간염, Hepatitis
(You may visit www.drleepediatrics.com – Volume 7,
Pediatric Adolescent Infectious Diseases or제 7권, 소아 청소년 감염병 질환 웹사이트)
간염의 원인
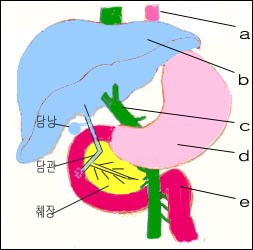
그림 3-97. a-식도, b-간, c-문맥, d-위, e-십이지장
Copyright ⓒ 2013 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
-
곰팡이(진균), 아메바, 박테리아, 바이러스 등 병원체나 약물, 유기 화학 물질, 무기 화학 물질 등 여러 가지 원인으로 생긴 간의 염증을 간염이라 한다.
-
간염을 일으킬 수 있는 바이러스에는 여러 종류가 있다.
-
A형 간염바이러스(전염성 간염바이러스)로 인한 A형 간염,
-
B형 간염바이러스(혈청성 간염바이러스)로 인한 B형 간염,
-
C 형 간염바이러스로 인한 C형 간염 등이 있고, 그 외 E형 간염, D형 간염 등이 있다.
-
감염성 간염에 관해 구체적으로 더 설명한다.
표 3-5. A형 간염, B형 간염, C형 간염의 감염 경로, 증상, 치료, 예방
| 특성 | A형 간염 | B형 간염 | C형 간염 |
|
바이러스 RNA 형, DNA 형 |
picornavirus(RNA) | hepadnavirus(DNA) | flavivirus(RNA) |
| 전염 방법 | 대변-경구를 통해(드물게는 피하, 근육, 정맥주사 등을 통한 비경구적으로) | 피하, 근육, 정맥주사 등을 통한 비경구적으로) | 피하, 근육, 정맥주사 등을 통한 비경구적으로) |
| 전염 경로 | 사람-사람 접촉, 성교, 음식물을 통해서 | 성교, 습관성 약물 주사, B형 간염 바이러스를 보균한 모체나 B형 간염을 앓는 모체로부터 출생하는 동안 | 습관성 약물 주사, 1990년 전 수혈이나 피로 만든 약물 사용, 성교(?), C형 간염 바이러스를 보균한 모체나 C형 간염을 앓는 모체로부터 출생하는 동안 |
| 황달이 나타나는 빈도 | 성인에서는 흔하지만 소아에서는 흔치 않다 | 성인에서는 흔하지만 소아에서는 흔치 않다. | 흔치 않다. |
| 급성간염이 만성간염으로 되는 빈도 | 없다. | 성인에서는 10% 이하이고 영유아에서 흔하다. | 70% 이상 |
| 매년 급성감염 발생 예상 수(미국내) | 179,000 | 185,000 | 38,000 |
| 미국 내 만성간염 발생 예상 수 | – | 1,250,000 | 2.700,000 |
| 세계적으로 만성간염 발생 예상 수 | – | 350,000,000 | 170,000,000 |
| 치료 약 | 없음 | Interferon alfa, Lamivudine |
전에 치료받지 않은 만성 c형 간염을 Boceprevir (상품명; Victrelis)와 Ribavirin/Copegus/ Rebetol)와 Peginterferon alfa (Pegasys)으로 치료할 수 있다. 또는 전에 치료받지 않은 만성 c형 간염을 Telaprevir (상품명;Incivek), Ribavirin/Copegus/ Rebetol)와 Peginterferon alfa (Pegasys)으로 치료할 수 있다. 소스:Journal Watch, The NEJM July 2011 |
| 예방접종 및 면역글로불린 | A형 간염 예방접종 및, 또는 면역글로불린 | B형 간염 예방접종 및, 또는 면역 글로불린 | 없음 |
출처 및 참조 문헌
New England J Med, Vol 345, No 1 July 5, 2001
www.nejm.org”에서.
소아청소년 간염의 원인과 종류
-
A형 간염,
-
B형 간염,
-
C형 간염,
-
D형 간염,
-
전염성 단핵구증 간염,
-
박테리아 간염,
-
사이토메갈로 바이러스 간염,
-
톡소플라스모시스성 간염,
-
선천성 풍진 증후군성 간염,
-
단순포진 바이러스 간염,
-
콕삭키바이러스 간염,
-
B형 간염,
-
INH나 아목시실린 등의 약물로 인한 간염,
-
연소성 류마토이드 관절염 간염,
-
유기 화학물질이나 무기 화학물질의 중독성 간염,
-
담관 폐쇄증으로 생긴 간염,
-
종양으로 생긴 간염,
-
말라리아성 간염,
-
매독성 간염,
-
우유로 인한 간염 등이 있다.
|
다음은 “간염과 간수치”에 관한 인터넷 소아청소년 건강상담 질의응답의 예 입니다. |
Q&A. 간염과 간 수치에 대한 질문입니다.
Q.
아이가 17개월입니다. 일주일전 아니 벌써 2주가 되었군요.
