, 바이러스 감염병 등으로 인해 커질 수 있다.
간 비대의 진단
- 병력, 진찰, 피검사, 초음파 검사, CT 스캔 검사 등으로 진단한다.
간 비대의 치료
- 원인에 따라서 치료한다.
Hepatomegaly 간 비대
Overview and causes of hepatomegaly
• An enlarged liver is called an enlarged liver(hepatomegaly).
• Instead of talking about an enlarged liver, many people say that the liver has become enlarged or that the liver is swollen.
• The liver may be slightly larger than normal, and sometimes the entire liver may be swollen so that the upper right abdomen is markedly swollen.
• An enlarged liver is a symptom of a disease, not a disease name.
• When the liver is abnormally large, check for certain reasons why the liver is enlarged.
• Treatment depends on the cause.
• There are many times when it is not clear whether the liver is abnormally enlarged by physical examination.
• An enlarged liver can sometimes be accompanied by an enlarged spleen.
• There are many causes of liver hypertrophy in children and adolescents.

Figure 249. Liver, bile ducts and surrounding organs. There are many causes of enlarged liver (hepatomegaly). a-liver, b-gallbladder, c-duodenal duct papilla (exit where bile and pancreatic fluid are secreted), d-left adrenal gland, e-left kidney, f-spinal, g-duodenal duct, h-pancreas, i-common bile duct , j-vessel, upper case R-right lobe liver, L is left lobe liver, C is the graceful lobe liver. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
Causes of hepatomegaly in newborn
- Congenital rubella syndrome,
- congenital toxoplasmosis,
- congenital syphilis,
- congenital chickenpox
- congenital herpes simplex infectious disease,
- congenital infectious hepatitis,
- congenital coxsackie virus infectious disease,
- congenital cytomegalovirus infectious disease,
- or hemolytic anemia,
- Rh incompatibility or ABO blood type incompatibility.
- Heart failure,
- bile duct atresia,
- etc.
can cause the liver of newborns to become enlarged.
• A newborn’s liver can be enlarged by an acquired infectious disease.
Causes of hepatomegaly in infants, school-age children, and adolescent children after neonatal period
• The liver of children and adolescents (28 days after birth to end-stage puberty) after neonatal period is liver tumor, liver abscess, hepatitis A, hepatitis B, hepatitis C, hepatitis D, hepatitis E, biliary atresia, heart failure, budding. Metabolic abnormalities, Wilson’s disease, galactosemia, leukemia, malaria, infectious mononucleosis (infectious mononucleosis), sepsis, juvenile rheumatoid arthritis, drugs, and many other bacterial infections, viral infections, etc.
Diagnosis of hepatomegaly
• Diagnosis is based on medical history, medical examination, blood test, ultrasound test, and CT scan test.
Hepatomegaly treatment
• Treat according to the cause.
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제9권 소아청소년 소화기 질환
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th — 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
-
Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, harvey grant and robert murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
-
The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
-
Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies , Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care
-
응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
-
Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
-
Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
-
Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
-
소아과학 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”