일주일동안 고열이 떨어지지 않고(약한 감기증상 동반 콧물 목이 붓고) 아이가 자꾸 토하고 하루 종일 잠만 자서 큰 병원에 갔더니 간수치가 400까지 올라갔다고 하더군요.
지금은 수치가 떨어져 안전하다하여 퇴원한 상태입니다. 다름이 아니오라 아직 간염이 된 원인 결과가 나오지 않아 이유는 모릅니다. 근데 자꾸 답답하군요. 왜 이렇게 어린 아기가 간수치가 400까지 올라갈 정도로 간염이 된 원인이 몰까 해서요. 답답해 여쭈어 봅니다. 이런 어린아가에 간수치를 오르게 하는 원인이 어떤 것이 있는지, 천성적으로 태어났다가 지금 나타날 수 있는지, 아님 다른 간염이나 약물에 의해 그럴 수 있는지 가르쳐주십시오.
A.
예림님
안녕하세요. 질문해 주셔서 감사합니다. 좋은 질문입니다.
자녀의 나이, 성별, 과거 병력, 가족 병력, 진찰소견, 임상검사 등의 정보를 많이 알수록 답변을 드리는데 도움이 됩니다.
주신 정보를 토대로 해서 답변을 드리겠습니다.
걱정이 많이 되시겠습니다.
A형 간염, B형 간염, C형 간염, D형 간염, 전염성 모노 간염(전염성 단핵구증 감염), 사이토메갈로바이러스 간염, 선천성 풍진 증후군에 의한 간염, 단순포진바이러스 간염, 콕삭키바이러스 감염, B형 간염 등 각종 바이러스 감염으로 인한 간염, INH나 아목시실린 등의 약물로 인한 간염, 연소성 류마토이드 관절염 등 자가면역 이상으로 생기는 간염, 유기 화학물질 또는 무기 화학물질 중독으로 인한 간염, 담관 폐쇄증 등 선천성 기형으로 인한 간염, 종양 등으로 인한 간염, 말라리아 간염이나 톡소플라스모시스 간염, 매독 등 박테리아 간염 등으로 간염이 생길 수 있습니다.
이상 열거한 간염들 중 한 종류의 간염으로 간 기능에 이상이 생길 수 있고 간기능 검사에 이상이 나타날 수 있습니다. 어떤 원인으로 간 기능 검사의 결과가 비정상적이었는지 주신 정보로는 확실히 알 수 없습니다.
더 자세한 것은 소아청소년과에서 문의 상담하시기 바랍니다. [부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다–소아가정간호백과]-제6권 신생아 성장 발육 양호 질환–신생아 간염, 황달과 감염병, 간염] 등을 참조하시기 바랍니다. 질문이 더 있으시면 다시 연락 주시기 바랍니다. 감사합니다. 이상원 드림
Hepatitis 간염
Causes of hepatitis

Figure 3-97. a-esophagus, b-liver, c-portal, d-stomach, e-duodenum Copyright ⓒ 2013 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
• Inflammation of the liver caused by various causes such as fungi (fungi), amoeba, bacteria, viruses, pathogens, drugs, organic chemicals, inorganic chemicals, etc. is called hepatitis.
• There are several types of viruses that can cause hepatitis. • Hepatitis A due to hepatitis A virus (contagious hepatitis virus),
• Hepatitis B due to hepatitis B virus (serum hepatitis virus),
• Hepatitis C due to hepatitis C virus, and other hepatitis E and D infection.
• Explain more specifically about infectious hepatitis.
Table 3-5. Hepatitis A, hepatitis B, and hepatitis C infection route, symptoms, treatment, prevention 표 3-5. A형 간염, B형 간염, C형 간염의 감염 경로, 증상, 치료, 예방
| characteristic | Hepatitis A, | hepatitis B | hepatitis C |
|
Viral RNA type, DNA type |
picornavirus(RNA) | hepadnavirus(DNA) | flavivirus(RNA) |
| Transmission method | Fecal-orally (rarely parenterally through subcutaneous, intramuscular, intravenous, etc.) | Parenterally through subcutaneous, intramuscular, intravenous injection, etc.) | Parenterally through subcutaneous, intramuscular, intravenous injection, etc.) |
| Transmission route | Through person-to-person contact, sexual intercourse, or food | Sexual intercourse, injections of habitual drugs, during birth from a mother carrying the hepatitis B virus or from a mother with hepatitis B | Injection of habitual drugs, blood transfusions or blood-based drugs before 1990, sexual intercourse (?), during birth from a mother carrying the hepatitis C virus or from a mother with hepatitis C infection |
| How often jaundice appears |
Common in adults but less common in children
|
Common in adults but less common in children
|
less common |
| How often acute hepatitis becomes chronic hepatitis | none | It is less than 10% in adults and is common in infants and toddlers. | 70% or more |
| Estimated number of acute infections each year (in the US) | 179,000 | 185,000 | 38,000 |
| Estimated number of chronic hepatitis outbreaks in the U.S. | – | 1,250,000 | 2.700,000 |
| Estimated number of chronic hepatitis outbreaks worldwide | – | 350,000,000 | 170,000,000 |
| therapeutic medicine | none | Interferon alfa, Lamivudine |
Untreated chronic hepatitis c infection can be treated with Boceprevir (trade name; Victrelis) and Ribavirin/Copegus/ Rebetol) and Peginterferon alfa (Pegasys). Alternatively, untreated chronic hepatitis c infection can be treated with Telaprevir (brand name: Incivek), Ribavirin/Copegus/ Rebetol) and Peginterferon alfa (Pegasys). Source: Journal Watch, The NEJM July 2011 |
| Vaccination and Immunoglobulin | Hepatitis A vaccination and/or immunoglobulins | Hepatitis B vaccination and/or immunoglobulins | none |
Source: New England J Med, Vol 345, No 1 July 5, 2001. www.nejm.org”
Causes and types of hepatitis in children and adolescents
• hepatitis A,
• hepatitis B,
• hepatitis C,
• hepatitis D,
• infectious mononucleosis hepatitis
• bacterial hepatitis,
• cytomegalovirus hepatitis,
• Toxoplasmosis hepatitis,
• congenital rubella syndrome hepatitis,
• Herpes simplex virus hepatitis,
• Coxsackie virus hepatitis,
• hepatitis B,
• Hepatitis caused by drugs such as INH or amoxicillin,
• juvenile rheumatoid arthritis hepatitis,
• Toxic hepatitis of organic or inorganic chemicals,
• hepatitis caused by biliary atresia,
• hepatitis caused by tumors,
• malarial hepatitis,
• syphilitic hepatitis,
• Hepatitis caused by milk.
The following is an example of a question-and-answer on “Hepatitis and Liver Count” on the Internet for child and adolescent health counseling.
Q&A. Questions about hepatitis and liver levels.
Q. The child is 17 months old.
A week ago, it’s already been two weeks. The child kept vomiting for a week without a high fever (runny nose and swelling with a mild cold symptom) and went to a large hospital after sleeping all day, and the number of guards rose to 400. Now he is discharged from the hospital because his figure has fallen and he is safe. It’s no different, so I don’t know why because the cause of hepatitis has not yet come out. But it keeps getting stuffy. I wondered why such a young baby had hepatitis so that his liver count went up to 400. I am frustrated and ask. Please tell me what causes these infants to rise to their guards, whether they can be born by nature and appear now, or can they be caused by other hepatitis or medications.
A.
Yerim Good morning. Thanks for asking. That’s a good question. The more information you know about your child’s age, gender, past medical history, family medical history, medical examination findings, clinical examination, etc., the more helpful it is to give an answer. We will respond based on the information you provided. You will be worried a lot.
Hepatitis A, Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C, Hepatitis D, Infectious Mono Hepatitis (Infectious Mononucleosis Infection), Cytomegalovirus Hepatitis, Hepatitis Due to Congenital Rubella Syndrome, Herpes Simplex Virus Hepatitis, Coxacchi Virus Infection, Hepatitis B Hepatitis caused by various viral infections, hepatitis caused by drugs such as INH or amoxicillin, hepatitis caused by autoimmune abnormalities such as combustible rheumatoid arthritis, hepatitis caused by poisoning with organic or inorganic chemicals, hepatitis caused by congenital malformations such as bile duct obstruction,
Hepatitis can be caused by hepatitis due to tumors, malaria hepatitis, toxoplasmosis hepatitis, and bacterial hepatitis such as syphilis. One type of hepatitis listed above can cause abnormal liver function and abnormal liver function tests.
The information given is not sure of what caused the abnormal liver function test results. For more information, please inquire at the Department of Pediatrics and Adolescents. Please refer to www.drleepediatrics.com-Volume 6, Neonatal Growth and Development Diseases-Newborn Hepatitis, Jaundice and Infectious Diseases, Hepatitis], etc. If you have more questions, please contact us again. Thank you. Lee Sang-won ..MD
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권. 소아청소년 감염병
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th – 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
-
B형 간염 Hepatitis B
-
B형 간염 예방접종 Hepatitis B immunization
-
B형 간염 예방접종을 꼭 받아야 하는 사람들 Persons who should have hepatitis B immunization
-
피나 피로 만든 약을 쓸 때 B형 간염에 대한 유의할 사항 Hepatitis B Precaution for using blood or product medicine Precaution for hepatitis B vaccination
-
B형 간염을 한 번도 앓은 적이 없는 사람들에게 B형 간염 예방접종을 해 주는 방법 How to give hepatitis B vaccine C형 간염/HCV 간염 Hepatitis C
-
D형 간염 Hepatitis D
-
E형 간염 Hepatitis E
-
G형 간염 Hepatitis G
-
Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, harvey grant and robert murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
-
The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
-
Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies , Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Manual of Emergency Care
-
응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
-
Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
-
Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
-
Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gerhon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
-
소아과학 안효섭 외 대한교과서
-
제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
-
Other
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”